Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 43001. |
A defect of vision in which lines in one plan of an object appear in focus while those i another plane are out of focus is called ...... |
|
Answer» ASTIGMATISM |
|
| 43002. |
Three large plates are arranged as shown. The charge will flow through the key K if it is closed if (nQ)/(6) find the value of n. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43003. |
A capacitance C, a resistance R and an emf (epsilon)are connected in series at t=0.What is the maximum value of (a) the potential difference across the resistor, (b) the current in the circuit,(c )the potential difference across the capacitor, (d) the energy stored in the capacitor ,(e)the power delivered by the battery and (f) the power converted int heat. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Potential diff. = `epsilon across resister` (B) Current in CIRCUIT = `epsilon /R` ` (C) Potential diff. across capacitor = epsilon / r ` `(d) Energy STORED in capacitor = 1/2 Cepsilon ^2 ` ` (e) power delivered by battery = epsilon^2 / r ` ` (f) Power converted to heat = epsilon^2/r` . |
|
| 43004. |
1/(sqrt25-sqrt24) निम्न में से किस के बराबर है : |
|
Answer» `(5+2sqrt6)` |
|
| 43005. |
A force of 500kg.wt can break a wire . What is the force necessary to break another wire of same material and same length but of half the cross sectional area. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`F_1//A_1 = F_2//A_2` but `A_2 = A_1//2` `THEREFORE F_1//A_1 = (2F_2)/A_1 therefore F_2 = F_1/2 = 250KG WT` |
|
| 43006. |
(a) Using the Bohr’s model calculate the speed of the electron in a hydrogen atom in the n = 1, 2, and 3 levels. (b) Calculate the orbital period in each of these levels. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(a) `2.18 XX 10^(6) m//s , 1.09 xx 10^(6) m//s , 7.27 xx 10^(5) m//s` (B) `1.52 xx 10^(-16) s, 1.22 xx 10^(-15) s , 4.11 xx 10^(-15) s`. |
|
| 43007. |
If q_(1)+q_(2)=q, then the value of the ratio q_(1)/q, for which force between q_1 and q_2 is maximum is |
|
Answer» 0.25 |
|
| 43008. |
Which of the following radiations alpha,beta and gamma are : similar to the nature of cathode rays ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`BETA`-PARTICLE. | |
| 43009. |
A microscope is used to resolve two self luminous objects separated by a distance of 5 xx 10^(-5)cm and placed in air. What should be the minimum magnifying power of the microscope in order to see the resolved images of the objects? The resolving power of the eye is 1.5 and teh least distance of distinct vision is 25 cm. |
| Answer» ANSWER :C | |
| 43010. |
In the circuit shown in the figure, the input voltage V_i = +5 V, V_(BE) = + 0.8 V and V_(CE) = +0.12 V. Find the values of I_B I_C and beta. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`I_B=V_i/R_B=(5V)/(80kOmega)` `=5/(80xx10^3)=5/8xx10^(-4)=0.625xx10^(-4)=62.5xx10^(-6)` `I_B=62.5muA` `I_C=V_"CC"/R_C =(12V)/(5kOmega)` `=12/(5xx10^3)=2.4xx10^(-3)` `I_C`=2.4 mA `beta=I_C/I_B=(2.4xx10^(-3))/(62.5xx10^(-6))=0.0384xx10^3 , beta=38` 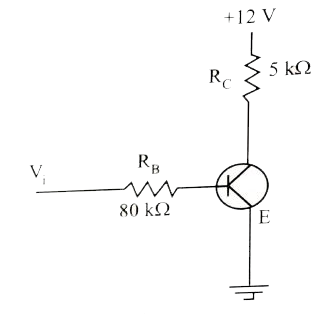
