Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 43451. |
When an ac source of emf E = E_(0) Sin (100pit) is connected across a circuit, the phase difference between the emf E and the current I in the circuit is observed to be pi//4, as shown in the fig. If the circuit consists only of R-C(or) R-L (or) L-C series. Possible values of the elements of the circuit are |
|
Answer» `R = 1KOmega, C= 10MUF` |
|
| 43452. |
Consider a source of sound S and an observer P. The sound source is of frequency n_0 . The frequency observed by P is found to be n_1 if P approaches S at speed v and S is stationary, n_2 if S approaches P at a speed v and P is stationary and n_3 if each of P and S has speed v/2 towards one another. Now, |
|
Answer» `n_1 = n_2 = n_3` |
|
| 43453. |
A thin equiconvex lens is made of glass of refractive index 1.5 and its focal length is 0.2 m, if it acts as a concave lens of 0.5 m focal length when dipped in a liquid, the refractive index of the liquid is : |
|
Answer» `(17)/(8)` `rArr.^(1)mu_(g)=0.8=(4)/(5)rArr(.^(a)mu_(1))/(.^(a)mu_(1))=(4)/(5)rArr(1.5)/(.^(a)mu_(1))=(4)/(5)` `rArr"" .^(a)mu_(1)=(15)/(8).` |
|
| 43454. |
The force between two parallel wires carrying current is ______. |
|
Answer» `F = mu_(0)/(2 pi) (I_(1)I_(2)l)/a` |
|
| 43455. |
A star is at a distance of 50xx10^(12) km from earth. If the star disappears due to collision with some other star so that its light is extinguished, how long would we continue the star (even after it stops) existing. Velocity of light in vacuum =3xx10^(8)ms^(-1). |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43456. |
if in a nuclear fusion reaction, mass defect to 0.3% , then energy released in fusion of 1 kg mass |
|
Answer» `27xx10^10` J `=0.3/100 kg =3XX10^(-3)` kg `THEREFORE E=(Deltam) c^2=3xx10^(-3)xx(3xx10^8)^2=27xx10^13` J |
|
| 43457. |
A conducting sphere of radius 10 cm has an unknown charge. If the electric field 20 cm from the centre of the sphere is 1.5xx10^(3) N//C and points radially inward, what is the net charge on the sphere? |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) `-10^(3) N m^(2)//C`because the charge enclosed is thesame in thetwo CASES (B) -8.8 NC |
|
| 43458. |
The first nuclear reaction ever observed was by ernest Rutherford in 1919. It was triggered by alpha particles incident on an isotope of nitrogen ._(7)^(14) N. He observed a proton was emitted along with another element x. Let us assume that ._(7)^(14) N nucleus was initially stationary. For this reaction to occur, alpha-particle must touch the nitrogen nucleus. The distance between their centres at this moment is d. For this problem, we will neglect the effect of outer electrons in ._(7)^(14) N. Symbols have their usual meanings. The minimum initial kinetic energy of alpha-particle so that reaction can occur is |
|
Answer» `(18ke^(2))/(R_(0)(2^(2//3)+14^(2//3)))` `1/2xx(4mxx14m)/(4m+14m)v_(rel)^(2)=(kxx2xxexx7e)/(R_(0)(14^(1//3)+2^(2//3)))` `1/2xx4m v_(rel)^(2)=(18ke^(2))/(R_(0)(14^(1//3)+2^(2//3)))` |
|
| 43459. |
In a parallel plate capacitor with air between the plates, each plate has an area of 6xx10^(-3)m^2and the distance between the plates is 3 m. Calculate the capacitance of the capacitor. If this capacitor is connected to a 100V supply. What is the charge on the each plate of the capacitor? |
