Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 42551. |
According to Boher atom model where can an electron be observed in an atom?What is the angular momentum of an electron? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Electrons can be observed in orbits (around the NUCLEUS) Angular momentum of the electron =nh//2 PI where h is the plank CONSTANT | |
| 42552. |
A conducting rod PQ of length l is connected to a resistance .R. is moved at a uniform speed V, normal to a uniform magnetic field .B.. Find the magnitude and direction of current through the conductor. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The CURRENT FLOWS in CLOCKWISE DIRECTION `[I = epsilon/R = Blv/R]` | |
| 42553. |
A single circular loop of write radius 0.02 m carries a current of 8.0 A. It is placed at the centre of a solenoid that the length 0.65 m, radius 0.080m and 1300 turns. |
|
Answer» The value of the current in the SOLENOID so that the magnetic field at the centre of the LOOP becomes zero, is equal to 44 mA. Magnitudde of `B_("solenoid")=` Magnitude of `B_("loop")` `mu_(0)ni=(mu_(0)I)/(2R)` here `n=("Total no. of turn")/("Total length")=(1300)/(0.65)` `i=(I)/(2R)xx(1)/(n)=(8xx0.65)/(2xx0.02xx1300)=100mA` For given condition: Total magnetic field at the contre of loop `=|B_("loop")|+|B_("solenoid")|:.|B_(loop)|=||B_("solenoid")` `=2|B_("loop")|=2xx(mu_(0)I)/(2R)` `=(2xx4pixx10^(-7)xx8)/(2xx0.02)=16pixx10^(-5)T` . |
|
| 42554. |
A ball thrown vertically upward with initial velocity u. Which of the following graphs represent the velocity of ball correctly as function of time? (Take upward direction as positive) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 42555. |
A source S_1, is producing 10^(15) photons per second of wavelength 5000 Å. Another source S_(2) is producing 1.02xx10^(15) photons per second of wavelength 5100 Å. Then, (powerr of S_(2)) is equal to (power of S_(1)) |
|
Answer» `1.04` `therefore (P_(2))/(P_(1))=(n_(1))/(n_(2))XX(lamda_(1))/(lamda_(2))=(1.02xx10^(15)xx(5000Å))/(10^(15)xx(5100Å))=1.00` |
|
| 42556. |
In a junction transistor, the current gain B is defined as |
|
Answer» The ratio of the change in COLLECTOR current to the change in EMITTER current for a CONSTANT collector voltage in the COMMON base configuration. `beta=((DeltaI_(C ))/(DeltaI_(B)))_(V_(CE))` |
|
| 42557. |
The current I drawn from the 5 volt source will be |
|
Answer» `0.5 A` |
|
| 42558. |
Two capacitors C_(1)"and"C_(2) are charged to the same potential V, but with opposite polarity as shown in the figure. The switch S_(1)"and"S_(2) are then closed. |
