Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 43501. |
The string beween blocks of mass m and 2m is massless and inextensible. The system is suspended by a massless spring as shown. If the string is cut find the magnitudes of accelerations of mass 2m and m (immediately after cutting): |
|
Answer» g.g  By equilibrium of 2m, T=2 mg - T From (i) & (ii), `T = 2mg - mg = mg` When the string is cut: For mass m:`F_(net) = ma_(m)` `IMPLIES mg = ma_(m)` `impliesa_(m)=g` For mass 2m :`F_(net) = 2ma_(2m)` ` implies 2mg - T = 2ma_(2m )` `= 2mg - mg = 2ma_(2m)` `impliesa_(2m)=(g)/(2)` HENCE choice is (C). |
|
| 43502. |
State whether true or false and justify. in a transistor amplifier all the frequency will have exactly equal gain. |
|
Answer» REMAINS constant for all frequencies. |
|
| 43503. |
Why are Si and GaAs preferred materials for solar cells ? Explain. |
|
Answer» Solution :The solar radiation received by us on earth is as shown in . From the FIGURE, it is clear that maximum solar intensity corresponds to energy of about 1.5 eV. For photo excitation energy of incident radiation (E = hv) should be S greater than the ener8y band gap `E_(s)` for given semiconductor. Hence, semiconductor with band gap of~1.5 eV or lower is likely to GIVE better solar conversion efficiency. As silicon has band gap of 1.1 eV and GaAs a band gap of 1.53 eV, hence these materials are preferred for solar cells. Out of Si and GaAs we prefer GaAs, INSPITE of its higher band gap energy value, because its absorption COEFFICIENT is relatively higher. ` ` |
|
| 43504. |
In series L-C-R circuit, resistance, inductance and capacitance are connected in series. The value of potential difference across three are 70 V, 90 V and 65 V respectively. The value of potential difference of A.C. source is …... |
|
Answer» Solution :`V_R=70V, V_L=90 V, V_C=65` V `V^2=V_R^2+(V_L-V_C)^2` `V=SQRT((70)^2 +(90-65)^2)` `=sqrt((70)^2 + (25)^2)` `=sqrt(4900+625)` `=sqrt5525`=74.3 V |
|
| 43505. |
Two samples X and Y contain equal amount of radioactive substances. If 1^(th)/16 of the sample Y , remain after 8 hours, then the ratio of half life periods of X and Y is |
|
Answer» `2:1` where, number of HALF lives , `n=t/T` T is the half LIFE period For SAMPLE X `1/16=(1/2)^(8//T_X)` or `(1/2)^4 =(1/2)^(8//T_X)` `RARR 4=8/T_X` ….(i) For sample Y `(1/256)=(1/2)^(8//T_Y)` or `(1/2)^8=(1/2)^(8//T_Y)` `8=8/T_Y` ...(II) Dividing (i) by (ii) , we get `4/8=8/T_X xx T_Y/8` `1/2=T_Y/T_X` or `T_X/T_Y=2/1` |
|
| 43507. |
A beam of monochromatic light is refracted from vacuum into a medium of refractive index 1.5. The wavelenght of refracted light will be |
|
Answer» same |
|
| 43508. |
Which of the following radiations has the least wavelength |
| Answer» Solution :`lambda_(gamma) lt lambda_(X) lt lambda_(alpha) lt lambda_(beta)` | |
| 43509. |
A rope of length 5 m has uniform mass per unit length. lambda = 2 kg/m The rope is pulled by a constant force of 10N on the smooth horizontal surface as shown in figure The tension in the rope at x = 2 m from polit A is |
|
Answer» 2 N |
|
| 43510. |
Two rocks are dropped simultaneously from the top of a tall building. Rock 1 has mass M_(1), and rock 2 has mass M_(2). If air resistance is negligible, what is the ratio of rock 1's momentum to rock 2's momentum just before they hit the ground? |
|
