Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 43101. |
A beaker contains 0.1 kg of water, initially at room temperature (20^(@)C). If the specific heat of water is 4.2 kJ/kg*""^(@)C and the latent heat of vaporization is 2,300kJ/kg, how much thermal energy would the water need to absorb to turn completely to steam? |
|
Answer» Solution :First we NEED to HEAT the water to the boiling point, `100^(@)C`, then we need to continue to add heat until all the liquid is vaporized. The AMOUNT of THERMAL energy required of the first step is `Q_(1)=m_("water")c_("water")(100^(@)C-20^(@)C)` `=(0.1kg)(4.2kJ//kg*""^(@)C)(80^(@)C)` `=33.6 kJ` and the amount of energy required for the second step is `Q_(2)=m_("water")L_("vap")=(0.1kg)(2,300kg//kg)=230kJ` Therefore, the total amount of thermal energy requires is `Q_("total")=Q_(1)+Q_(2)=33.6 kJ+230kJ=264kJ`. |
|
| 43102. |
Two circular coils of radii 5cm and 10cm carry currents of 2A. The coils have 50 and 100 turns respectiely and are placed in such a way that their planes as well as their cetre coincide. Magnitude of magnetic field at the common centre of coils is |
|
Answer» `8pixx10^-4T` if CURRENTS in the coils are in same sense `=((4pixx10^I-7)(50)(2))/(2(5xx10^-2))` `=4pixx10^-4T` `B_2=(mu_0N_2i_2)/(2R_2)` `=((4pixx10^-7)(100)(2))/((2)(10xx10^-2))` `=4pixx10^-4T` When currets are in the same direction then `B_("NET")=B_1+B_2` When curents are in the opposite direction, then `B_("net")=B_1-B_2` |
|
| 43103. |
Define excitation potential. |
| Answer» Solution :EXCITATION potential is DEFINED as excitation energy per UNIT CHARGE. | |
| 43104. |
A yo-yo has mass M = 0.550 kg and rotational inertia I = 3.40 xx 10^(-4) kg m^(2)?. It rolls from rest down a string of length L = 17.0 cm. What is its angular speed at the bottom? |
|
Answer» Solution :The mechanical energy of the yo-yo is conserved during the descent. Calculations: Let the bottom position be the reference LEVEL for zero gravitational potential energy. Then at the initial POINT (at height y = L) the mechanical energy is `E_(i) = K_(i) + U_(i) = 0+ MgL`. The symbol `K_(i)` is the sum of the translational kinetic energy and ROTATIONAL kinetic energy, both of which are zero. At the bottom (at height y= 0), the translational kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy are zero. So, the mechanical energy is just the rotational kinetic energy `1//2Iomega^(2)` and we have `E_(f) = K_(f) +U_(f) =(1)/(2)Iomega^(2)` Because the mechanical energy does not change, `E_(f)=E_(i)` `(1)/(2)Iomega^(2) = MgL` Solving for omega and SUBSTITUTING the given values LEAD to `omega= 73.4 "rad"//s` |
|
| 43105. |
In the Hall effect, we have a current flowing in the presence of a uniform magnetic field, and we get a potential difference across the conductor. Which is incorrect statement? |
|
Answer» a changing magnetic FIELD PRODUCES an induced EMF |
|
| 43106. |
Two point charges q_(1) , q_(2) initially at infinity are brought one by one points P_1 and P_2 specified by position vectors r_1 and r_2 , relative to some origin . What is the potential energy of this energy configuration ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The potential ENERGY of the given charge configuration is `U = (1)/(4 PI in_(0)) * (q_(1) q_(2))/(|vecr_(2) - vecr_(1)|)` | |
