Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 42501. |
Repeaters used in tlephone links are: |
|
Answer» Rectifiers |
|
| 42502. |
What is corona discharge? |
|
Answer» Solution :The ELECTRIC field near the edge is very high and it IONIZES the SURROUNDING air. The positive ions are REPELLED at the sharp edge and negative ions are attracted towards the SHARPER edge. This reduces the total charge of the conductor near the sharp edge. This is called action at points or corona discharge |
|
| 42503. |
Consider the D - T reaction (deuterium - tritium fusion) ._(1)^(2)H+ ._(1)^(3)H to ._(2)^(4)He + n Consider the radius of both deuterium and tritium to be approximately 2.0 fm. What is the kinetic energy needed to overcone the Coluomn repulsion between the two nuclei ? To what temperature must the gas heated to initiate the reaction ? |
|
Answer» Solution :HINT : KINETIC energy required for one fusion event = average thermal kinetic energy available with the interacting particles = 2(3kt/2) , k = Boltzman's CONSTANT, T = absolute temperature. Repulsive potential energy of two nuclei when they almost touch each other is `= (q^(2))/(4pi epsilon_(0)(2r))=(9xx10^(9)(1.6xx10^(-19))^(7))/(2xx2xx10^(-15))` Joule `= 5.76xx10^(-14)` Joule Classically KE atleast equal to this amount is required to overcome Coulomb repulsion. Using the relation `K.E. = 2xx(3)/(2)KT` `T=(K.E)/(3k)=(5.76xx10^(_14))/(3xx1.38xx10^(-23))=1.39xx10^(9)K` In actual PRACTISE the temperature required for trigerring the reaction is somewhat less. |
|
| 42504. |
A body of density D is droped gently on the surface layer of liquid of density 'd' and depth 'h'. If D > d, the downward acceleration of the body while sinking is : |
|
Answer» g `=mg-M/Dxxdxxg` `therefore`acc.a=`(mg[1-d/D])/m=g[1-d/D]` CORRECT CHOICE is (b). |
|
| 42505. |
If a convex lens of focal length 20 cm is held close to the eye of observer and the near point of the observer is 25 cm from the eye, find the distance of the object from the lens. |
|
Answer» Solution :`f=+20cm` `v=-25cm` `(1)/(f)=(1)/(v)-(1)/(U)` `(1)/(u)=(1)/(v)-(1)/(f)` `=-(1)/(25)-(1)/(20)` `u=(-100)/(9)CM` |
|
| 42506. |
(A) : In case of M.C.G the torque on the coil is maximum in any position of the coil (R) : In case of M.C.G the concave shaped magnetic poles render the field to be radial between them so that the plane of the coil is always parallel to the lines of induction even after deflection |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are true and 'R' is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of 'A'. |
|
| 42507. |
Capacitor is an arrangement to increase the charge carrying capacity of a conductor.Each plate of parallel plate capacitor has a charge q on it.The capacitor is now connected to a battery .pick out the correct statement. |
|
Answer» The facing surface of plates have equal and OPPOSITE charge |
|
| 42508. |
A conducting bar of mass m length lis pushed with a speed V_(0) on a smooth horizontal conducting rail containing an inductance L. If the applied magnetic field has inward field induction B find the maximum distance covered by the bar before it stops. Assume that the induced current i=0 when the bar is at the position of the inductor . (##FIITJEE_PHY_MB_05_C02_SLV_018_Q01.png" width="80%"> |
