Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 43201. |
Using Biot-Savart's law obtion the equation for the magnetic field on the axis of a circular current loop. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :REFER TEXT | |
| 43202. |
In the circuit (Figure ) , the current it to be measured. What is the value of the current if the ammeter shown (a) is galvanometer with a resitance R_(G) = 60,00 Omega, (b) is a galvanometer by a shunt resitance r_(s) = 0.02 omega (c) is an ideal ammter with zero resitance ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Total resistance in the CIRCUIT is `R_(G) + 3 = 63 omega` Hence `I = (3)/(63)` = 0.02 `omega` Total resistance in the circuit is `0.02 omega + 3 omega = 3.02 Omega` Hence `I= (3)/(3.02)` = 0.99 A c. For the IDEAL ammerter with ZERO resistance `I = (3)/(3) = 1.00 A` |
|
| 43203. |
For a transistor beta=45, the change in the voltage across 5kOmega resistor which is connected in collector circuit is 5 V. Find the change in base current. |
|
Answer» Solution :`BETA=((DeltaI_(C))/(DeltaI_(B)))_(V_(CE))` (If only d.c. values are considered) `THEREFORE I_(C)=betaI_(B)=40xx25xx10^(-6)=1000xx10^(-6)A` `therefore I_(E)=I_(B)+I_(C)=(25xx10^(-6)+1000xx10^(-6))" AMP"` `=1025muA=1.025mA` |
|
| 43204. |
A 200 mH (pure) inductor and a 5uF (pure) capacitor are connected, one by one, across a sinusoidal a.c. voltage source V= 70.7 sin (1000 t) volts. Obtain the expression for the current in each case. |
|
Answer» Solution :Here L = 200 mH = 0.2 H, `C = 5muF xx 10^(-6)F` and V = 70.7 sin(1000 t) means that `omega = 1000 s^(-1)` For inductive cirucit`I_(m) = V_(m)/X_(L) = V_(m)/(Lomega) = (70.7)/(0.2 xx 1000) = 0.354 A` So expression for current will be, `I_(L) = I_(m) sin (omega t -pi/2) = 0.354 sin(1000 t - pi/2) A` For CAPACITIVE circuit, `I_(m) = V_(m)/X_(L) =V_(m).C.omega = 70.7 xx 5 xx 10^(-6) xx 1000 = 0.354 A` `therefore` Expression for current will be, `I_( c) = I_(m) sin (omega t + pi/2) = 0.354 sin (1000 t + pi/2) A` |
|
| 43205. |
A block weighing 10.0 N is attached to the lower end of a verticle spring (k = 200.0 N//m), the other end of which is attached to a ceiling. The block oscillates vertically and has a kinetic energy of 2.00 J as it passes through the point at which the spring is unstretched. What is the period of the oscillation? |
|
Answer» 0.45 s |
|
| 43206. |
Anelectron falls throgh a distance of 1.5 cm in a uniform electric field of magnitude2.0 xx10^(4) N c^(-1)the direction of the fieldis reversed keeping its magnitude unchangedandaproton falls throughthe same distance computethe time of falls in each case contrastthe situation with that of free fall under gravity |
|
Answer» Solution :The field is upward so the negatively CHARGED the magnitude of the electricof the ELECTRON is`a_(e )=eE//m_(e )` where `m_(e )` is the mas of the electron distanceh is given by `t_(e )=sqrt(2h)/(a_(e ))=sqrt(2hm_(e ))/(e E)` For e=`1.6 xx10^(-19) C, m_(e )=9.11 xx10^(-31)` kg `t_(e )=2.9n xx10^(-9)` S where `m_(p)` is the mass of the proton `m_(p)=1.67 xx10^(-27)` kg the time of fall for the proton is `t_(p)=sqrt(2h)/(a_(p))=sqrt(2hm_(p))/(eE)=1.3 xx10^(-7)` S `a_(p)=(eE)/(m_(p))` `=1.9xx10^(12) ms^(-2)` which is enormous compared to the value of g (9.8 `ms^(-2)`)the ACCELERATION due to gravity thethus the effect of acceleration due to gravity can be ignored in this EXAMPLE |