|
Answer» Solution :Here `A = 6xx10^(-3) m^(2) , d = 3XX10^(-3), epsilon_(0) = 8.85 xx10^(-12) "Fm"^(-1) V = 100 V` we have `C = (epsilon_(0)A)/d` `= (8.85xx10^(-12) xx6xx10^(-3))/(3xx10^(-3))` `C = 17.7 xx10^(-12)F` The charge on each plate is EQUAL and OPPOSITE and the charge `Q = CV` `Q = 17.7 xx10^(-12) xx100` `= 17.7 xx10^(-10)C` `Q = 1.77 nC` |
|
| 43460. |
In an a.c. series circuit, the instantaneous current is maximum when the instantaneous voltage is maximum. The circuit element connected to the source will be |
|
Answer» Pure inductor |
|
| 43461. |
When we avoid overlapping and different colors the prism should be placed in a position of ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :MINIMUM DEVIATION | |
| 43462. |
In Young's double slit experiment, fringes of width beta are produced on a screen kept at a distance of 1 m from the slit. When the screen is moved away by 5 xx 10^(-2)m, fringe width changes by 3 xx 10^(-5) m. The separation between the slits is1 xx 10^(-5) m. The wavelength of the light used is : |
|
Answer» 400 nm Wavelength `lambda = (Deltabetad)/(DELTAD) = (3 XX 10^(-5) xx 1 xx 10^(-3))/(5 xx 10^(-2))` ` = 6 xx 10^(-7) m` or `lambda = 600 nm` |
|
| 43463. |
The equation of state for a real gas such as hydrogen oxygen etc. is called the Van der waal's equation which reads: -(P+(a)/(V^(2)))(V-b)-=n RT where a and b are constants of the gas. The dimensional formula of constant a is: |
|
Answer» `M^(-1)L^(5)T^(-1)` `"DIM"((a)/(V^(2)))=" dim "(P)` `THEREFORE ([a])/((L^(3))^(2))=[ML^(-1)T^(-2)]` `rArr [a] =[ML^(5)T^(-2)]` Thus, correct CHOICE is (B). |
|
| 43464. |
Close packing is maximum in crystal which is |
|
Answer» BCC |
|
| 43465. |
Derive an expression for electric intensity E due to a uniformly charged thin spherical shell at a point outside the shell. |
|
Answer» Solution :Gauss Theorem It states that the TOTAL electric flux through a closed surface is equal to `(I)/(epsi_(0))` times the magnitude of the charge enclosed by the surface (`epsi_(0)` is permittivity of FREE space) i.e., `phi=ointvec(E).VEC(dS)=(q)/(epsi_(0))` where `vec(E)` is the electric field intensity and `vec(dS)` is the AREA vector. Consider a thin sphericalshell of radius R. let q be the charge distributed UNIFORMLY all over the surface of the shell. Imagine a gaussian surface of radius r, fing (a) the intensity at every point of it is the same and directed radially outwards so that angle bewtween `vec(E) and vec(dS)=0^(@)` `therefore oint_(S)vec(E).vec(dS)=oint_(S)EdScos0^(@)=(q)/(epsi_(0))` 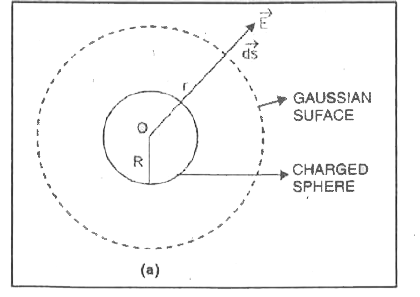 or `Eoint_(S)dS=(q)/(epsi_(0))` or `E4pir^(2)=(q)/(epsi_(0))` or 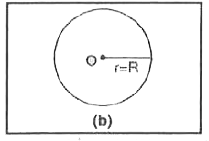 i.e., electric intensity at any pointe outside the spherical shell is such as if whole of charge were concentrated at the centre of the shell. At a point on the hollow sphere, r=R `therefore E=(q)/(4piepsi_(0)R^(2))` If `sigma` is the surface density of charge on the shell, then `q=4piR^(2)sigma` or `E=(4piR^(2)sigma)/(4piepsi_(0)R^(2))=(sigma)/(epsi_(0))` or `E=(sigma)/(epsi_(0))` 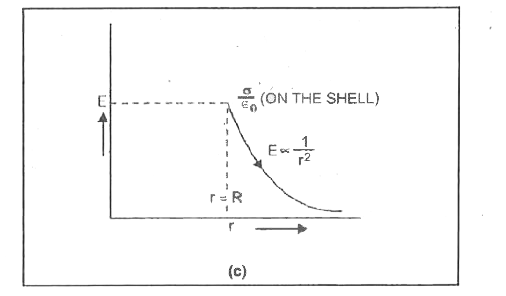 At a point inside. for a point P inside the shell E=0 since q=0 inside the shell. `therefore `Electric field intensity the shell is always zero. The variation ofelectric field intensity E with distance from the centre of a uniformly charged spherical shell is as shown in fig (c). |