|
Answer» Solution :If the bar slides a distance dx the flux LINKAGE `dphi = 8l ` dx `implies `The induced emf = - `(dphi)/(DT ) =- (Bldx )/(dt)` Since the induced emf across the inductor = `(Ldi)/(dt)` `implies -(Bldx)/(dt)= -(Ldi)/(dt)` `implies L int_(0) di = B l int_(0)^(x) dx ` `implies Li =B l x implies i = (Bl)/(L)x` This induced current interacts with the applied magnetic field of induction and imparting a restoring ( magnetic ) force F = `-ILB`. `implies F =- ((Bl)/(L) x)l`B `implies (mvdv)/(dx) =-(B^(2)l^(2))/(L) x` `implies int_(V0)^(0) vdv = -(B^(2)l^(2))/(mL) int_(0)^(s) xdx , -(v_(0)^(2))/(2) = (B^(2)l^(2)s^(2))/(2mL)` `implies S = sqrt((my_(0)^(2)L)/(B^(2)l^(2)))=(sqrt(mL)).(v_(0))/(Bl)` 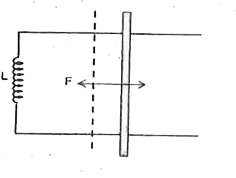
|
|
| 42509. |
The surface charge density of a thin charged disc of radius R is sigma. The value of the electric field at the centre of the disc (sigma)/(2 in_(0)). With respect to the field at the centre, the electric field along the axis at a distance R from the centre of the disc is |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The electric FIELD strength on the axis at a distance ..x.. from its centre of uniform charged circular disc is `E= (sigma)/(2 epsi_(0)) (1- (x)/((x^(2) + R^(2))^(1//2)))`. At centre, `E_(0) = (sigma)/(2 epsi_(0))` At distance `x= R, E = (sigma)/(2 epsi_(0)) (1-(x)/((x^(2) + R^(2))^(1//2)))= (sigma)/(2 epsi_(0)) (1- (R )/((R^(2) + R^(2))^(1//2)))` `=(sigma)/(2 epsi_(0)) (1- (1)/(sqrt2)) = (sigma)/(2 epsi_(0)) (0.37) = 0.37 E_(0)` |
|
| 42510. |
What is meant by equipotential surface? Show that the amount of work done in moving a test positive charge along the equipotential surface is zero. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :An EQUIPOTENTIAL surface is that at every point of which the electric POTENTIAL is same i.e., there is no difference of potential between any two points on it. Since potential difference `dV=(dW)/(q)` In an equipotential surface, `dV=0` `THEREFORE (dW)/(q)=0` or `dW=0` i.e. no work is done in moving a test charge ALONG the equipotential surface. |
|
| 42511. |
Two identical coils having radius R and number of turns N are placed co-axially with their centres separated by a distance equal to their radius R. The two coils are given same current I in same direction. The configuration is often known as a pair of Helmholtz coil. (i)Calculate the magnetic field (B) at a point (P) on the axis between the coils at a distance x from the centres of one of the coils. (ii)Prove that(dB)/(dx) = 0 and(d^(2)B)/(dx^(2)= 0[ In fact(d^(3)B)/( dx^(3))is also equal to zero ]at the point lying midway between the two coils. What conclusion can you draw from these results? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 42512. |
If a hyperbola centred at origin, has one of its directrix as x=2.Also ordinate of one of the end point of a latus rectum is 12. Then find its eccentricity. |
|