Answer» `(sqrt(M_(1)))/(M_(2))` |
|
| 43511. |
A coil of inductance 0.2 henry is connected to 600volt battery. At what rate will the current in the coil grow when circuit is completed? |
|
Answer» Solution :As the battery and inductor are in parallel, at any instant, EMF of the battery and self emf in the inductor are EQUAL `|e|= L (DI)/(DT) or (dI)/(dt)= (|e|)/(L)= (600V)/(0.2H)= 3000A s^(-1)` |
|
| 43512. |
The total energy of an electron in the ground state of a hydrogen atom is -13.6 eV. : What do you mean by ground state of a hydro gen atom ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :NEGATIVE SIGN IMPLIES that the ELECTRONS are strongly bounded to the nucleus. | |
| 43513. |
The potential energy of a particle executing SHM in its rest position is 15 J. The average kinetic energy of the particle during one oscillation is 5 J. The total energy of the particle is |
|
Answer» 10 J (U other FORM of potential energy) position where potential energy is MAXIMUM which will be the total energy. |
|
| 43514. |
(a) A particle is acted upon by a force vec(F) given by vec(F)=A cos omega t hat(i) + B hat(k) and its position vector vec(r)=a[(cos) ( omega t) hat(i)+ sin(omega t) hat(j)]+1/2 bt^(2)hat(k). Find the work done on the particle by the force vec(F) from time t= pi // 2omegato time t=pi //omega. (b) A particle moves under a force vec(F)= xy hat(i)+y^(2)hat(j) and traversesalong a path y=4x+1. Find the work done by the force when the particle is displaced from the point P(1, 5) to Q(2, 9). |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) The POSITION vector of the particle is `vec(r)=a[COS omega t hat(i)+sin omega t hat(j)]+1/2 bt^(2)hat(k)` `:.`The velocity is given by, `vec(V)=(d vec(r))/(dt)=(-a omega sin omega t)hat(i)+(a omega cos omega t ) hat(i)+ ( bt) hat(k)` Work done `W=INT vec(F).vec(v)dt=-(a A omega)/(2) int_(pi//2 omega)^(pi//omega) sin 2 omega t dt + B b int_(pi//2omega)^(pi//omega)tdt` `=(a Aomega)/(2)xx(cos 2 omega t)/(2 omega)|_(pi//2 omega)^(pi//omega)+Bb 1/2t^(2)|_(pi//2 omega)^(pi//omega)=(a A omega)/(2)[(1)/(2 omega)-(-1)/(2 omega)]+Bb.1/2[(pi/omega)^(2)-((pi)/(2 omega))^(2)]` `=(a A omega)/(2)xx1/omega+3/8 Bb ((pi^(2))/(omega^(2)))=1/2 AA+(3 pi^(2))/(8omega^(2))Bb`. (b)Work done `W=vec(F).d vec(r)= int ( F_(x) hat(i)+F_(y)hat(j)).(dx hat(i)dy hat(j))` `= int(F_(x)dx)+int(F_(y)dy)=int xydy + int y^(2)dy=int x ( 4x+1)dx+int y^(2)dy` `=[4/3 x^(3)+(x^(2))/(2)]_(1)^(2)+[(y^(3))/(3)]_(5)^(9)=212` units. |
|
| 43515. |
An uncharged particle is moving with a velocity of in non-uniform magnetic ficld as shown. velocity vecv would be |
|
Answer» Maximunm at A & B |
|
| 43516. |
There are two concentric spheres of radius (a) and (b) respectively. If the space between them is filled with medium of resistivity rho, then the resistance of the intergap between the two spheres will be |
|
Answer» Solution :CONSIDER a cocentric spherical shell of radius x and thickness dx, its RESISTANCE is dR, `dR=(RHO dx)/(4pix^(2))` Total resistance `R=int_(a)^(b)dR=R=((rho)/(4pi))int_(a)^(b)(dx)/(x^(2))=(rho)/(4pi)[(1)/(a)-(1)/(b)]` |
|
| 43517. |
Two object A and B when placed in turns infront of a concave mirror, give images of equal size. The focal length of the concave mirror is 7.5cm and size of object A is three times the size of object B from the mirror , if A is placed 30cm from the mirror. |