|
|
| 43011. |
Consider a uniform electric field E=3xx10^(3) N//C. (a) What is the flux of this field through a square of 10 cm on a side whose plane is parallel to the yz plane? (b) What is the flux through the same square if the normal to its plane makes a 60^(@) angle with the x-axis? |
| Answer» Solution :Charges 1 AMD 2 are negative charge 3 is positiveparticle 3 has the HIGHEST charge to MASS RATIO | |
| 43012. |
A metal rod of length L is clamped at a distance L/4 from one end. It is set into longitudinal vibrations by pulling on length - wise a resin cover cloth piece . The wavlength for fundamental mode of vibrations will be |
|
Answer» L/4 |
|
| 43013. |
The temperature at which the speed of sound in air becomes double of its value at 0^@Cis |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 43014. |
Eight point charges of magnitude Q are arranged to form the corners of a cube of side L. The arrangement is made in manner such that the nearest neighbour of any charge has the opposite sign. Initially, the charges are held at rest. If the system is let free to move, what happens to the arrangement? Does the cube-shape shrink or expand? Calculate the velocity ct each charge when the side-length of the cube formation changes from L to nL. Assume that the mass of each point charge is m. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :There are total 28 pairs of charges 12 pairs `to Q` and `-Qto` distance L 12 pairs `to` (Q and Q)or (`-Q` and `-Q`)`to sqrt2L` 4pairs`toQ` and -`Qto` `sqrt3L` `:. U=12(1/(4piepsilon_0))((-Q^2)/L)+12(1/(4piepsilon_0).Q^2/sqrt((2L)))=4(1/(4piepsilon_0)((-Q^2)/sqrt(3L))` `=- Q^2/(piepsilon_0L)((3sqrt6+sqrt2-3sqrt3)/sqrt6)` 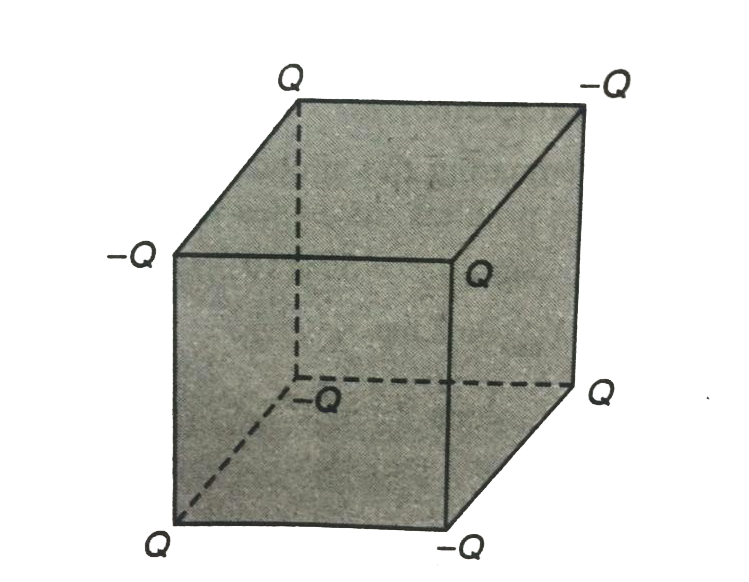 ltbr With decrease in L, potential energy wil decrease. ltbr With decrease in L, potential energy wil decrease. therefore, CUBE should shrink a the CONSERVATIVE forces act in the direction of decresing potential energy. Increase in KE of the system = decrease in PE ltbr. or `8(1/2mv^2)=U_i-U_f` `=Q^2/(piepsilon_0)((3sqrt6+sqrt2-3sqrt3)/sqrt6)(1/(nL)-1/L)` or `v=sqrt((Q^2(1-n)(3sqrt6+sqrt2-3sqrt3)/(4nmpiLepsilon_0sqrt6))` |
|
| 43015. |
An electron is located in a unidimensional square potential well with infinitely high walls. The width of the well is l. From the uncertainty principle estimate the force with which the electron possessing the minimum permitted energy acts on the walls of the well. |
|
Answer» Solution :BY uncertainty principle, the uncertainty in momentum `DeltaP UNDERSET(~)gt(ħ)/(L)` For the ground state, we expect `Delat P~P` so `E~(ħ^(2))/(2 m l^(2))` The force exceted on the wall can be OBTAINED most simply from `F= -(delU)/(dell)=(ħ^(2))/(m l^(3))` |
|
| 43016. |