Answer» `3/2` `rArr 12=2e. (e^2-1)` `e^3-e-6=0` `rArr (e-2)xx(e^2+2e+3)=0` `rArr` e=2 |
|
| 42513. |
Plane wave front is not producedby a |
|
Answer» only point SOURCE of LIGHT at finite distance |
|
| 42514. |
A current of 2A is passed through a coil of 1000 turns, to produce a flux of 0.5wb. Calculate the self inductance of the coil. |
|
Answer» 100H |
|
| 42515. |
(A) : Choke coil is preferred over a resistor to adjust current in an A.C. circuit. (R) : Power factor for pure inductance is zero. |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are TRUE and 'R' is the correct explanation of 'A'. |
|
| 42516. |
If radius of a hollow metallic sphere is 'R'. If the P.D between it's surface and a point at a distance 3R from it's centre is V then the electric field intensity at a distance 3R from it's centre is |
|
Answer» `(V )/(2R ) ` |
|
| 42517. |
The law of conservation of mass is not obeyedby a |
|
Answer» CONSERVATION of mass |
|
| 42518. |
(a) For the telescope described in Exercise 9.28 (a), what is the separation between the objective lens and the eyepiece? (b) If this telescope is used to view a 100 m tall tower 3 km away, what is the height of the image of the tower formed by the objective lens? (c) What is the height of the final image of the tower if it is formed at 25cm? |
| Answer» Solution :28 cm | |
| 42519. |
In the above question, the tolerance when resistors are connected in parallels : |
|
Answer» Solution :In parallel, `R_(p)=(R_(1)R_(2))/(R_(1)R_(2))` `:.(DeltaR_(p))/(R_(p))xx100=(DeltaR_(1))/(R_(1))xx100+(DeltaR_(2))/(R_(2))xx100` `+(Delta(R_(1)+R_(2)))/(R_(1)+R_(2))xx100` `=10%+10%+10%=30%.` THUS correct CHOICE is `(b)`. |
|
| 42520. |
(i) Derive the expression for the specificfor the electricpotentialdue to an electricdipole at a point on its axial line. (ii) Depietthe equivpotentialsurfacesdue to an electricdipole. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Expression : Potentialat P due to CHARGE `+Q` and -q. `V_(-q) = (-q)/(4piin_(0)r_(1))` and`V_(+q) = q/(4piin_(0) r_(2))` Potentialat P due to DIPOLE `V = V_(-q) + V_(+q) = (q)/(4piin_(0)) [1/(r_(2))- 1/(r_(1))] "…….." (i)` 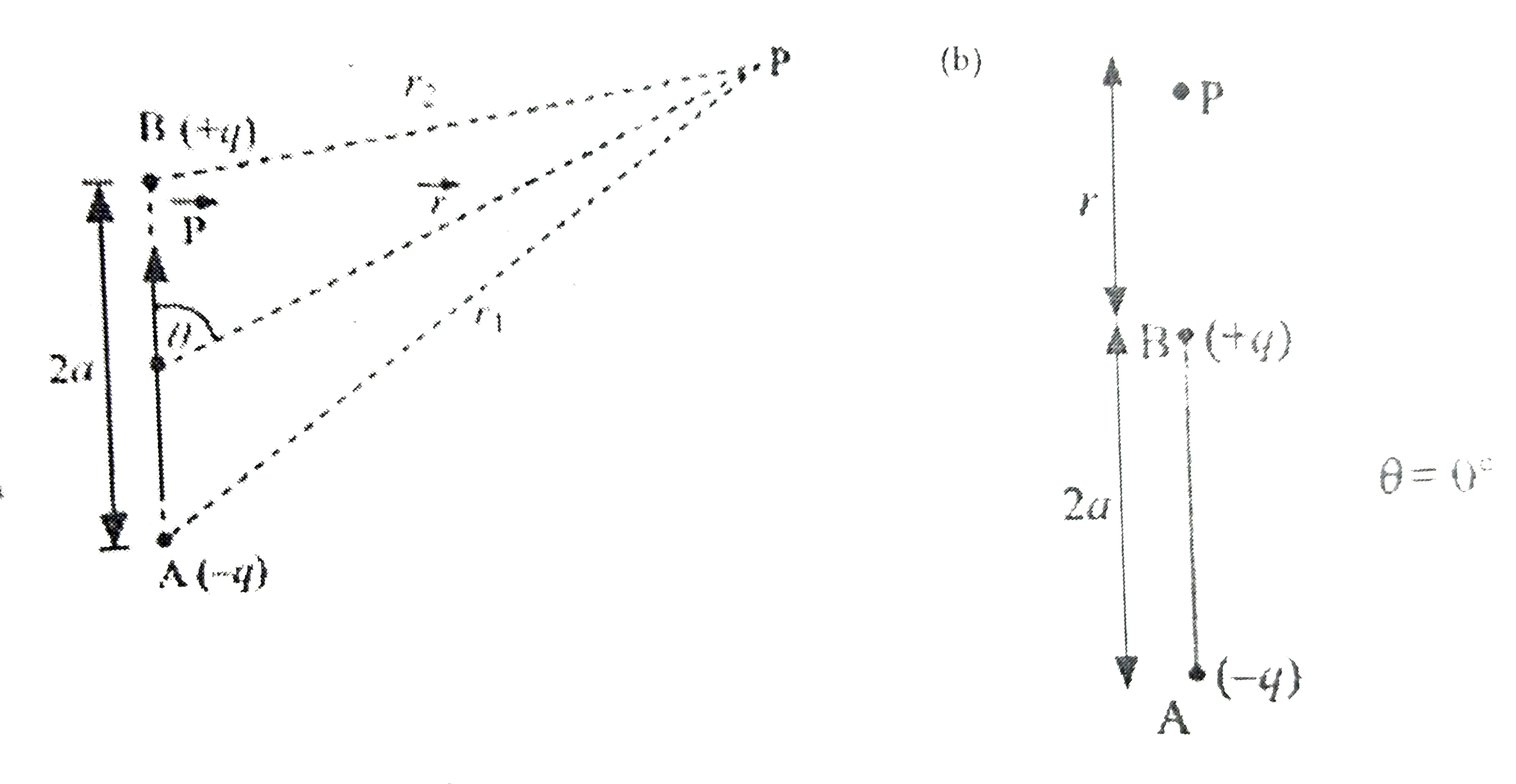 From the figure, `r_(1)^(2) = r^(2) +d + 2ar cos THETA` and, `r_(2)^(2) = r^(2) + a^(2) + 2ar cos(180^(@) - theta) = r^(2) + a^(2) - 2ar cos theta` `rArr r_(1)^(2)= r^(2)[1+(a^(2))/(r^(2)) +(2a)/(r ) costheta] = r^(2)[1+(2a)/(r) costheta]` as `r gt gt a, (a^(2))/(r^(2)) = 0` `rArr r_(1) = r[1+(2a)/(r) cos theta]^(1/2)` So `1/(r_(1)) = 1/r[1+(2a)/(r) cos theta]^(-1/2)` and `1/(r_(2)) = = 1/r [1-(2a)/(r) cos theta]^(-1//2)` Using it for `(i)` `V = (q)/(4piin_(0)r)[1+a/r cos theta - (1- a/r cos theta)]` [Applying Binomial Theorem and neglectinghighest power of `(2a)/(r)` ] Hence, `V = (q)/(4piin_(0)r) [1+q/r cos theta - 1+ a/r cos theta]` `= (qxx2a cos theta)/(4piin_(0)r^(2))` `rArrV = (p cos theta)/(4piin_(0)r^(2)) , {p = q xx 2a = " dipole moment"}` Vaxial `= (pcos theta)/(4piin_(0)r^(2))` ( `:' theta = 0^(@)` on axialline) `= (p)/(4pi in_(0)r^(2))` (ii) `V_("net") = V_(A) + V_(B)= (-kq)/((r^(2)+a^(2))) + (-kq)/((r^(2)+a^(2)) = 0` 
|
|
| 42521. |