|
| 43466. |
In Youngs double slit experiment, the phase different between two coherent sources of equal intensity is π/3.The intensity at a point which is at equal distance from the two slits is (l0 is maximum intensity) |
|
Answer» (`l_@)/2` |
|
| 43467. |
A bomber flying horizontally with constant speed releases a bomb from an aeroplane. a) The path of bomb as seen by the observer on the ground is parabola b) The path of the bomb as seen by a pilot is a straight line. c) The path of the aeroplane with respect to bomb is a straight line d) The path of the bomb as seen by pilot observed as parabola. |
|
Answer» a is CORRECT |
|
| 43468. |
The path executed by a charged particle, whose motion is perpendicular to a uniform megnetic field, is |
|
Answer» a STRAIGHT line |
|
| 43469. |
Find the total energy stored in the capacitors in the given network of Fig. |
Answer» Solution :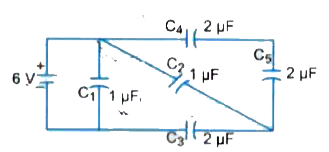 In fig , capacitors `C_4` and `C_5` of 2` mu F ` each are in series , their equivalent capacitance `C. = (C_(4) C_(5))/(C_(4) + C_(5)) = (2 xx 2)/( 2 + 2) = 1 mu F ` Now C. and `C_2` are in parallel , hence their equivalent capacitance `C.. = C_(2) + C. = 1 + 1 = 2 mu F` Further C.. and `C_3` are in series , their equivalent capacitance `C_(0) = (C.. C_(3))/(C.. + C_(3)) = (2 xx 2)/(2 + 2) = 1 mu F ` Now C. and `C_2` are in parallel , hence their equivalent capacitance `C.. = C_(2) + C. = 1 + 1 = 2mu F ` Further C.. and `C_3` are in series , their equivalent capacitance `C_(0) = (C.. C_(3))/(C.. + C_(3)) = (2 xx 2)/(2 + 2) = 1 mu F` Finally , `C_0` is in parallel with `C_1` , hence net resultant capacitance `C = C_(0) + C_(1) = 1 + 1 = 2 mu F ` `therefore` Total energy stored in the capacitors in the GIVEN network `U = (1)/(2) C V^(2) = (1)/(2) xx 2 xx 10^(-6) xx (6)^(2) = 3.6 xx 10^(-5) J` |
|
| 43470. |
A circle of 2.5 meter radius is made using a wire of uniform cross section and resistivity 1 m^(2). If resistance of this wire is 10 pi Omegaresistivity of the material of the wire is ........ |
|
Answer» `4 pi Omega` m `R = (l rho)/(A)"" therefore R = (2 pi r rho)/(A)` `therefore rho = (RA)/(2 pi r)=(10 pi xx 1 )/(2pi xx 2.5) = 2 Omega` m |
|
| 43471. |
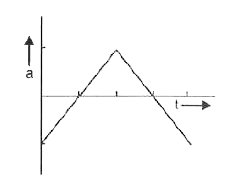
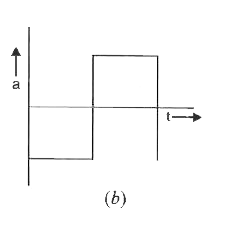
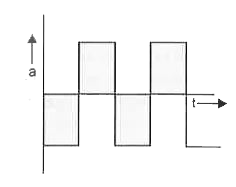
The graph shown in Fig. shows the velocity v tk versus time for a body, Which of the graphs shown below represents the corresponding accelera-tion versus time graphs ? |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 43472. |
Two parallel horizontal conductors are suspended by light vertical threads each of length 75cm. Each conductor has a mass of 0.4 gm perm. When no current flows through them, they are 0.5 cm apart. When same current flows through each conductor the separation is 1.5 cm. The value and direction of current is |
