Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 43151. |
You have learnt in the text how Huygens’ principle leads to the laws of reflection and refraction. Use the same principle to deduce directly that a point object placed in front of a plane mirror produces a virtual image whose distance from the mirror is equal to the object distance from the mirror |
| Answer» SOLUTION :With the point object at the CENTRE, draw a CIRCLE touching the MIRROR. This is a plane section of the spherical wavefront from the object that has just reached the mirror. Next draw the locations of this same wavefront after a TIME t in the presence of the mirror, and in the absence of the mirror. You will get two arcs symmetrically located on either side of the mirror. Using simple geometry, the centre of the reflected wavefront (the image of the object) is seen to be at the same distance from the mirror as the object. | |
| 43152. |
The energy levels of a hypothetical atom are shown in Fig.12.13. Which of the shown transitions will result in the emission of a photon of wavelength 275 nm ? Which of these transitions correspond to emission of radiation of (i) maximum and (ii) minimum wavelength ? |
|
Answer» Solution :If a lightphoton of wavelenght`lambda = 275 NM = 2.75 xx 10^(-7)` m is emitted , thenenergyof photon `E= (hc)/(lambda) J = (hc)/( lambda xx 1.60 xx 10^(-19)) eV` ` = (6.63 xx 10^(-34) xx 3 xx 10^(8))/(2.75 xx 10^(-7) xx 1.60 xx 10^(-19)) eV = 4.5 eV` 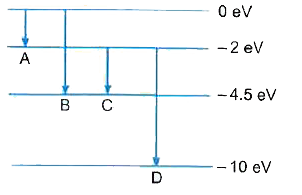 From the energy level diagram given, we find that a light photon of energy 4.5 eV can be emitted only when electron transition TAKES from 0 eV energy level to -4.5 eV energy level because then `E_(1)-E_(2) = 0 - (-4.5) = + 4.5 eV.` Hence, transition B will result in the emission of a photon of WAVELENGTH 275 nm. (i) For emission of radiation of maximum wavelength the energy of emitted photon should be minimum. Obviously, the transition A corresponds to emission of maximum wavelength radiation because energy in this transition [0 eV -(-2 eV) = 2 eV] is minimum. (ii) For emission of radiation of minimum wavelength the energy of emitted photon should be maximum. Obviously, the transition D corresponds to emission of minimum wavelength radiation because energy in this transition [(-2 eV)-(-10 eV) = 8 eV] is maximum. |
|
| 43153. |
What happensto the interference pattern if the phase difference between the two sources continuously change ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :As the phase difference, continuosly change, the position of MAXIMA and minima continuously change. HENCE, the interference pattern will not be SUSTAINED and the patteren will not OBSERVED. | |
| 43154. |
A circular coil of 20 turns and radius 10 cm is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 0.10 T normal to the plane of the coil. If the current in the coil is 5.0 A, what is the (a) total torque on the coil, (b) total force on the coil, (c) average force on each electron in the coil due to the magnetic field? (The coil is made of copper wire of cross-sectional area 10^(-5) m^2, and the free electron density in copper is given to be about 10^29 m^(-3) .) |
| Answer» Solution :(a) Zero, (b) zero, (c) FORCE on each ELECTRON is `evB = IB//(nA) = 5 ×x 10^(-25)`N. Note: Answer (c) denotes only the magnetic force. | |
| 43155. |
The ratio of the masses and radii of two planets are 2:3 and 8:27.The ratio of respective escape speeds from their surfaces are |
|
Answer» `sqrt3:sqrt2` |
|
| 43156. |
Two long conductors, separated by a distance 'd' carry current I_(1) and I_(2) in the same direction. They exert a force F on each other. Now the current in one of them is increased to two times and its direction is reversed. The distance is also increased to 3d. The value of the force between them is |
| Answer» ANSWER :C | |
| 43157. |
Two positive charges separated by a distance 2m each other with a force of 0.36N. If the combined charge is 26muC, the charges are |
|
Answer» `20muC, 6muC` |
|
| 43158. |