Two point charges having equal charges separated by 1 m distance experience a force of 8 N. what will be the force experienced by them . If they are held in water at the same distance?(Given:K_("water")=80 ) |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :In freee space force between two equal POINT charges separated by 1m is , F =8 N. ` THEREFORE ""F_("WATER") =(F)/(K_("water"))=(8N)/(80 )=0.1 N ` |
|
| 42522. |
The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor does not depend on |
|
Answer» area of the PLATES |
|
| 42523. |
How many alpha and beta- particles are emitted when uranium nucleus (""_(92)^(238)U) decay to ""_(82)^(214)Pb ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Let n be the number of `alpha` - particles and m be the number of `beta` - particles emitted. `""_(92)U^(238)RARR ""_(82)Pb^(214)+n_(2)He^(4)+m""_(-1)e^(0).` As mass is conserved , 238 = 214 + 4N + m (0) `= 214 + 4n implies 4n = 24 , n = 6` As charge is conserved , 92 = 82 + 2n + m (-1) 10 = 2 (6) - m`(:.n = 6) implies m = 2 ` `:. 6 alpha` particles and `2 beta` - particles are emitted |
|
| 42524. |
A thin conducting ring of radius R is given a charge +Q. The electric field at the centre o of the ring due to the charge on the part AKB of the ring is E. The electric field at the centre due to the charge on the part ACDB of the ring is |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 42525. |
You are provided with four convex lenses of focal length 1cm, 3cm, 10 cm and 100 cm. Which two would you prefer for a microscope and which two for a telescope. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`f_0=1 CM and f_e=3cm `for MICROSCOPE and `f_0=100 cm and f_e=1 cm` For a TELESCOPE |
|
| 42526. |
A 2muF Capacitor is connected to a.d.c source of 100 volt through1 M Omega series resistance . Calculate time taken for the capacitor to be fully charged. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :TIME taken for the capacitor to be FULLY charged `=5RC = 5xx 2 =10 ` SEC | |
| 42527. |
A 2muF Capacitor is connected to a.d.c source of 100 volt through1 M Omega series resistance . Calculate voltage across the capacitor 6 seconds after the application of voltage . |
|
Answer» Solution :`V- V_0 (1- e^(-t//RC))` `=100 (1-e^(-6//2)) = 100 (1-e^(-3)) = 95.1 ` Volt |
|
| 42528. |
A 2muF Capacitor is connected to a.d.c source of 100 volt through1 M Omega series resistance . Calculate initial rate of rise of p.d across the capacitor. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Now, `V_0 = V+ CR (DV)/(dt)` At the instant , the switch is CLOSED , V=0 so, `V_0= CR((dV)/(dt))` or `(dV)/(dt) = (V_0)/(CR)= (100)/(2)=50`V/s |
|
| 42529. |
A 2muF Capacitor is connected to a.d.c source of 100 volt through1 M Omega series resistance . Calculate initial charging current . |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :INITIAL charging current, `I_0 = (V_0)/(R) = (100)/(10^6)=100 mu_A` |
|
| 42530. |
A 2muF Capacitor is connected to a.d.c source of 100 volt through1 M Omega series resistance . Calculatetime constant . |
| Answer» Solution :TIME constant , `tau_C= RC = 10^6 XX(2xx10^(-6))= 2s` | |