|
Answer» 14 A in same direction |
|
| 43473. |
The current passing through a choke coil of self inductance 5 H is decreasing at the rate of 2 A//s. The emf developed across the coil is |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 43474. |
Four concentric hollow spheres of radii R, 2R, 3R, and 4R are given the charges as shown in figure. Then the conductors 1 and 3, 2 and 4 are connected by conducting wires (both the connections are made at the same time.) |
|
Answer» `3Q//40piepsilon_0R`  Let the CHARGE distribution be as shown in fig From gauss's theorem we know that facing surface s of the conductor acquire equal and oppsite charges. So `V_(1)=V_(3)` and `V_(2)=V_(4)` `q_(1)+q_(3)-q_(2)=+4Q`.(i) Now, `q_(2)-q_(1)+q_(4)-q_(3)=-6Q`..(ii) `V_(1)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))[(q_(1))/(R)+(q_(2)-q_(1))/(2R)+(q_(3)-q_(2))/(3R)+(q_(4)-q_(3))/(4R)]` `V_(2)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0)[(q_(1))/(2R)+(q_(2)-q_(1))/(2R)+(q_(3)-q_(2))/(3R)+(q_(4)-q_(3))/(4R)]` `V_(3)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))[(q_(1))/(3R)+(q_(2)-q_(1))/(3R)+(q_(3)-q_(2))/(3R)+(q_(4)-q_(3))/(4R)]` `V_(4)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))[(q_(1))/(4R)+(q_(2)-q_(1))/(4R)+(q_(3)-q_(2))/(3R)+(q_(4)-q_(3))/(4R)]` from `V_(1)=V_(3),q_(1)=-(q_(2))/(3)` from `V_(2)=V_(4),q_(2)=-(q_(3))/(2)` On SOLVING eq. (ii) `q_(1)=(2Q)/(5),q_(2)=-(6Q)/(5)` and `q_(3)=(12Q)/(5)` Substituting these values in Eq (ii) we GET `q_(4)=-2Q` charge on the inner surface of the third conductor is `-q_(2)=6Q//5` charge on the fouth conductor is `q_(4)-q_(3)=-2Q-(12Q)/(5)=(-22Q)/(5)` potential of conduction 1, `V_(1)=(-3Q)/(40piepsilon_(0)R)=V_(3)` Potential of conductor 2, `V_(2)=(Q)/(8piepsilon_(0)R)=V_(4)` |
|
| 43475. |
Four concentric hollow spheres of radii R, 2R, 3R, and 4R are given the charges as shown in figure. Then the conductors 1 and 3, 2 and 4 are connected by conducting wires (both the connections are made at the same time.) |
|
Answer» `22Q//5`  Let the charge distribution be as shown in fig From gauss's theorem we know that facing surface s of the conductor acquire EQUAL and oppsite charges. So `V_(1)=V_(3)` and `V_(2)=V_(4)` `q_(1)+q_(3)-q_(2)=+4Q`.(i) Now, `q_(2)-q_(1)+q_(4)-q_(3)=-6Q`..(ii) `V_(1)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))[(q_(1))/(R)+(q_(2)-q_(1))/(2R)+(q_(3)-q_(2))/(3R)+(q_(4)-q_(3))/(4R)]` `V_(2)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0)[(q_(1))/(2R)+(q_(2)-q_(1))/(2R)+(q_(3)-q_(2))/(3R)+(q_(4)-q_(3))/(4R)]` `V_(3)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))[(q_(1))/(3R)+(q_(2)-q_(1))/(3R)+(q_(3)-q_(2))/(3R)+(q_(4)-q_(3))/(4R)]` `V_(4)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))[(q_(1))/(4R)+(q_(2)-q_(1))/(4R)+(q_(3)-q_(2))/(3R)+(q_(4)-q_(3))/(4R)]` from `V_(1)=V_(3),q_(1)=-(q_(2))/(3)` from `V_(2)=V_(4),q_(2)=-(q_(3))/(2)` On solving eq. (ii) `q_(1)=(2Q)/(5),q_(2)=-(6Q)/(5)` and `q_(3)=(12Q)/(5)` Substituting these values in Eq (ii) we get `q_(4)=-2Q` charge on the inner surface of the third conductor is `-q_(2)=6Q//5` charge on the fouth conductor is `q_(4)-q_(3)=-2Q-(12Q)/(5)=(-22Q)/(5)` potential of conduction 1, `V_(1)=(-3Q)/(40piepsilon_(0)R)=V_(3)` Potential of conductor 2, `V_(2)=(Q)/(8piepsilon_(0)R)=V_(4)` |
