Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 38701. |
A body of mass m is tied to one end of a spring and whirled round in a horizontal plane with a constant angular velocity and elongation in the spring is 1 cm. If the angular velocity is doubled, the elongation in the spring becomes5 cm. The original length of spring is |
|
Answer» 13 cm |
|
| 38702. |
What is the phase difference the velocity and acceleration of a particle executing SHM? |
|
Answer» `pi` INSTANTANEOUS velocity `v= (DY)/(dt)= A omega cos omega t` `=A omega sin(omega t +(pi)/(2))` and instantaneous acceleration `a= (DV)/(dt)= -omega^(2)y = -omega^(2) [A sin omega t]` `therefore a= A omega^(2) sin (omega t+pi)`. Hence, phase difference between instantaneous velocity and acceleration. `=|(pi)/(2)-pi|=|-(pi)/(2)|=0.5pi`. |
|
| 38703. |
A smooth ball of mass 1 kg is projected with velocity 7 m//s horizontal from a tower of height 3.5 m. It collides elastically with a wedge of mass 3 kg and inclination of 45^(@) kept on ground. The ball collides with the wedge at a height of 1 m above the ground. Find the velocity of the wedge and the ball after collision. (Neglect friction at any contact.) |
|
Answer» `v_(y)=sqrt(2xx9.8x2.5)=7m//s` As `v_(x)=v_(y)` so it strikes the plane of incline perpendicularly. Let the ball rebound with velocity `V` and `v_(1)` be the velocity of the wedge 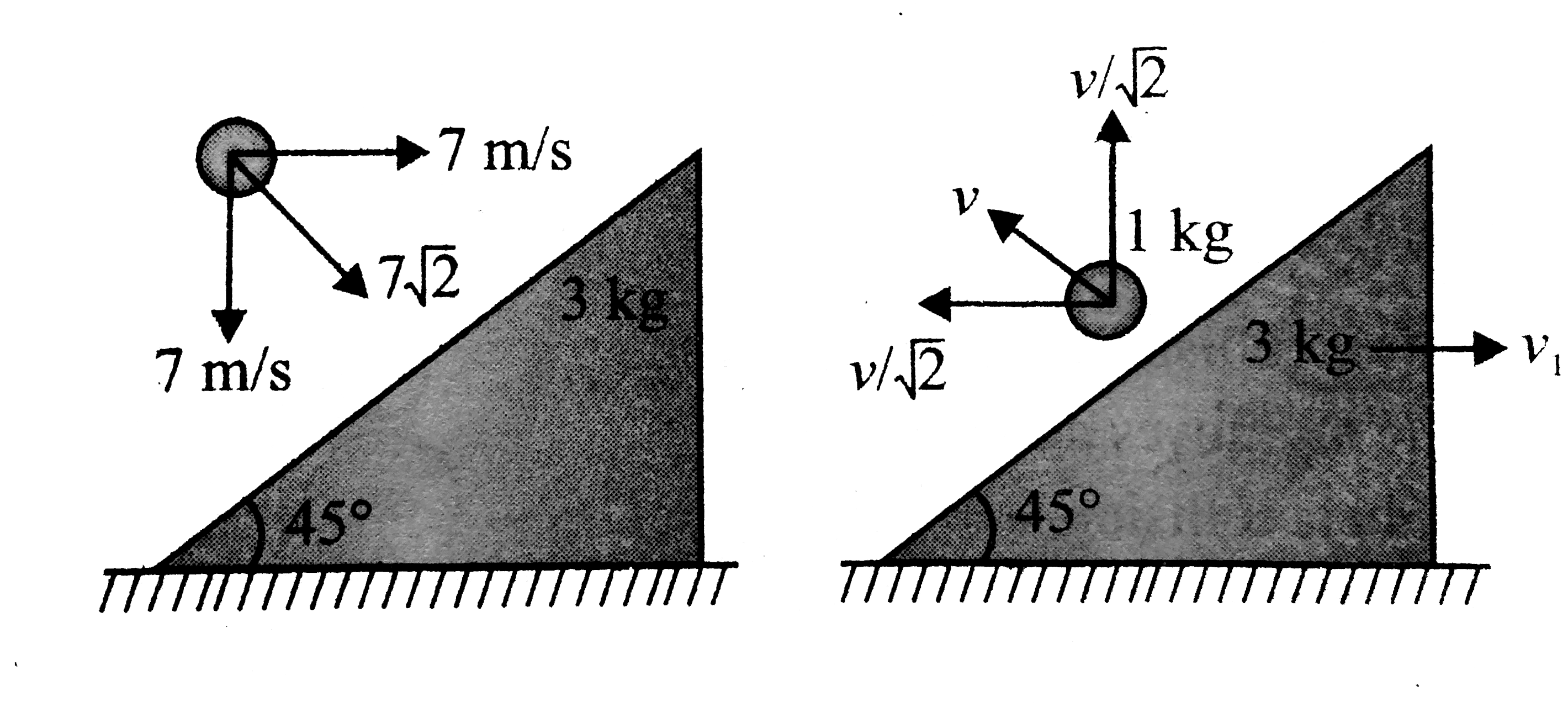 Applying the principle CONSERVATION of MOMENTUM in horizonal direction, we get `1xx7=1xxv/(sqrt(2))+3v_(1)` `7sqrt(2)=3sqrt(2)v_(1)-v`...........i Applying the equation for coefficient of restitution, we get `e=1=(v_(1)//sqrt(2)+v)/(7sqrt(2)),7sqrt(2)=v_(1)/sqrt(2)+v`.........ii Solving eqn i and ii `v_(1)=4m//s` and `v=5sqrt(2)m//s` |
|
| 38704. |
Which of the following is the most precise device for measuring length (i) a vernier calipers with 20 divisions on the sliding scale (ii) a screw gauge of pitch 1mm and 100 divisions on the circular scale (iii) an optical instrument that can measure length to within a wavelength of light? |
|
Answer» VERNIER calipers |
|
| 38705. |