A system has two charges q_A =2.5 xx 10 ^(-7)C and q_B =-2.5 xx 10 ^(-7)Clocated at points A : (0,0,-15 cm) and B: (0,0+15 cm),respectively. What are the total charges and electric dipole moment of the system ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Here ` q_A =2.5 xx 10 ^(-7)C, q_B =-2.5 xx10 ^(-7)C ` and distance between them `2a=15-(-15) =30 cm =0.3 m ` ` therefore ` Total charges of the system `=q_A +q_B =2.5 xx 10^(-7) +(-2.5xx 10^(-7) ) =0 .` Electric dipole moment of the system `p=q.2a= 2.5 xx 10 ^(-7) xx0.3 =7.5 xx10 ^(-8) C-m ` The dipolemoment is directed from charges `q_B `towards charge `q_A ` i.e. ALONG -z-axis.. |
|
| 43159. |
Mention the expression for the time period of oscillation of a small compass needle in a uniformmagnetic field .Explainthe terms. |
|
Answer» Solution :Time period : `T=2pisqrt(I/(mB))` Where I-momentof INERTIA, B-magnetic FIELD and m-magnetic MOMENT of the COMPASS NEEDLE. |
|
| 43160. |
When two identical wires made of different materials having resistivity s_(1) and s_(2) and conductivities sigma_(1) and sigma_(2) are connected in series, Effective resistivity is |
|
Answer» `(s_(1)+s_(2))/(2)` |
|
| 43161. |
An object is placed at a distance 40 cm in front of concave mirror. Focal length of mirror is 20 cm, so what will be type of image ? |
|
Answer» real and erect `therefore R = 2 XX 20` radius of curvature R = 40 cm Now, object DISTANCE = radius of curvature so image produced is, real inverted and of same size. |
|
| 43162. |
Draw the equipotential surfaces due to an electric dipole. Locate the points where potential due to the dipole is zero. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Equipotential SURFACES due to an ELECTRIC dipole have been drawn in FIG. Electric potential dueto the dipole is zero at all the points lying on the equatorial plane of given dipole. | |
| 43163. |
Does a bar magnet exert a torque on itself due to its own field '? Does one element of a current-carrying wire exert a force on another element of the same wire ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(d) No force or torque is exerted on any bar magnet due to its own magnetic field. Similarly no force or torque is exerted on a current ELEMENT due to magnetic field produced by that element. But if current carrying WIRE is not STRAIGHT then on every current element there is some net force or torque due to magnetic fields produced by other current ELEMENTS of same wire. (For a straight wire, such a force or torque is zero). |
|
| 43164. |
Define dispersive power of the material of a prism. How can it be measured? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The dispersive power of the material is its ability to DISPERSE the constituent colours of incident light. The dispersive power of the material of the prism can be measured by the RATIO of ANGULAR dispersion between any two colours to the mean of the angle of deviation of the two colours. Dispersive power has no UNIT. It is a dimensionless quantity. `omega=(d_(v)-d_(R))/(d)=(n_(v)-n_(R))/(n-1)` |
|
| 43165. |
An isotropic point source emits light at wavelength 500 nm at the rate of 200 W.A light detector is positioned 400 m from the source . What is the maximum rate at which the magnetic component of the light changes with time at the detector's location ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`3.44xx10^(6) ` T/s | |
| 43166. |
Thermal neutrons fall normally on the surface of a thin gold foil consisting of stable Au^(197) nuclide. The neutron flux density is J=1.0.10^(10) "part"//(1s,cm^(2)). The mass of the foil is m= 10 mg. Then neuteron capture produces beta-active Au^(198) nuclei with half-life T= 2.7 days. The effective capture cross-section is sigma= 98 b. Find : (a) the irradiation time after which the number of Au^(197) nuclei decreases by eta= 1.0%, (b) the maximum number of Au^(198) nuclei that can be formed during protracted irradiation. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Suppose `N_(0)=` no. of `Au^(197)` nuclei in the foil. Then the number of `Au^(197)` nuclei transformed in time `t` is `N_(0).J.sigma.t` For this to equal `etaN_(0)`, we must have `t= eta//(J. sigma)= 323 YEARS` (b) Rate of formation of the `Au^(198)` nuclei is `N_(0).J.sigma` per sec and rate of decay is `lambda n,` where `n` is the number of `Au^(198)` at any instant. Thus `(dn)/(dt)=n_(0).J.sigma-lambda n` The maximum number of `Au^(198)` is clearly `n_(max)=(N_(0).J.sigma)/(lambda)=(N_(0).J.sigma.T)/(In 2)` beacuse if `n` is smaller, `(dn)/(dt) gt 0` and `n` will increase further and if `n` is larger `(dn)/(dt) lt 0` and `n` decrease. (ACTUALLY `n_(max)` is approached steadily as `trarr oo`) Substitution gives using `N_(0)= 3.05xx10^(19), n_(max)= 1.01xx10^(13)` |