|
| 43476. |
Certain amount of an ideal gas is contained in a closed vessel. The vessel is moving with constant velocity v. The rise in temperature of the gas when the vessel is suddenly stopped is (M is molecular weight of the gas and gamma=C_p//C_v) |
|
Answer» `(Mv^2(gamma-1))/(2R)` |
|
| 43477. |
Four concentric hollow spheres of radii R, 2R, 3R, and 4R are given the charges as shown in figure. Then the conductors 1 and 3, 2 and 4 are connected by conducting wires (both the connections are made at the same time.) , The charge on the inner surface of the third conductor is |
|
Answer» `-6Q//5`  Let the charge distribution be as shown in fig From gauss's theorem we know that facing surface s of the CONDUCTOR acquire equal and oppsite CHARGES. So `V_(1)=V_(3)` and `V_(2)=V_(4)` `q_(1)+q_(3)-q_(2)=+4Q`.(i) Now, `q_(2)-q_(1)+q_(4)-q_(3)=-6Q`..(ii) `V_(1)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))[(q_(1))/(R)+(q_(2)-q_(1))/(2R)+(q_(3)-q_(2))/(3R)+(q_(4)-q_(3))/(4R)]` `V_(2)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0)[(q_(1))/(2R)+(q_(2)-q_(1))/(2R)+(q_(3)-q_(2))/(3R)+(q_(4)-q_(3))/(4R)]` `V_(3)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))[(q_(1))/(3R)+(q_(2)-q_(1))/(3R)+(q_(3)-q_(2))/(3R)+(q_(4)-q_(3))/(4R)]` `V_(4)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))[(q_(1))/(4R)+(q_(2)-q_(1))/(4R)+(q_(3)-q_(2))/(3R)+(q_(4)-q_(3))/(4R)]` from `V_(1)=V_(3),q_(1)=-(q_(2))/(3)` from `V_(2)=V_(4),q_(2)=-(q_(3))/(2)` On solving EQ. (ii) `q_(1)=(2Q)/(5),q_(2)=-(6Q)/(5)` and `q_(3)=(12Q)/(5)` Substituting these values in Eq (ii) we get `q_(4)=-2Q` charge on the INNER surface of the third conductor is `-q_(2)=6Q//5` charge on the fouth conductor is `q_(4)-q_(3)=-2Q-(12Q)/(5)=(-22Q)/(5)` potential of conduction 1, `V_(1)=(-3Q)/(40piepsilon_(0)R)=V_(3)` Potential of conductor 2, `V_(2)=(Q)/(8piepsilon_(0)R)=V_(4)` |
|
| 43478. |
A very long straight uniformly charged thread carries a charge lambda per unit length, Find the magnitude and direction of the electric field strenght at a point which is at a distance y from the thread and lies on the perpendicular passing through one of the thread.s ends. |
|
Answer» `(lambdasqrt(3))/(4piepsilon_(0)y),theta=40^(0)` |
|
| 43479. |
He wrote his name with flourish and added |
|
Answer» HEREDITARY ASTROLOGER to the MAHARAJA of Ninnore. |
|
| 43480. |
Briefly state the working principle of microwave ovens. |
| Answer» Solution :It is observed that the FREQUENCY of rotation of WATER molecules is about `3GHZ (3xx10^(@)Hz)`. If water receives microwaves of this frequency, its molecules absorb this radiation. In a microwave oven the frequency of the microwaves is SELECTED to match the resonant frequency (i.e., 3 GHz) of water molecules so that ENERGY from the microwaves is transferred efficiently to the kinetic energy of water molecules. As a RESULT, water is heated up. Water molecules share this energy with neighbouring food molecules, heating up the food. | |
| 43481. |