In Example 10.3, what should the width of each slit be to obtain 10 maxima of the double slit pattern within the central maximum of the single slit pattern? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :We want `a theta=lambda, theta=(lambda)/(a)` `10(lambda)/(d)=2(lambda)/(a)a=(d)/(5)=02mm` Notice that the WAVELENGTH of light and distance of the screen do not ENTER in the calculation of a. |
|
| 43017. |
A letter 'A' is constructed of a uniform wire with resistance 1.0Omega per cm. The sides of the letters are 20 cm and the cross piece in the middle is 10cm long. The apex angle is 60^(@). The resistance between the ends of the legs is close to : |
|
Answer» `50.0Omega` |
|
| 43018. |
An electron moves with speed 2 xx 10^(5) ms^(- 1) along the positive x-direction in the presence of a magnetic induction barB = hati + 4hatj - 3hatk tesla. The magnitude of the force experienced by the electron in newton is (charge on the electron = 1.6 x 10^(-19)C) |
|
Answer» `1.18xx10^(-13)` |
|
| 43019. |
A gun fires a small bullet with kinetic energy K. Then kinetic energy of the gun while recoiling is |
|
Answer» K `i.e. MV = - mv` Now K.E. of bullet `E = ((-mupsilon)^(2))/(2m)` and K.E. of Gun `E.=((Mupsilon)^(2))/(2M)=((mupsilon)^(2))/(2M)` `:.` Since `Mgtm` .Kinetic energy of Gun is less than K.E. of bullet. |
|
| 43020. |
Ratio of intensities of two waves is 9:1. If these two are superimposed, what is the ratio of maximum and minimum intensities? |
|
Answer» `10:8` `I_(max)=(sqrt(I_(1))-sqrt(I_(2)))^(2)=[sqrt((I_(1))/(I_(2)))-1]^(2)` `:.(I_(max))/(I_(MIN))=([sqrt((9)/(1))+1])/([sqrt((9)/(1))-1]^(2))=([3+1]^(2))/([3-1]^(2))` `=(16)/(4)=(4)/(1)` |
|
| 43021. |
A 0.5 m long metal rod PQ completes the circuit as shown in the Fig. 6.47. The area of the circuit is perpendicular to the magnetic field of flux density 0.15 T. If the resistance of the total circuit is 3Omega, calculate the force needed to move the rod in the direction as indicated with a constant speed of 2 m s^(-1). |
|
Answer» Solution :When a conductor of length l moves with a speed v in a uniform magnetic field B such that all the three terms are mutually perpendicular to each other, then induced emf `|varepsilon| = B l v` and induced current for a closed circuit `I = varepsilon/R = (B l v )/R`, where R = RESISTANCE of the circuit. Now the force needed to move the ROD in the direction indicated in FIG. 6.47 against the induced BACK current is `F = B I l = (B^(2)l^(2)v)))/R` In present problem, `I = 0.5 m, B = 0.15 T, v = 2ms^(-1) and R = 3Omega`, hence `F = ((0.15)^(2) xx (0.5)^(2) xx 2)/3 = 3.75 xx 10^(-3)N.` |
|
| 43022. |
(a) A particle is moving three times as fast as an electron. The ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength of the particle to that of the electron is 1.813xx10^(-4). Calculate the particle's mass and identify the particle. (b) An electron and proton have the same kinetic energy. which of the two will have larger de Broglie wavelength ? Give reason. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) As per question `v_("particle")=3v_("electron") and lamda_("particle")=1.813xx10^(-4)lamda_("electron")`. From the relation `lamda=(h)/(mv)`, we have `(m_("particle"))/(m_("electron"))=(lamda_("electron")xxv_("electron"))/(lamda_("particle")xxv_("particle"))=(lamda_("electron")xxv_("electron"))/((1.813xx10^(-4)lamda_("electron"))xx(3v_("electron")))=1839` `implies m_("particle")=1839m_("electron")=1839xx9.1xx10^(-31)kg=1.673xx10^(-27)kg` It SHOWS that the given particle is either a PROTON or a neutron. (b) From the relation `lamda=(h)/(SQRT(2mK))`, it is clear that for same kinetic energy, de-Broglie wavelength of electron is more because its mass is less than that of proton. |
|
| 43023. |
Find the minimum energy of electron-hole pair formation in an impurity-free semiconductor whose electric conductor increase eta=5.0 times when the temperature increases from T_(1)= 300K t o T_(2)= 400K |
|
Answer» Solution :In a pure(intrinsic) SEMICONDUCTOR the conductivity is related to the temperature by the FOLLOWING formula very closely: `sigma= sigma_(0)e^(-Delta epsilon//2kt)` where `Delta epsilon` is the ENERGY gap between the top of valence BAND and the bottom of conduction band, it is also the minimum enrgy required for the FORMATION of electron-hole pair. The conductivity increases with temperature and we have `eta=2^(+(DeltaE)/(2k)((1)/(T_(1))-(1)/(T_(2)))` or In `eta=(Deltaepsilon)/(2k)(T_(2)-T_(1))/(T_(1)-T_(2))` Hence `Delta epsilon=(2kT_(1)T_(2))/(T_(2)-T_(1)) In eta` Substitution gives delta epsilon= 0.333eV`=E_(mi n)` |
|
| 43024. |
A galvanometer has resistance 500 ohm. It is shunted so that its sensitivity decreases by 100 times. Find the shunt resistance. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :SENSITIVITY`PROP1/("RANGE")thereforen=100` `S=G/((n-1))=500/((100-1))=500/99OmegarArrS=5.05Omega` |
|
| 43025. |
A light wire of length l (figure-1) is cut into two pieces in two different ways as shown in (figure -2&3). Different pieces can be arranged in placed of wire as shown and a load can be placed on the massless hanger. Choose the correct statement(s). |
|
Answer» The load required to break the wire `B'` is 6 TIMES that required to break `B` Load `=` stress `xx` cross `-` SECTIONAL area |
|
| 43026. |
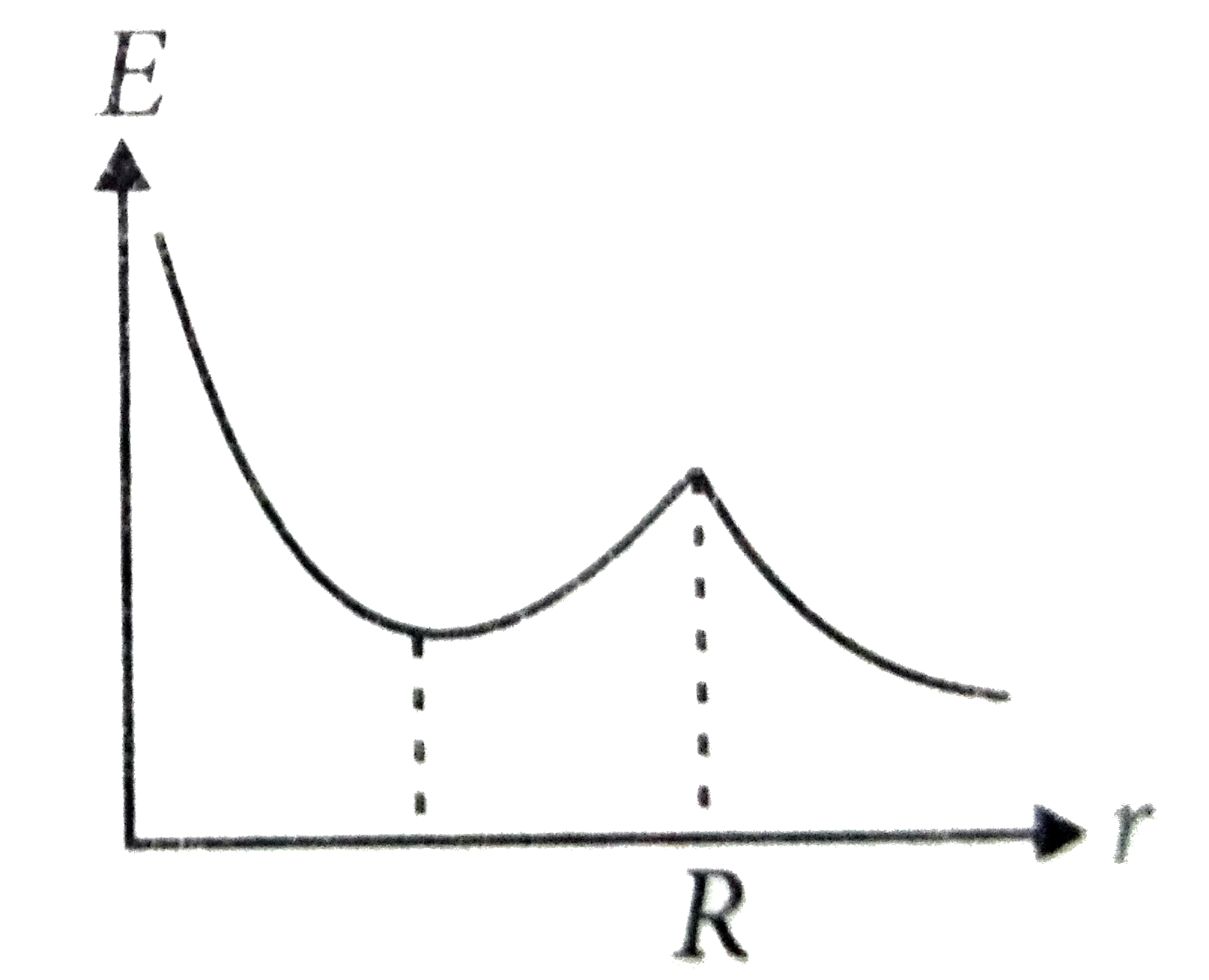
A spherical insulator of radius R is charged uniformly with a charge Q throughout its volume and contains a point charge Q/16 located at its centre. Which of the following graphs best represents qualitatively, the variation of electric field intensity E with distance r from the centre? |
|
Answer»
`(dE)/(dx)=0implies(Q)/(4piepsi_(0))=((1)/(R^(3))-(2)/(16X^(3)))=0` `(d^(2)E)/(dx^(2))=(6Q)/(4piepsi_(0)(16x^(4)))gt0` `thereforeAt x=(R)/(2),E` is minimum. For `(x gt R), E=((Q+Q//16))/(4piepsi_(0)x^(2))` |
|
| 43027. |
The electric supply line in house works on 220 V . The amplitude of e.m.f. will be : |
|
Answer» 110 V |
|
| 43028. |