|
Answer» PDsacross. Two capacitors are the same and is GIVEN by `((C_(1)-C_(2))V)/((C_(1)+C_(2))` |
|
| 42559. |
A horizontal converyor belt moves with a constant velocity V. A small block is projected with a velocity of 6 m/s on it in a direction opposite to the direction of motion of the belt. The block comes to rest relative to the belt in a time 4s. mu=0.3, g=10 m//s^(2). Find V |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`|vec(V)_(b,c)|=V_(b)+V_(c )=6+V` `f=mu mg=0.3xx m xx10=3M` Retardation `a=(3m)/(m)=3m//s^(2)` `u_(r )=6+V, V_(r )=0, t=4 sec` `a_(r )=-3 MS^(-2)` `V_(r ) =u_(r )+a_(r )t` `0=(6+V)-3xx4` `V=6m//s` |
|
| 42560. |
Which of the following relation is correct for a transistor? |
|
Answer» `I_C=I_B+I_E` |
|
| 42561. |
A car moves towards a hill with speed v_c.It blows a horn of frequency f which is heard by an observer following the car with speed v_0.The speed of sound in air is v. |
|
Answer» the WAVELENGTH of sound reaching the HILL is `v/f` Frequency of echo =`v/(v+v_c)f` Frequency of echo of horn as heard by observer. `v/(v-v_c)f.((v+v_0)/v)` Frequency of Beats : `=(v+v_0)f {1/(v-v_c)-1/(v+v_c)}=(2v_c(v+v_0))/((v_2-v_c^2))f` |
|
| 42562. |
Three immiscible liquids of densities d_1 gt d_2 gt d_3 and refractive indices mu_1 gt mu_2 gt mu_3 are put in a beaker. The height of each liquid column is (h)/(3). A dot is made at the bottom of the beaker. For near normal vision, find the apparent depth of the dot. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION : (Hint : the image FORMED by FIRST medium act as an object for second medium) Let the apparent depth be `O_1` for the object seen from`O_1 =mu_2/mu_1 h/3` image formed by medium 1, O ACTS as an object for medium2. It is seen from `M_3`, the apparent depth is `O_2`.Similarly, the image found by medium 2, `O_2` act as an object formedium 3 `O_2=mu_3/mu_2(h/3+O_1)` `O_3=mu_3(h/3 + O_2)` putting value of `O_2 and O_1` `O_3=h/3(1/mu_1+1/mu_3+1/mu_3)` |
|
| 42563. |
Figure 22-24 shows a plastic rod having a uniformly distributed charge. The charge per unit length of the rod is lambda. Find the electric field due to the rod at a point P which is at a distance r from the rod. |
|