| 43107. |
Read the following statements and choose the correct answer. a)For a freely falling body the average velocity is proportial to square root of height of fall. b)For a freely falling body the displacements in successive equal time intervals are in the ratio 1:4:9...... c)For a vertically projected body the displacement during last second time of flight changes with velocity of projection. d)For a body projected from the top of the tower the displacement of the body is negative when the body crosses the poiny of projection. |
|
Answer» a,C,d are true |
|
| 43108. |
Assertion: The earth without atmosphere would be inhospitably cold. Reason: All heat would escape in the absence of atmosphere. |
|
Answer» If both ASSERTION and REASON are true and the reason is the CORRECT explanation of the assertion. |
|
| 43109. |
Number of chromosomes in secondary oocyte stage in humans is |
|
Answer» 23 |
|
| 43110. |
Explain the three magnetic elements of earth at a place. |
|
Answer» Solution :Earth has three magnetic elements : (i) Declination (ii) Dip or Inclination (iii) Horizontal component of the earth.s field. Let us consider each of them in detail. (i) Declination. It is defined as the angle between the magnetic meridian and the geographic meridian at a PLACE. It is denoted by angle `theta` in FIG (a). In Fig., let PKLM represents the magnetic meridian and PK.L.M represents the geographic meridian at the place P. Then angle `theta` between these two planes, by definition, is the angle of declination at the place P. 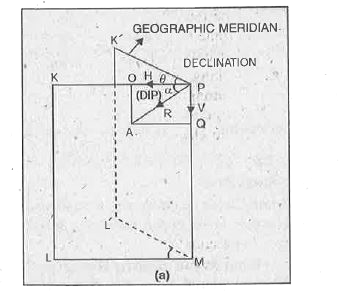 (ii) Dip or inclination `(delta)`. Dip at a place is defined as the angle between the direction of the total INTENSITY of the earth.s magnetic field and a horizontal line in the magnetic meridian. In Fig. (a), PA represents the total or resultant intensity of the earth.s magnetic field R in magnitude as well as in direction. As PA makes an angle `delta` with PO, the angle of dip at the place P is `delta`. (iii) Horizontal Component (H). The total intensity of the earth.s magnetic field at any point can be resolved into two rectangular components, one along the horizontal and the other along the vertical direction. The component of the resultant intensity of the earth.s magnetic field in the horizontal direction in magnetic meridian is called its horizontal component. It is denoted by H. The component of the resultant intensity of the earth.s magnetic field in the vertical component. It is denoted by V. 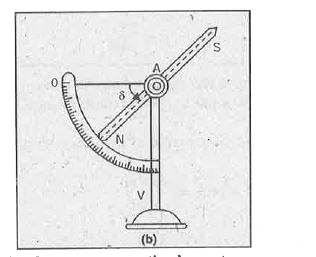 Relation between magnetic elements In Fig. (a) the resultant intensity, i.e. R along PA has been resolved into two rectangular components. CLEARLY, the horizontal component is along PO `i.e,""H=Rcosdelta""...(1)` and the vertical component is along PQ `i.e,""V=Rsindelta""...(2)` Dividing (2) by (1), we get `V/H=(Rsindelta)/(Rcosdelta)=tandelta""...(3)` Squaring (1) and (2) and adding, we get `H^(2)+V^(2)=R^(2)(cos^(2)delta+sin^(2)delta)` or `H^(2)+V^(2)=R^(2)` |
|
| 43111. |
Surface density of change is maximum at the point where |
|
Answer» Curvature is a MINIMUM |
|
| 43112. |