|
| 43167. |
Mood of the poem is _______. |
|
Answer» Joyful |
|
| 43168. |
Find the typical de-Broglie wavelength associated with a He atom in helium gas at room temperature (27^(@)C) and 1atm pressure, and compare it with the mean separation between two atoms under these conditions. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Mass of He atom `=("ATOMIC mass of He")/("Avogadro.s number")=(4xx10^(-3))/(6xx10^(26))kg`[Taking `N_(A)=6xx10^(26)kg" "mol^(-1)`] `lamda_("de-broglie")=(h)/(p)=(h)/(sqrt(3mk_(B)T))""[becausep=mv_(rms)=msqrt((3k_(B)T)/(m))=sqrt(3mk_(B)T)]` `=(6.63xx10^(-34))/(sqrt(3xx.67xx10^(-27)xx1.38xx10^(-23)xx300))m=(6.63xx10^(-10))/(sqrt(82.84))m=7.3xx10^(-11)m` For one MOLE of a gas, `PV=RT=N_(A).k_(B)T` MEAN separation between atoms is `r=((V)/(N_(A)))^(1//3)=((k_(B)T)/(P))^(1//3)=((1.38xx10^(-23)xx300)/(1.01xx10^(5)))^(1//3)=3.4xx10^(-9)m` Therefore, `lamda_("de-Broglie") lt lt r`. |
|
| 43169. |
On rotating a point charge g around a charge Q in a circle of radius r, the work done is |
|
Answer» `q. 2 pi R` |
|
| 43170. |
A simple pendulum has a time period T_(1)when on the earth's surface and T_(2) when taken to a height R above the earth's surface where R is the radius of the earth. The value of T_(2)//T_(1) is |
|
Answer» 1 `RARR T_(2) = 2T_(1) rArr T_(2)/T_(1) =2` |
|
| 43171. |
Mention the difference of the three important methods of radiowave propagation. In which of these three methods, are microwaves transmitted? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The difference between the three important methods of radio wave propagation is: (i) Propagation through atmosphere: Radiowaves of very low to very HIGH frequency are transmitted through atmosphere as ground waves, sky waves and space waves. But the atmosphere itself can not provied worldwide propagation unless artificial satellites are used. (ii) Propagation through coaxial cables: This method MAY be used only for SHORT-distance propagation. For EXAMPLE, a Local Area Network(LAN) with a few computers, telephone communication within a short region. (iii) Propagation through optical fibres: This is a highly efficient method for worldwide propagation of waves of almost infinite range of frequencies. This method is extremely useful in international communications.Space waves transmitted through the atmosphere and artificial satellites for their effective reflections are used for microwave communications. |
|
| 43172. |
What is resolving power of Optical Instruments ? Derive the condition under which images are resolved. |
|
Answer» Solution :Resolving power : The resolving power of a LENS is its ability to resolve two points that are close to each other. Resolving power of optical instruments (i) Consider a parallel beam of light falling on a convex lens. Due to DIFFRACTION EFFECT, thebeam focussed to a spot of finite area. (ii) . Taking into account the effects due to diffraction, the pattern on the focal plane A parallel beam of light is incident on a convex lens. Because of diffraction effects, the beam gets focused to a spot of radius - 0.61 Af/a. would CONSIST of a central bright region (circular) surrounded by a concentric dark and bright rings. (iii) The radius of the central bright region is given by r, = where f is focal length of the lens 2a = diameter of the lens. Derive the condition under which images are resolved : The size of the spot is very small, plays an important role in determining the limit of resolution. For the two stars to be just resolved `f Deltatheta=r_(0)=(0.61lambdaf)/(a)` `Deltatheta=(0.61lambda)/(a).....(1)` Thus, `Deltatheta` will be small, if the diameter (2a) of the objective is large. This imlies that telescope will have better resolveing power if a is large. In case of microscope, the object is placed slightly beyond f. The corresponding minimum seperation `(d_(Min))` between the object and the objective lens is given by `d_("Min")=(1.22lambda)/(2musin beta)` `"Where "mu="Refractive index"` `mu sin beta`= Numerical aperture. 