Answer» Solution :KEY IDEA Because the rod has a continuous charge distribution, we must find an expression for the electric fields due to differential elements of the rod and then sum those fields via calculus. Calculations : An element : CONSIDER a differential element having length dx. If the length ofa line segment is dx, the charge on it is `lambda dx`. Here `lambda` is the charge per unit length of the line (assumed to be constant). Thus, `dq=lambda dx`. The element.s field: Our element produces a differential electric field. Treating this element as a point charge, the electric field due to this small charge at a distance r from the line is `dE=(k lambda dx)/((sqrt(x^(2)+r^(2))^(2)))`. The electric field is AWAY from the charge because the charge is positive . Summing: Thus, to find the electric field set up by the rod, we need sum (via integration) the parallel as well as perpendicular components of the differential electric field is setup by all the differential elements of the rod. 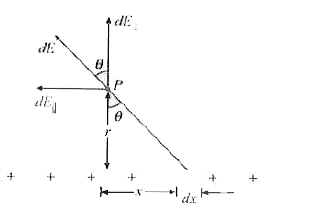 Let us resolve this electric field in a direction parallel and perpendicular to the line charge. `dE_("||")=dEsin theta`, `dE_(bot)=dE cos theta`, `dE_("||")=(k lambda dx)/((x^(2)+r^(2))) sin theta`. From the GEOMETRY of Fig. 22-25, we can say that `(x)/(r )=tan theta`, `x= r tan theta`. Since we need to replace x everywhere by the variable `theta`, we need to DIFFERENTIATE this expression with respect to `theta`. `(dx)/(d theta)=r sec^(2) theta`, `dx=r sec^(2)theta d theta`. By replacing this expression for dE, we get `dE_("||")=(k lambda xx r sec^(2)theta xx sin theta)/((r^(2)+r^(2)tan^(2)theta)) d theta`, `dE_("||")=(k lambda)/(r ) sin theta d theta`, `E_("||")=(k lambda)/(r ) int_(-beta)^(alpha) sin theta d theta ` `=(k lambda)/(r )[cos alpha-cos(-beta)]=(k lambda)/(r )[cos beta-cos alpha]`. Similarly resolving the electricfield in the perpendicular direction, we have `E_(bot)=(k lambda)/(r ) int_(-beta)^(a) cos theta d theta` `=(k lambda)/(r )[ sin alpha+sin beta]` Note: If the line is infinite which means that it EXTENDS from `-oo` to `+oo`, we can assume `alpha=90^(@) and beta=90^(@)`. Then `E_("||")=(k lambda)/(r )[cos90^(@)-cos90^(@)]=0` `E_(bot)=(k lambda)/(r )[sin 90^(@)-sin90^(@)]=(2k lambda)/(r )`. If the line is semi-infinite, extending from `-oo` to the foot of the perpendicular, we can assume `alpha=90^(@) and beta=0^(@)`. Then `E_("||")=(k lambda)/(r )[cos0^(@)-cos90^(@)]=(k lambda)/(r )` `E_(bot)=(k lambda)/(r )[sin 90^(@)-sin0^(@)]=(klambda)/(r )`. |
|
| 42564. |
Three capacitors are connected in triangle as shown in the figure . The equivalent capacitance between the points A and C is ………. . |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 42565. |