|
| 43207. |
In an electronic communication system define modulation. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Modulation. The process by which some CHARACTERISTICS of a relatively high frequency wave ( called carrier wave ) is VARIED in accordance with the instantaneous VALUE of a low frequency wave ( called modulating wave ) is called modulation. Demodulation : |
|
| 43208. |
The displacement time graphs of two moving particles make angles of 30^@ and 45^@ with the X-axis. The ratio of the two velocities is |
| Answer» ANSWER :D | |
| 43209. |
What is Doppler effect in light? Write the expression for Doppler shift. |
|
Answer» Solution : DOPPLER effect: The apparent CHANGE in frequency of WAVES from a source due to therelative motion between an observer and the source is called Doppler effect. Expression for Doppler shift is given by `(Delta V)/(v) = - (v_("radial"))/(e )` Where, e = SPEED of light `v_("radial") ` = Radial component of the source velocity |
|
| 43210. |
The angle of incidence at which reflected light totally polarised for reflection from air to glass (refractive index n), is ...... |
|
Answer» <P>`sin^(-1)(n)` `n= tan I "[:. theta_(p)=i]` `:. i=tan^(-1)(n)` |
|
| 43211. |
When does a convex lens behave as a concave lens. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :By surrounding the lens in a MEDIUM of HIGHER REFRACTIVE index. | |
| 43212. |
The given four terminal net work is a part of larger circuit. The points A, B, C are at the same potential. The P.E. between any one of A, B or C and D is 40 V. Find the P.D. between A & O. |
|
Answer» Solution :Potentials of POINTS A, B and C are 40 V. POTENTIAL of D is 0V. Potential at O is `V_(0)`, Then ACCORDING Kirchoff.s first LAW `i_(1)+i_(2)+i_(3)=i_(4)`  `(40-V_(0))/(R )+(40-V_(0))/(R )+(40-V_(0))/(R )=(V_(0)-0)/(R )` `120-3V_(0)=V_(0)" so "V_(0)=30V""V_(AO)=10V` |
|
| 43213. |
The frequency of vibrations of a mass m suspended from a spring of spring const. k is given by v=cm^(x)k^(y), where c is a dimensionless constant. The values of x and y are respectively : |
|
Answer» `(1)/(2),(1)/(2)` WRITING DIMENSIONS on both sides, `[M^(0)L^(0)T^(-1)]=M^(x)[ML^(0)T^(-2)]^(y)` `[M^(0)L^(0)T^(-1)]=[M^(x+y)T^(-2y)]` Comparing dimensions on both sides, we have `0=x+y` and `-1=-2yimpliesy=(1)/(2)` `:.x+(1)/(2)=0impliesx=-(1)/(2)` So carrect choice is `(d)`. Aliter. Remembering that FREQUENCY of oscillation of loaded spring is `v=(1)/(2PI)SQRT((k)/(m))=(1)/(2pi)(k)^(1//2).m^(-1//2)` which gives `x=-(1)/(2)andy=(1)/(2)` |
|
| 43214. |
A conductor is moving with the velocity 'v' in the magnetic field and the induced current 'I'. If the velocity becomes half,the induced current becomes: |
|
Answer» 0.5I |
|
| 43215. |
According to Huygens' principle, during refraction of light from air to a denser medium |
|
Answer» wavelength and speed decrease |
|
| 43216. |