| 42531. |
What is the value of relative magnetic permeability of perfectly diamagnetic substance ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The value of `mu_(r)` of a DIAMAGNETIC substance is SLIGHTLY less than 1. | |
| 42532. |
The current gain in common-base configuration of n-p-n transistor is 0.8. The current amplification factor in common-emitter configuration is |
|
Answer» 0.8 |
|
| 42533. |
Determine the potential difference between the points C and D in figure. |
|
Answer» Solution :Since the capacitors are in series, charge on each capacitor is the same. At steady state, the charge on the capacitor is due to terminal patential differnee of cell `EPSILON`. When steady state is reached, no current FLOWS throught the capaciotrs. The current in the circuit is, `I = 12/( 1 + 3 +6)=1.2A` Terminal pot. diff. across A and B, `V = epsilon - I r= 12 -1.2 xx 1 = 10.8V` Capacitors are in series, their effective capacitance `C= ( 1 xx 2)/(1 +2) = 2/3 mu F` `:.` Charge on each capacitor, `q = 2/3 xx 10^(-6) xx 10.8 = 7.2 xx 10^(-6)C`. Pot. diff. between A and C `V_(A) - V_(C) = q/C_(2) = (7.2 xx 10^(-6))/(2 xx 10^(-6)) = 3.6 V` po. diff. between A and D `= V_(A) - V_(D) = IR_(2)` ` = 6 xx 1.2 = 7.2 V` Pot. diff. between C and D `= V_(C) - V_(D)` ` (V_(A) - V_(D)) - (V_(A) - V_(C))= 7.2 -3.6 = 3.6V` |
|
| 42534. |
Obtain an expression for equivalent resistance of two resistors connected in parallel. |
Answer» Solution : Consider two cells of emf `EPSI _(1) and epsi_(2)` and internal resistances `r _(1) and r _(2)` connected in PARALLEL as shoen in fig(a). Let ` I _(1) and I _(2)` be the curents through the cells. At `B_(1)` currents `I _(1) and I _(2)` flow in wheres the current I flows out. `therefore I = I_(1) + I_(2)""...(1)` Let `V_(1) and V _(2)` be the potentials at `B _(1) and B _(2)` respectively. Pd between first cell, `V - V _(1) = V _(2) = epsi _(1) - I _(1) r _(1)` `implies I _(1) = (epsi _(1) -V)/(r _(1)) ""..(2)` Pd between second cell, `V = V_(1) -V_(2) =epsi _(2) - I _(1) r _(2)` `implies I _(2) = (epsi _(2) -V)/(r _(2))""...(3)` `therefore` Eq1uation (1) becomes `I = ( epsi _(1)- V )/( r _(1)) + (epsi _(2 ) - V)/( r _(2))` `1= (epsi _(1))/( r _(1)) - (V)/( r _(1))+ (epsi _(2))/( r _(2))- ( V )/( r _(2))` `I = ((epsi _(1))/( r _(1)) + ( epsi _(2))/( r _(2))) - ((V)/(r _(1)) + ( V)/( r _(2)))` ` I = ((epsi _(1))/( r _(1)) + (epsi _(2 ))/( r _(2 ))) - V ((1)/( r _(1)) + (1)/( r _(2)))` `I = ((epsi_(1) r _(2) + epsi _(2) r _(1 ))/( r _(1 ) r _(2)))- V (( r _(1) + r _(2))/( r _(1) r _(2)))` `V ((r _(1) + r _(2))/( r _(1 ) r _(2))) = (( epsi_(1) r _(2) + epsi_(2) r _(1))/( r _(1) r _(2)))-1` `V = ((e _(1)r _(1) + epsi _(2 ) r _(1))/( r _(1) r _(2)))((r _(1) r _(2))/( r _(1) + r _(2))) - I ((r_(1) r _(2))/( r _(1) + r _(2)))` `V = (( epsi _(1) epsi _(2) + epsi _(2)r _(1))/( r _(1) r _(2))) -I ((r _(1) r _(2))/( r _(1)+ r _(2)))` Let the parallel COMBINATION of two cells be replaced by a single cell between `B _(1) and B _(2).` Let `epsi _(eq)` be its emf and `r _(eq)` be its internal resistance. Then `V = epsi _(eq) - I r _(eq) ""...(5)` From equation (4) and (5), we have `epsi _(eq)= ( epsi _(1) r _(2) + epsi _(2) r _(1))/( r _(1) + r _(2)) ""...(6)` `r _(eq) = (r _(1) r _(2))/( r _(1) + r _(2))""...(7)` Equation (6) and (7) can also be WRITTEN as `(epsi _(eq))/( r _(eq))=(epsi _(1))/(r _(1)) + ( epsi _(2))/( r _(2))""...(8)` `(1)/( r _(eq)) = (1)/( r _(1)) + (1)/( r _(2))""...(9)` |