Plot a graph showing variation of de-broglie wavelength lambda versus 1//sqrtV, where V is accelerating potential for two particle A and P carrying same charge but of masses m_1 and m_2(m_1gtm_2). Which one of the two represents a particle of smaller mass and why? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The quality factor (Q) of series LCR circuit is DEFINED as the ratio of the resonant to frequency band width of the resonant curve. `Q = omega_r/(omega_2-omega_1)=(omega_rL)/R` Clearly, SMALLER the value of R, LARGER is the quality factor and sharper the resonance. Thus quality factor determines the nature of sharpness of resonance. In has no units. |
|
| 43029. |
What is an I-beam? |
| Answer» Solution :An I-beam is a beam with an I-shaped CROSS section and usually MADE of STEEL. It is used as a horizontal structural ELEMENT to withstand FORCES transverse to its axis. | |
| 43030. |
Let us take an electrical conductor in which the electrical energy supplied is entirely converted into heat . If , for the conductor , the terminal potential difference= V, the curent through it = I and its resistance = R , then the electrical energy cnsumed in its t is ,W=I^(2)t(from Ohm'slaw R=(V)/(I)) . So , if thr electrical and the heat energies both are expressed in joule , the heat developed in tiem t isH=I^(2)Rt . However , If H is expressed in the conventional unit calorie , then from the law , W = JH , we may write H=(I^(2)Rt)/(J) , where , J = mechanical equivalent of heat=4.2J."cal"^(-1) . The resistance R of a conducting wire depends on its material , its lengthl and its area of cross section a .The resistivity of the meterial of the conductor is , rho=(RA)/(l) . When more than one heat -producing conductors are kept in series in a circuit , the same current passes through each of them , but as their resistance are f=different in general , the terminal potential differences are also unequal . On the other hand , each conductor has the same terminal potential difference in a parallel combination , however , the curents through them are different .The first one of two wires ,m of the same meterial and of equal cross section , is longer than the second . A current through their series combination produces heat in them at the rates h_(1)andh_(2),respectively . |
|
Answer» `h_(1)=h_(2)` |
|
| 43031. |
The moment of inertia of a uniform circular disc of mass M and radius R about any of its diameter is (1)/(4)MR^(2). What is the moment of inertia of the disc about an axis passing through its centre and normal to the disc? |
|
Answer» `MR^(2)` `I_(Z Z.)=I_(AB)+I_(CD)=(1)/(4)MR^(2)+(1)/(4)MR^(2)`  `I_(Z Z.)=(1)/(2)MR^(2)` |
|
| 43032. |
Let us take an electrical conductor in which the electrical energy supplied is entirely converted into heat . If , for the conductor , the terminal potential difference= V, the curent through it = I and its resistance = R , then the electrical energy cnsumed in its t is ,W=I^(2)t(from Ohm'slaw R=(V)/(I)) . So , if thr electrical and the heat energies both are expressed in joule , the heat developed in tiem t isH=I^(2)Rt . However , If H is expressed in the conventional unit calorie , then from the law , W = JH , we may write H=(I^(2)Rt)/(J) , where , J = mechanical equivalent