A body is moving under the acton of central force vrc(F)(r ) hat(e ). Then, choose the correct statement (symbols are having usual meaning and hat(e ), hat(e ), denote unit vectors along the radial and tangential direction, respectively ) from the following. |
|
Answer» `vec(v) = (dr)/(dt) hat(e)_(r ) + r(d THETA)/(dt) hat(e)_(theta), vec(a) = [(d^(2)r)/(dt^(2)) - r ((d theta)/(dt))^(2)] hat(e)_(r ), 2(dr)/(dt) (d theta)/(dt) + r (d^(2)theta)/(dt^(2)) = 0` |
|
| 42566. |
(A): An induced emf is generated when magnet is withdrawn from the solenoid. (R) : The relative motion between magnet and solenoid induces emf. |
|
Answer» Both .A. and .R. are TRUE and .R. is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of .A. |
|
| 42567. |
If lamda_(1) and lamda_(2)denote the wavelengths of de-Broglie waves for electrons in the first and second Bohr orbits in hydrogen atom, then (lamda_(1))/(lamda_(2)) is equal to : |
|
Answer» `(2)/(1)` `E_(1)=-13*6eV` For Bohar.s second orbit n=2 `E_(2)-(13*6)/(2^(2))=(-13*6)/(4)eV` As `E=(hc)/(lambda)rArr Eprop (1)/(lambda)` `:. (lambda_(1))/(lambda_(2))= sqrt((E_(2))/(E_(1)))= sqrt((1)/(4))=(1)/(2)` |
|
| 42568. |
Two equalballs having equal positive charges q coulombsare suspended by two insulating strings of equallength . What would be the effect on the force when a plastic sheet is inserted beteween the two? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The VALUE of ‘g’ decreases due to rotation of earth. If the earth STOPS rotating, the value of ‘g, will INCREASE. The effect should be MAXIMUM at .equator. | |
| 42569. |
An-type semiconductor is negatively charged but a p-type semiconductor is positively charged. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FALSE - Both n-type and p-type SEMICONDUCTORS all ELECTRICALLY NEUTRAL. | |
| 42570. |
A solid conducting sphere having a change .Q. is surrounded by an uncharged concentric conducting hollow spherical shell. Let the P.D between the surface of the solid sphere and that of the outer surface of the hollow shell be V. If the shell is now given a charge of - 3Q. The new PD between the same two surface is |
|
Answer» V |
|
| 42571. |
The nuclear mass density is of the order of |
|
Answer» `10^(10) " KG m"^(-3)` |
|
| 42572. |
A transverse wave is. tranveling in a string at any moment a small element .dx. is at inclination 30° with the direction o£ propagation of the wave. After some time interval its inclination changes to 60° with direction of propagation. Potential energy of this small element is initially U_0 and finally it is Ku_0, value of K is |
|
Answer» 2 |
|
| 42573. |
