Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 43401. |
According to Maxwell a changing electric field gives rise to |
|
Answer» an cmf |
|
| 43402. |
A charge Q is situated at the centre of a cube. The electric flux through one of the faces of the cube is |
|
Answer» `Q//epsilon_(0)` |
|
| 43403. |
The writer decided to learn to swim when he was about |
|
Answer» TEN or ELEVEN YEARS old |
|
| 43404. |
Give the expression for maximum induced emf in an ac generator. |
|
Answer» Solution :Let the call be rotating with angular velocityat any INSTANT .t. when the normal to the plane of the coil makes an angle `THETA`with the magnetic field. Hence magnetic flux, `phi = NBA cos omega t`,There for induced EMF `(epsilon)` `epsilon = -(d phi)/(d t)` `rArr epsilon = NBA omega SIN omega t` Induced emf will be maximum when `omega t = 90^(@)` Hence, `epsilon_(max) = NBA omega` Direction of induced emf can be determined using Flemming.s right hand rule. [ALTERNATIVELY :Statement of the above rule.] |
|
| 43405. |
The refractive index of the material of a prism is sqrt2 and the angle of the prism is 30^@. One of the two refracting surfaces of the prism is made a mirror inwards, by silver coating. A beam of monochromatic light entering the prism from the other face will retrace its path (after reflection from the silvered surface) if its angle of incidence on the prism is |
Answer» SOLUTION : `A=30^@,r_1=30^@,r_2=0^@` `therefore A=r_1+r_2` `30^@=r_1+r_2` `therefore r_1=30^@` From Snell.s law, `n_1sini=n_2sinr_1` (1)SINI=`sqrt2sin30^@` `therefore sini=sqrt2xx1/2` `therefore sini =1/2` `therefore i=45^@` |
|
| 43406. |
If alpha -particle (""_(2)He^4) is revolving in a circular orbit of radius 3.14 A with speed of 8 xx 10^6m/s. Then the equivalent current is |
|
Answer» `6. 4 XX 10^(-12) A ` |
|
| 43407. |
What is magnetic susceptibility ? |
|
Answer» Solution :MAGNETIC SUSCEPTIBILITY is defined as the ratio of the intensity of magnetisation `(vecM)`induced in the MATERIAL due to the MAGNETISING field `(vecH)` `X_m = abs((vecM)/(vecH))` |
|
| 43408. |
A spring can be used to determine the mass m ofan object in two ways: (i) by measuring the extension in the spring due to the object, and (ii) by measuring the oscillation period for the given mass. Which of these methods can be used in a space-station orbiting Earth? |
|
Answer» Both |
|
| 43409. |
Is Ohm's law a fundamental law? |
| Answer» Solution :Ohm.s law is not a fundamental law. Ohm.s law does not HOLD GOOD in case of gases, crystal rectifier, thermionic valves, TRANSISTOR etc., and it is applicable only at CONSTANT temperature. | |
| 43410. |
An ac emf is given by e= 220 sin 314t volt. Find the frequency, e= E_0 sin omegat. |
|
Answer» Solution :e=220 sin 314 volt. `RARR``OMEGA`= 314 rad/sec. `V = 314/(2pi) = 157/(PI) =50 Hz` |
|
| 43411. |
In order to increase the sensitivity of a moving coil galvanometer one should decrease |
|
Answer» STRENGTH of the magnet |
|
| 43412. |
Is it possible that a body be in accelerated motion under a force acting of the body, yet, no work is being done by the force ? Give example. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Yes , it is possible when a force is perpendicular to the direction of motion. For example, the MOON REVOLVES AROUND the earth under centripetal force of attraction of the earth but the earth does no work on the moon. | |
| 43413. |
(a) What is amplitude modulation? Draw a diagram showing an amplitude modulated wave obtained by modulation of a carrier sinusoidal wave on a modulating signal. (b) Define the terms (i) modulation index, and (ii) side bands. Mention the significance of side bands. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(b) (i) Modulation Index : (ii) SIDE Bands : Side band is the portion of a modulated carrier wave that is either above or below the BASE band signal. `(w_(1)-w_(m))` is the lower side band `(w_(1)+w_(m))` is called the upper side band. Both side bands are used to carry a MESSAGE. |