|
Answer» `18cm` Here `l_(A)=O_(A)` and `O_(A)=3O_(B)` `(m_(A))/(m_(B))=(l_(A))/(O_(A))XX(O_(B))/(l_(B))=(l_(A))/(O_(A))=1/3` also, `m_(A)=f/(f-u_(A))` and `m_(B)=f/(f-u_(B))` ` (m_(A))/(m_(B))=((f-u_(B))/(f-u_(A)))` `1/3=(-7.5-u_(B))/(-7.5-(-30))` `u_(B)=-15cm` |
|
| 43518. |
Young's double slit experiment gives interference fringes of width 0.3 mm. A thin plate made of material of refractive index 1.5 is kept in the path of light from one of the sits, then the fringe width becomes |
|
Answer» zero `y_(0)=D/d(mu-1)t`. Shifting is towards the side in which the plate is introduced without any change in fringe width as shownn in figure. 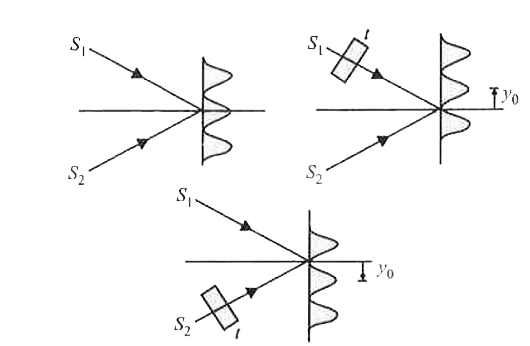 Therefore, when a thin glass plate of refractive index 1.5 is kept in the path of light from one of the slits, only the fringes get shifted bu the fringe width remains unchanged i.e. 0.3 mm. |
|
| 43519. |
Which one of the following is correct ? The wavelength of the X-rays |
|
Answer» is LONGER than the wavelengthofsoundwaves |
|
| 43520. |
When a resistor of 11Omega is conntected in series with an electric cell, the current flwoing in it is 0.5 A. Instead, when a resistor of 5Omega is conntected to the same electric cell in series, the current increase by 0.4 A , The internal resistance of the cell is |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :We KNOW `V=i(R+r)=0.5(11+r)+………….(1)"` `V=0.9(5+r)"………… (2)"` From `(1)&(2)0.5(11+r)=0.9(5+r)` `0.5xx11+0.5r=0.9xx5+0.9r` `5.5xx0.5r=4.5+0.9r RARR 0.4r=1` `r=2.5Omega` |
|
| 43521. |
Find the potential difference between points A and B (V_(B)-V_(A)) in the network |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43522. |
LED converts---energy to light energy |
| Answer» SOLUTION :ELECTRICAL | |
| 43523. |
Derive th lens maker's formula. |
Answer» Solution : Consider a THIN convex lens placed in a medium of refractive index `n_1`. Let `n_2` be the refractive index of the material of the lens. Let O be the a point luminous object placed on the principle axis at a distance u from its optic centre as shown in fig. A RAY OP incident ALONG the principle axis proceeds undeviated. Another paraxial ray incident on the lens along OM is refracted along MN and emerges along NI. The emergent ray meet at I on the principle axis.I is the real image of object O. The formation of image I can be considered in two stages. 1. Refraction at surface APB: In the absence of the second surface AQB, the refracted rays MN and PQ intersect at `I^1` in the medium of refractive index `n_1`. `I_1` is real image of object O formed due to refraction at the surface APB.For this refraction from rarer to denser medium. Object distance =OP=u. Image distance `=PI^1=v^1` `therefore n_2/(v.)=n_1/u=(n_2-n_1)/R_1` ....(1) Refraction at a surface AQB: Rays MN and PQ incident on the surface AQB undergo refraction and emerge out of the lens.The emergent rays intersect at I on the principal axis `I^1` acts as virtual object for the refraction at AQB and its real image is I. The refraction is from denser to rarermedium. For the refraction Object distance = `QI^1=v^1` Image distance =QI=v. i.e., `n_1/v-n_2/(v.)=-((n_2-n_2)/R_2)` ...(2) Adding equations (1) and (2) `n_1/v-n_1/u=(n_2-n_1)/R_1-(n_2-n_1)/R_2=(n_2-n_1){1/R_1-1/R_2}` Dividing throughout by `n_1` `1/v-1/u=(n_2-n_1)/n_1{1/R_1-1/R_2} =(n_2/n_1-1){1/R_1-1/R_2}` i.e., `1/v-1/u=(n_21-1) {1/R_1-1/R_2}` where `n_(21)=n_2/n_1` If `u=oo` then the incident beam on the lens is a parallel beam. The final image will be formed at the principal focus . In this case, v=f. `therefore 1/f=(n_21-1){1/R_1-1/R_2}` This RELATION is known as lens maker.s formula. If the refractive index of the material of the lens is N and it is placed in air then `1/f=(n-1){1/R_1-1/R_2}` |