How many electrons must be removed from a piece of metal to give it a positive charge of 1.0 xx 10^(-7)C. |
|
Answer» `6.25 XX 10^11` |
|
| 43217. |
In the cylindrical region of radius R=2m, there exists a time varying magnetic field B such that (dB)/(dt)=2"Tesla"//sec. A charged particle having charge q=2C is placed at the point P at a distance d from its center O. Now, the particle is moved in the direction perpendicular to line OP by an external agent up to infinity so that there is no gain in kinetic energy of charged particle. Then |
|
Answer» WORK DONE by external agent is `4pi` Joule when `d=4m` `E=2pisqrt(x^(2)+d^(2))=piR^(2)k`, where `((dB)/(dt)=k)` `E=(R^(2)k)/(2sqrt(x^(2)+d^(2)))` `W=int_(0)^(oo) dvecE.dvecx` `=int_(0)^(oo) qEcostheta.dx=int_(0)^(oo) (qR^(2)k)/(2sqrt(x^(2)+x^(2)))d/(sqrt(x^(2)+x^(2)))dx=(qR^(2)kpi)/4` Alternate solution By applying Faraday's Law for an IMAGINARY triangular loop having vertex `O,P` and point at infinity, `qintvecE.vec(dl)` can be found out. 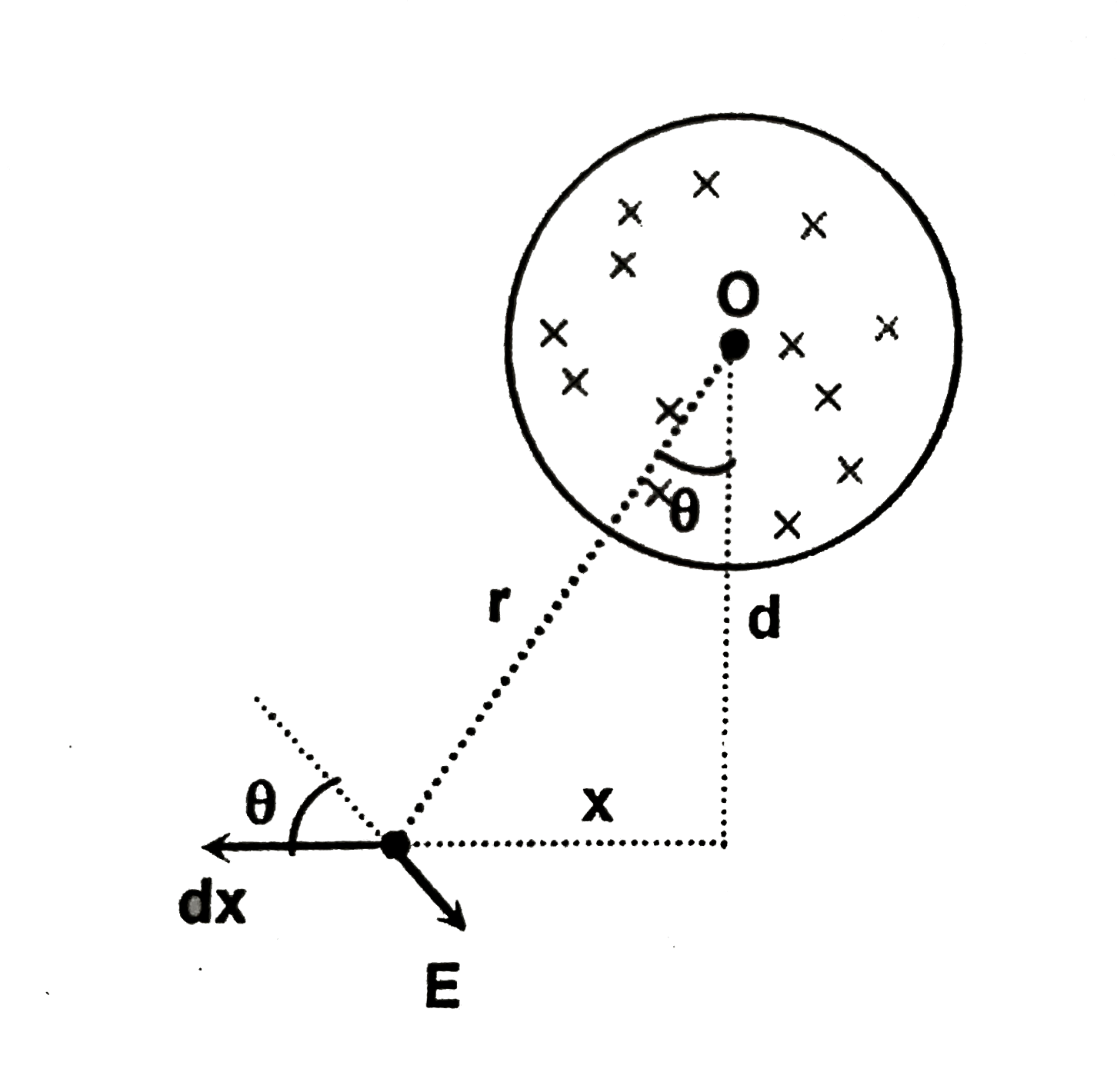
|
|
| 43218. |
Discuss the intensity of transmitted light when a polaroid sheet is rotated between two crossed polaroids? |
|
Answer» Solution :LET `I_(0)` be the intensity of polarised light after passing through the first polariser `P_(1)` . Then the intensity of light after passing through second polariser `P_(2)` will be `I=I_(0)cos^(2)theta`. where `theta` is the angle between pass axes of `P_(1) and P_(2)` . Since `P_(1) and P_(3)` are crossed the angle between the pass axes of `P_(2) and P_(3)` will be `(PI//2-theta)`. Hence the intensity of light EMERGING from `P_(3)` will be `I=I_(0)cos^(2)theta cos^(2)((pi)/(2)-theta)` `=I_(0)cos^(2)theta sin^(2)theta=(I_(0)//4)sin^(2)2theta` Therefore, the transmitted intensity will be maximum when `theta=pi//4` |
|
| 43220. |
For what distance is ray optics a good approximation when the aperture is 3mm wide and the wavelength is 500 nm? |
| Answer» Solution :`Z_(F)=(a^(2))/(lamda)=((3xx10^(-3))^(2))/(5XX10^(-7))=18m` | |
| 43221. |
The height of F_(2) layer is (1) 240 km to 400 km in day time (2) 300 km to 400 km in day time (3) 240 km to 400 km at night time (4) 30 km to 400 km at night time |
|
Answer» 2 & 3 |
|
| 43222. |
The potentiometer wire AB shown is 40 cm long of resistance 50 Omega//m, free end of an ideal voltmeter is touching the potentiometer wire at the middle initially. What should be the velocity of the jockey as function of time so that reading in voltmeter is varyingwith time as (2 sin pi t). |
|
Answer» `10 PI sin pi t cm//s` |
|
| 43223. |
A wave is represented by the equation y = 7 sin (7 pi t - 0.04 pi x + (pi)/(3) ) where x is in metre and t is in second. The speed of the wave is : |
|
Answer» 175 m/s y = a SIN `(OMEGA t - kx + phi)`, we get ` omega = 7pi` , k = 0.04 c = `(omega)/(k)= (7 pi)/(0.04)= 175 ms^(-1)` . Hence the correct choice is (a). |
|
| 43224. |
What will be the number of photons emitted per second by a 10 w sodium vapour lamp assuming that 90% of the consumed energy is converted into light ? ( wavelength of sodium light is 590 nm, h =6.63 xx 10^(-34) Js) |
|
Answer» `0.267 xx 10^(18)` |
|
| 43225. |