|
|
| 43173. |
A galvanometer coil has a resistance of 15 Omega and the meter shows full scale deflection for a current of 4 mA. How will you convert the meter into a voltmeter of range 0 to 6A ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Here `R_G = 15 Omega , I_g = 4 mA = 4 XX 10^(-3)A` and ammeter.s rangeI = 6A To convert galvanometer into a ammeter of desired RANGE, we should join a resistance `r_s` in parallel to the galvonometer, where `r_s= (I_g)/(I - I_g) cdot R_G = (4 xx 10^(-3))/(6 - 4 xx 10^(-3)) xx 15 = 10^(-2) Omega = 10 m Omega`. |
|
| 43174. |
In an LCR circuit , L = 88 mH and C = 1muF and the value of the resistor is unknown . The AC source has a frequency of 1000 Hz and the phase between emf and current is 70^@ . Calculate the value of R of the resistor . |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`tan phi = (X_L - X_C)/(R )` ` R = (X_L - X_C)/( tan phi) ` `phi = 70^@, omega = 2pi f = 2pi xx 1000 = 2000 pi , L = 88 xx 10^(-3) H , C = 1 xx 10^(-6) F` ` X_L = omega L = 2000 xx 3.14 xx 88 xx 10^(-3)= 553 Omega` ` X_C = (1)/(omega C) = (1)/(2000 xx 3.14 xx 10^(-6) ) = (10^6)/(2000 xx 3.14) = (1000)/(2 xx 3.14)` `X_C = 159 Omega` ` R = (X_L - X_C)/(tan phi) = (533 - 159)/(tan 70) = (394)/(2.75) = 143 Omega ` |
|
| 43175. |
A soldier walks towards a high wall taking 120 steps per minute. When he is at a distance of 90 m from the wall he observes that echo of step coincides with the next step. The speed of sound must be |
|
Answer» 340 m/s |
|
| 43176. |
The field due to a long straight wire carrying a current I is proportional to |
| Answer» ANSWER :A | |
| 43177. |
A double convex lens of focal length 20 cm is made of glass of refractive index 3/2. When placed completely in water (._(a)mu_(w)=4//3), its focal length will be : |
|
Answer» 80 cm |
|
| 43178. |
A particle located at x = 0 at time t=0 starts moving along positive x-direction with velocity v that varies as v = asqrt(x). The displacement of the particle varies with time as : |
|
Answer» `t^(2)` `(dx)/(DT)=ax^(1//2)` or `x^(-1//2)dx=a dt` Intergrating, we GET `(x^(1//2))/(1//2)`=at `xprop t^(2)` |
|
| 43179. |
The figure shows two points source which emit light of wavelength lambda in phase with each other and are at a distance d = 5.5 lambda apart along a line which is perpendicular to a large screen at a distance L from the centre of the source. Assume that d is much less than L. Which of the following statement is (are) correct ? |
|
Answer» only five BRIGHT fringes appear on the screen |
|
| 43180. |
The splitting occurs due to different colors have different _____ and _____ are different in a medium. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :WAVELENGTH, SPEED | |
| 43181. |
A steel wire of length lm, mass 0.1 kg and uniform cross-sectional area 10^(-6)m^(2) is rigidly fixed at both ends. The temperature of the wire is lowered by 20^(0)C. If the transverse waves are set up by plucking the string in the middle, calculate the frequency of the fundamental mode of vibration [Y=2xx10^(11)N//m^(2) and alpha=1.21xx10^(-5)l^(0)C] |
|
Answer» 21Hz |
|
| 43182. |
Unpolarised light of intensity I_0 is incident on surface of a block of glass at Brewster's angle. In that case which one of the following startements is true? |
|
Answer» TRANSMITTED LIGHT is partially polarised with INTENSITY `I_0//2.` |
|
| 43183. |
Two magnetic poles of pole strength 20 Am and 15 Am are kept at a distance of 10cm. The force acting on one of the poles is ...... .. |
|
Answer» `3 xx 10^(2)` N `r= 10 cm = 10 xx 10^(-2) `m `F = (mu_0)/( 4pi ) . (P_1 P_2)/( r^2) ` `= (4pi xx 10^(-7) )/( 100 xx 10^(-4)) THEREFORE F=3 xx 10^(-3) N` |
|
| 43184. |