|
| 43524. |
If 2.2 kW power is transmitted through a 100 Omega line at , 000,22 V the power loss in the form of heat will be |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 43525. |
If the electric field in a region is given by vec(E) = 5 hat(i) + 4 hat(j)+ 9 hat(K) , then the electric flux through a surface of area 20 units lying in the y-z plane will be |
|
Answer» 20 units flux `(phi) = vec(E).vec(A) = 5 xx 20` = 100 units |
|
| 43526. |
Explain the effect of potential difference on photoelectric current. |
|
Answer» Solution :Effect of potential difference on photoelectric current: To study the effect of potential difference V between the electrodes on photoelectric current, the frequency and intensity of the incident light are kept constant. Initially the potential of A is kept positive with respect to C and the cathode is irradiated with the given light. Now, the potential of A is increased and the corresponding photocurrent is noted. As the potential of A is increased, photocurrent is also increased. However a stage is reached where photocurrent reaches a saturation value (saturation current) at which all the photoelectrons from Care COLLECTED by A. This is represented by the flat portion of the graph between potential of A and photocurrent. 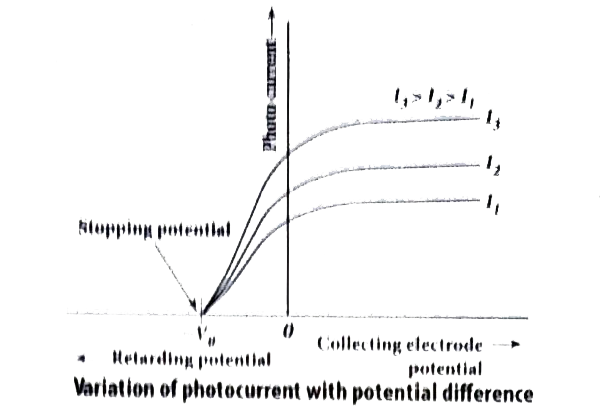 When a negative (retarding) potential is applied to A with respect to C, the current does not Immediately drop to vero because the photoelectrons are emitted with some definite and DIFFERENT kinetic ENERGIES. • The kinetic energy of some of the photoolectrons is such that they could overcome the retarding electric field and rench the electrode A. • When the negative (rotarding) potential of A is gradually increased, the photocurrent starts to decrease because more and more photoclectrons are being repelled away from reaching the electrode A. The photocurreunt becomes zero at a particular negative potential CALLED stopping or cut-off potential • Stopping potential is that the value of the negative (retarding) potential given to the collecting electrode A which is just sufficient to stop the most energetic photoelectrons emitted and make the photocurrent zero. • Aribe stopping potential, even the most energetic ELECTRON is brought to rest. Therefore, the Initial kinetic energy of the fastest electron `(k_(max)) ` is equal to the work done by the stopping potential to stop it `(eV_(0))` `K_(max)=1/2 mv_(max)^(2)=eV_(0) .........(1)` where `v_(max)` is the maximum speed of the emitted photoelectron `v_(max)=sqrt(2eV_(0))/m` `v_(max)=sqrt((2 xx 1.602 xx 10^(-19))/(9.1 xx 10^(-31)) xx V_(0))=5.93 xx 10^(5) sqrt(V_(0)) .........(2)` From equation (1) `K_(max)=eV_(0) ("in joule") (or) K_(max)=V_(0) ("in eV")` • From the graph, when the intensity of the incident light alone is increased, the saturation current also increases but the value of `V_(0)` remains constant. • Thus, for a given frequency of the incident light, the stopping potential is independent of intensity of the incident light. This also implies that the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons is independent of intensity of the incident light. |