The position x of a particle varies with time t as x = at^(2) -bt^(3). For what value of time acceleration is zero? |
|
Answer» `(2a)/(3B)` `v=(dx)/(dt)=2at-3bt^(2)` ACCELERATION =`F=(dv)/(dt)=2a-6bt` Now when f=0 2a-6bt=0 `2a=6bt` or `t=(a)/(3b)` |
|
| 43226. |
The magneticfieldan electromangeticwavein a substanceis givenbyB = ( 2 xx 10^(-6) T) cos[ pi( 0.04 xx 10^7t)]. Findthe electromagneticwavespeed. |
|
Answer» Solution :Comparingthe givenequationwith thestandardwaveequation`B=B_0 cos( omegat+ k x)` we have ` , omega= PI XX 10^7rad // s andk =pixx ( 0.04 ) m^(-1)` ` therefore ` speedof electromangeticwavein thismedium is ` V=(omega )/(k)= 2.5xx 10^8 m/s` |
|
| 43227. |
Consider a circular current-carrying loop of radius R in the x-y plane with centre at origin. Consider the line integral (L)=|int_(-L)^(L)vecB*vec(dl)| taken along z-axis. (a) Show that (L) monotonically increases with L. (b) Use an appropriate Amperian loop to show that (oo)=mu_(0)I, where I is the current in the wire. ( c) Verify directly the above result. (d) Suppose we replace the circular coil by a square coil of sides R carrying the same current I. What can you say about (L) and (oo)? |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) B(z) is same at every point on z-axis. So, is monotonically function for L. `vecBandvec(dl)` are in same direction. So, `VECB*vec(dl)=Bdlcos0=Bdl` (b) (L) + by circumference at large distance `C=mu_(0)I` Now, `Ltooo` At large distance `TO0" "(becauseBprop1/r^(3))` `(oo)-mu_(0)(I)` ( c)  Current CARRYING ring of radius R is in xy-plane. Centre of it is at origin point, magnetic field at any point from centre of loop is, `B_(z)=(mu_(0)IR^(2))/(2(z^(2)+R^(2))^(3/2))` `int_(-oo)^(oo)B_(z)dx=int_(-oo)^(oo)(mu_(0)IR^(2))/(2(z^(2)+R^(2))^(3/2))dz` Taking `z=Rtantheta` `dz=Rsec^(2)thetad theta` `int_(-oo)^(oo)B_(z)dz=(mu_(0)I)/2int_((-pi)/2)^((+pi)/2)(costheta)d theta=mu_(0)I` (d) `B(z)_("square")ltB(z)_("circular loop")` `thereforeJ(L)_("square")ltJ(L)_("circular loop")` but as per DISCUSSION of option (b), `J(oo)_("square")=J(oo)_("circular loop")` |
|
| 43228. |
What is the frequency of the K.E. and total energy of a body inS.H.M. if the time period of S.H.M. is T? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`2//T, 0` | |
| 43229. |
A ray PQ is incident normally on the face AB of a triangular prism of refracting angle of 60^(@), mae of a transparent material of refractive index ( sqrt(3))/( 2) , as shown in the figure. Trace the path of the ray as it passes through the prism. Also calculate the angle of emergence and angle of deviation. |
|
Answer» Solution :If `i_(c)` is the critical ANGLE for the prism `//` material, `mu = ( 1)/( sini_(c ))` `:.Sini_(c ) = ( 1)/( mu ) = ( sqrt(3))/( 2)` `rArr i_(c) = ( 60^(@)` Angle of incidence at face AC of the prism `= 60^(@)` Hence, refracted ray GRAZES the SURFACE AC. `rArr` Angle of emergence `= 90^(@)` `rArr ` angle of deviation `= 30^(@)` 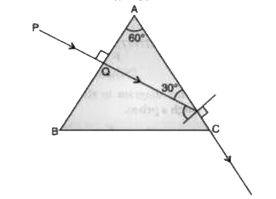
|
|
| 43230. |