|
| 43414. |
What we call to the velocity of electron which is very small of the order of few millometer per second ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :DRIFT VELOCITY | |
| 43415. |
The difference in the speed of light in water and glass of refractive indices 1.33 and 1.5 respectively is : |
|
Answer» `2.5xx10^7 m//s` |
|
| 43416. |
Energy of a capacitor of capacitance C, when subjected to a pontential V, is given by |
|
Answer» `(1)/(2) CV^(2)` |
|
| 43417. |
Four positive point charges( +q) are kept at the four corners of a square of a side 'l'. The net electric field at the mid point of any one side of the square is, (take 1/(4 pi epsilon_0) = K) |
|
Answer» `(4Kq)/(1^2)` |
|
| 43418. |
The dimensional formula of mobility is ... . |
|
Answer» `M^(-1) L^(1)T^(2) A^(1)` Mobility `mu = (v_(d))/(E)` `[ mu] = ([V_(d)])/([E]) = ([v_(d)])/([N]) XX [C]` ` = ([M^(0) L^(1) T^(-1)] xx [A^(1) T^(1)])/([M^(1) L^(1) T^(-2) ] ) = [M^(1) L^(0) T^(2) A^(1)] ` |
|
| 43419. |
In Fig frame S' has velocity 0.90c relativeto frame S. An observer in frame S' measures two events as occurring at the following spacetime coordinates: event Yellowat (5.0m, 20ns) and event Green at (-2.0m, 4.5 ns). An observer in frame S wants to find the temporal separationDeltat_(GY)=t_(G)-t_(Y) between the events. (a) Which equation in Table 36-2 should be used? (b) Should +0.90c or -0.90c be substituted for v in the parentheses on the equation's right side and in the Lorentz factor gamma? What value should be substituted into the (c ) first and (d) second term in the parentheses? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43420. |
An engine approaches a hill with a constant speed. When it is at a distance of 0.9 km it blows a whistle, whose echo is heard by the driver after 5 sec. If the speed ofsound in air is 330 m/s, calculate the speed of the engine. |
|
Answer» Solution :If the speed ofthe ENGINE is V, the distance travelled by the engine in 5 SEC, will be 5V. And hence, the distance travelled by SOUND in reaching the HILL and coming back to the moving driver = 900 + (900 - 5V) =(1800 - 5V). So time interval between the original sound and its echo `(1800-5V)/330 = t = 5s` (given) The above equation on solving gives V = 30 m/s. |
|
| 43421. |
If two electrons are forced to come closer to each other, the P.E. of the system of 2 electrons will: |
|
Answer» Becomes zero |
|
| 43422. |
A very long, strainght, thin wire carries -3.60 nCm^(-1) of fixed negative charge. The wire is to be surrounded by a uniform cylinder of positive charge, radius 1.50 cm, coaxial with the wire. The volume charge density rho of the cylinder is to be selected is zero. Calculate the required positive charge density rho (in muCm^(-3)). |
|
Answer» 6 `rho =(3.60nC m^(-1))/(piR^(2))=(3.60nCm^(-1))/(pi(0.015m)^(2))=5 MUC m^(-3).` |
|
| 43423. |
Which of the following devices is sometimes called an electric eye? |
|
Answer» LED |
|
| 43424. |
Gauss's law is true for any closed surface,no matter what its shape or size ''Say the following statements are true or false.In uniform electric field we know that the dipole experience no net force but experience a torque having a relation with p and E is given by |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`barT=barpxxbarE` or `pEsintheta` | |
| 43425. |