the average depth ofindian ocean is about 3000m.Thevalue of frictional compression((DeltaV)/V) of water at the bottom of the ocean is (given that the bulk modulus of water is (2.2xx10^(9)Nm^(-2),g=9.8ms^(-2),PH_(2)O=1000kg.m^(-3)) |
|
Answer» Solution :The pressureexertedby a 3000 m columnof wateron the BOTTOM layer `p=h rho g=3000 m xx 1000 kg m^(-3) xx 10ms^(-2)` `=3xx10^(7)Nm^(-2)` FRACTIONAL COMPRESSION `DeltaV//V`, is `DeltaV//V = "stress" //B=(3xx10^(7))//(2.2xx10^(9)) ` `=1.36 xx 10^(-2) or 1.36%` |
|
| 38706. |
Estimate the mean free path and collision frequency of a nitrogen molecule in a cylinder containing nitrogen at 2.0 atm and temperature 17^(@)C. Take the radius of a nitrogen molecule to be roughly 1.0 Å. Compare the collision time with the time the molecule moves freely between two successive collisions (Molecular mass of N_(2) = 28.0 u). |
|
Answer» Solution :Use the formula for mean free path: `barl= (1)/(SQRT(2)pind^(2))` where d is the diameter of a molecule. For the given PRESSURE and temperature `N//V= 5.10 XX 10^(25) m^(-3)` and `= 1.0 xx 10^(-7) m. v_("rms") = 5.1 × 10^(2) m s^(-1)`. `"collisional FREQUENCY" = (v_("rms"))/(l) = 5.1xx 10^(9)s^(-1)`. Time taken for the collision= `d//v_("rms") = 4xx 10^(-13) s`. Time taken between successive collisions = `1//v_("rms")= 2 xx 10^(- 10) s`. This the time taken between successive collisions is 500 times the time taken for a collision. Thus a molecule in a gas moves essentially free for most of the time. |
|
| 38707. |
What happens to coefficient offriction when weight of the body is doubled. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Remainsunchanged. | |
| 38708. |
At the two ends of a light string, passing over a stationary, light, smooth pulley, two masses m and 2m are attached. Length of the string on either side of the pulley was the same initially, and the two masses were at a height of 13.08. After the system is released, what will be the velocities of the two masses when the mass m rises by 6.54m? At that moment, if the string snaps suddenly, find the time taken by the masses to reach the ground. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :VELOCITY of each 6.54 m`CDOT s^(-1) ,t_(1) = 2.77 s, t_(2) = -0.67 `s | |