A thin prism P_(1) with angle 4^(@) and made from glass of refractive index 1.54 is combined with another thin prism P_(2) made from glass of refractive index 1.72 to produce dispersion without deviation. The angle of prism P_(2) is |
|
Answer» `2.6^(@)` `(4)/(A_(F))=((1.72-1))/((1.54-1))=(0.72)/(0.54) or A_(F) = (4xx0.54)/(0.72)=3^(@)` |
|
| 43482. |
Whensolid is heated , its length changes according to the relation l=l_0(1+alphaDeltaT) , where l isthe final length , l_0 is the initial length , DeltaT is the change in temperature , and alpha is the coefficient of linear is called super - facial expansion. the area changes according to the relation A=A_0(1+betaDeltaT), where A is the tinal area , A_0 is the initial area, and beta is the coefficient of areal expansion. On heating a liquid of coefficient of cubical or volume expansion gammain a container having coefficient of linear expansion gamma//3 , the level of liquid in the container |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 43483. |
Four concentric hollow spheres of radii R, 2R, 3R, and 4R are given the charges as shown in figure. Then the conductors 1 and 3, 2 and 4 are connected by conducting wires (both the connections are made at the same time.) |
|
Answer» `-Q//8piepsilon_0R`  Let the charge distribution be as shown in fig From gauss's theorem we know that facing surface s of the conductor acquire equal and oppsite charges. So `V_(1)=V_(3)` and `V_(2)=V_(4)` `q_(1)+q_(3)-q_(2)=+4Q`.(i) Now, `q_(2)-q_(1)+q_(4)-q_(3)=-6Q`..(II) `V_(1)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))[(q_(1))/(R)+(q_(2)-q_(1))/(2R)+(q_(3)-q_(2))/(3R)+(q_(4)-q_(3))/(4R)]` `V_(2)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0)[(q_(1))/(2R)+(q_(2)-q_(1))/(2R)+(q_(3)-q_(2))/(3R)+(q_(4)-q_(3))/(4R)]` `V_(3)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))[(q_(1))/(3R)+(q_(2)-q_(1))/(3R)+(q_(3)-q_(2))/(3R)+(q_(4)-q_(3))/(4R)]` `V_(4)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))[(q_(1))/(4R)+(q_(2)-q_(1))/(4R)+(q_(3)-q_(2))/(3R)+(q_(4)-q_(3))/(4R)]` from `V_(1)=V_(3),q_(1)=-(q_(2))/(3)` from `V_(2)=V_(4),q_(2)=-(q_(3))/(2)` On solving eq. (ii) `q_(1)=(2Q)/(5),q_(2)=-(6Q)/(5)` and `q_(3)=(12Q)/(5)` SUBSTITUTING these values in Eq (ii) we GET `q_(4)=-2Q` charge on the inner surface of the third conductor is `-q_(2)=6Q//5` charge on the fouth conductor is `q_(4)-q_(3)=-2Q-(12Q)/(5)=(-22Q)/(5)` potential of conduction 1, `V_(1)=(-3Q)/(40piepsilon_(0)R)=V_(3)` Potential of conductor 2, `V_(2)=(Q)/(8piepsilon_(0)R)=V_(4)` |
|
| 43484. |
To destroy cancer cells……. Are used. |
|
Answer» X - RAYS |
|
| 43485. |
What is the Brewster angle for air to glass transition? (Refractive index of glass = 1.5.) |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`TAN^(-1)(1.5)~=56.3^(@)` | |
| 43486. |
Two masses of 3 kg and 4 kg are connected at the two ends of a light inextensible string that passes over a frictionless pulley. Find the acceleration of the masses and the tension in the string, when the masses are released. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) `a=((M_(1)-M_(2))g)/(M_(1)+M_(2))=((4-3)9.8)/(4+3)=1.4 ms^(-1)` (II)`T=(2M_(1)M_(2)g)/(M_(1)+M_(2))=(2(4)(3)(9.8))/(4+3)=33.6 N`. |