|
| 42535. |
The figure shows four progressive waves A, B, C 8 l D. It can be concluded from the figure that with respectto wave A: |
|
Answer» The wave C is AHEAD by a phase ANGLE of `pi//2` & the waveB lags behind by a phase angle `pi//2` And A reaches the positions where B already reached after `omegat = (pi)/(2)` |
|
| 42536. |
Van de Graaff generator producers large electrostatic potential difference of the order of ................ . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 42537. |
An electric field is uniform and E=200 hatiNC^(-1) along +xs and E=-200hatiNC^(-1) along -x direction. A right circular cylinder of length 0.20 m and radius 0.05 m has its centre at the origin and its axis along the x-axis so that one face is x=+0.10m and the other =x-0.10m. a. What is the net outward flux through each flat face? b. What is the flux through the side of the cylinder? c. What is the net outward flux throught the cylinder? d. What is the net charge inside the cylinder? |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) we cansee from thethat on the leftfaceE and `triangle S`are parallel THEREFORE the outward fluxis (b) for any pointon the side of the CYLINDER E is perpwendicular to `triangle S` and hence E `triangleS=0`thereforethe fluxout of the side ofthe cylinder is zero (c ) net outward flux throughthe cylinder `Phi =1.57 +1.57 +0=3.14 N m^(2) c^(-1)`  (d) the netcharge WITHIN the cylinder can be foundby using gauss.slaw which GIVES `q=epsilon_(0) Phi` `=2.78 xx10^(-11) c` |
|
| 42538. |
A solenoid of length 0.5 m has a radius of 1 cm and is made up of 500 turns. It carries a current of 5 A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field inside the solenoid? |
|
Answer» Solution :The number of turns per unit length is, `n = (500)/(0.5) = 1000` turns/m The length l = 0.5 m and RADIUS r = 0.01 m. Thus, l/a = 50 i.e., l > >a. Hence, we can use the long solenoid formula, namely, Eq. `B = mu_0 n I` ` = 4 pi xx 10^(-7) xx 10^3 xx 5` `= 6.28 xx 10^(-3) T` |
|
| 42539. |
To shield an instrument from external magnetic field, it is placed inside a cabin made of |
|
Answer» WOOD |
|
| 42540. |
For example, the true value of a certain length is near 3.678 cm. In one experiment, the measured value is found to be 3.5 cm.while in another experiment, the length is determined to be 3.38 cm. The first measurement has |
|
Answer» more ACCURACY but LESS PRECISION |
|
| 42541. |
The emf of a thermocouple, one junction of which is kept at 0^(@)C is given by e=at+bt^(2) the Peltier co-efficient will be |
|
Answer» `(t+273) (a+2bt)` |
|
| 42542. |
What is the energy of He^(+) electron in first order? |
|
Answer» `40.8` eV For `He^(+),. Z = 2 and n = 1` `E_(1) = (-13.6 xx 2^(2))/(12) = -54.4 eV` |
|
| 42543. |