A conducting shell has inner radius R and outer radius 2R. A charge + q is given to the spherical shell. (a) Find the electric field at a point which is at a distance x from the centre of the shell. Give your answer for three cases(i) x lt R (ii) R lt x lt 2R (iii) x gt 2R (b) Find the electric potential in all the three cases mentioned in (a) (c) Find field and potential in all the three cases mentioned in (a) after a point charge – q is introduced at the centre of the shell. (d) Write the electrical potential energy of the system consisting of the shell and the point charge at its centre. (e) Find the electrostatic force that the shell exerts on the point charge. (f) Now, another point charge + q is placed at a distance 4R from the centre of the shell. Find electric field and potential in following cases. (i) x lt R (ii) R lt x lt 2R |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43113. |
A negative charge is placed at the centre of the non-conducting sphere. The direction of electric field on any point at the surface of the sphere is |
|
Answer» radially inward 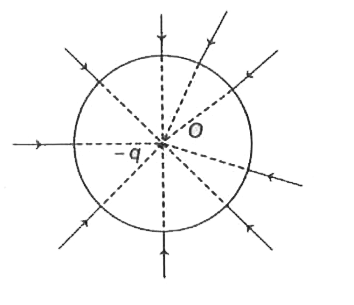
|
|
| 43114. |
Ozone layer absorbs…… |
|
Answer» INFRARED radiaiton |
|
| 43115. |
The radius of gyration of a ring about a tangent and axis perpendicular to its plane is |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 43116. |
A gun fires a bullet at a speed of 140ms^(-1) If the bullet is to hit a target at the same level as the gun and at 1km distance, the angle of projection may be |
|
Answer» `60^(@) or 30^(@)` |
|
| 43117. |
A series circuit consistingof a capacitor and a coil with active resistance is connected to a source of harmonic voltage whosefrequency can be aried, keeping the voltage amplitdue are n times less than the resonance amplitude. Find : (a) the resonance frequency, (b) the quality factor of the circuit. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :At RESONANCE `omega_(0)L=(omega_(0)C)^(-1)` or `omega_(0)=(1)/(sqrt(LC))` `(I_(m))_(res)=(V_(m))/(R)`. Now `(V_(m))/( nR)=(V_(m))/sqrt(R^(2)+(omega_(1)L-(1)/(omega_(1)C))^(2))=(V_(m))/( sqrt(R^(2)+(omega_(2)L-(1)/( omega_(2)C))^(2)))` Then `omega_(1)L-(1)/( omega_(1)C)=sqrt(n^(2)-1)R` `omega_(2)L-(1)/( omega_(2)C)=sqrt(n^(2)-1)R`( assuming `omega_(2) gt omega_(2))` or `omega_(1)-(omega_(0)^(2))/( omega_(1))=- omega_(2)+(omega_(0)^(2))/( omega_(2))=- sqrt (n^(2)-1 )(R)/(L)` or` omega_(1)+ omega_(2)=( omega_(0)^(2))/( omega_(1)omega_(2))(omega_(1)+ omega_(2))implies omega_(0)=sqrt( omega_(1) omega_(2))` and ` omega_(2) - omega_(1)= sqrt( n^(2)-1) (R)/(L)` `beta=(R)/(2L) = ( omega_(2)-omega_(1))/( 2 sqrt( n^(2)-1))` and `Q=sqrt( (omega_(0)^(2))/(4 beta^(2))-(1)/(4))=sqrt(((n^(2)-1)omega_(1)omega_(2))/( (omega_(2)-omega_(1))^(2))=(1)/(4))` |
|
| 43118. |
A cloud is at a potential of 8 xx 10^(6) volt relative to the ground. A charge of 80 coulomd is transferred in lightening stroke betwee the cloud and the gorund. Assuming the potential of the cloud of remain constant, the energy dissipated is |
|
Answer» `6.4 XX 10^(8)` JOULE |
|
| 43119. |
(a) The threshold frequency of photoelectric effect supports the particle nature of sunlight. ( b) The specific charge of positive rays is constant. ( c ) Photosensitive of a metal is high of its work function is small. ( d ) The stopping potential is independent of intensity of the incident light. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43120. |