| 38709. |
When 10 observation are taken the random error is x when 100 observation are taken the random error becomes |
|
Answer» `X // 10` |
|
| 38710. |
Water is falling down at the rate of 1.8 Kg per minute from a vetical tube. The radius at the bottom of the tube is 0.004 m and pressure around it is 0.76m of Hg. The diameter of the tube at a height of 0.5 m from the bottom is 0.005 m. find the pressure at that point. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :0.724 m of HG | |
| 38711. |
The mass of a body at the centre of the earth is |
|
Answer» infinite |
|
| 38712. |
A bullet of mass 0.012kg and horizontal speed 70 ms^(-1) strikes a block of wood of mass 0.4kg and instantly comes to rest with respect to the block. The block is suspended from the ceiling by means of thin wires. Calculate the height to which the block rises. Also, estimate the amount of heat produced in the block. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`= 21.2 CM, 28. 5J` | |
| 38713. |
Two heavenly bodies S_(1) and S_(2), not far off from each other are ssen to revolve in orbit |
|
Answer» AROUND their COMMON centre of mass |
|
| 38714. |
Draw the diagram to depict reflection of sound (a) plane surface, (b) convex surface and (c) concave surface. |
Answer» SOLUTION :
|
|
| 38715. |
A piece of metal of mass 112g is heated to 100^@Cand dropped into a copper calorimeter of mass 40g containing 200g of water at 16^@C Neglecting heat loss, the specific heat of the metal is nearly, if the equilibrium temperature reached is 24.1^@C |
|
Answer» `0.294 "cal/gm"^@C` |
|
| 38716. |
A bubble of radius 2cm is blown inside a cold drink using a straw. If the surface tension of liquids is 60 dyme/cm. Find the workdone (in ergs) in blowing the bubble? |
|
Answer» `960pierg` |
|
| 38717. |
The isothermal Bulk modulus of an ideal gasat pressure P is |
|
Answer» <P>P |
|
| 38718. |
When a stopper is pulled from a filled wash basin, the water drains out while circulating like a small whirl pool. The angular velocity of a fluid element about a vetical axis through the orifice appears to be greater near the orifice. The angular velocity of fluid element varies |