|
| 43487. |
The dipole moment of a coil of radius 1 cm , number of turns 10^4 , carrying a current of 100 mA is -------- Am^2 : |
| Answer» ANSWER :A | |
| 43488. |
Due to a vertical temperature gradient in the atmosphere, the index of refraction varies. Suppose index of refraction varies as n=n_0 sqrt( 1+ ay), where n_0 is the index of refraction at the surface and a = 2.0 xx 10^(-6)m^(-1). A person of height h = 2.0m stands on a level surface. Beyond what distance will he not see the runway? |
|
Answer» Solution :As refractive INDEX is changing along y - direction, we can assume a number of thin layers of air placed parallel to x - axis. Let O be the distant object just visible to the man. Consider a layer of air at a distance y from the GROUND. Let P be a POINT on the trajectory of the ray. From FIGURE, `theta= 90-i`. The slope of tangent at point P is `theta = dy//dx = coti`, From Snell.s law, n sin i = constant At the surface, `n = n_0and i = 90^@ .`  `n_0 sin 90^@ =n sin i= (n_0sqrt(1+ ay))sin i` `sin i = (1)/( sqrt(1+ay))implies cot i = (dy)/(dx) = sqrt(ay)` `int_(0)^(y) (dy)/(sqrt((ay)) = int_(0)^(x) dx implies x=2 sqrt((y)/(a))` Onsubstituting`y=2.0m anda=2 xx 10^(-6) m^(-1)` we have `x_("max") = 2 sqrt((2)/(2 xx 10^(-6)) =2000 m` |
|
| 43489. |
Select and write the corrcet answer : A transistor acts as a ' closed switch' when it is in |
|
Answer» the CUT off REGION |
|
| 43490. |
In a dc motor if E is the applied emf and e is the back emf then the efficiency is . |
|
Answer» `(E -e)/(E)` |
|
| 43491. |
A block of mass m is hanging from a light string of length l . A bullet of mass m strikes the hanging mass and gets embedded into it. The value of v such that tension in string and the speed of combined mass becomes zero simultaneously during the subsequent motion , is:- |
|
Answer» `SQRT(5gl)` |
|
| 43492. |
Unpolarised light of intensity 32 Wm^(-2) passes through three polarisers such that the transmission axis of the last polariser is crossed with first. It the intensity of the emerging light is 3Wm^(-2), the angle between the axes of the first two polarisers is |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 43493. |
Assertion: Sharper is the curvature of spot on a charged body lesser will be the surface density of charge at that point. Reason:Electric field is zero inside a charged non conducting sphere . |
|
Answer» Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of Assertion |
|
| 43494. |
A thin uniform ring of mass 5 kg and radius 0.2 metre is making 2100 r.p.m. about its central axis. Its moment of inertia and kinetic energy of rotation is : |
|
Answer» `0.2kgm^(2),4836J` K.E. = `(1)/(2)Iomega^(2)` Substitute and calculate |
|
| 43495. |
Mention any two methods of increasing the resolving power of a microscope. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Decreasing wave LENGTH, INCREASING refractice index | |
| 43496. |
A point object O is placed in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10cm. A glass slab of refractive index mu=3//2 and thickness 6cm is inserted between the object and mirror. Q. Find the position and nature of the final image when the distnace x shown in figure, is 20cm. |