|
| 43527. |
(a) Draw a ray diagram for final image formed at distance of distinct vision (D) by a comppound microscope and write expression for its magnifying power. (b) An angular magnification (magnifying power) of 30x is desired for a compound microscope using as objective of focal length 1.25 cm and eye piece of focal length 5 cm. How will you set up the compound microscope? |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) The labelled ray diagram showing image formation in a compound microscope has been shown here. MAGNIFYING POWER of a travelling microscope is given by the relation : `m=(v_(0))/(u_(0))(1+(D)/(f_(e)))=(L)/(f_(0))(1+(D)/(f_(e)))` 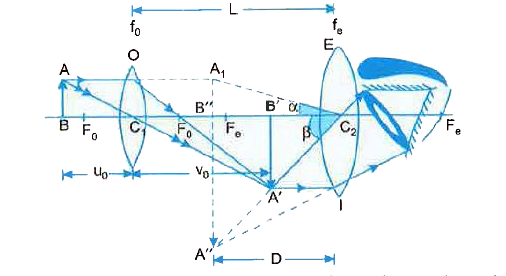 (b) In normal adjustment of microscope, the final image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision i.e., D = 25 cm. In that case, angular magnification of eyepiece `m_(e)=(1+(D)/(f_(e)))=1+(25)/(5)=6""[because f_(e)=+5cm]` As magnification of microscope m = 30 and `m=m_(0)xxm_(e)` `rArr""m_(0)=(m)/(m_(e))=(30)/(6)=5` `therefore""m_(0)=(v_(0))/(u_(0))=5` or `v_(0)=5u_(0)` and as per sign convention `u_(0)` is `-ve` but `v_(0)` is `+ve` and `f_(0)=+1.25cm`. Hence, we have `(1)/(v_(0))-(1)/(u_(0))=(1)/(f_(0)) or (1)/(5u_(0))-(1)/((-u_(0)))=(1)/(1.25) or (6)/(5u_(0))=(1)/(1.25)` `rArr""u_(0)=1.5 cm` and hence `|v_(0)|=|5u_(0)|=7.5cm` Moreover `m_(e)=|(v_(e))/(u_(e))|=(D)/(|u_(e)|)`, hence `|u_(e)|=(D)/(m_(e))=(25)/(6)=4.17cm` `therefore` Separation between the objective and eye-LENS `L=|v_(0)|+|u_(e)|=7.5+4.17=11.67cm` and the object should be placed 1.5 cm from the objective lens to obtain the desired magnification. |
|
| 43528. |
A thin wire of length L and uniform linear mass density p is bent into a circular loop with centre at O as shown. The moment of inertia of the loop about the axis XX' is |
|
Answer» `(pL^(3))/(8pi^(2))` `therefore` Mass of wire = pL Since the wire of length L is TURNED into a circle, `2piR=LrArrR=L/(2PI)` M.I. of loop about given axis = `MR^(2)+(MR^(2))/2=3/2MR^(2)` M.I. of loop =`3/2xx(pL)(L/(2pi))^(2)=3/8.(pL^(3))/(pi^(2))` |
|
| 43529. |
Find the capacitance of the infinite ladder of capacitors shown in Fig between points A and B . |
|
Answer» Solution :Let the net capacitance of the given INFINITE ladder of capacitors between POINTS A and B be C . As the ladder is infinite , addition of one more element of two capacitors `(1 mu F and 2 mu F)` across the points A and B does not change the total capacitance C i.e., value of C should remain unchanged . Let us do it as shown in Fig. 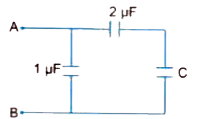 Here , CAPACITOR of `2 mu F ` is in series with C , hence their combined capacitance will be `C. = (C XX 2)/(C + 2) = (2C)/(C + 2) mu F ` This combination is in parallel with capacitor of `1 mu F ` , hence , we have `C = C. + 1 = (2C)/( C+2) + 1` or `C (C +2) = 2C + (C + 2) or C^(2)+ 2 C = 3 C + 2 or C^(2) - C - 2 = 0` On solving the quadratic equation we find that `C = +2` or `-1 mu F ` However , capacitance cannot be negative . Hence , net capacitance of infinite ladder of capacitors `C = +2mu F ` |