A closed cubical box made of perfectly insulating material has walls of thickness 8 cm and the only way for heat to enter or leave thebox is through two solid, cylindrical, metallic plugs, each of cross-sectional area 12 cm^(2) and length 8 cm in opposite walls of the box. The outer surface of one plug is kept at 100^(@)C while the outer surface of the other plug is maintained at 4^(@)C. The thermal conductivity of the plug is 50 cal s^(-1) m^(-1) K^(-1). A source of energy generating 36 cal s^(-1) is enclosed inside the box. Find the equilibrium temperature of the inner surface of the box, assuming that it is the same at all points on the inner surface. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43231. |
Two plane wave fronts of light, one incident on a thin convex lens and another on there fraction face of a thin prism. After refraction at them, the emerging wave fronts respectively become |
|
Answer» a. PLANE WAVEFRONT and plane wavefront |
|
| 43232. |
What is a photo cell ? Mention the different types of photocells. |
|
Answer» Solution :PHOTOCELLS : PHOTO ELECTRIC cell or photo cell is a device which converts light energy into electrical energy. It WORKS on the principle of photo electric effect. Types : Photo emissive cell Photo voltaic cell Photo conductive cell |
|
| 43233. |
Write a note on transformer. |
|
Answer» Solution :Energy losses in transformer: TRANSFORMERS do not have any moving parts so that its efficiency is much higher than that of ROTATING machines like generators and motors. But there are many factors which lead to energy loss in a transformer. (i)Core loss or Iron loss: This loss takes place in transformer core. Hysteresis loss and eddy current loss are known as core loss or Iron loss. In transformer core is magnetized and demagnetized repeatedly by the alternating voltage applied across primary coil, hysteresis takes place due to which some energy is lost in the form of heat. Hysteresis loss is minimized by using steel of high silicon CONTENT in making transformer core. Alternating magnetic flux in the core induces eddy currents in it. Therefore there is energy loss due to the flow of eddy current, called eddy current loss which is minimized by using very thin laminations of transformer core. (ii)Copper loss: Transformer windings have electrical resistance. When an electric current flows through them, some amount of energy is dissipated due to Joule heating. This energy loss is called copper loss which is minimized by using wires of larger diameter. (iii)Flux leakage: Flux leakage happens when the magnetic lines of primary coil are not COMPLETELY linked with secondary coil. Energy loss due to this flux leakage is minimized by winding coils one over the other. |
|
| 43235. |
Two small spheres each carrying a charge q are placed r metre apart. If one of the spheres is taken around the other one in a circular path of radius 1, the work done will be equal to |
|
Answer» FORCE between them `XX` R |
|
| 43236. |
Two identical slabs, of a given metal, are joined together, intwo different ways, as shown in Fig.(i) and (ii). What isthe ratio of the resistances of these two combinations ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Let each slab has LENGTH l and cross-section AREA A. Then in combination (i), `R_1 = (rho 2l)/(A)` and in combination (II), `R_2 =(rho l)/(2A)` `RARR R_1/R_2 =4/1 " or"R_1 = 4R_2` |