|
Answer» INVERSELY as the square of its DISTANCE from the AXIS through the ORIFICE |
|
| 38719. |
A circular disc of mass 10 kg is suspended by a wire attached to its centre. The wire is twisted by rotating the disc and released. The period of torsional oscillations is found to be 1.5s. The radius of the disc is 0.15m. Determine the torsional spring constant of the wire. (Note : Torsional spring constant 'alpha' is defined by the relation J=-alpha theta where J is the restoring couple is torque). |
|
Answer» Solution :`T=2pisqrt((I)/(ALPHA))or alpha=(4pi^(2)I)/(T^(2))` `"i.e."alpha=(4pi^(2)((MR^(2))/(2)))/(T^(2))=(2pi^(2)MR^(2))/(T^(2))""THEREFORE alpha=(2XX(3.142)^(2)xx10xx(0.15)^(2))/((1.5)^(2))=(4.4425)/(2.25)` `alpha="1.974 Nm rad"^(-1)` |
|
| 38720. |
A cyclic process is shown on the p-T diagram. Which of the curves show the same process on a V-T diagram ? |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 38721. |
What is the work done in holding a 15 kg suitcase while waiting for a bus for 15 minutes? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :ZERO. As the DISPLACEMENT is zero, W=0. | |
| 38722. |
Find the false statement |
|
Answer» Gravitational FORCE acts along the line joining the TWO interacting particles |
|
| 38723. |
A vehicle of mass 120kg is moving with a velocity of 90kmph. What force should be applied on the vehicle to stop it in 5s. = |
| Answer» ANSWER :A | |
| 38724. |
A stone falls freely under gravity. It covers distance h_1, h_2 and h_2.In first 5 sec, next 5 sec and next 5 sec respectively. The relation between h_1, h_2 and h_3 is |
|
Answer» `h_1 = (h_2)/(3) = (h_3)/(5)` |
|
| 38725. |
Can we boil water inside a satellite revolving earth? |
| Answer» Solution :No, water gets boiled with the process of CONVECTION and it is based on the fact that a liquid becomes lighter on becoming hot and rises up. Now INSIDE the satellite REVOLVING around earth, everything is under the STATE ofweightlessness, so this process cannot take place and hence, boiling of water is not POSSIBLE. | |
