Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 43551. |
Which law helps to find direction of magnetic field around a current carrying conductor? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :RIGHT HAND GRIP RULE | |
| 43552. |
A point source S emits light of wavelength 600 nm. It is palced at a very small distance from a flat reflecting mirror AB. Interface. Frignes as observed on the screen placed parallel to reflecting surface at very large distance D from it. The ratio of minimum to maximum intensities in the interference frignes formed near the point P is 1/6. Q. If the intensity of P correspoonds to a maximum, calculate the minimum distance through which the reflecting surface AB should so that intensity at P again becomes maximum. |
|
Answer» 150 nm |
|
| 43553. |
A mass m is suspended to a spring of length L and force constant k. The frequency of vibration is f_(1). The spring is cut into two equal parts and each half is loaded with same mass m. The new frequency f_(2) is given by : |
|
Answer» `f_(2)=sqrt(2)f_(1)` and `""k_(1)=(mg)/(DeltaL)`. Now `""k_(2)=(mg)/(DeltaL//2)=2k_(1)` `f_(2)=(1)/(2pi)sqrt((2k_(1))/(m))` and `f_(2)=sqrt(2)f_(1)`. Correct CHOICE is (a). |
|
| 43554. |
A point source S emits light of wavelength 600 nm. It is palced at a very small distance from a flat reflecting mirror AB. Interface. Frignes as observed on the screen placed parallel to reflecting surface at very large distance D from it. The ratio of minimum to maximum intensities in the interference frignes formed near the point P is 1/6. Q. What is the percentage intensity of the reflected light to the intensity of the reflectd light to the intensity of incident light? |
|
Answer» 0.49 |
|
| 43555. |
A point source S emits light of wavelength 600 nm. It is palced at a very small distance from a flat reflecting mirror AB. Interface. Frignes as observed on the screen placed parallel to reflecting surface at very large distance D from it. The ratio of minimum to maximum intensities in the interference frignes formed near the point P is 1/6. Q. What is the shape of interference fringes on the screen? |
|
Answer» elliptical |
|
| 43556. |
A sustained current circulates in a ring-shaped superconductor. Assuming the superconductor to be a gigantic Bohr orbit show that the current and the magnetic flux are quantized. Take into account the pairing of electrons in a superconductor. |
|
Answer» `i=N(nS)/r*(eh)/(2m_(e))` where S is the conductor.s cross section, and r is the radius of the ring. Clearly the current is quantized: `i=N_(i_(0))`, where `i_(0)` is the MINIMUM current, `i_(0)=(nS)/r*(eh)/(2m_(2))` Since the magnetic flux is proportional to the current, it too turns out to be quantized: `Phi=Li=NLi_(0)=NPhi_(0)` where L is the INDUCTANCE of the ring, and `Phi_(0)` is the minimum magnetic flux. Rigorous theory yields `Phi_(0)=h//2e=2.07xx10^(-15)` Wb. |
|
| 43557. |
A copper coil is moving out of a magnetic field with a constant velocity. If the ohmic resistance of the coil is increased then will it be easy or difficult to remove the coil from the same magnetic field? |
| Answer» Solution :When copper coil is moving out of a magnetic field with CONSTANT velocity then induced EMF (`EPSILON`) is developed. The work done against induced `"emf" = epsilon L`. If resistance of the coil is increased, then current will decrease and hence, work required against induced emf will also decrease and it will be easier to remove the coil from the magnetic field. | |
| 43558. |
In an experiment similar to Young's experiment, interference is observed using waves associated with electrons. The electrons are being produced in an electron gun.In order to increase the fringe width : |
|
Answer» electron gun VOLTAGE be increased But `lambda = (h)/(p) = (lambda)/(sqrt(2m Ve)) therefore lambda infty (1)/(sqrt V)` So as V decreases, `lambda` increases & hence `beta` increases. |
|
| 43560. |