|
Answer» 17CM, virtual `Deltax=(1-(1)/(mu))t=(1-(2)/(3))(6)=2cm` i.e., for the mirror, the object isplaced at a distanced `(32-Deltax)=30cm` from it. APPLYING mirror formula, `(1)/(v)+(1)/(u)=(1)/(F)` `(1)/(v)+(1)/(30)=-(1)/(10)` or, `v=-15cm` a. when `x=5cm:` The light FALLS on the slab on its return journey as shown. But the slab will again shift it by a distance `Deltax=2cm` . Hence the FINAL real image is formed at a distance `(15+2)=17cm` from the mirror.  b. When `x=20cm:` This time also the final image is at a distance of 17cm from the mirror but it is virtual as shown. BMS_V04_C01_E01_384_S02.png" width="80%"> |
|
| 43497. |
A point object O is placed in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10cm. A glass slab of refractive index mu=3//2 and thickness 6cm is inserted between the object and mirror. Q. Find the position and nature of the final image when the distance x shown in figure, is 5cm. |
|
Answer» 11cm, virtual `Deltax=(1-(1)/(mu))t=(1-(2)/(3))(6)=2cm` i.e., for the MIRROR, the object isplaced at a distanced `(32-Deltax)=30cm` from it. Applying mirror formula, `(1)/(v)+(1)/(u)=(1)/(f)` `(1)/(v)+(1)/(30)=-(1)/(10)` or, `v=-15cm` a. when `x=5cm:` The light falls on the slab on its RETURN journey as shown. But the slab will again shift it by a distance `Deltax=2cm` . Hence the final real image is formed at a distance `(15+2)=17cm` from the mirror.  b. When `x=20cm:` This TIME also the final image is at a distance of 17cm from the mirror but it is virtual as shown. BMS_V04_C01_E01_383_S02.png" width="80%"> |
|
| 43498. |
Inside an ionization chamber there are two planar electrodes of 300cm^(2) area, 2 cm apart. The chamber is filled with air under normal conditions. At a voltage of 200 V the current is equal to 1.8muA which is far below the saturation value. Find the ion concentration and the ionization coefficient of air. The mobilities of the ions are: b_(+)=1.37xx10^(-4)m^(2)//(V.s),b_(-)=1.89xx10^(-4)m^(2)//(V.s). |
|
Answer» `n=(id)/(eUS(b_(+)+b_(-)))` The concentration of air MOLECULES in normal CONDITIONS is equal to the Loschmidt numberwhich gives the ionization coefficient `alpha=n//N_(L)`. |
|
| 43499. |
The conductor ABCDE has the shape shown. It is lies in the YZ plane, with A and E on the yaxis. When it moves with a velocity v in a magnetic field B , an emf e is induced between A and E . (Choose the incorrect option) |
|
Answer» `e0` , if `V` is the `y`-direction and `B` is in the `x`-direction (1) `e=0` (3) `VEC(v)=vhatk` , `vec(B)=Bhati` , `vec(L)=lambdahatj` `e=Bvlambda` (4) `vec(v)=vhati , hatl=lambdahatj , vec(B)=Bhatk` `e=Bvlambda` (3) Magnetic field at distance `x` due to long wire `B=(mu_(0)i)/(2pix),ox` `de=Bvdx` `e=(mu_(0)iv)/(2pi)int _(a)^(a+L)(dx)/(x)=(mu_(0)iv)/(2pi)|1nx|_(a)^(a+L)` `=(mu_(0)iv)/(2pi)1n((a+L)/(a))` `=(mu_(0)iv)/(2pi)1n(1+(L)/(a)) V_(A)-V_(B)=e` 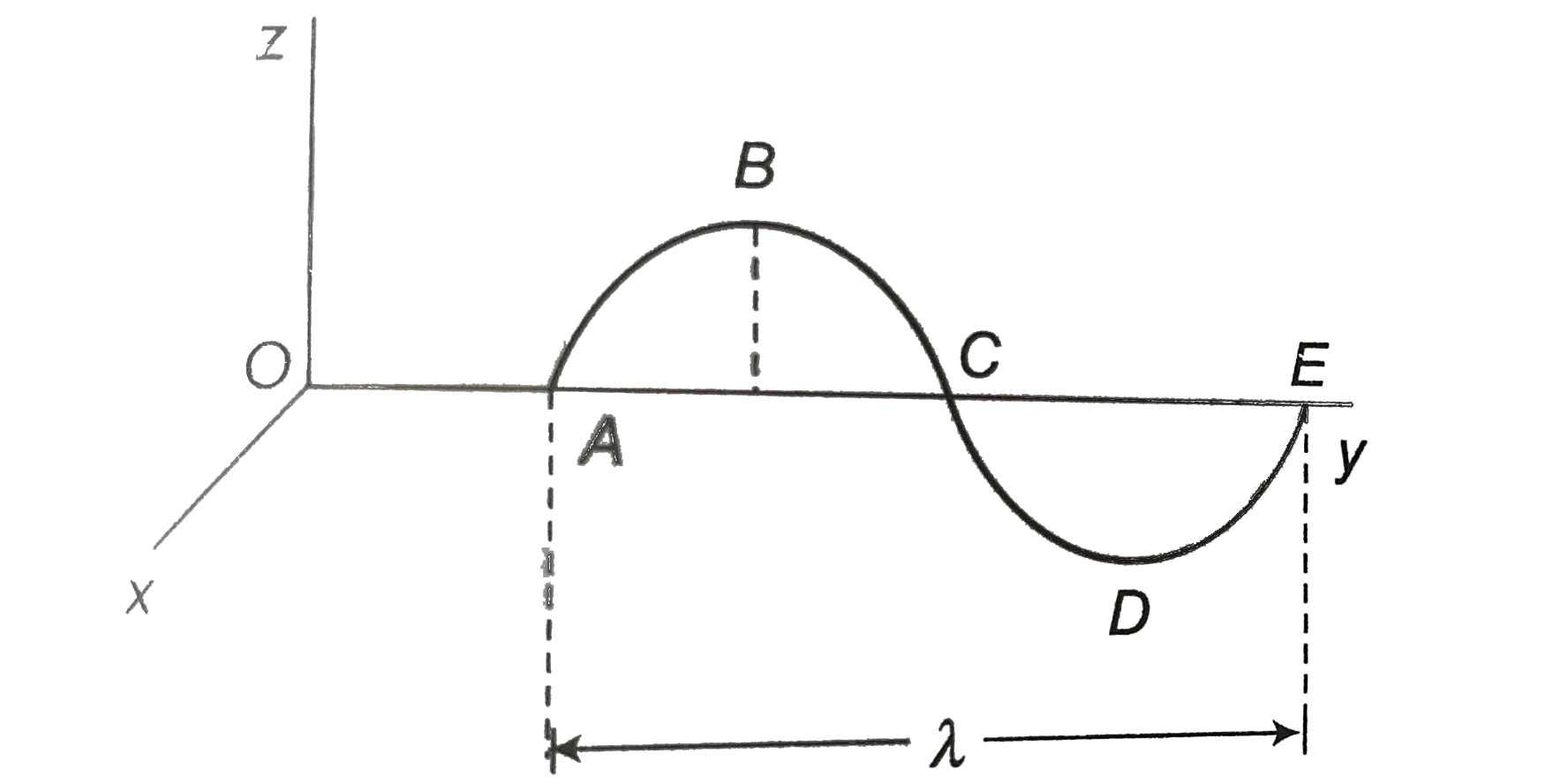 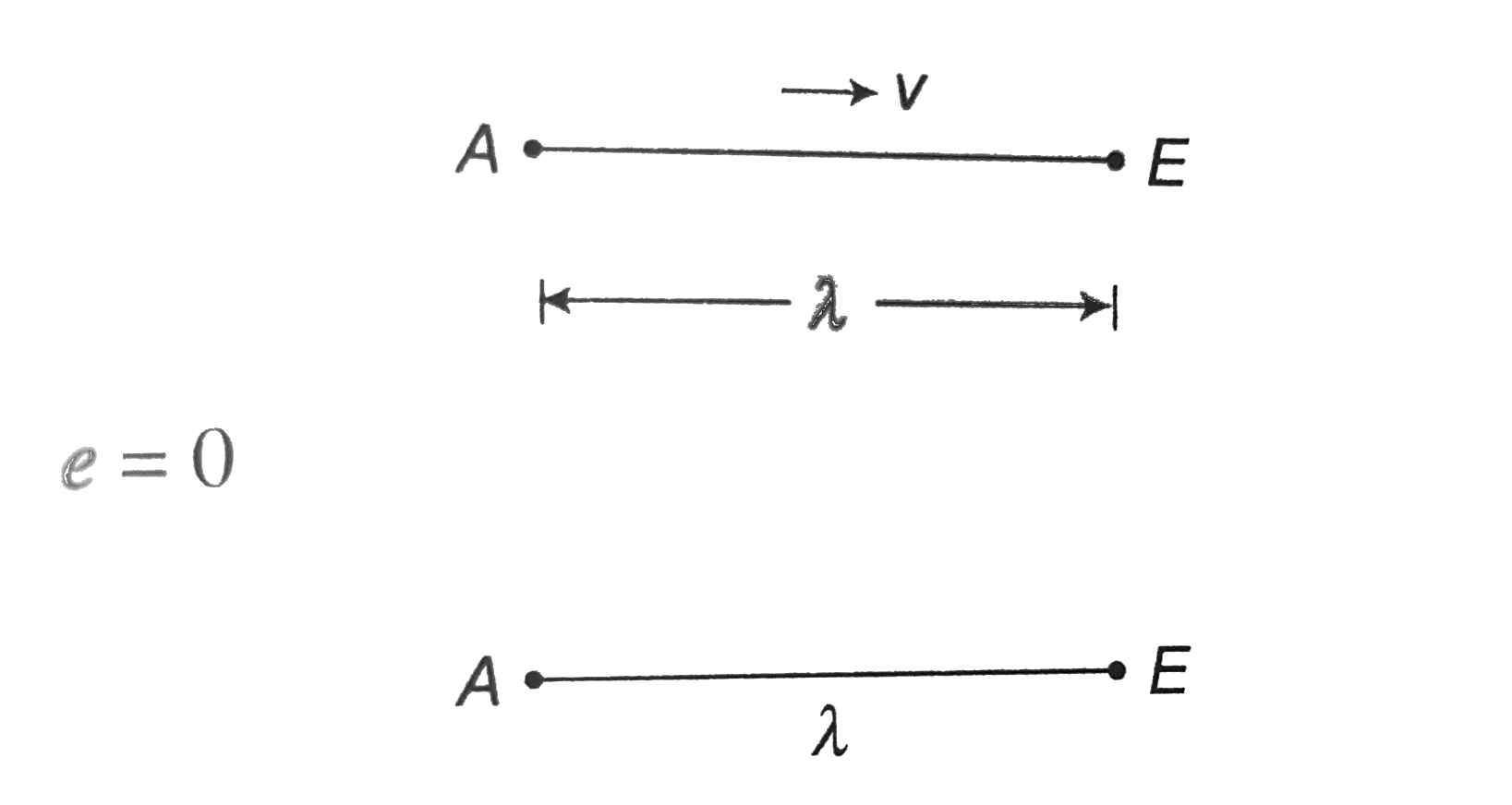  
|
|
| 43500. |
If lambda_0, lambda_x and lambda_m represent the wavelengths of visible light, x-rays and microwaves respectively: |
|
Answer» `lambda_mgtlambda_xgtlambda_v` |
|