The amplitude of the magnetic field part of a harmonic electromagnetic wave in vacuum is B_(0)=510 nT. What is the amplitude of the electric field part of the wave ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`B_(0)=510 nT =510xx10^(-9)T` `E_(0)=?` `c=(E_(0))/(B_(0)), E_(0)=c, B_(0)=3xx10^(8)xx510xx10^(-9)=153 NC^(-1)`. |
|
| 43185. |
Find the change in the focal lengthof the lens, if a convex lens of focal length 20cm and refractive index 1.5, is immersed in water having refractive index 1.33. |
|
Answer» `62.2cm` `1/20=(1.5-1)(1/(R_(1))-1/(R_(2)))` or `(1/(R_(1))-1/(R_(2)))=1/10` When lens is in water `1/(f_(w))=((mu_(G)-mu_(w))/(mu_(w)))(1/(R_(1))-1/(R_(2)))=((1.5-1.33)/1.33)xx1/10` `f_(w)=78.2cm` The change in FOCAL length`=78.2-20=58.2cm` |
|
| 43186. |
In a black body radiation at certain temperature T_1 the wave length having maximum intensity of radiation equals 9000A^@ . When the temperature is increased from T_1 "to" T_2 the total radiation increases 16 times. The peak radiation at T_2 is found to be capable of ejecting photoelectrons. The maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons is the same as the energy of photon that one gets when one of electron in the M -shall of hydrogen atom jumps to L-shell the work function of the metal will be |
|
Answer» 0.88 eV |
|
| 43187. |
A particle is dropped from a height H.The de-Broglie wavelength of the particle as a function of height is proportional to |
|
Answer» H `v^(2)-(0)^(2)=2(-g)(-H)` `THEREFORE v^(2)=2gh`…..(1) `therefore v=sqrt(2gh)` (velocity of particle when it is aout to TOUCH the ground) Now,according to formula,when above particle is about to touch the ground ,de-Broglie wavelength of a WAVW ,representing that particle is, `lmbda=(h)/(mv)` (where h=plank.s constant) m=mass of a particle v=velocity of particle ) `=(h)/(msqrt(2gh))`(from equation(1)) `lambda PROP(1)/(sqrt(H))` (`therefore` h,m and g are constants) `therefore lambda prop H^((-1)/(2))` `implies` Option (D) is correct. |
|
| 43189. |
A ball is projectedfrom ground at an angle 45^(@) with horizontal from distance d_(1) from the foot of a pole and just after touching the top of pole it the falls on ground at distance d_(2) from pole on other side, the height of pole is |
|
Answer» `2sqrt(d_(1)d_(2))` |
|
| 43190. |
Line spectrum can be obtained from |
|
Answer» sun |
|
| 43191. |
Two satellite orbiting round the earth have their cirtical speed in the ratio 4:5, the ratio of their orbital radius is, |
| Answer» ANSWER :A | |
| 43192. |
Two coherent light sources A and B with separation 2 lamdaare placed on the x-axis symmetrically about the origin. They emit light of wavelength lamda. Obtain the positions of maxima on a circle of large radius, lying in the x-y plane and with centre at the origin. |
Answer» Solution : For P to have maximum intensity, d cos `theta =n lamda` `2 lamda cos theta = n lamda RARR cos theta =n/2 ` where n is integer For `n = 0, theta =90^@ , 270^@` `n= pm 1, theta =60^@ , 120^@ , 240^@, 300^2` `n = pm2, theta =0^@ , 180^@` So, POSITIONS of MAXIMA are at `theta = 0^@ , 60^@ , 90^@ , 120^@ , 180^@, 240^@, 270^@` and `300^@`i.e., 8 positions will be obtained. |
|
| 43193. |
Explain in detail the construction and working of a Van de Graaff generator. |
|