1 kg of ice at 0^(@)C is mixed with 1 kg of steam at 100^(@)C. Find the equilibrium temperature and the final composition of the mixture. Given that latent heat of fusion of ice is 3.36xx10^(5) J/kg and latent heat of vaporization of water is 2.27xx10^(6) J/kg. Specific heat of water is 4200J//kg.^(@)C^(-1) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43561. |
A photon emitted during the de-excitation of electron from a state to the first excited state in a hydrogen atom, irradiates a metallic cathode of work function 2eV, in a photo cell, with a stopping potential of 0.55 V. Obtain the value of the quantum number of the state. |
|
Answer» Solution :When an electron in a hydrogen atom is DE excited from a staten to the firstexcited state (ie,. =2), the ENERGY of emitted photonis. `E = [-(13.6)/(n^(2))] - [- (13.6)/((2)^(2))] = [3.4 - (13.6)/(n^(2))]eV` As work function of photo cell `phi_(0) = 2 eV` and stopping potential `V_(0) =0.55 V`, the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectron `K_("max") - eV_(0) =0.55 eV`. As per Einstein.s photoelectric equation `=E = phi_(0) + k_("max")` `rArr "" [3.4 -(13.6)/(n^(2))] = 2+ 0.55 = 2.55 rArr (13.6)/(n^(2)) = 3.4 - 2.55 = 0.85rArr n = SQRT((13.6)/(0.85)) = 4` |
|
| 43562. |
The Rydberg constant of H_2 atom is 10967700 m^(-1). Calculate the short and long wavelength limits in its Lyman series : |
|
Answer» 602 Å, 906Å `1/(lambda_("short"))=R [1/1^(2)-(1)/((oo)^(2))]=R=10967700` `lambda_("short")=(1)/(10967700)=0.911 XX 10^(-7) m=911Å` For long wavelength, n=2 `1/(lambda_("short"))=R [1/1^(2)-(1)/((oo)^(2))]=R=10967700` `lambda_("short")=(1)/(10967700)=0.911xx 10^(-7)m=911Å` For long wavelength, n=2 `1/lambda_("long")=R [1/1^(2)-1/2^(2)]=3/4R` `lambda_("long")=1212 Å` |
|
| 43563. |
Interference pattern is obtained with a red light of wavelength 6400overset@A. The source is then replaced by another light of wavelength 4000overset@A. It is found that nth bright fringes of first source coincides with (n + 3)th bright fringe of second source. The order of fringe n is : |
|
Answer» 3 |
|
| 43564. |
A drops of water is placed between two parallel glass plates which are then pressed together until the water film is 0.01 cm thick. If the area of water in contact with the plates is 10 cm^2. What is the force due to surface tension drawing the plated together? (T for water 75 dyne/cm) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43565. |
The electric potential due to any point electric dipole varies as ......... . |
|
Answer» `(1)/(r)` |
|
| 43566. |
Define relaxation time of the free electrons drifting in conductor. How is it related to the drift velocity of free electrons? Use this relation to deduce the expression for the electrical resistivity of the material. |
|
Answer» Solution :RELAXATION TIME : The time of free travel of electrons between successive collisions is called the relaxation time. It is denoted by `tau.` when temperature INCREASES, the thermal speed of electrons increases, so collisions of electrons occur more frequently. As a RESULT, the relaxation time decreases of temperature. Relaxation between resistivity and relaxation time is `rho=(M)/(N e^(2)tau).` |
|
| 43567. |
Two elementary particles which have almost infinite life time are |
|
Answer» ELECTRON and neutron |
|
| 43568. |
A man with a near pointof 25 cm reads a book small print using a maagnifying glass, a convex lens of focal length 5 cm. (a) What is the closest and the farthest distance at which he should keep the lens from the page so that he can read the book when viewing through the magnifying glass? (b) what is themaximum and the minimum magnification(magnifying power) possible using the above simple microscope? |
|