|
| 43530. |
In diffraction from a single slit, the angular width of the central maxima does not depend on |
|
Answer» WAVELENGTH of light |
|
| 43531. |
Identify the correst statements from the following: I. Sulphur sol is an example of a multimolecular colloid. II. Tyndall effect is observed when the diameter of the dispersed particles is not much smaller than the wavelength of the light used. III. The process of removing a dissolved substance from a colloidal solution by means of diffusion through a suitable membrane is called peptisation. IV.Eosin,gelatin are examples of negatively charged sols, |
|
Answer» I,II,III II. For tyndall effect to be observed diameter of dispersed particles should not be much SMALLER than the wavelength of the light used. III. Peptisation is the process of forming stable colloid by using an electrolyte to break up a precipitate and dispersed into the colloids hence, given STATMENT is wrong about peptisation. IV. Eosin and GELATIN are examples of negatively charged sol. Hence option (b) is correct. |
|
| 43532. |
Calculate the angle of dispersion between red and violet colours produced by a flint glass prism of refracting angle of 60^@ . Givenmu_v = 1.663 " and " mu_r 1.622 . |
|
Answer» Solution :For MINIMUM deviation position, ` mu_(red) = (sin (A+ delta_(red)))/(sin A/2)` or ` sin ( (A + delta_(red))/(2)) = n_(red)` `sin A/2 = 1.622 xx 0.5 = 0.811` ` therefore (60 + delta_(red))/(2) = 54^@ 12'` ` delta_(red) = 108^@ 24'- 60^@ = 48^@ 24'` SIMILARLY `sin ((A+ delta_("violet"))/(2)) = 1.663 xx 0.5` ` = 0.8315 " or " (60^@ + delta_("violet"))/(2) = 56^@ 15'` ` delta_("violet") = 112^@ 30' - 60^@ = 52^@ 30'` `therefore _("violet") - delta_(red) = (52^@ 30') - (48^@ 24') = 4^@ 6'` It is not advisable to use the formula `delta_v - delta_r = (mu_v - mu_r) ` in the above solution . |
|
| 43533. |
The temperature at which average kinetic energy of an atom in gaseous hydrogen becomes equal to the binding energy of the electron in hydrogen atom, is of the order of |
|
Answer» `10^(4)K` Hence, `13.6eV =(3/2)Kt` `T=(13.6 xx 1.6 xx 10^(-19)xx 2)/(3 xx 1.380 xx 10^(23)) approx 10^(5)K` |
|
| 43534. |
What will be the BE of a satellite of mass 80 kg revolving in an orbit at a height 1600 km from the earth’s surface is |
|
Answer» `2:1` |
|
| 43535. |
For the redox reaction , MnO_(4)^(-) + C_(2)O_(4)^(-2) + H^(+) toMn^(+2) + CO_(2) + H_(2)O the correct coefficient of reactants MnO_(4)^(-), C_(2)O_(4)^(-2) H^(+) for the balanced reaction are respectively : |
|
Answer» 2, 5, 16 `2MnO_(4)^(-) + 5C_(2)O_(4)^(-2) + 16H^(+) to 2 Mn^(+2) + 10 CO_(2) + 8H_(2)O` |
|
| 43536. |
The force acting on a north pole of magnet of pole strength 3200 Am and 10 cm away from the south pole of a point bar magnet of pole strength 40 Am is .......... N. |
|
Answer» `-1.28` `= 10^(-7) xx (3200 xx 40)/((0.1)^(2))` `=12800000 xx 10^(-7) ` `therefore F=1.28 N` |
|
| 43537. |
The energy received from sun on earth is 8.4 J//"minute" - cm^(2). The solar energy incident on an area of 10m2 is given to 100 gm of water in a bowl at 0^(@)C .The water will start boiling after – |
|
Answer» 1s |
|
| 43538. |
A long wire of finite resistance is connected to an ac generator . This wire is then wound into a coil of many loops and reconnected to the generator . Is the current in the circuit with the coil greater than, less than, or the same as the current in the circuit with the uncoiled wire ? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43539. |