| 38726. |
Its wished to prepare four lenses double convex, convexo concave double concave and concavo- convex by the two cusued surfaces of radii of curvature +20cm and +30cm of refractive index 1.5. What are the values of their focal lengths in the given order. |
|
Answer» `+20CM,-20cm,+120CM,-120cm` |
|
| 38727. |
A lift is moving up with a constant retardation of 2 m//s^(2). When its upward velocity is 5 m/s, a boy in the lift tosses a coin, imparting it an upward velocity of 3 m/s, w.r.t. himself. His fingers at the moment of toss are midway between the floor and cciling, whose total height is 2 m. Displacement of coin when it hits the ground is x metre (in earth frame). Value of x is : (g = 10 m//s^(2)) |
|
Answer» Acceleration `= - 10 m//s^(2)` Now, `h = ut + (1)/(2) a t^(2)` 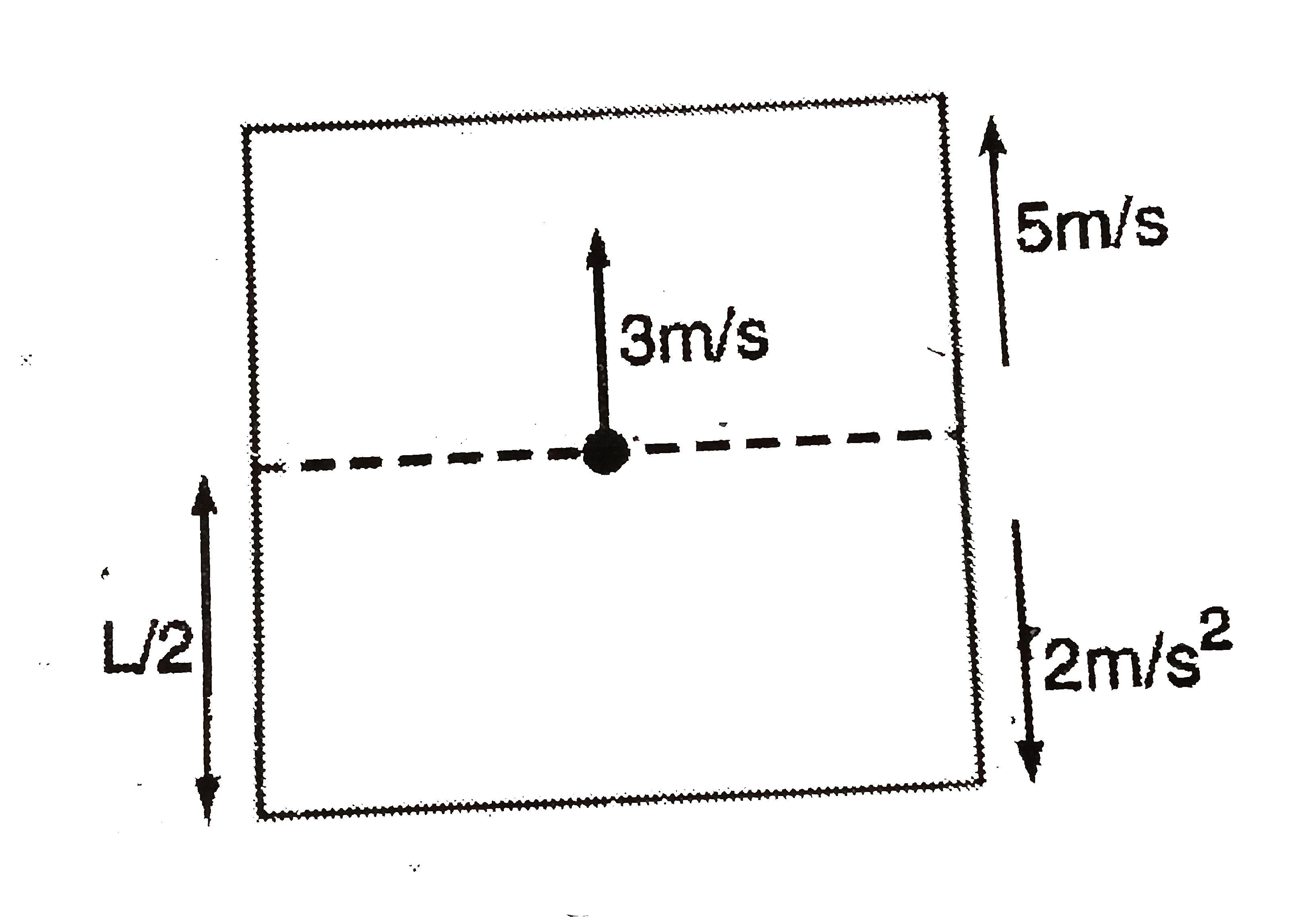
|
|
| 38728. |
(A) : In rolling, all points of a rigid body have the same linear speed. (R) : The rotational motion donot change the linear velocity of rigid of rigid body. |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are true 'R' is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of 'A' |
|
| 38729. |
A machine gun having a power 27 kW fires .n. bullets per second each of mass 10 gm. If the velocity of each bullet is 300 ms^(-1), the value of .n. is |
|
Answer» 60 |
|
| 38730. |
Explain the variations of acceleration due to gravity inside and outside the earth and draw the graph. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`implies`In `g(r) = 4/3 pi Grrho, 4/3 piGrho`Gp is CONSTANT . `:. g(r) prop r ` Means, the gravitational ACCELERATION (g) at a point inside the earth is directly proportional to the distance of that point from the centre of the earth. `implies` And `g(r) = (GM)/r^2` where `r gt gt R_E`so ,where `g(r) prop 1/r^2` where ` r gt gt R_E`. Hence starting from the centre of the earth g(r) increases in directly proportion as r increases and then OUTSIDE the surface g(r) decreases as inverse square of distance. `implies` The variations in gravitational acceleration with below the surface of earth and above the height from the surface is shown as in figure. 