of heat=4.2J."cal"^(-1) . The resistance R of a conducting wire depends on its material , its lengthl and its area of cross section a .The resistivity of the meterial of the conductor is , rho=(RA)/(l) . When more than one heat -producing conductors are kept in series in a circuit , the same current passes through each of them , but as their resistance are f=different in general , the terminal potential differences are also unequal . On the other hand , each conductor has the same terminal potential difference in a parallel combination , however , the curents through them are different .Heat is produced at hte rate of8"cal".s^(-1) in a uniform wire , when its terminal potential difference is 10 V What would be the rate in another wire of the same material , of the same potential difference ? |
|
Answer» `32"cal".s^(-1)` |
|
| 43033. |
Let us take an electrical conductor in which the electrical energy supplied is entirely converted into heat . If , for the conductor , the terminal potential difference= V, the curent through it = I and its resistance = R , then the electrical energy cnsumed in its t is ,W=I^(2)t(from Ohm'slaw R=(V)/(I)) . So , if thr electrical and the heat energies both are expressed in joule , the heat developed in tiem t isH=I^(2)Rt . However , If H is expressed in the conventional unit calorie , then from the law , W = JH , we may write H=(I^(2)Rt)/(J) , where , J = mechanical equivalent of heat=4.2J."cal"^(-1) . The resistance R of a conducting wire depends on its material , its lengthl and its area of cross section a .The resistivity of the meterial of the conductor is , rho=(RA)/(l) . When more than one heat -producing conductors are kept in series in a circuit , the same current passes through each of them , but as their resistance are f=different in general , the terminal potential differences are also unequal . On the other hand , each conductor has the same terminal potential difference in a parallel combination , however , the curents through them are different . The terminal potential difference and the currents through two conducting wires are both in the ratio2 : 1 The ratio of the rates of heat evolved in them is |
|
Answer» `1:1` |
|
| 43034. |
If the velocity of light c, gravitational constant G and Planck's constant h be taken as fundamental units the dimension of mass in the new system will be- |
|
Answer» `C^(1//2)G^(1//2)H^(1//2)` |
|
| 43035. |
The electrical resistance of depletion layer is large because |
|
Answer» It CONTAINS ELECTRONS as CHARGE CARRIERS |
|
| 43036. |
In a circuit containing internal resistane r. Find the power delivered. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) DUE to this internal RESISTANCE, the power delivered to the circuit is not equal to power RATING mentioned in the battery. (ii) For a battery of emf `xi` with an internal resistance r, the power delivered to the circuit of resistance R is given by `P= I xi=I(V+Ir)` Here Vis the voltage drop acrossthe resistane Randit is equal to IR. Therefore `P=I(IR+r)` `P=I^(2)R+I^(2)r` (iiii) Here `I^(2)` r is the power delivered to the internal resistane and `I^(2)` R is the power delivered to the electrical device (here it is the resistance R). For a good battery, theinternal resistance r is very SMALL, then `I^(2) r lt lt I^(2)` and almost ENTIRE power is delivered to the resistance. |