The half life of a radioactive decay is 'n' times its mean life, n is equal to |
|
Answer» 0.0693 |
|
| 42574. |
The figure below shows the plot of (PV)/(nT) versus P for oxygen gas at two different temperatures (##ARH_EGN_PRG_PHY_C17_E01_014_Q01.png" width="80%"> Read the following statements concerning the above curves. (i) The dotted line corresponds to the ideal gas behaviour (ii) T_(1)gtT_(2) The value of (pV)/(nT) at the point where the curves meet on the y-axis is the same for all gasesWhich of the above statements is true ? |
|
Answer» (i) only (ii) At high temperature , the deviation of the gas is LESS and al low temperature the deviation of gas is more . In the graph, deviation for`T_(2)` is greater than for `T_(1) ` . Thus , (iii) Since , the two curves intersect at dotted line so, the value of `(pV)/(nT)` at that point on the the y-axis is same for all gases. |
|
| 42575. |
If maximum peak to peak voltage of an AM wave is 24 mV and the minimum peak to peak voltage is 8 mV, then the modulation factor is |
|
Answer» `25%` |
|
| 42576. |
Which among the following is incorrect ? |
|
Answer» <P>In meld's experiment `p^2T` remain CONSTANT . (p = loop , T = TENSION) |
|
| 42577. |
How much work is required separate the two charges infinitely away from each other ? |
|
Answer» Solution :The WORK required to separate the two charges infinitely away from each other is `w= U_(2)-U_(1)` =0-U where `U_(2)` = potential energy at infinite distance =0 `=-U` `=-(-0.7)` `=0.7` J |
|
| 42578. |
Suppose a pure Si crystal has 5 xx 10^(28)atoms m^(-3). It is doped by 1 ppm concentration of pentavalent As. Calculate the number of electrons and holes. Given that n_(i) = 1.5 xx 10^(16) m^(-3). |
|
Answer» Solution :`n_(c) = 4.95 xx 10^(22), n_(h) = 4.75 xx 10^(9)`, n-type since `n_(e) gt gt n_(h)` For charge NEUTRALITY `N_(D)-N_(A) = n_(e).n_(h) = n_(i)^(2)` Solving these EQUATIONS, `n_(e) = 1/2 [(N_(D)-N_(A)) + sqrt((N_(D)-N_(A))^(2) + 4n_(i)^(2))]` |
|
| 42579. |
Hertz, in his historical experiment, produced stationary EM waves and measured the distance between two successive nodes. Explain how this measurement enabled him to show that EM waves travelled with the same speed as the speed of light. |
|