Answer» Solution :Principle : Electrostatic induction and action at points Construction : A large hollow spherical conductor is fixed on the insulating stand . A pulley B is mounted at the CENTER of the hollow sphere and another pullel C is fixed at the bottom . A belt made up of insulating materials like silk or rubber RUNS over both pulleys. The pulley C is driven continuously by the electric motor. Two comb shaped metallic conductors E and D are fixed near the pulleys . The comb D is maintained at a positive of 104 V by a power supply . The upper comb E is conncected to the inner side of the hollow metal sphere. Working : Due to the high electric field near comb D air between the belt and comb D gets ionized. The positive charges are pushed towards the belt and negative charges are attracted towards the comb D. The positive charges stick to the belt and move up. When the positive charges reach the comb E, a large amount of negative and positive charges are induced on either side of comb E due to electrostatic induction . As a result the positive charges are induced on either side of comb E due to electrostatic induction . As a result the positive charges are pushed away from the comb E and they rech the positive charges are pushed away from the comb E and they reach the outer surface of the sphere. Since the sphere is a conductor the positive charges are distributed uniformly on the outer surface of the hollow sphere . At the same time the negative charges NULLIFY the positive charges in the belt due to corona discharge before it passes over the pulley.  When the belt descends it has almost no net charge . At the bottom it again gains a large positive charge . The belt goes up and delivers the positive charges to the outer surface of the positive sphere . This process continues until the outer surface produces the potential difference of the order of `10^(7)` which is the limiting value . We cannot store charges beyond this limit since the extra charge starts leaking to the surroundings due to ionization of air . The leakage of charges can be reduced by enclosing the machine in a gas filled steel chamber at very high pressure. Uses: The high voltage produced in this Van de Graaff generator is used to accelerate positive ions ( protons and deuterons) for nuclear disintegrations and other applications . |
|
| 43194. |
Figure shows tracks of three charged particles in a uniform electrostatic field. Give the signs of the three charges. Which particle has the highest charge to mass ratio ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Here, electric field is vertically downward (from upper POSITIVELY charged plate to negatively charged plate). As per the statement, since `q_(1)`and `q_2` are deflected towards positive plate, they must be negatively charged particles. But `q_3` is deflected towards negative plate and so it must be positively charged. Here, if all the THREE particles enter UNIFORM electric field E, perpendicularly with same horizontal constant velocity then vertical displacement undergone by them while coming out of electric field is, `d =v_(0)t + 1/2 at^(2)` `therefore y =(0)t + 1/2 (F_(e)/m) (1/v)^(2)` `(therefore v_(0) = 0, v=1/t " and " F_(e) = ma)` `therefore y=1/2 (qE)/(m) (l/v)^(2), (therefore F_( e) = qE)` `therefore y prop q/m` (`therefore` E, I, v are same for all the three charges) `q_3` must have maximum specific charge (which is charge to mass ratio or charge per unit mass) because it undergoes maximum vertical displacement as shown in the figure 3.), |
|
| 43195. |
A blind person after walking10 steps in one direction each of length 80 cm, turns randomly to the left or right by 90^@. After walking a total of 40 steps the maximum displacement of the person from his starting position could be . |
|
Answer» 32 m |
|
| 43196. |
Find out the Relation betweenC_1, C_2, C_3 and C_4such that point A and B are equipotential.[Balanced wheat stone bridge ] |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :When A and B are EQUIPOTENTIAL then there will be no charge on capacitors ` C_5^(-) ` So remove . It Now `C_1, C_2` are in series and ` C_3, C_4`are in series so they will have some charges RESPECTIVELY ` rArr "" (q_1)/( C_1) =(q_2)/(C_2) ""....(1) ` ` 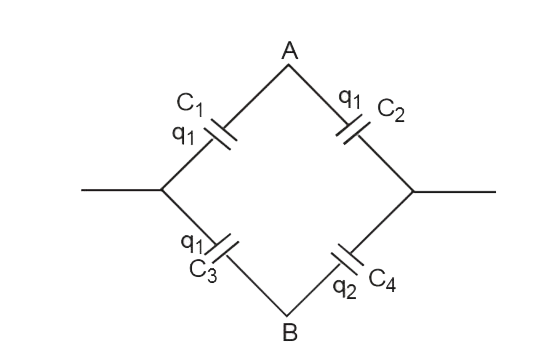 and ` (q_1)/(C_2) = (q_2)/(C_4) "" ...(2) ` ` (C_2)/( C_1)=(C_4)/( C_3) ""rArr ""C_2C_3 = C_1C_4` |