|
| 43037. |
Find the velocity of the moving rod at time t if the initial velocity of the rod is v and a constant force F is applied on the rod. Neglect the resistance of the rod. |
|
Answer» Solution :At any time , let the velocity of the ROD be v . Applying NEWTONS law: F-iIB=ma…..(1) Also `Biv=i_(1)R=(q)/( c)` Applying Kcl, `i=i_(1)+(dq)/(dt)=(BlV)/( R)+(D)/(Dt)(BIvC) or i=(B l V)/( R)+B l C a ` Putting the VALUE of `i` in eq. (1), `F-(B^(2)l^(2)V)/( R)=(m+B^(2)l^(2)C)a=(m+B^(2)l^(2)C)(dv)/(dt)` `(m+B^(2)l^(2)C)(v)/(F-(B^(2)I^(2)v)/( R))=dt` Integrating both sides, and solving we GET `v=(FR)/(B^(2)l^(2))(1-e^((tB^(2)l^(2))/(R(m+CB^(2)l^(2)))))` |
|
| 43038. |
A baby radiates heat at the rate of 50 J/s when at 300^@K. When the same body is at 600^@K then its rate of radiation of heat will be |
|
Answer» 100 `J/s` |
|
| 43039. |
Find the minimum magnitude of the magnetic field induction B at which a spectral instrument with resolving power lambda//delta lambda==1.0.10^(5) is capable of resolving the components of the spectral line lambda= 536 nm caused by a transition between singlet terms. The observation line is at right angles to the magnetic field direction. |
|
Answer» Solution :From the previous problem, if the components are `lambda,lambda+-Delta lambda`, then `(lambda)/(Delta lambda)=(2pi ħc)/(mu_(B)B lambda)` For resolution `(lambda)/(Delta lambda)LER=(lambda)/(delta lambda)` of the instrument. Thus `(2 pi ħc)/(mu_(B)B lambda)leR or BGE(2pi ħc)/(mu_(B)LAMBDAR)` Hence the MINIMUM MEGNETIC induction is `B_(m in)=(2pi ħc)/(mu_(B)lambdaR)= 4kG= 0.4T` |
|
| 43040. |
A astronomical telescope has objective and eyepiece of focal length 40 cm and 4 cm respectively. To view an object 200 cm away from the objective, the lenses must be separated by a distance |
|
Answer» 50.0 cm `(1)/(f_0)=(1)/(v_0)-(1)/(u_0)` `THEREFORE (1)/(v_0)=(1)/(f_0)+(1)/(u_0)` `=(1)/(40)+(1)/(-200)` `=(5-1)/(200)=(4)/(200)=(1)/(50)` `therefore v_0=50` cm Here,TUBE length L=`v_0+f_e` =50+4=54 cm |
|
| 43041. |
(A): Transistor in C.E. mode can be used as amplifier (R): A small change in base current producesa relatively large change in collector current |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are true and 'R' is the correct explanation of 'A' |
|
| 43042. |
What happens when a non polar molecule is placed in an external electric field? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43043. |
A short linear object of length 'b' lies along the axis of a concave mirror of focal length 'f' at a distance 'u' from the pole of the mirror. The size of the image is approximately equal to |
|
Answer» `B( (u-F)/(f))^(1//2)` |
|
| 43044. |