Answer» Solution :D = 25 cm, f = 5 cm, For closest object distance, U, the image distance, v is, - 25 cm. (near point focusing) For FARTHER object distance, (u): the corresponding distance (v.) is, `v = oo`(normal focusing) (a) To find closest IMAGEDISTANCE, lens equaiton, `(1)/(v)-(1)/(u)=(1)/(f)` Rewriting for closest object distance, `(1)/(u)=(1)/(v)-(1)/(f)` Substituting, `(1)/(u)=(1)/(-25)-(1)/(5)=(1)/(25)-(1)/(5)=((-1-5)/(25))=-(6)/(25),` `u = (25)/(6) = - 4.167 cm` The closest distance at which the person should can KEEP the book is, u = - 4.167cm. To find farthest object distance, lens equation is, `(1)/(v.)-(1)/(u.)=(1)/(f.)` Rewriting for farthestobjectdistance, `(1)/(u.) = (1)/(v.) - (1)/(f.)` Substituting, `(1)/(u.)=(1)/(oo)-(1)/(5),u=-5cm` The farthst distance at which the person can keep the book is, u = - 5 cm (b) To find magnification in near point focusing, `m=1+(D)/(f)=1+(25)/(5)=6` To findmagnification in normal focusing, `m=(D)/(f)=(25)/(5)=5` |
|
| 43569. |
The reaction time for an automobile driver is 0.7 sec .If the automobile can be decelerated at 5m//s^(2) calculate the total distance travelled in coming to stop from an initial velocity of 8.33 m/s after a signal is observed. |
|
Answer» 12.77 m |
|
| 43570. |
If a diamagnetic substance is brought near North or South pole of a bar magnet, it is |
|
Answer» REPELLED by North POLE and attracted by the South pole |
|
| 43571. |
For increasing the efficiency of Carnot's engine, which of the folowing is most effective: |
|
Answer» increasing the temperature of SOURCE by `80^(@)C` `T_(2)` is most effective. Thus, correct choice is (B). |
|
| 43572. |
In FM, the centre frequency is alloted to the __________ |
|
Answer» transformer |
|
| 43573. |
A reniform rope of mass 0.7 kg and length 2.45 in hangs from a ceiling (a) Find the speed of Transverse wave in the rope at a point 0.5m distrus from the lower end, b) Puste Calculate the time taken by a transverse wave to travel the full length of the rope (g=9.8m//s^(2)). |
|
Answer» Solution :Suppose the `.mu.` be the linear density of ROPE. Let T be the tension at a point .p. at a DISTANCE .x. from lower end of rope. The tension is `T= x mug` The vel. Of wave at the point is `v=SQRT((T)/(mu))= sqrt((muxg)/(mu))= sqrt(xg)` At `x=0.05m v= sqrt(0.5xx9.8)=2.21m//s` At lower end U=0 Attop end `v= sqrt(gl)` `a=(v^(2)-u^(2))/(2s)=(gl-0)/(2l)=(g)/(2)` time taken to travel the wave from lower end to upper end is `t=(v-u)/(a)=(sqrt(gl)-0)/(g//2)=2 sqrt((l)/(g))=2 sqrt((2.45)/(9.8))= 1 sec`. |
|
| 43574. |
An inductor of inductance L and resistance R is connected of A.C. circuit having angular frequency of omega . The value of quality factor Q is …… |
|
Answer» `((OMEGAL^2)/R)^2` `THEREFORE Q=V_L/V_R` or `V_C/V_R` `=(I_(RMS)X_L)/(I_(rms)R)` or `(I_(rms)X_C)/(I_(rms)R)` `=X_L/R` or `X_C/R` `=(omegaL)/R` or `1/(omegaCR)` |
|
| 43575. |
In the circuit shown in the figure, if both the lamps L_(1) and L_(2) are identical |
|
Answer» Their brightness will be same `X=omegaL=2pi(50)(10xx10^(-3))=piOmega` `X_(C)gtX_(L)` |
|
| 43576. |
For any charge configuration, equipotential surface through a point is normal to the electric field. Justify. |
|
Answer» Solution :We KNOW that, the work done (W) in moving a test charge along an equipotential surface is zero. This is because an equipotential surface with a constant vale of potential at all the points on the surface. `therefore""W=FS cos theta=0.` Here, F is the electric force and S is the magnitude of displacement of the charge. For non-zero displacement, this is POSSIBLE only when `cos theta` is equal to 0. i.e. `cos theta=0 rArr =90^(@)`. Thus, the force acting on the point charge is perpendicular to the equipotential surface. We know that the lines of force or the electric field lines indicate the direction of electric force on a charge. Thus, for any charge CONFIGURATION, equipotential surface through a point is normal to the electric field. |
|
| 43577. |
The maximum distance upto which TV transmission from a TV tower of height h can be received is proportional to |
|
Answer» `H^(3//2)` |
|
| 43578. |
A thin conductingstrip of width h = 2.0 cm is tightlywoudnd in the spaheof a verylong coil with cross-secitonradius R = 2.5 cmto make a single-layerstraightsolenoid. A directcurretnt I = 5.0A flows throughthe strip. Find the magneticinductininsideand outsidethe solenoidas a funcitionof the distanance r from its axis. |