The equation of S.H.M. with amplitude 10cm and period 0.2sec is given by |
|
Answer» `y=10sin2pit` |
|
| 43121. |
A prism of prism angle 50^(@) has angle of minimum deviation 30^(@).Determine the velocity of the light inside the prism. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`1.97xx10^(8)MS^(-1)` | |
| 43122. |
What is depletion region in p-n junction ? |
| Answer» Solution :A THIN LAYER between p and n regions of the junction diode devoid of free electrons and HOLES is called DEPLETION layer. | |
| 43123. |
A white light which contains many wavelengths from sources of sun light, light emitted by mercury vapor lamp is called ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :POLYCHROMATIC | |
| 43124. |
Temperature coefficient of resistivity of manganin is very high and due to this reason manganinis used as a resistance wire. |
| Answer» SOLUTION : FALSE - TEMPERATURE coefficient of resistivity of manganin is LEAST. | |
| 43125. |
A mica strip and a polysterence strip are fittedon the two slite of a double slit apparatus.The thickness of the strips is 0.50 mm and the separation between the slits is 0.12 cm. The refractive index of mica and polysterene are 1.58 and 1.55 respectively for the light of wavelength 590 nm which is used in the experiment. Theinterference is observed ona screen a distance one meter away. (a) What would be the fringe- width ? (b) At what distance from the centre will the first maximum be located ? |
|
Answer» `mu_m = 0.5 xx 10^(-3)m` `mu_m = 1.58 and mu_p = 1.55` `lambda = 590 nm` `= 590 xx 10^(-9) m,` `d = 0.12 cm = 12 xx 10^(-4)m` D =1m (a) Fringe width ` =(D lambda)/(d)` ` =(1xx 590xx 10^(-9))/(12 xx 10^(-9))` `=4.91 xx 10^(-4)m` (b) When both the strip are fitted, the optical path CHANGES by `Delta x = (mu_0 -1 ) t - (mu_p - 1)t` `=(mu_m - mu_p)t` `=(1.58 - 1.55) xx (0.5) (10^(-3))` `=(0.15) xx 10^(-3)m` So, no of FRINGES SHIFTED ` = (0.015 xx 10^(-3))/(590 xx 10^(-9)) = 25.43` `RARR` There are 25 fringes and `0.43th` of a fringe. `rArr` There are 13 bright fringes and 12 dark fringes and `0.43th` of a dark fringe. So, position of first maximum on both sides will be given by, `:. x = (0.43) xx 4.91 xx 10^(-4)` = 0.021 cm `x ' = (1 - 0.43) xx 4.91 xx 10^(-4)` = 0.028 cm [Since, fringe width `= 4.91 xx 10^(-4)m]` |
|
| 43126. |
Archaebacteria do not show |
|
Answer» PEPTIDOGLYCAN in cell wall |
|
| 43127. |
In coulomb's law, on what factors does the value of electrostatic force constant K depend ? |
|
Answer» The value of K depends on NATURE of MEDIUM separating the CHARGES and on the SYSTEM of units. |
|
| 43128. |
In amplitude modulation, the total modulation index should not exceed one, otherwise |
|
Answer» the SYSTEM will FAIL |
|
| 43129. |
A candle flame gives |
|
Answer» LINE spectrum |
|
| 43130. |
In an ac circuit containing pure capacitance whether emf is lagging or leading ? |
| Answer» Solution :In an a.c. CIRCUIT containing PURE capacitance the emf is BEHIND the CURRENT by a PHASE difference of `pi/2` . | |
| 43131. |
The kinetic energy of rotation E and the angular momentum L of a rigid body are related to each other by the relation.(I= moment of inertia) |
|
Answer» `L=(E^2)/(2I)` |
|
| 43132. |