What is the de Broglie wavelength of a. a bullet of mass 0.040 kg travelling at the speed of 1.0 km/s, b. a ball of mass 0.060 kg moving at a speed of 1.0 m/s, and c. a dust particle of mass 1.0xx10^(-9) kg drifting with a speed of 2.2 m/s ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`m=0.04kg, v=1xx10^(3)ms^(-1)` a.`LAMBDA=(h)/(mv)=(6.6xx10^(-34))/(0.04xx10^(3))=1.65xx10^(-35)m` b. `lambda=(h)/(mv)=(6.6xx10^(-34))/(0.06xx1)=1.1xx10^(-32)m` c. `lambda=(h)/(mv)=(6.6xx10^(-34))/(1xx10^(-9)xx2.2)=3xx10^(-23)m ` |
|
| 43426. |
A charged particle of charge 4 mC enters a uniform magnetic field of induction vecB = 3bari+6barj+6bark tesla with a velocity barv = 4bari-xbarj+y bat k. If the particles continues to move undeviated, then the magnitude of velocity of the particle is |
| Answer» ANSWER :C | |
| 43427. |
One end of each of two identicalsprings, each of force-constant 0.5N are attached on the opposite sides of a wooden block of mass 0.01 Kg. The other ends of the springs are connected to separaterigid supports such that the springs are unstretchedan are collinear in a horizontal plane. To the wooden piece is fixed a pointerwhich touches a vertically moving plane paper. The wooden piece, kept on a smooth horizontal table is now displaced by 0.02 m along the line of springs and released. If the speed of paper is 0.1 m/s. The distance between two consecutive maxima on this path is 6.28 xx 10^(-y) mtrs. Find y |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43428. |
At what temperature will the average K.E. of a gas molecule be twice its value at N.T.P. ? |
|
Answer» `546^@C` |
|
| 43429. |
Mark out the correct options. |
|
Answer» Diamagnetism occurs an all materials. Diamagnetic material do not have permanent magnetic moment on their own. When they are placed in magnetic field, dipole moments are induced by the applied magnetic field. THUS, there is no net alignment of permanent magnetic moment so these materials do not have any permanent magnetic moment of their own. Hence, option (b) is incorrect. Magnetic field intensity is not vero in free space. Hence, option (c) is incorrect. |
|
| 43430. |
Refraction index of medium-2 with respect to medium-1 is ...... . |
|
Answer» `n_(12)=(n_1)/(n_2)` |
|
| 43431. |
A rectangular conductor LMNO is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 0.5 T. The field is directed perpendicular to the plane of the conductor. When the arm MN of length of 20 cm is moved towards left with a velocity of 10 ms^(-1), calculate the emf induced in the arm. Given the resistance of the arm to be 5Omega (assuming that other arms are of negligible resistance) find the value of the current in the arm. |
|
Answer» Solution :Here B = 0.5T, length of moving conductor l =20 cm = 0.2 m and speed `v = 10 m s^(-1)` `therefore` INDUCED emf `|varepsilon| = Blv = 0.5 xx 0.2 xx 10 = 1.0` VOLT As resistance of RECTANGULAR conductor `R = 5Omega` `therefore` Current `I = varepsilon/R=(1.0)/5 = 0.2A` 
|
|
| 43432. |
A Huygens eye-piece is made by arranging two planoconvex lenses of focal lengths 0.03m and 0.09m in the usual manner. Light falls directly on the field lens of the eye-piece. Calculate the position of the final image formed by the eye-piece and trace the path of rays showing the formation of images. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43433. |
A body is released from the top of a smooth inclined plane of inclination q. It reaches the bottom with velocity V. If the angle of inclination is doubled for the same lengh of the plane, what will be the velocity of the body on reaching the ground: |
|
Answer» `V` |
|
| 43434. |
Nuclei having the same ................ but different ................ are called isotopes. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :ATOMIC NUMBER (or number of PROTONS), mass number (or number of neutrons) | |
| 43435. |