Answer» Solution :Hertz made the experiment to find out the distance between consecutive NODES and he made an experiment to detect electromagnetic WAVES which travel with the same velocity of light `c = 3 xx 10^8` m/s. We know that the light is an electromagnetic wave, which propagate through a material MEDIUM say, glass. We also know that the total electric and magnetic fields inside a medium are described in terms of permittivity and magnetic permeability `mu` (these describe the factors by which the total fields differ from the external fields). These replace `epsi_0` and `mu_0` in the description to electric and magnetic fields in Maxwell.s equations with the result that in a material medium of permittivity `epsi` and magnetic permeability `mu`, the velocity of light BECOMES, `v = (1)/(SQRT(muepsi))` |
|
| 42580. |
Unpolarised light is incident on a plane glass surface. What should be the angle of the incidence so that the reflected and refracted rays are perpendicular to each other ? |
| Answer» Solution :For i+r to be equal to `lambda//2,` we should have TAN `i_B= mu=1.5` This GIVES `i_B= 57^(@)`. This is the BREWSTER's angle for AIR to glass INTERFACE. | |
| 42581. |
Diffusion of free electrons across the junction of an unbiased diode produces |
|
Answer» forward bias |
|
| 42582. |
Deduce the expression for electric potential in a region of electric field vecE=(K)/(x^(2))hati. Consider that electric potential at infinity is zero. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`(K)/(X)` | |
| 42583. |
A lamp is connected in series with a capacitor A) When a de source is connected to the combination, the lamp will not glow in steady state B) When ac source is connected to the combination, the brightness of glow of lamp increases with increases of frequency of ac. |
|
Answer» A is true B is FALSE |
|
| 42584. |
The largest and the shortest distance of the earth from the sun are r_(1) and r_(2). Its distance from the sun when it is at perpendicular to the major -axis of the orbit drawn from the sun is |
|
Answer» `(ETA+eta_(2))/(4)`  `(2)/(R )=(1)/(r_(1))+(1)/(r_(2))=(r_(1)+r_(2))/(r_(1)r_(2)) rArr R=(2r_(1)r_(2))/(r_(1)+r_(2))` |
|
| 42585. |
22g of CO_(2)" at "27^(@)C is mixed with 16g" of "O_(2)" at "37^(@)C. The temperature of mixture is: |
|
Answer» `27^(@)C` `=150+155=305 K=32^(@)C` `therefore` CORRECT choice is (a). |
|
| 42586. |
Find the charge on the three capacitors shown in figure. (a) (b) |
Answer» Solution :(a) 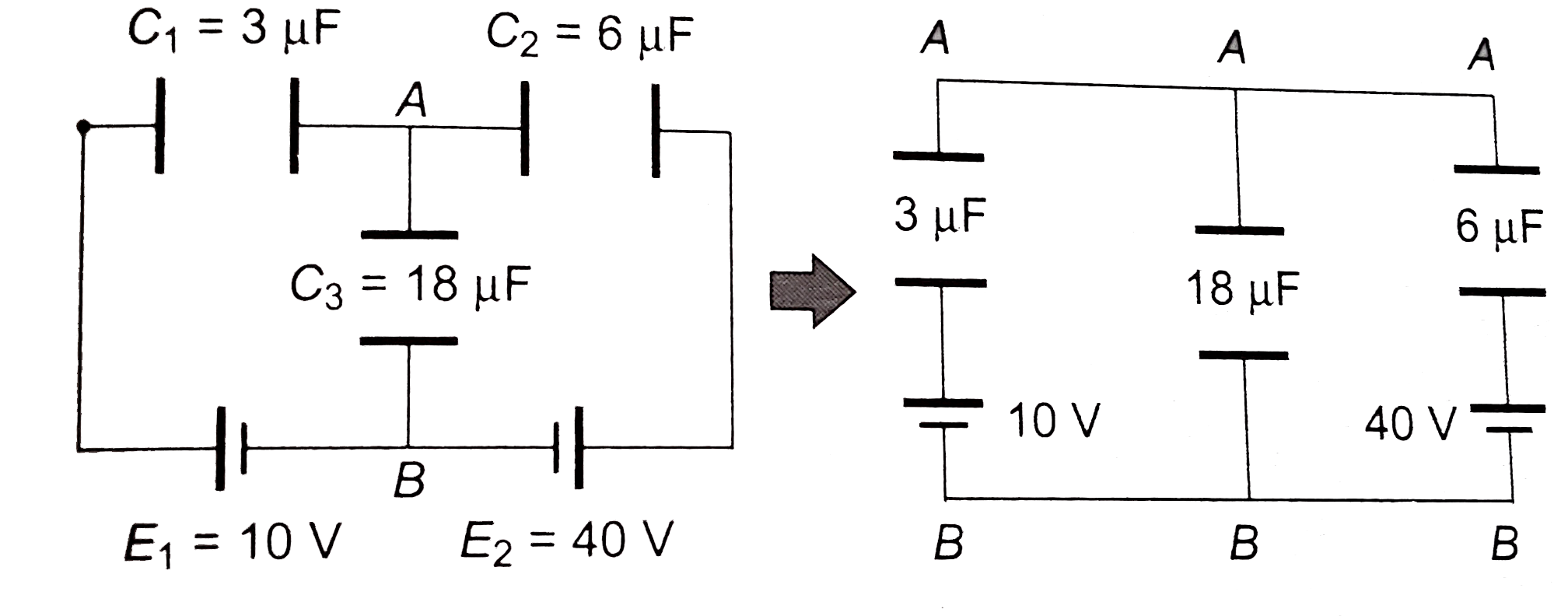 The CELLS is parallel can be replaced by a single cell. `E = (C_1 E_1 + C_2 E_2)/(C_1+ C_2) = (3 xx 10 + 6 xx 40)/(3 + 6) = (30 + 240)/(9) = 30 V` `C = C_1 + C_2 = 3 + 6 = 9 mu F` 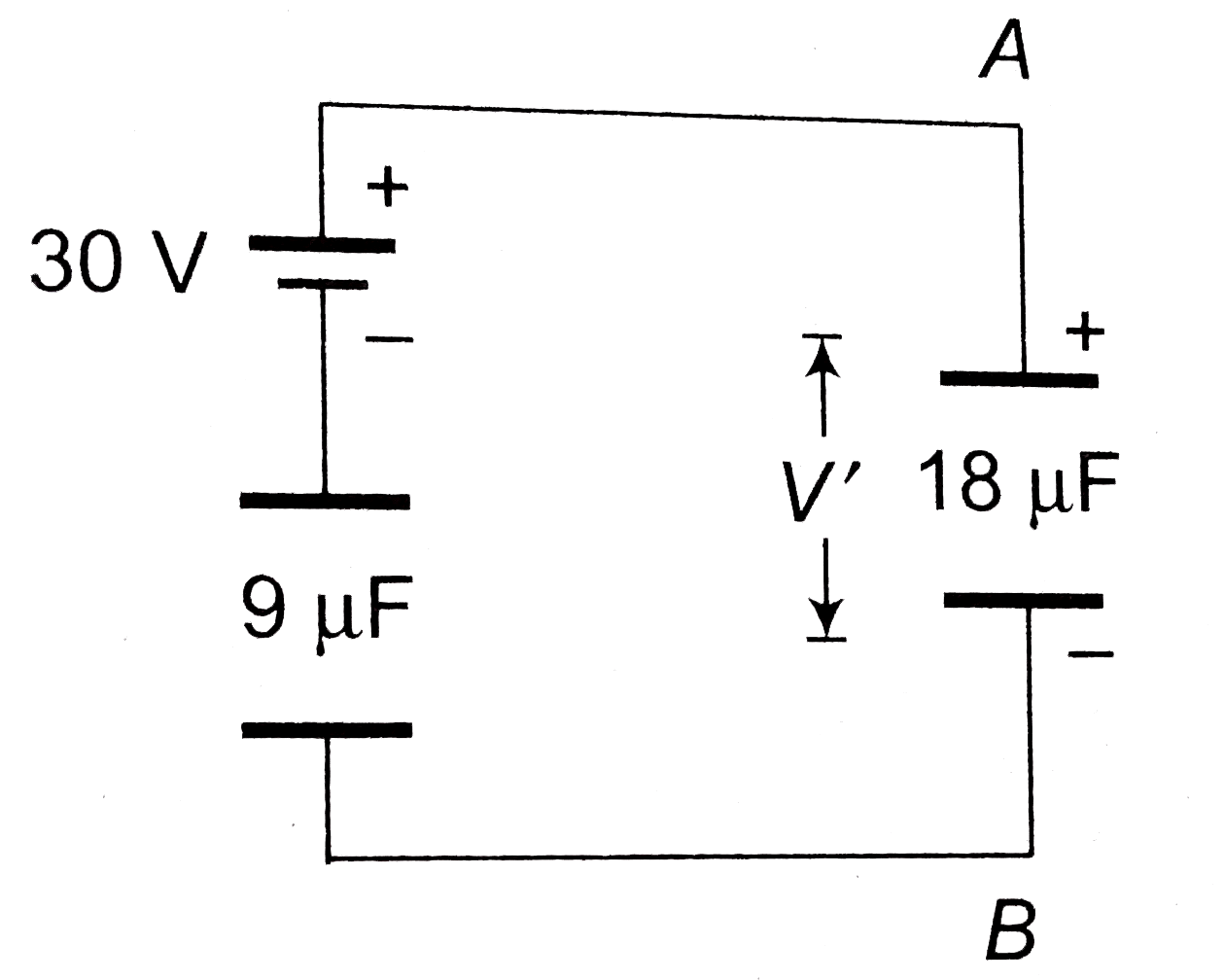 `V' = ((9)/(9 + 18)) xx 30 = 10 V` `V_A - V_B = 10 V` Now return to previous diagram :  Branch `A xx B` `V_A - (Q_2)/(3) - 10 = V_B` `V_A - V_B - 10 = (Q_2)/(3)` `10 - 10 = (Q_2)/(3) rArr Q_2 = 0` Branch `A Y B` : `V_A -(Q_1)/(6) - 40 = V_B` `V_A -V_B - 40 = (Q1)/(6)` `10 -40 = (Q_1)/(6) rArr Q_1 = - 180 mu C` `Q_1 + Q_2 = -180 mu C` 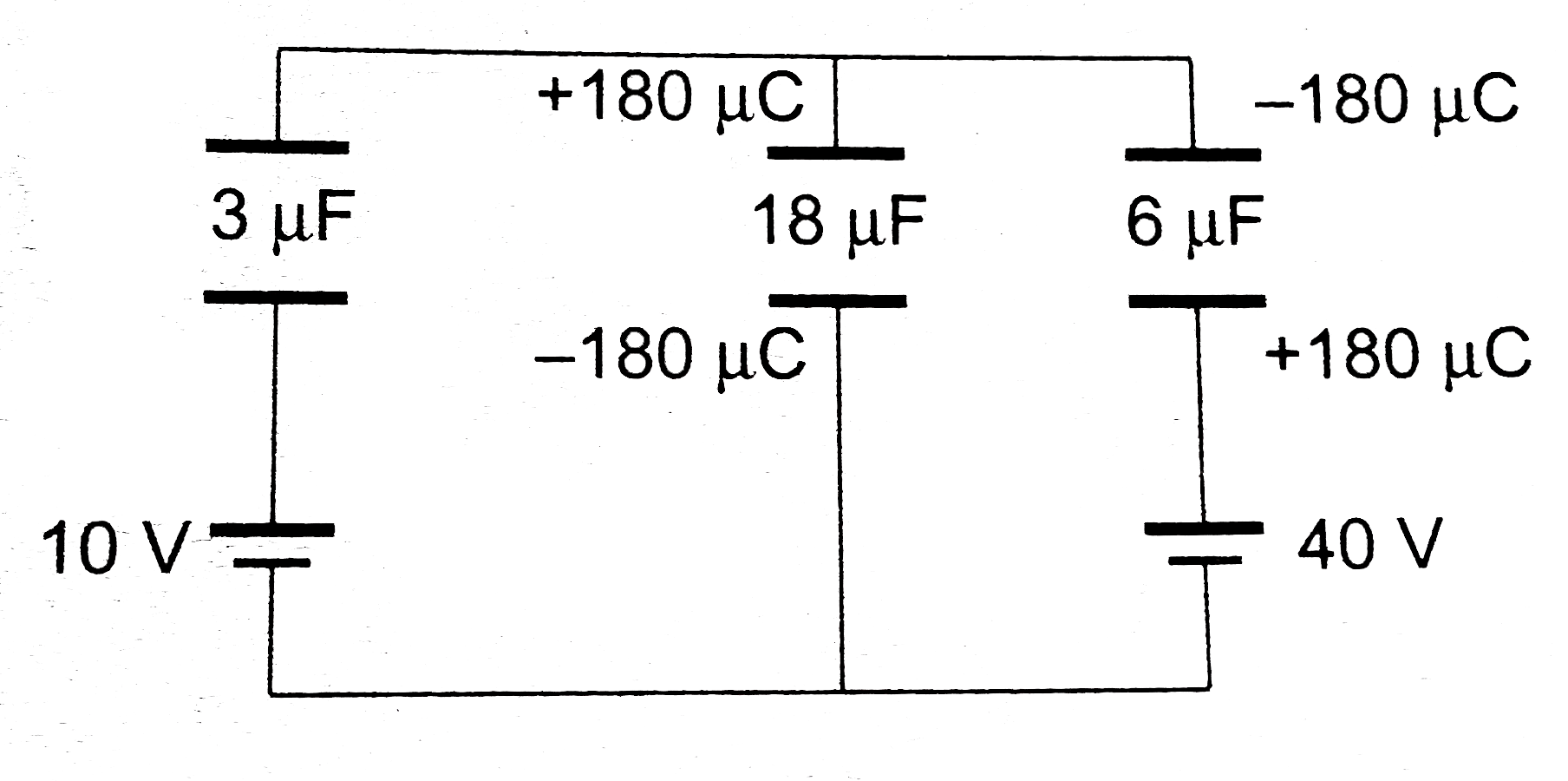 Charge on capacitor `3 mu F : 0 , 18 mu F: 180 mu C, 6 mu F : 180 mu C`. Alternatively by Kirchoff's rules Assume charge in branches, balancing at junctions. 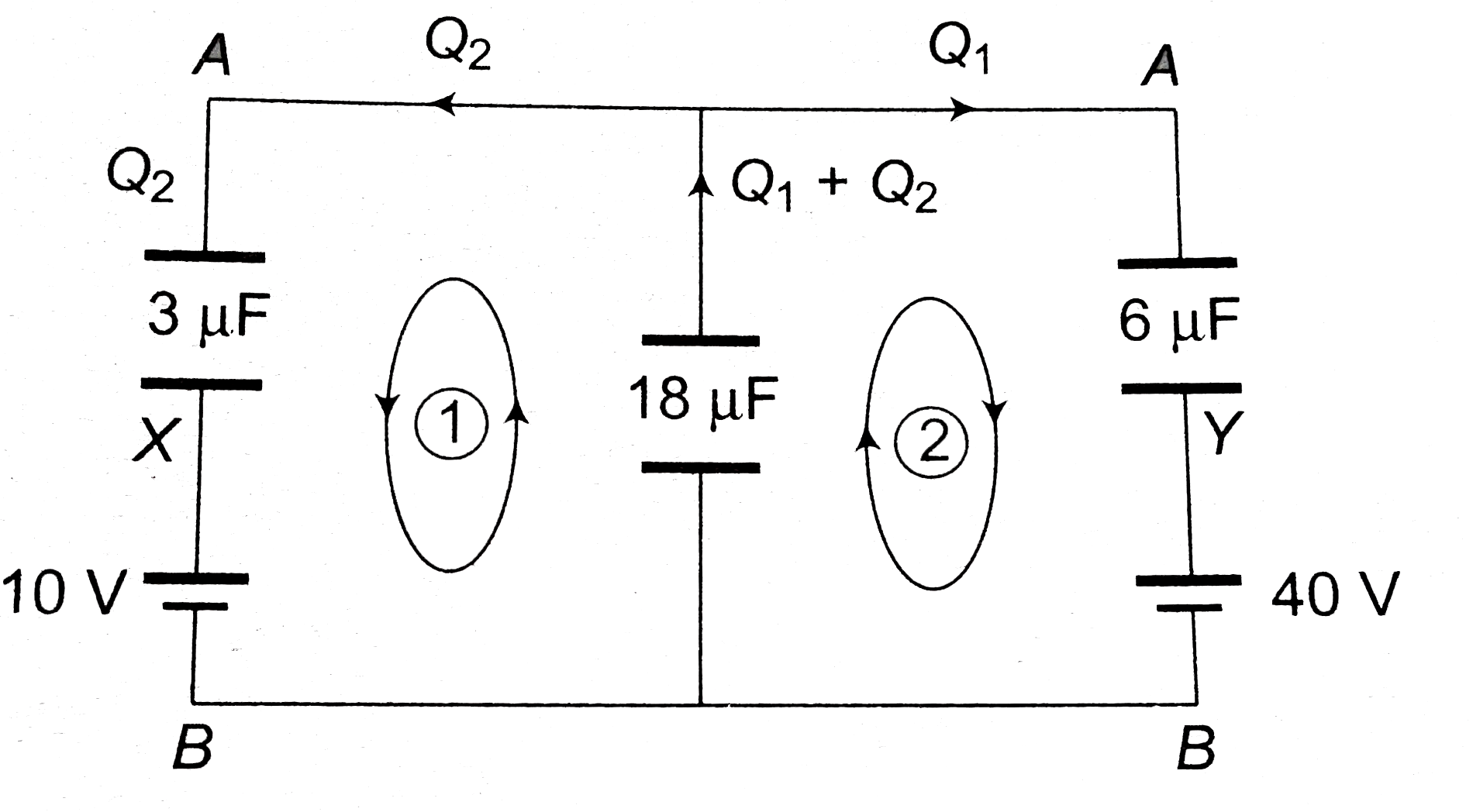 LEFT loop : `V_A - (Q_2)/(3) -10 -((Q_1 + Q_2))/(18) = V_A` `-Q_1 - 7 Q_2 = 180` `Q_1 + 7 Q_2 = -180`....(i) Right loop : `V_A -(Q_1)/(6) - 40 -(Q_1 + Q_2)/(18) = V_A` `4 Q_1 + Q_2 = - 720` Solving (i) and (ii) `Q_1 = -180 mu C, Q_2 = 0` (b) 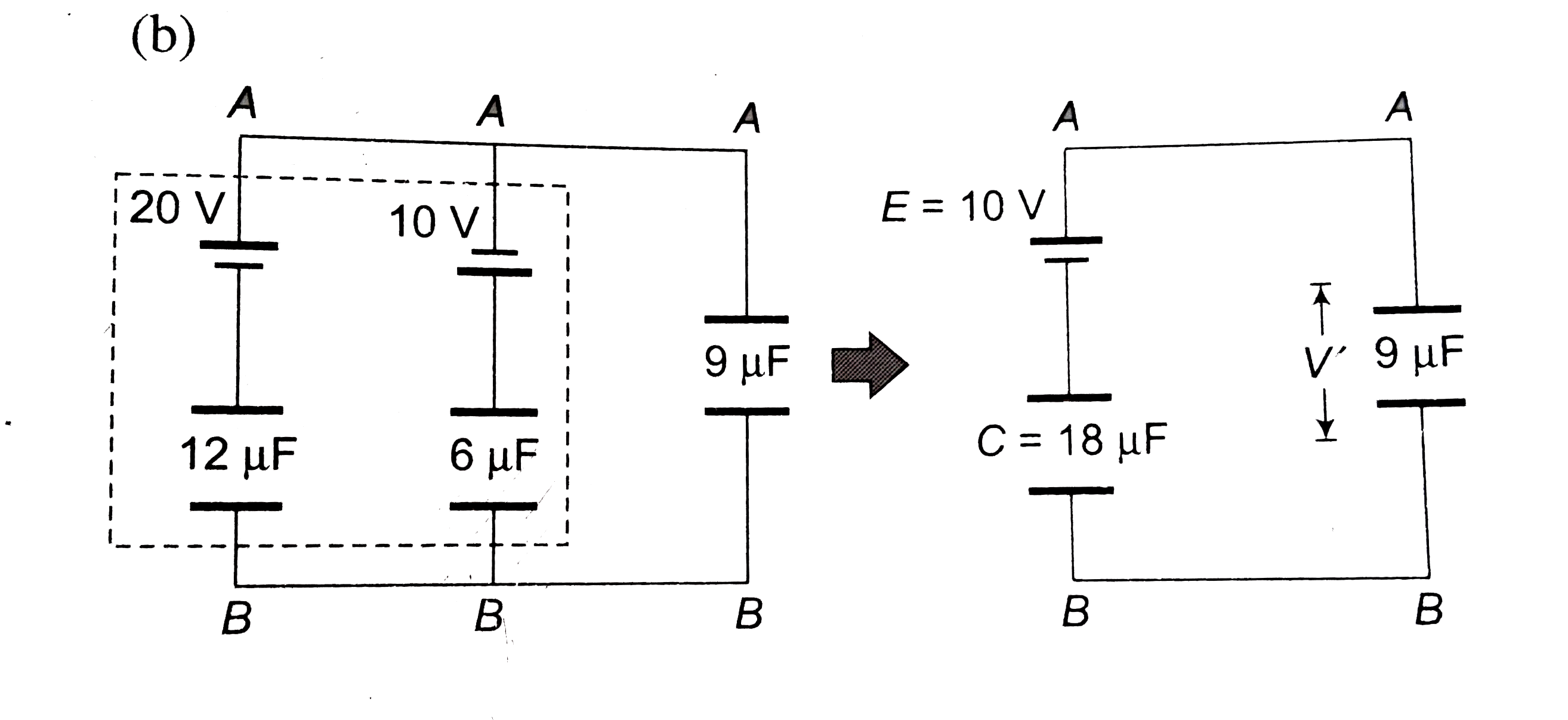 `E = (20 xx 12 - 10 xx 6)/(12 + 6) = 10 V` `C = 12 + 6 = 18mu F` `V' = ((80)/(18 + 9)) xx 10 = (20)/(3) V` charge on `9 mu F : 9 xx (20)/(3) = 60 mu C` 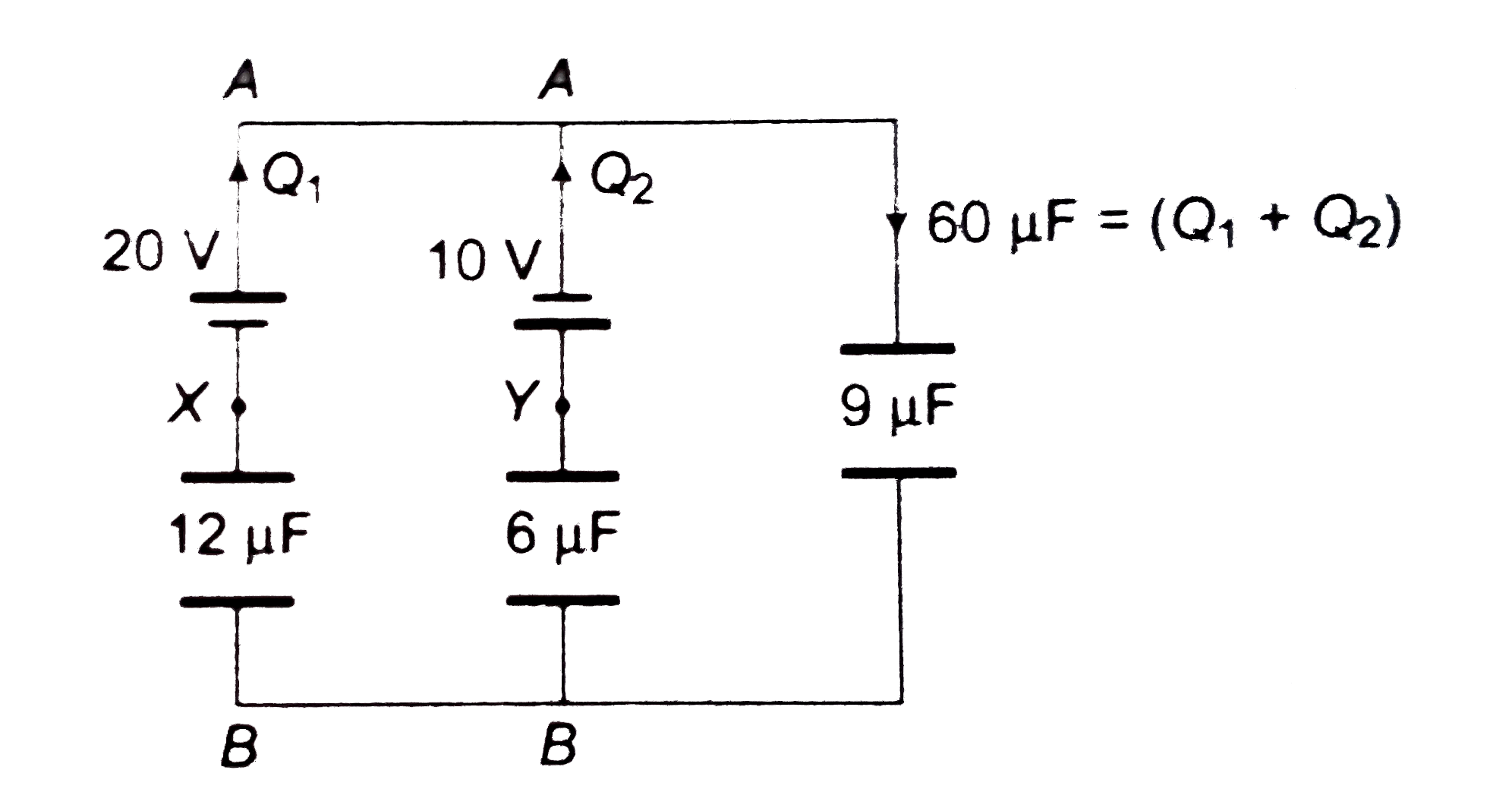 Branch `AXB` : `V_A - 20 + (Q_1)/(12) = V_B` `(Q_1)/(12) = V_B - V_A + 20 = -(20)/(3) + 20 = (40)/(3)` `Q_1 = 160 mu C` Branch `AYB` : `V_A + 10 + (Q_1)/(6) = V_B` `V_A - V_B + 10 = - (Q_2)/(6)` `(20)/(3) + 10 = (-Q_2)/(6)` `Q_2 =- 100 mu C` CHECK : `Q_1 + Q_2 = 60 mu C, O.K.` 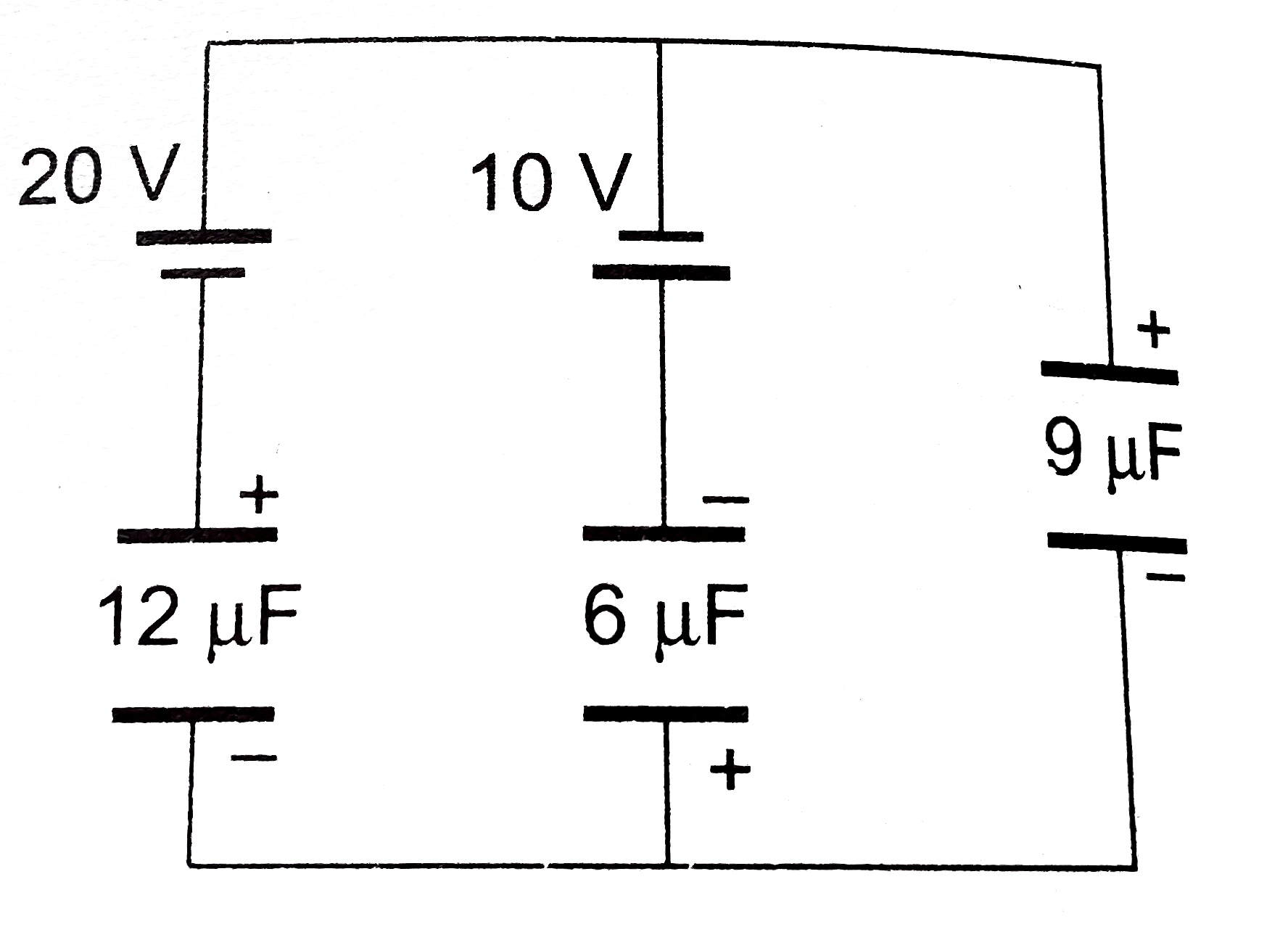 ( c) 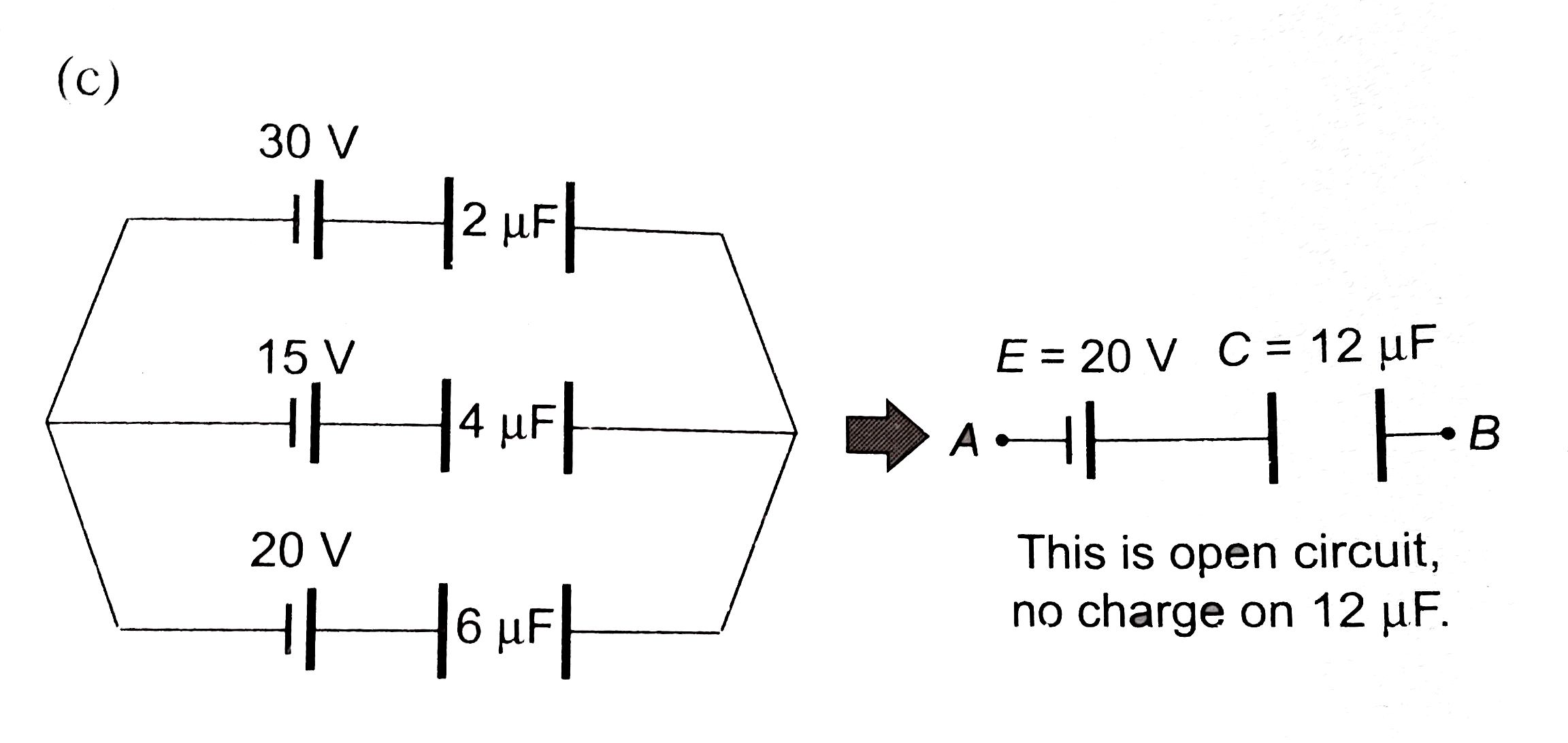 `E = (30 xx 2 +15 xx 4 + 20 xx 6)/(2 + 4+ 6) = 20 V` `C = 2 + 4 + 6 = 12 mu F` 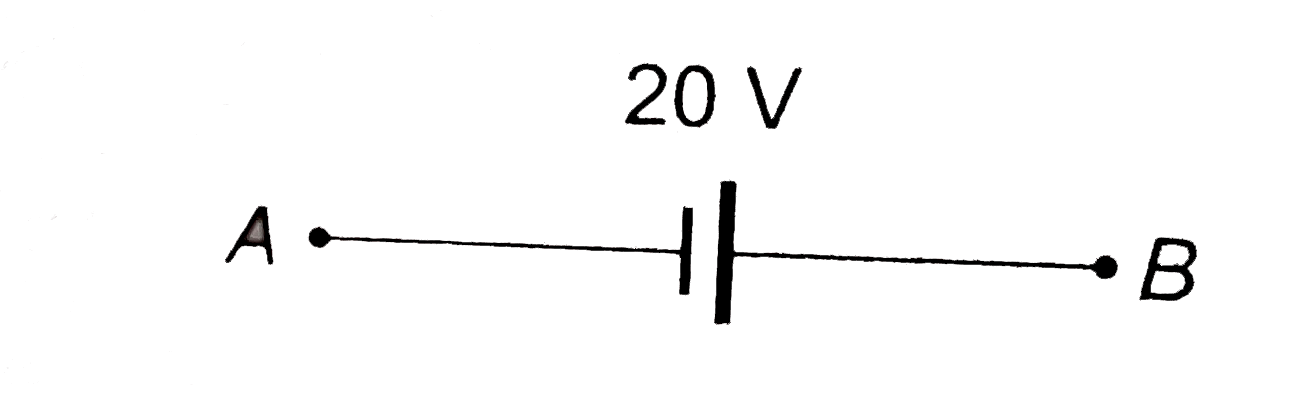 `V_B - V_A = 20 V` 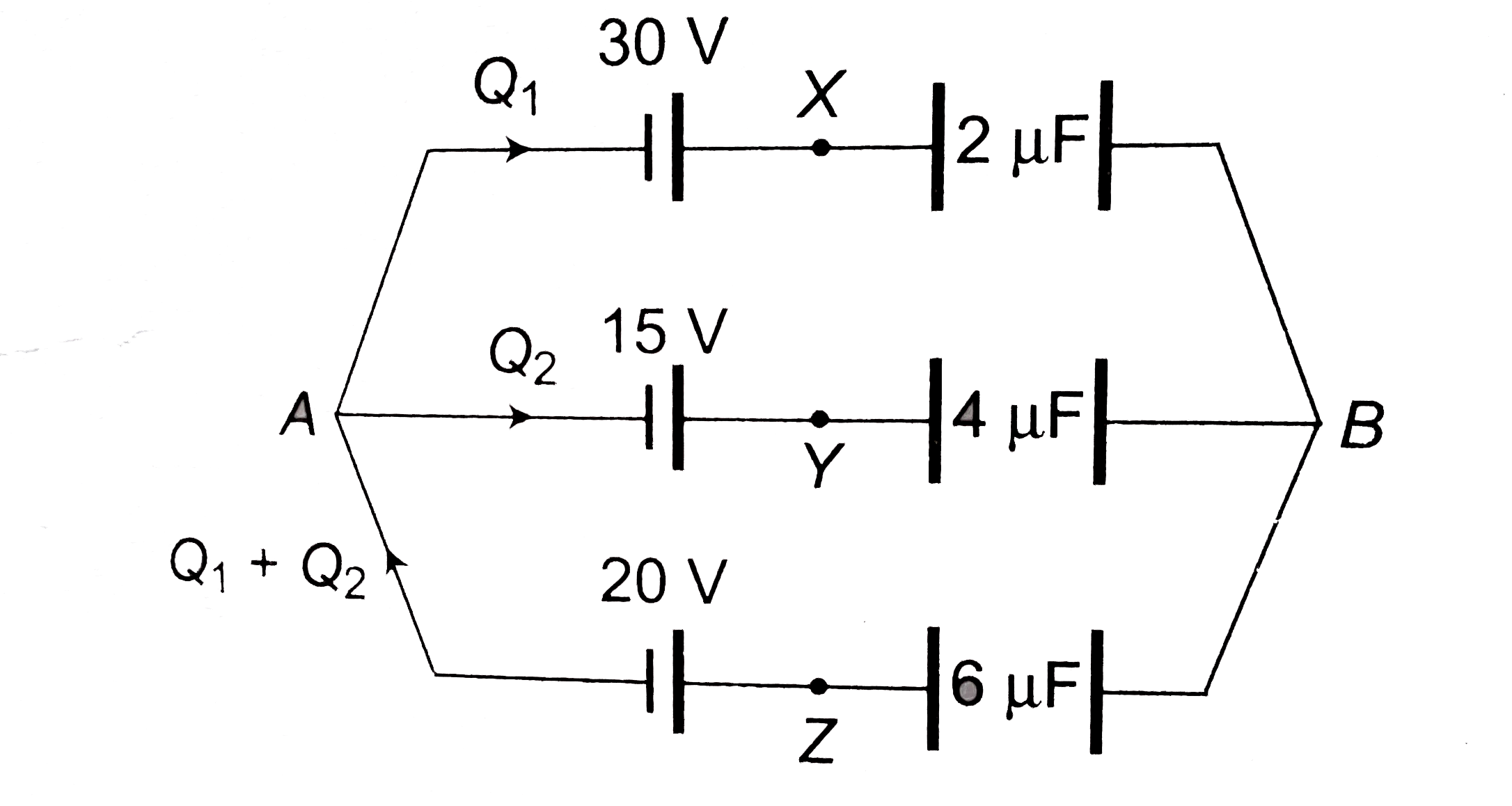 `AXB` : `V_A + 30 - (Q_1)/(2) = V_B rArr V_A - V_B + 30 = (Q_1)/(2)` `-20 + 30 = (Q_1)/(2) rArr Q_1 = 20 mu C` `AYB` : `V_A + 15 -(Q_2)/(4) = V_B rArr V_A - V_B + 15 = (Q_2)/(4)` `-20 + 15 = (Q_2)/(4) rArr Q_2 = -20 mu C` Check `AZB` : `V_A + 20 -(Q_1 + Q_2)/(6) = V_B` `V_A - V_B + 20 = (Q_1 +Q_2)/(6)` `-20 + 20 = (Q_1 + Q_2)/(6)` `Q_1 + Q_2 = 0`. |
|
| 42587. |
In a uniform electric field find the total flux associated with the given surfaces |
|
Answer» `a - 0, b - 0,c - 0` |
|
| 42588. |
A plane progressive wave of frequency 25Hz amplitude 2.5xx10^(-5)m and initial phase zero propagates along negative x-direction with a velocity of 300 m/s. At any instant, the phase difference between the oscillations at two points 6m apart along the line is phiand the corresponding amplitude difference is A |
|
Answer» A = 0 |
|
| 42589. |
Define angle of dip. Deduce the relation connecting angle of dip and horizontal component of earth's magnetic field at a place. |
|