|
| 43197. |
The work function of a certain metal is 3.31xx10^-(-19) jthen, the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectronsemitted by incident radiation of wavelength 5000ÅIS1(GIVEN,H=6.62XX10^(-34)J_(-s),c=3xx10^(8)ms^(-1),e=1.6xx10^(-19)C) |
|
Answer» 2.48 eV |
|
| 43198. |
Discuss the working of cyclotron in detail. |
|
Answer» Solution :Cyclotron : Cyclotron is a device used to accelerate the charged particles to gain large kinetic energy. It is also CALLED as high energy accelerator. It was invented by Lawrence and Livingston in 1934. Principle : When a charged PARTICLE moves normal to the magnetic FIELD , it experiences magnetic Lorentz force. Construction : (i) The schematic diagram of a cyclotron is shown in Figure . (ii) The particles are allowed to move in between two semi - circular metal containers called Dees (hollow D - shaped objects). (iii) Dees are enclosed in an EVACUATED chamber and it is kept in a region with uniform magnetic field controlled by an electromagnet. (iv) The direction of magnetic field is normal to the plane of the Dees. (v) The two Dees are kept separated with a gap and the source S ( which ejects the particle to be accelerated ) is placed at the center in the gap between the Dees. (vi) Dees are connected to high frequency alternating potential difference. Working : (i) Let us assume that the ion ejected from source S is positively charged. (ii) As soon as ion is ejected, it is accelerated towards a Dee( say, Dee- 1) which has negative potential at that time. (iii) Since the magnetic field is normal to the plane of the Dees, the ion undergoes circular path.  (iv) After one semi- circular path in Dee - 1 , the ion reaches the gap between Dees. (v) At this time, the POLARITIES of the Dees arereversed so that the ion is now accelerated towards Dee - 2 with a greater velocity. (vi) For this circular motion , the centripetal force of the charged particle q is provided by Lorentz force. `(mv^(2))/r = qvB` ` r = m/(qB) v ` ` r alpha v ` .....(1) (vii) From the equation (1), the increase in velocity increases the radius of circular path . (viii) This process continues and hence the particle undergoes spiral path of increasing radius. (ix) Once it reaches near the edge, it is taken out with the help of deflector plate and allowed to hit the target T. (x) Very important condition in cyclotron operation is the resonance condition. It happens when the frequency f at which the positive ion circulates in the magnetic field must be equal to the constant frequency of the electrical oscillator `f_("osc") ` From equation `f_("OSC") = (qB)/(2pim) `,we have The time period of oscillation is ` T = (2 pi m)/(qB) ` The kinetic energy of the charged particle is `KE = 1/2 mv^(2) = (q^(2)B^(2)r^(2))/(2m) ` Limitations of cyclotron : (a) the speed of the ion is limited (b) electron cannot be accelerated (c ) uncharged particles cannot be accelerated |
|
| 43199. |
Statement I: The energy of e.m wave is (1)/(2) epsilon_(0)E_(0)^(2) Statement II: The intensity of radiation of e.m. wave is (1)/(2) epsilon_(0)cE^(2) |
|
Answer» STATEMENT I is CORRECT, statement II is FALSE. |
|
| 43200. |
A block weighing 10.0 N is attached to the lower end of a verticle spring (k = 200.0 N//m), the other end of which is attached to a ceiling. The block oscillates vertically and has a kinetic energy of 2.00 J as it passes through the point at which the spring is unstretched. Use the law of conservation of energy to determine the maximum distance the block moves both above and below the point at which the spring is unstretched (these are not necessarily the same) |
|
Answer» 0.05 m and 0.25 m |
|