|
Answer» Solution :If the strip is tightly wound it must have a picvh of `h`. This means that the current will FLOW obiliquenlty, party along `hat(e)_(varphi)` and partly along `hat(e)_(z)`. Obvioulsy the surface current densityin, `vec(J)_(s) = (I)/(h) [sqrt(1 - (4//2 pi R)^(2)) hat(e)_(varphi) + (h)/(2PI R) hat(e)_(z)]`. By comparision with the case of a selenoid and a hollow straightconductor, we SEE that field inside the coll `= mu_(0) (I)/(h)sqrt(1 - (h//2pi R)^(2))` `(CF. B = mu_(0) nI)` outside only the other term CONTRIBUTES, so `B_(varphi) xx 2pi = mu_(0) (I)/(h) xx (h)/(2pi R) xx 2pi R` or, `B_(varphi) = (mu_(0))/(4pi). (2l)/(r)`. |
|
| 43579. |
The drift velocity of electrons in a wire of radius r is proportional to |
|
Answer» R |
|
| 43580. |
In photoelectric effect, electrons are ejected from metals, if the incident light has a certain minimum |
|
Answer» wavelength |
|
| 43581. |
f_(B) and f_(R) are focal lengths of a convex lens for blue and red light respectively and F_(B_ and Fr are the focal lengths of the concave lens for blue and red light respectively. We must then have |
|
Answer» `f_(B)gtf_(R)` and `f_(B)ltf_(R)` |
|
| 43582. |
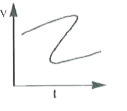
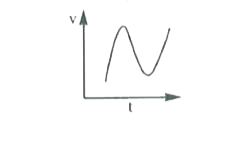
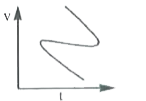
Which of the following velocity-time graphs show a realistic situation for a body in motion |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 43583. |
A small transparent slab containing material of mu=1.5 is placed along AS_(2)(figure). What will be the distance from O of the principle maxima and of the first minima on either side of the principal maxima obtained in the absence of the glass slab ? |
|
Answer» 0.19 D and -0.33 D |
|
| 43584. |
In Q.36, the external resistance that must be connected is series with the main circuit so that the total current in the main circuit remains unaltered even when the galvanometer is shunted is |
|
Answer» `3663 OMEGA` `G - (SG)/(S + G) = 3663 - 107.7 = 3555.3 Omega` |
|
| 43585. |
Two wires of same material have their lengths in the ratio 2:3 and radii 8:9 . Equal value of p.d is applied between their ends (separately). Calculate the ratio of current through those two |
|
Answer» Solution :We know that `R= (rhol)/(A) =(rhol)/(pir^2)` `R= (rhol)/(pir^2)` SUBSTITUTE `R= V/I` `V/I =(rhol)/(pir^2) impliesI = (Vpir^2)/(rhol)` `I PROP (r^2)/(l)` `(I_1)/(I_2) =(r_1^2)/(l_1) XX(l_2)/(r_2^2)` `(I_1)/(I_2) =(r_1^2)/(r_2^2) xx ((l_2)/(l_1)) = (8^2 xx 3)/(9^2 xx 2) =(64xx3)/(81xx2) = (32)/(27)` `I_1 :I_2 =32:27` |
|
| 43586. |
What will be power of a crane in watts which lifts a stone of mass 100 kg to a height of 10 min 20 seconds ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Here `P+W/t=("ENERGY")/(t)` =`(100xx10xx10)/(20)=500 W` |
|
| 43587. |
A part of straight stick is immersed in water in an inclined way. When the immersed portion is viewed normally from the air above, it appears to be inclined at an angle of 30^(@) with the surface of water. Calculate the actual angle of the stick with the surface of water. Refractive index of water = (4)/(3)."" [tan 37.6^(@) = 0.77] |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43588. |
The region between two concentric spheres of radii 'a' and 'b', respectively (see figure), has volume charge density rho =A/r, where A is a constant and r is the distance from the centre. At the centre of the spheres is a point charge Q. The value of A such that the electric field in the region between the spheres will be constant is : |
|
Answer» `(2Q)/(pia^(2))` where `rho =A/r^(2), S = 4pir^(2)` 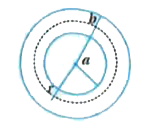 `Q + int_(a)^(r ) 4pir dr = epsilon_(0) [THEREFORE phi =E_(S)]` `therefore phi + (4piAr^(2))/2 -(4piAa^(2))/2 = E xx 4pir^(2)epsilon(0)` E is constant in between the spheres. So that it is independent of r. `therefore phi - 2piAa^(2) =0` `therefore A = Q/(2pia^(2))` |