|
|
| 38731. |
Calculate the centripetal acceleration of moon towards the earth |
|
Answer» Solution :The centripetal acceleration is given by `a = (v^2)/(r )` .This expression EXPLICITLY depends on Moon.s speed which is nontrivial. We can work with the formula `omega^2 R_m = a_m` `a_m`is centripetal acceleration of the Moon due to Earth.s GRAVITY. `omega `is angular VELOCITY `R_m`is the distance between Earth and the Moon, which is 60 times the radius of the Earth. `R_m = 60 R = 60 xx 6.4 xx 10^6 = 384 xx 10^6 m` As we know the angular velocity `omega = (2pi)/(T)` and `T = 27. 3 days = 27.3 xx 24 xx 60 xx 60 sec= 2.358 xx 10^6 sec ` By substituting these values in the formula for acceleration `a_m = ((4pi^2) (384 xx 10^6) )/((2.358 xx 10^6)^2) = 0.00272 MS^(-2)` The centripetal acceleration of Moon towards the Earth is` 0.00272 ms^(-2)` |
|
| 38732. |
Water with detergent dissolved in it should have small angles of contact. |
|
Answer» Solution :The clothes have narrow PORES or spaceswhich act as capillaries . The HEIGHT of liquid in capillary, `h=(2Tcostheta)/(rrhog)` `therefore` Height h is proportinal to `costheta` (Where `theta` is ANGLE of CONTACT). As the `theta` is smaller for DETERGENT , therefore `costheta` will be large . Due to this the detergent will penetrate more in the narrow pores of the clothes. |
|
| 38733. |
Establish the following vector inequalities geometrically or otherwise :(a)|a+b|le|a|+|b| (b) |a+b|ge||a|-|b||(c ) |a-b|le|a|+|b|(d)|a-b|ge||a|-|b||When does the equality sign above apply ? |
| Answer» Solution :HINT : The sum (difference ) ofany two sides of a TRANGLE is never less third side . EQUALITY HOLDS for collinear vectors. | |
| 38734. |
A car moving on a straight road accelerates from a speed of 4.1m//sto a speed of 6.9m//s in 5.0s. What was its average acceleration ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`u=4.1m//s, v=6.9m//s`, TIME `=t=5sec` AVERAGE ACCELERATION `a=(v-u)/t=(6.9-4.1)/5=0.56ms^(-2)` |
|
| 38735. |
Among the four graphs shown in the figure there is only one graph for which average velocity over the time interval (0,T) can vanish for a suitably chosen T. Which one is it ? |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 38736. |
Write the expressionfor impulse in terms of average force |
|
Answer» `F. DELTA t` |
|
| 38737. |
Forceand motion acts in the same direction given example |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Whenan applefallstowardsthe Earththe directionfo motionofthe APPLEAND THATOF forceare in thesamedownwarddirection. | |
| 38738. |
Relation between the colour and the temperature of a star in given by |
|
Answer» WIEN's DISPLACEMENT law |
|
| 38739. |
Find the work done in increasing the volume of a soap bubble by 700% if its radius is R and surface tension is T? |
|
Answer» `94R^(2)J` |
|
| 38740. |
1672 cal of heat is given to one mole ofoxygen at 0^(@)Ckeeping the volume constant. Rise in temperature is (R = 2 cal/mole/""^(@)K) |
|
Answer» `33.6^(@)C` |
|
| 38741. |
In the above problem it body is thrown down with velocity .u. the equation for the descent time is |
|
Answer» `h=1/2gt^2` |
|
| 38742. |
A vessel contailis 8 gm of air at 400K. Some amount of air leaks out through the hole provided to it. After some time, the pressure is halved and the temperature is changed to 300 K. Find the mass of the air escaped. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :According to the gas equation , `(P_(1))/(m_(1)T_(1)) = (P_(2))/(m_(2)T_(2)) m_(2)= (P_(2))/(P_(1)) xx (T_(1))/(T_(2)) xx m_(1)` `= (1)/(2) xx (4)/(3) xx 8 = (16)/(3) = 5.33 "" therefore m_(2) = 5.33` GM `rArr `MASSOF the gas ESCAPED `= m_(1)- m_(2) = 8-5.33 = 2.67` gm |
|
| 38743. |