The moving coil of a galvanometer made of 200 turns of thin wire is suspended from an elastic thread. The area of the coil is 1 cm^2, it coincides in direction with the lines of induction of a magnetic field with induction of 15 mT. When the current of 5.0 A is passed through the coil it turns through 15^@. By what angle will the coil turn with a current of 7.5 muA? What is the torsion modulus of the thread? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43436. |
In the Geiger-Marsden scattering experimenl of the number of scattered particles detected are maximum and minimum at the scattering angles respectively at |
|
Answer» `0^(@) and 180^(@)` |
|
| 43437. |
Find the refractive index of the material, if a prims having an angle A=60^(@) which produces a minimum deviation of 30^(@). |
| Answer» Solution :(b) | |
| 43438. |
The rms voltage of the generator is V_0 The frequency of the ac generator is verynear zero. What is the rms current through the circuit? |
Answer» Solution :As we just now discussed, at small frequencies, the circuit is like a dc circuit. So, the capacitor can be replaced by a open circuit and inductor by a short circuit. Figure 31-22 shows the circuits as they would appear according to these CHANGES. 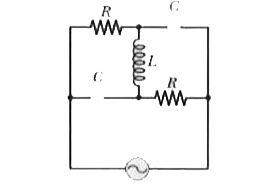 It is obvious from the circuit that it is not a circuit of series elements , nor elements in parallel. 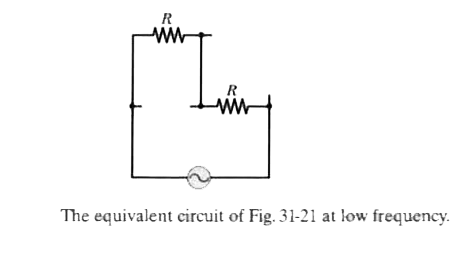 Calculation : The rms current is given by `I_(rms)=V_(rms)/Z`. However, the impedance Z . because the circuit is not series RCL circuit. The circuit behaves as if it contained only two identical resistors in series, with a total impedance of Z=2R. Thus circuit has `I_(rms)=V_(rms)/(2R)`. Learn: If the source had a very HIGH frequency (much HIGHER than the RESONANCE frequency), the capacitor would be treated as short-circuited and inductor as open-circuited. Figure 31-23 shows the circuits as they would appear according to these changes. So, at this frequency, the impedance of the circuit would be R/2. Hence `I_(rms)=(2V_(rms))/R`. 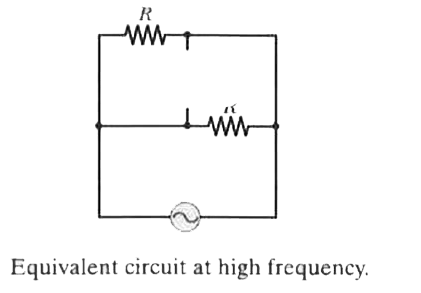
|
|
| 43439. |
Making use of the Hund rules, find the numbers of electrons in the only partially filled subshell of the atom whose basic term is (a) .^(3)F_(2)(b) .^(2)P_(3//2),(c ) .^(6)S_(5//2). |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) `.^(3)F_(2)` The MAXIMUM value of spin is `S=1` here. This means there are `2` electrons. `L= 3` so `p` electrons are ruled out. This is simplest plssiblility is `d` electrons. This is the CORRECT choice for if we were considering `f` electrons, the maximum value of `L` allowed by Pauli priciple will be `L=5` (maximum value ofthe magnitude of megnetic quantum number will be `3+2=5`). Thus the atom has two `d` electrons in the unfilled shell. (b) `.^(2)P_(3//2)` Here `L=1,s=(1)/(2)` and `J=(3)/(2)` Since `J=L+S`, Hund's rule implies the shell is more than half FULL. THSI means one electron less than a full shell. On the basis of hole picture it is easy to see that we have `p` electrons. Thus the atom has `5p` electrons. (c )`.^(6)S_(5//2)` Here `S=(5)/(2), L=0` we either have five electrons of five holes. The angular part is antisymmertic. For five `d` electrons, the maximum value of the quantum number cosistent with Pauli exclution principle is `(2+1+0-1-2)=0` so `L=0` for `f` or `g` electrions `L gt 0` whether the shell has five electrohns or five holes. Thus the atom has five `d` electrons. |
|
| 43440. |
The susceptibility (X_(m)) of bismuth is ................. . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43441. |
In the figure shown i=10 e^(-41) A.Find B_(L) "and" V_(ab) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43442. |