The wavelength of matter wave is independent of |
|
Answer» MASS |
|
| 43045. |
A coil of inductance 0.50 H and resistance 100Omega is connected to a 240 V, 50 Hz ac supply. (a) What is the maximum current in the coil? (b) What is the time lag between the voltage maximum and the current maximum? |
|
Answer» Solution :For an LR circuit, if `V=V_(0)sin OMEGA t` `I=(V_(0))/(sqrt(R^(2)+omega^(2)L^(2))) sin (omega t -phi)`, where `tan phi=(omega L//R)`. (a) `I_(0)=1.82A` (b) V is MAXIMUM at t = 0, I is maximum at `t=(phi//omega)`. Now, `tan phi=(2PI VL)/(R ) = 1.571 or phi ~~57.5^(@)` Therefore, TIME lag `=(57.5pi)/(180)xx(1)/(2pi xx 50)=3.2 ms` |
|
| 43046. |
Two charged particles of charges +0.1 muC and -0.1 muC are kept on the vertices of an equilateral triangle of side 10 cm. Calculate the electric field intensity at the centroid of the triangle. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`4.7xx10^5 NC^(-1)` | |
| 43047. |
The cinema combine the cold logic of ………. . |
|
Answer» SCIENCE |
|
| 43048. |
A 3310 Å photon liberates an electron from a material with energy 3 xx 10^(-19) J while another 5000 Å photon ejects an electron with energy 0.972 xx 10^(-19) J from the same material. Determine the value of Planck's constant and the threshold wavelength of the material. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :To find `:` Planck's constant `H = upsilon_(0)` `h upsilon_(1) = phi + K.E_(1) , h upsilon_(1) rarr` Energy of photon 1 `h rarr` Plank's constant `phi rarr `Work funcltion `K.E_(1) rarr `Kinetic energy of an electron 1 `upsilon_(1) rarr` Frequency of photon 1 For photon 2, `h upsilon_(2) = phi + K.E_(2)` Given `:` `lambda_(1) = 3310Å = 3310 xx 10^(-10)m ` and `lambda_(2) = 5000 xx 10^(-10) m ` `h upsilon_(1) = ( h^(@) C )/( lambda_(1)) , K.E_(1) = 3xx 10^(-19) J, K.E_(2) = 0.972 xx 10^(-19) J ` `( hc)/( 3310 xx 10^(-10)) = phi + 3 xx 10^(-10)`...(1) `( hC )/( 5000 xx 10^(-10)) = phi + 0.972 xx 10^(-19) `...(2) `hc = 3310 xx 10^(-10) phi + 9930 xx 10^(-29) `.....(3) (2) can be rewritten as `hc = 5000 xx 10^(-10) phi+ 0972 xx 5000 xx 10^(-29)`....(4) From ( 3) `hc = 3310 xx 10^(-10) phi + 9930 xx 10^(-29)` `- 3310 xx 10^(10) [hc] = +- 16,086,600 xx 10^(-39)` `5000 xx 10^(-10) [hc = +49,650,000xx10^(-39)` `1690 xx 10^(10) hc = 33,563,4000 xx 10^(-39)` `rArr h=(33,563,400 xx 10^(-39))/(1690 xx 3 xx 10^(8)) = 6,620 xx 10^(-31)` `h = 6.62 xx 10^(-34)` Solving equation (3) and ( 4) `( 5000 - 3310 ) xx 10^(-10) phi = 5070 xx 10^(-29) = 0` `phi = ( 5070 xx 10^(-29))/( 1690 xx 10^(-10)) , phi = 3 xx 10^(-19)` `( hc)/(lambda_(0)) = 3 xx 10^(-19)` `lambda_(0) = ( 6.62 xx 10^(-34) xx 3 xx 10^(8))/( 3 xx 10^(-19)) = 6620 xx 10^(-10)` `= 6620 =6.62 xx 10^(-7) Js= 6620 xx 10^(-10) m ` |
|
| 43049. |
Light of wavelength 6000A is coming from a star. What is the limit of resolution of a telescope whose objective has a diameter of 100 inch? |
|
Answer» `2.9 TIMES 10^-7 RADIAN` |
|
| 43050. |
v=u+at |
Answer» SOLUTION :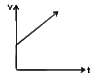
|
|