|
| 43237. |
The same mass of copper is drawn into two wires 1 mm thick and 2mm thick. Two wires are then connected in series and current is passed. The heat produced in the wires in the ratio |
|
Answer» `16:1` |
|
| 43239. |
A metal block has lengths 50 cm, breadth 30cm and thickness 20cm. When current passes through it parallel to its length and parallel to its breadth, the ratio of maximum to minimum resistance of that block is |
|
Answer» `4:25` |
|
| 43240. |
A slit of width .a. is illuminated by white light. The first minimum for red light (lambda= 6500 A^(0)) will fall at theta= 30^(@). Then .a. will be |
|
Answer» `3250 A^(0)` |
|
| 43241. |
The focal lengths of a lens are in the ratio 8:3 when it is immersed in two differentliquids of refractive induces 1.6 and 1.2 respectively. The refractive index of the material of the lens is |
|
Answer» 1.25 |
|
| 43242. |
When 0.005A current flows through a moving coil galvanometer, it gives full scale deflection. It is converted into a voltmeter, it gives full scale deflection. It is converted into a voltmeter to read 5 Volt, using an external resistance of 975Omega. The resistance of galvanometer in ohms is |
|
Answer» 5 |
|
| 43243. |
The binding energy of deuteron is 2.2MeV and that of ._2^4He is 28MeV. If two deuterons are fused to form one ._2^4He then the energy released is |
|
Answer» 30.2 MeV |
|
| 43244. |
Einstein's work on photoelectric effect gives support to |
|
Answer» `E = MC^(2)` |
|
| 43245. |
Deuteron and alpha-particle are put 1 A^(@) apart in Air. Magnitude of intensity of electric field due to deuteron at alpha-particle is (N/C). |
|
Answer» Zero |
|
| 43246. |
The graph between the path difference versus phase difference is a/an 1) straight line 2) parabola 3) sine curve 4) none of these |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Since, a path difference of `lambda` corresponding to a phase difference of `2pi` `triangle X= (lambda)/(2pi) triangle phi ""THEREFORE triangle x propto triangle phi`. A STRAIGHT LINE. |
|
| 43247. |
Why do clouds appear white ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :WHITE CLOTHES reflect all the lights that falls on it. | |
| 43248. |
A grinding machine whose wheel has a radius of 1/(pi) is rotating at 2.5 rev/sec. A tool to be sharpened is held against the wheel with a force of 40N. If the coefficient of friction between the tool and wheel is 0.2, power required is |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 43249. |
A bar magnet with poles 25.0 apart and of polestrength 14.4 am rests with its cent4re on a frictionless point12 cm from its pivot the magnitude of the force is |
|
Answer» `15sqrt(3) N` `Fxx0.12 =MB sin THETA` `F=(3.6xx0.25 xxsqrt(3)//2)/(0.12)` `=3.75 sqrt(3)N` 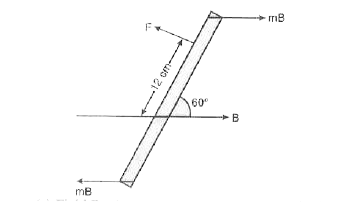
|
|
| 43250. |
de-Broglie wavelength lambda associated with neutrons is related with absolute temperature T as |
|
Answer» `lambda PROP T` `lambda = (h)/(sqrt(2 MK)) = (h)/(sqrt(3 m KT)) rArr lambda prop (1)/(sqrt(T))` |
|