|
| 43589. |
In each fission of U^(235) , 200 MeV of energy is released. If a reactor produces 100MW power the rate of fission in it will be |
|
Answer» `3.125 xx10^(18) ` PER MIN |
|
| 43590. |
When a positively charged particle enters into a uniform magnetic field with uniform velocity its trajectory can be i) a straight line ii) a circle iii) a helix |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 43591. |
A moon of Jupiter has a nearly circular orbit of radius R and an orbit period of T. which of the following expressions gives the mass of Jupiter? |
|
Answer» `(2piR)/(T)` `G(Mm)/(R^(2))=(mv^(2))/(R)` `G(M)/(R)=V^(2)` `=((2piR)/(T))^(2)` ltBrgt `M=(4pi^(2)R^(3))/(GT^(2))`. |
|
| 43592. |
Assuming a ball of mass m and of radius r to roll down from the top without slipping. Neglect energy losses due to rolling friction. |
|
Answer» `N=(mg)/7(17cos alpha - 10)` |
|
| 43595. |
A ring angled isosceles prism KLM of refractive index n_(1) is placed inside a rectangular block PQRS of refractive index n_(2) as shown in the adjoining Fig. The rectangular box is surrounded by a medium of refractive index n_(3). A ray of light AB enters the rectangular block normally. Depending upon the relationships between n_(1), n_(2) and n_(3). it takes one of the four possible paths. State the condition for light ray to travel along path no. 3 (i.e., path ABCGH). |
| Answer» Solution :The ray no. 3 goes STRAIGHT without UNDERGOING deviation at C. Hence we conclude that `n_(1)=n_(2)` and `n_(3)` may have any value. | |
| 43596. |
Four charges of same magnitude q are placed at four corners of a square of side a . The value electric potential at the centre of the souare will be (wherek = (1)/(4 pi epsilon_(0)) ) |
|
Answer» `(4 kq)/(a ) ` |
|
| 43597. |
A ring angled isosceles prism KLM of refractive index n_(1) is placed inside a rectangular block PQRS of refractive index n_(2) as shown in the adjoining Fig. The rectangular box is surrounded by a medium of refractive index n_(3). A ray of light AB enters the rectangular block normally. Depending upon the relationships between n_(1), n_(2) and n_(3). it takes one of the four possible paths. Under what condition the ray follows the path no. 2 (i.e., path ABCIJ)? |
| Answer» Solution :The RAY no. 2 bends away from normal while undergoing REFRACTION at C and bends further away from the normal while undergoing refraction at I. It means that `n_(3) lt n_(2) lt n_(1)`. However, the light ray does not suffer total internal reflaction at C, hence it is CLEAR that `n_(2) gt (n_(1))/(SQRT2).` Hence we CONCLUDE that `n_(1) gt n_(2) gt (n)/(sqrt2) and n_(3) lt n_(2)`. | |
| 43598. |
A parallel plate condenser has plates of area 200 cm^(2)and separation 0.05 cm. The space between plates have been filled with a dielectric having k = 8 and then charged to 300 volts. The stored energy |
|
Answer» `1.6 xx10^(-5)J` |
|
| 43599. |
A ring angled isosceles prism KLM of refractive index n_(1) is placed inside a rectangular block PQRS of refractive index n_(2) as shown in the adjoining Fig. The rectangular box is surrounded by a medium of refractive index n_(3). A ray of light AB enters the rectangular block normally. Depending upon the relationships between n_(1), n_(2) and n_(3). it takes one of the four possible paths. Under what condition the ray follows the path no. 1 (i.e., path ABCI)? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Since the RAY shown as 1 suffers total internal reflection at C as well as D, where angle of incidence is `45^(@)`. It means that value of critical angle `i_(c) LE 45^(@)` and it is possible of `n_(12)(=(n_(1))/(n_(2)))ge(1)/(sin 45^(@)) RARR n_(1) ge sqrt2n_(2)` |
|
| 43600. |
The resistance of a potentiometer wire is 18Omega. A high resistance box and a 2 V accumulator are connected in series with it. What should be the value of the resistance in the box, if it is desired to have a potential drop of 1muV//mm? |
|
Answer» |
|