A copper wire of length 2.2 m and a steel wire of length 1.6 m, both of diameter 3.0 mm, are connected end to end. When stretched by a load , the net elongation is found to be 0.70 mm. Obtain the load applied. |
|
Answer» Solution :The copper and steel wires are under same tensile STRESS because they have the same TENSION (equal to the load W) and the same area of cross- section A. We have stress = strain `xx` Young.s modulus. Therefore `W//A=Y_(C )xx(DeltaL_(C )//L_(C ))=Y_(S)xx(DeltaL_(S)//L_(S))` `DeltaL_(c )//DeltaL_(s)=(Y_(s)//Y_(c ))xx(L_(c )//L_(s))` `=(2.0xx10^(11)//1.1xx10^(11))xx(2.2//1.6)=2.5"".....(1)` The TOTAL elongation is given to be `DeltaL_(c )+DeltaL_(s)=7.0xx10^(-4)m""....(2)` Solving the above equations (1) & (2). `DeltaL_(c )=5.0xx10^(-4)m and DeltaL_(s)=2.0xx10^(-4)m`. Therefore`W=(AxxY_(c )xxDeltaL_(c ))//L_(c )` `=pi(1.5xx10^(-3))^(2)X[(5.0xx10^(-4)xx1.1xx10^(11))//2.2]` `=1.8xx10^(2)N` |
|
| 38744. |
The resistances corresponding to the lower and the upper fixed points, in a platinum resistance thermometer are 3.59 Omega and 3.65 Omega. What would be the resistance at a temperature equal to the freezing point of mercury(-37^(@)C)? |
|
Answer» Solution :Given : `R_(0) = 3.50 OMEGA, R_(100) = 3.65 Omega` and t = `-37^(@)C, R_(t) ` = ? Using t = `[ (R_(t) - R_(0))/(R_(100) - R_(0)) ] 100^(@)C ` We have , - `37^(@)C = [ (R_(t) - 3.50)/(3.65 - 3.50) ] 100^(@)` C `RARR R_(t) - 3.50 = - 0.056 "" R_(t) = 3.55 Omega` . `THEREFORE ` The required RESISTANCE is `3.55 Omega` |
|
| 38745. |
A body is thrown horizontally with a velocity u from a tower of height h After how much time and at what distance from the base of the tower will the body strike the ground? |
| Answer» Solution :Consider the VERTICAL motion `h=0+1/2"gt"^2 ,t=sqrt((2h)/G)` Horizontal displacement = Horizontal velocity X Time `=musqrt((2h)/g)` | |
| 38746. |
The shaft of a motor rotates at a constant speed of 1800 rpm. What is the angle in radians it has turned through in one second ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION : ANGLE it has turned in one rotation `=2pi` radian Number of ROTATIONS per second = `(18000)/60 = 300` RPS Angle through which the shaft turns in one second = `=300 xx 2pi = 600 pi` radian. |
|
| 38747. |
A tank of height 5m is full of water. There is a hole of cross-sectional area 1cm^(2) at its bottom. The volume of water that will come out from this hole per second is (g=10m//s^(2)) |
|
Answer» `10^(-3)m^(3)//s` |
|
| 38748. |
The cross-section area of the pipe shown in Fig. is 50 cm^(2)at the wider portions and 20 cm^(2)at the constriction. The rate of flow of water through the pipe is 4000 cm^(3)//s. Find , (i) the velocities at the wide and the narrow portions (ii) the pressure difference between these portions (iii) the difference in height between the mercury columns in the U-tube. |
|
Answer» ` P_1 - P_2 = rho ( v_2^(2) -v_1^(2))//2 = 1680 PA, h= P_1 - P_2 //rhog =1680//13.6 XX 10 ^(3)xx 9.8 = 0.013 m.` |
|
| 38749. |
A balloon starts from rest from the ground and moves with uniform acceleration g/8. When it reaches a height h a ball is dropped from it. Find the time taken by the ball to reach the ground. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Velocity of ballon when is at a height is `v=sqrt((2gh)/(8)=sqrt(gh)/2` `-h=vt-1/2gt^(2)` `-h=sqrt(gh)/2 t-1/2gt^2`  `-h=sqrt(gh)/2 t-1/2 gt^(2)` `1/2 gt^(2)-sqrt(gh)/2 t-h=0` SIMPLIFYING and taking only the POSITIVE value as NEGATIVE value of t is not acceptable we get `t=2 sqrt(h/g)` |
|
| 38750. |
A man can jump on the moon six times as high as on the earth. Why? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The VALUE of G on MOON is 1/6th g on EARTH. | |