A gas bubble from an explosion under water oscillates with a period proportional to P^(a)d^(b)E^(c), where P is the static pressure, d is the density of water and E is the energy of explosion. Then a,b,c are respectively : |
|
Answer» `1,1,1` Writing dimensions on both SIDES, `[M^(0)L^(0)T^(0)]=[ML^(-1)T^(-2)]^(a)[ML^(-3)]^(b)[ML^(2)T^(-2)]^(c)` `:.[M^(0)L^(0)T]=M^(a+b+c)L^(-a_3b+2c)T^(-2a-2c)` Thus `a+b+c=0,-a-3b+2c=0,-2a-2c=0.` On solving eqns, we GET `a=(-5)/(6),b=(1)/(2)` and `c=(1)/(3)` Hence the correct `(c )`. |
|
| 43133. |
Obtain the equation for lateral magnification for thin lens. |
|
Answer» Solution :The mirror equation establishes a relation among object distance u, image distance v and focal length f for a spherical mirror. (i) An object AB is considered on the principal axis of a concave mirror beyond the center of curvature C. (ii) Consider three paraxial rays from point B on the object. (iii) The first paraxial ray BD TRAVELLING parallel to principal axis is incident on the concave mirror at D, close to the pole P. (IV) After reflection, the ray passes through the focus F. The second paraxial ray BP incident at the pole P is reflected along (v) The third paraxial ray BC passing through centre of curvature C, falls normally on the mirror at E is reflected back along the same path. The three reflected rays intersect at the point B'. (vi) A perpendicular drawn as A' B' to the principal axis is the real, inverted image of the object AB. (vii) As per law of reflection, the angle of incidence `angleBPA` is equal to the angle of reflection `angleB'PA' `. (viii) The triangles `DeltaBPA` and `DeltaBʻPA'` are similar. Thus, from the rule of similar triangles, ` (A' B')/(AB) = (PA')/(PA) "" ....(1)` (ix) The other set of similar triangles are, `DeltaDPF` and `DeltaB'A' F.` (PD is almost a straight vertical line) ` (A'B')/(PD) = (A'F)/(PF)` As, the distances PD = AB the above equation becomes, ` (A'B')/(AB) = (PA')/(PA) "" ...(2)` From equations (1) and (2) we can write, ` (PA')/(PA) = (A'F)/(PF)` As, A'F = PA' - PF, the above equation becomes, ` (PA')/(PA) = (PA' - PF)/(PF) "" ....(3)` Apply the sign conventions for the various distances in the above equation. ` PA = - u , PA' = -v , PF = - f` Negative sign is because they are measured to the left of the pole. Now, the equation (3) becomes, ` (-v)/(-u) = (-u - (-f))/(-f)` On further simplification, `1/u = 1/f - 1/v , v/u = v/f -1` Dividing either side with v, ` 1/u = 1/f - 1/v` After rearranging, ` 1/v + 1/u = 1/f "" ....(4)` The above equation (4) is called mirror equation. |
|
| 43134. |
Find total energy stored in capacitors given in the circuit. |
|
Answer» Solution :Capacitors `C_(4) and C_(5)` are in series, their EQUIVALENT capacitance `C.=(C_(4)C_(5))/(C_(4)+C_(5))=(2xx2)/(2+2)=1muF` C. and `C_(2)` are in parallel having equivalent capacitance `C..=C_(2)+C.=1+1=2muF` C.. and `C_(3)` are in series, their equivalent capacitance `C_(0)=(C..C_(3))/(C..+C_(3))=(2xx2)/(2+2)=1muF` `therefore` Total energy stored in the capacitors in the given network `U=(1)/(2)CV^(2)=(1)/(2)xx2xx10^(-6)xx(6)^(2)=3.6xx10^(-5)J`. |
|
| 43135. |
A ray of light incident normally on one of the faces of rt. Angled isosceles prism is found to be totally reflected, what is min. value of refractive index of material of prism ? |
|