Draw a schematic diagram of a step up transformer. Explain its working principle. Deduce the expression for the secondary to the primary voltage in terms of the number of turns in the two coils. In an ideal transformer, how is this ratio related to the currents in the two coils ? How is the transformer used in large scale transmission and distribution of electrical energy over long distances ? |
| Answer» Solution :We want to transmit electrical power over large distances at highest possible voltage so that transmission loss is LEAST possible. For this purpose the power output of electrical generators is fed to suitable step up transformers which raise the voltage to DESIRED limit (generally 400 kV). When at the consuming CENTRES the electrical power is to be distributed, its voltage is again reduced by the USE of suitable step down transformers. | |
| 42544. |
Does dispersive power of a prism material depend upon the shape, size and angle of the prism? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The dispersive POWER of a PRISM material is INDEPENDENT of SHAPE, size and angle of the prism. | |
| 42545. |
In the following circuit the resultant e.m.f. between AB is: |
|
Answer» `E_1+E_2+E_3+E_4` |
|
| 42546. |
A charge Q is fixed on the X-Y plane at point (0, a). Find the electric field strength component along the X-axis, at any point (x, 0). |
|
Answer» |
|
| 42547. |
In a double slit arrangement, the slits are separated by a distance equal to 100 times the wavelength of the light passing through the slits. (a) What is the angular separation in radian between the central maximum and an adjacent maximum? (b) What is the distance between these maxima on a screen 50.0 cm from the slits? |
| Answer» SOLUTION : (a) 0.01 RAD, (B) 0.2 MM | |
| 42548. |
In Young's double-slit experiment using monochromatic light of wavelength lambda, the intensity of light at a point on the screen where path difference is lambda, is K units. What is the intensity of light at a point where path difference is lambda//3? |
|
Answer» Solution :In YDSE (Young.s Double Slit Experiment), intensity of light at a given point on the screen is, `I=I_(0)COS^(2){(k(r_(2)-r_(1)))/(2)}` For first point, `r_(2)-r_(1)=LAMDA` I=K and so, `K=I_(0)cos^(2){(1)/(2)xx(2pi)/(lamda)xxlamda}` `:.K=I_(0)(1)` `:.I_(0)=K""....(1)` For second point, `(r_(2)-r_(1))=(lamda)/(3)` and so, `I.=I_(0)cos^(2){(k(r_(2)-r_(1)))/(2)}` `:.I.=Kcos^(2){(1)/(2)xx(2pi)/(lamda)xx(lamda)/(3)}` `:.I.=Kcos^(2)((pi)/(3))=K((1)/(2))^(2)` `:.I.=(K)/(4)` |
|
| 42549. |
Assertion: The surface charge densities of two spherical conductors of different radii are equal. Then the electric field intensities near their surface are also equal. Reason : Surface charge density is equal to charge per unit area. |
|
Answer» Both Assertion and REASON are TRUE and Reason is the CORRECT explanation of Assertion |
|
| 42550. |
(A ): A pulsar is a source of radio waves that varies in intensity at regular intervals. (R) : A pulsar is a rotating neutron star. |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are TRUE and 'R' is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of 'A'. |
|