Define 'electrostatic potential". |
| Answer» Solution :The electric potential at a point P is equal to the work DONE by an external force to bring a unit positive charge with constant VELOCITY from INFINITY to the point in the region of the external electric field `vecĒ` | |
| 43443. |
A ray of light is incident on the upper surface of a glass plate of thickness t (mu = "refractive index of glass"). If the angle of incidence I is very small, then lateral displacement of the emergent ray will be |
|
Answer» `(timu)/(MU + 1)` |
|
| 43444. |
A small block is projected with a speed v_( 0) on a horizontal track placed on a sufficientlyrough surface which turns into a semi circle ( vertical) of radius R. Find the min value of V_(o) so that the body will hit the point A after leaving the track at its highest point. The arrangement is shown in the figure, given that the straight part is rough & the curved path is smooth. The coefficient of friction is mu. |
|
Answer» `(2R)=1/2g t^(2)`, whrer `t=` time of its fall. `rArr t=2 sqrt(R//g)` `:.` The distance `AB=2vsqrt(R//g)` `rArr d=2v_(x) sqrt(R//g)`...(a) Work energy theorem is applied to the motion of the body from A to B leads `Delta KE=W_(f)` `rArr 1/2 mv_(o)^(2)-1/2 mv_(1)^(2)=mu mgd` `rArr v_(o)=sqrt(v_(1)^(2)+2mu gd)` ...(b) Energyconservation between B & C yields `1/2 mv_(1)^(2)-1/2 mv^(2)=mg(2R)` `rArr v_(1)=sqrt(v^(2)+4gR)` ...(c) When the block escapes C, its minimum speed v can be given as `(mv^(2))/(R)=mg` ( `:.` the normal CONTACT force `=0`) `rArr v=sqrt(gR)`...(d) (NOTE that if the particle has speed LESS than `sqrt(gR)` then it will not reach to the highest point of the curvature. By using (c) and(d) we obtain `v_(1)=sqrt(5gR)` ...(e) using (a) and (d) we obtain `d=(sqrt(gR))2(sqrt(R/g))=2R`...(f) `v_(o)=sqrt(5gR+2 mu g (2R))=sqrt((5+4 mu )gR)`. 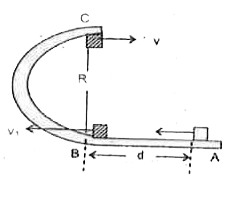
|
|
| 43445. |
How can you distinguish between hard boiled egg and a raw egg by spinning them on table top ? |
| Answer» Solution :When the RAW and hard boiled eggs are SPUN together the raw egg will have a greater moment of INERTIA as the FLUID in it will CONCENTRATE along it.s surface. | |
| 43446. |
The internal energy U is a unique function of any state because change in U |
|
Answer» Does not DEPEND upon PATH |
|
| 43447. |
The basic instrument employed to detect current is |
|
Answer» GALVANOMETER |
|
| 43448. |
Amplitude of a wave . |
| Answer» SOLUTION :AMPLITUDE of a wave is DEFINED as the magnitude of the maximum diplacement of a particle of the medium from its equilibrium position . | |
| 43449. |
When monochromatic, light is incident on a surface separating two media, the reflected and refracted light both have the same frequency as the incident frequency. Explain why? |
| Answer» Solution :Reflaction and refraction arise through INTERACTION of incident light with the ATOMIC constituents of matter. Atoms may be viewed as OSCILLATORS, which take up the frequency of the external agency (light) and undergo FORCED oscillations. The frequency of oscillation. Thus, the frequency of scattered light equals the frequency of incident light. | |
| 43450. |
Sphere 1 with radius R_1 has positive charge q. Sphere 2 with radius 2.00 R_1 is far from sphere 1 and initially uncharged. After the separated spheres are connected with a wire thin enough to retain only negligible charge, (a) is potential V_(1) of sphere 1 greater than, less than, or equal to potential V_(2) of sphere 2? What fraction of q ends up on (b) sphere 1 and ( c) sphere 2? ( d) What is the ratio sigma_(1)// sigma_(2) of the surface charge densities of the spheres ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) `EQUAL`, (B) `0.333`,( C) `0.667`, (d) `2.00` | |