Answer» 1.01 Now `45^(@) ge C` (for glass air interface) `SIN 45^(@) ge sin C` or `(1)/(sqrt(2)) ge (1)/(mu) or mu ge sqrt(2)` `mu_(min) = sqrt(2_ = 1.414`  If r is angle of refraction in water, then `sqrt(2) sin 45^(@) = (4)/(3) sin r` or `r = 48.6^(@)` |
|
| 43136. |
5A 50 mH inductor is in series with a 10 2 resistor and a battery with an emf oj 25 V. At t = 0 the switch is closed. Find Q(c) the rate at which energy is stored in the inductor, |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The rate at which energy is supplied to the inductor is (dU^(L))/(DT)=+ Li(di0/(dt)Rightarrow(di)/(dt)=+epsilon/Le^(-Rt/L)` Therefore `P_(L)=(dU_(L)/(dt)=iepsilone^(-t/zeta)` We now SUBSTITUTE for i to OBTAIN `P_(L)=(zeta^(2))/(R)[e^(-t/zeta]` |
|
| 43137. |
Derive de-Broglie wave equation (wavelength) for a material particle. |
|
Answer» Solution :The momentum of photon of frequency v is given by `p = (h upsilon)/(c) = (h)/(lambda)` since `c = upsilon lambda` The wavelength of a photon in TERMS of its momentum is `lambda = (h)/(p)""...(1)` According to de Broglie, the above equation is completely a GENERAL one and this is applicable to material particles as well. Therefore, for a particle of mass m travelling with speed v, the wavelength is given by `lambda = (h)/(mv) = (h)/(p)""...(2)` This wavelength of the matter waves is known as de Broglie wavelength. This equation RELATES the wave character (the wave length `lambda`) and the particle character (the momentum p) through Planck.s CONSTANT. |
|
| 43138. |
Consider a hypothetical field in which force acting on a particle varies with its horizonal distance from wall AB is F=alphax and always towards wall. Ceofficient of restitution for collision between particle and wall is e=1/2. Find the maximumforce (in N) acting on the particle after 3^(rd) collision. (use alphax_(0)=16N) |
|
Answer» Kinetic ENERGY just after `3^(rd)` collision `=(1/2)^(6)K_(0)=1/64K_(0)` `1/64(1/2 alpha x_(0)^(2))impliesx=(x_(0))/8` `F=alphax=(alpha x_(0))/8=2N` |
|
| 43139. |
The reactor in which the number of fissionable nuclides produced are more than the used is called |
|
Answer» BREEDER reactor |
|
| 43140. |
Two moving coil meters M_1 and M_2 have the following particulars: R_1 = 10 Omega , N_1 = 30A_1= 3.6 xx 10^(-3) m^2 , B_1 = 0.25 TR_2 = 14Omega , N_2 = 42A_2 = 1.8 xx 10^(-3) m^2 , B_2 = 0.50 T(The spring constants are identical for the two meters). Determine the ratio of (a) current sensitivity and (b) voltage sensitivity of M_2 and M_1. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) 1.4, (B) 1 | |
| 43141. |
Aplane glass is placed over a various coloured letters (violet, green, yellow, red) The letter which appears to be raisedmore is, |
|
Answer» RED |
|
| 43142. |
A vessel containing air of mass 8g at 400 K is provided with a hole so that some amount of air leaks out. After some time, the pressure is halved and temperature is changed to 300 K. The mass of air escaped is: |
|
Answer» 4g `therefore (P)/(mT)` = constant. Now `(P)/(8xx400)=(P)/(2) xx (1)/(m.) xx (1)/(300)` or `m.=(3200)/(600) =(16)/(3)=5.3 g` MASS escaped `=8-5.3 =2.7 g` `therefore` CORRECT choice is (b). |
|
| 43143. |
A charge of 1 muC is divided into parts such that their charges are in the ratio of 2: 3. These two charges are kept at a distance 1 m apart in vacuum. Then, the electric force between them (in N) is |