Answer» Solution :In fig. CDAB is the MAGNETIC MERIDIAN . Magnetic field to earth `vecB_E` at the place is inclined at an ANGLE, EQUAL to angle of dip , `delta` from horizontal direction ALONG magnetic meridian . Hence , horizontal component `vecB_H` of earth.s magnetic field will be given by `B_H = B_E . cos delta ` or `(B_H)/(B_E)= cos delta` 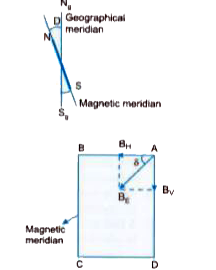
|
|
| 42590. |
A cyclotron in which protons are accelerated has a flux density of 1.57T. The variation of frequency of electric field is (in Hz) |
|
Answer» `4.8xx10^(8)` |
|
| 42591. |
A boyof mass M is applying a horizontal force to slide a boxof mass 'M'on a rough horizontal force to slide coefficient of friction between the shoes of the boyandthe flooris muandthat between the boxandthe flooris mu. Inwhichof the followingcases it is certainly not possible to slide the box ? |
|
Answer» `MU LT mu ,M lt M ` |
|
| 42592. |
Who is the poet of the poem "Dust of Snow"? |
|
Answer» ROBERT Charles |
|
| 42593. |
The time taken by the light to cross a glass of thickness 4 mm and refractive index (mu = 3), will be |
|
Answer» `4 xx 10^(-11) sec` |
|
| 42594. |
Which of the following particles has similar mass of electron ? |
|
Answer» Neutron |
|
| 42595. |
Electrostatic potential can be defined at any - point in the electric field because electric field is |
|
Answer» conseivative |
|
| 42596. |
The energy equivalent of one atomic mass unit is |
|
Answer» Solution :`E=Delta mc^2 Deltam= 1.6605 xx 10^(-27)KG` `=1.6605 xx 10^(-27)xx(3xx10^8)^2` `=1.4924 xx 10^(-4)J` `=(1.4924 xx 10^(-10))/(1.6 xx10^(-19))EV` `= 0.9315 xx 10^9 eV` = 931.5 MeV |
|
| 42597. |
One of the following does not apply to a concave mirror.This is : |
|
Answer» focal length is negative |
|
| 42598. |
Why do the electrostatic field lines not form closed loops ? |
|
Answer» Solution :The electric field lines have a TENDENCY to contract lengthwise like a STRETCHED ELASTIC string and separate from each other laterally. The reason is that opposite in chargres attract and similar CHARGES repel. The electric field lines do not form any closed LOOPS . |
|
| 42599. |
A Solid contains 5 xx 10^(21) number of atoms. If an electron is removed from each of 0.01% of number of atoms, find the charge gained by this solid? |
|
Answer» Solution :The solid gains positive charge hence Q= NE Where `N = (5 XX 10^(21) xx (0.01)/(100)) = 5 xx 10^(17)` `therefore Q= 5 xx 10^(17) xx 1.6 xx 10^(-19) therefore Q = +0.08C` |
|
| 42600. |
The orderly distribution of em. Waves according to their wavelengths is called _____. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Electromegnetic SPECTRUM | |