The ferromagnetic core of electromagnets should have |
|
Answer» a BROAD HYSTERESIS loop |
|
| 43540. |
At what time after t=0, x=0.2m will be at y =0.25nm and going up for the first time. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43541. |
A man of height h is waling away from a street lamp with a constant speed v. The height of the street lamp is 3h. The rate at which the length of the man's shadow is increasing when he is at a distance 10 hfrom the base of the street lamp is |
|
Answer» v/2 |
|
| 43542. |
The figure shows four pairs of polarizing sheets, seen face-on. Each pair is mounted in the path of initially unpolarized light. The polarizing direction of each sheet (indicated by the dashed line) is referenced to either a horizontal x -axis or a vertical y axis. Rank the pair according to the fraction of the initial intensity that they pass, greatest first |
|
Answer» `(i) GT (II) gt (iii) gt (iv)` |
|
| 43543. |
the ratio of the radii of n = 10 orbit of hydrogen and Li^(+2) ion is ..... |
|
Answer» Solution :`r_(n)=(n^(2))/(Z).a_(0)` where `a_(0)=` Bohr radius `=(H^(2)in_(0))/(pie^(2)m)=0.53Å` For H atom Z=1,n=10 `:.r_(10)=(100)/(1)a_(0)` and For `LI^(+2)` atom Z=3, n=10, R=R `:.R_(10)=(100)/(3)a_(0)"":.(r_(10))/(R_(10))-3` |
|
| 43544. |
The magnetic lines of force inside a bar magnet : |
|
Answer» do not exist |
|
| 43545. |
If one Al atom added to 10^(9) per atom of Si then charge on holes in one mole will be ………. |
|
Answer» `1.6xx10^(-10)C` 1 atom of Al PER `10^(9)` SI atom then at atom of `10^(23)` Si ? `N=(1xx10^(23))/(10^(9))=10^(14)` `therefore Q=Ne` `=10^(14)xx1.6xx10^(-19)` `therefore Q=1.6xx10^(-5)C` |
|
| 43546. |
Find critical angle of diamond whose refractive index is 2.42. |
|
Answer» 2.441 `thereforeC=sin^(-1)((1)/(2.42))=24.41` |
|
| 43547. |
Which of the following is used in optical fibres ? |
|
Answer» TOTAL INTERNAL REFLECTION |
|
| 43549. |
The electric susceptibility of water vapour is strongly dependent on temperature: {:("Temperature t,", ""^(@)C, 120,150,180,210),("Pressure p,", mm Hg, 565,609,653,698):} Electric susceptibility chi_(e) 4.00xx10^(-3),3.72xx10^(-3),3.49xx10^(-3)3.29xx10^(-3) Plot a graph and find the temperature dependence of the electric susceptibility. Calculate the dipole moment of a molecule of water. |
|
Answer» Solution :To plot the graph it is convenient to use new VARIABLES: `x=10^(3)//T` where T is the absolute temperature, and `y=10^(3)chi_(e)` where `chi_(e)` the electric susceptibility. The respective values are presented in Fig. 25.9, from which it may be SEEN that the Debye law is well satisfied in the experimental range (see38.6). Because of this, let us use formula (38.26) to calculate the DIPOLE moment of the water vapour molecule, and the GAS equation to calculate the molecular concentration. It is advisable to carry out the computations for all four experimental points and a verage the results. 
|
|
| 43550. |
A block of weight 200N is pulled along a rough horizontal surface at constant speed by a force 100N acting at an angle 30^(@) above the horizontal. The coefficient of friction between the block and the surface is |
|
Answer» 0.43 |
|