|
Answer» 0.216 |
|
| 43144. |
For a particle executing simple harmonic motion, the kinetic energy K is given by, K=K_(0)cos^(2)omegat The maximum value of potential energy is : |
|
Answer» `K_(0)` `:. U=K_(0)xx1=K_(0)`. CORRECT CHOICE is (a). |
|
| 43145. |
An electron microscope uses electrons accelerated by a voltage of 50 kV. Determine the de-Broglie wavelength associated with the electrons. Taking other factors, such as numerical aperture etc. to be same, how does the resolving power of an electron microscope compare with that of an optical microscope which uses yellow light? |
|
Answer» Solution :`lambda=5.5xx10^(-12)m` `lambda" (yellow light)"=5.9xx10^(-7)m` RESOLVING Power (RP) is inversely proportional to WAVELENGTH. THUS, RP of an electron microscope is about `10^(5)` TIMES that of an optical microscope. In practice, differences in other (geometrical) factors can change this comparison somewhat. |
|
| 43146. |
In double-slit experiment using light of wavelength 600 nm, the angular width of a fringe formed on a distant screen is 0.1°. What is the spacing between the two slits? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`3.4xx10^(-4)m`. | |
| 43147. |
The magnetic permeability of free space is …………………… . |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`mu_0 = 4 PI XX 10^(-7) T mA^(-1)` | |
| 43148. |
Calculate de Broglie wavelength associated with an electron moving with a speed of 2 xx 10^(5) ms^(-1). Given h = 6.625 xx 10^(-34)JS, m_(e) = 9.11 xx 10^(-31)kg. |
|
Answer» Solution :Given `v= 2XX 10^5ms^(-1)` ,`h =6.625 xx 10^(-34)` Js, `m_c=9.11 xx 10^(-31)`kg w.k.t. `lambda=h/(MV) =(6.625xx10^(-34))/(9.11xx10^(-31)xx2xx10^5)` i.e., `lambda=3.636xx10^(-9) m =3.636` nm |
|
| 43149. |
In an inertial reference frame Kthere is only a unifromelectricfield E = 8 kV//min strength. Find themodulus and direction (a) of the vector E' (b) of the vectorB'in the interialrefrernceframe K'movingwith aconstantvelocityvrelative to the frameK at an angle alpha = 45^(@)to the vectorE. The velocityof the frameK' is equlatoabeta = 0.60fractionof the velocityof light. |
|
Answer» Solution :Choose `VEC(E)` in thedirection of the z-axis, `vec(E) = (0,0,E)`. The frame `K'` is movingwith velocity `vec(v) = (v sin ALPHA, 0, v cosalpha)`, in the`x-z` plane . Thenin the frame`K'` `vec(E')_(|\|) = vec(E)_(|\|) vec(B')_(|\|) = 0` `vec(E')_(_|_) = (vec(E)_(_|_))/(sqrt(1 - v^(2)//c^(2))) vec(B)'_(_|_) = (-vec(v) xx vec(E)//c^(2))/(sqrt(1 - v^(2)//c^(2)))` The vectoralong `vec(v)` is `vec(e) = (sin alpha, 0, cos alpha)` ANDTHE perpendicular vectorin the `x-z` planeis, `vec(f) = (-cos alpha, 0, sin alpha)`, (a) Thususing `vec(E) = E cos alpha vec(e) + E sin alpha vec(f)`. `E'_(|\|) = E cos alpha` and `E'_(|\|) = (E sin alpha)/(sqrt(1 - v^(2)//c^(2))` So `E' = E sqrt((1 - BETA^(2) cos^(2) alpha)/(1 - beta^(2)))` and`tan alpha' = (tan alpha)/(sqrt(1 - v^(2)//c^(2)))` (b) `B'_(|\|) = 0, vec(B')_(_|_) = (vec(v) xx vec(E)//c^(2))/(sqrt(1 -v^(2)//c^(2)))` `B' = (beta E sin alpha)/(c sqrt(1 - beta^(2)))` |
|
| 43150. |
If one of the slits in the interference experiment is closed, what will be your observation? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :DIFFRACTION of LIGHT. | |