Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 44101. |
The relative permiability of a diamagnetic substance is ........ .. . |
|
Answer» (A) very large For a DIAMAGNETIC substance `chi_(m)` is negative, so `mu_(r)` will be less than 1. |
|
| 44102. |
A 1 Omega resistance in series with an ammeter is balanced by 25 cm of potentiometer by 50 cm. The ammeter shows a reding of 1.5 A. Then, the error in ammeter reading is |
|
Answer» `0.03 A` |
|
| 44103. |
In the above problem, when will be the fourth echo heard |
|
Answer» 4s |
|
| 44104. |
A cell of constant emf is first connected a resistance R_1 and then connected to a resistance R_2. If power delivered in both the cases is the same, then internal resistance of the cell is: |
|
Answer» `SQRT(R_1R_2)` |
|
| 44105. |
Which of the following has negative temperature coefficient of resistance? |
|
Answer» Copper |
|
| 44106. |
Figure shows four plates each of plate area A and separated between plates is d. Two switches S_(w1) and S_(w_2) can activate two batteries in the circuit. Now switch S_(w_2) is opened, what is the charge on plate 4? |
|
Answer» `-5/3 (epsilon_0AV)/(d)`  When both the switches are closed, CIRCUIT is Charge on plate 2 `C_(EQ)=(2C)/(3)=(2epsilon_(0)A)/(3d)` `q_(0)=((2C)/(3))(2V)=(4CV)/(3)` Charge on plate 1 Where switch `Sw_(2)` is opened, circuit is  `[((x-V))/(-2V)]C+(x-2V)C+xC=0` or `x=(5)/(3)V` Charge on plate 4 is `-(5)/(3)CV=(-5epsilon_(0)AV)/(2d)` Alternative method `(-q_(1))/(C)+V+(q_(2))/(C)=0` or `-q_(1)+q_(2)=-CV` `(-q_(1))/(C)-((q_(1)+q_(2)))/(C)+2V=0` or `q_(1)+2q_(2)=2CV` `q_(1)=(4CV)/(3),q_(2)=(CV)/(3)` |
|
| 44108. |
In a metre bridge, the balance point is found to be at 39.5 cm from the end A, when the resistor Y is of 12.5 Omega. Determine the resistance of X. Why are the connections between resistors in a Wheatstone or meter bridge made of thick copper strips? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`X =8.2 Omega` to MINIMISE RESISTANCE of the CONNECTIONS which are not accounted for in the bridge formula. | |
| 44109. |
Four transparent slabs having thickness t_(1)= 2cm, t_(2)= 4 cm, t_(3)= 3 cm" and "t_(4)= 5cm are introduced in one of the paths of light emitted by two narrow slits the ascending order of shift of the central fringe |
|
Answer» `t_(1), t_(2), t_(3), t_(4)` |
|
| 44110. |
Figure shows four plates each of plate area A and separated between plates is d. Two switches S_(w1) and S_(w_2) can activate two batteries in the circuit. What is the charge passing through battery 1? |
|
Answer» `3/2 (epsilon_0AV)/(D)`  When both the switches are closed, circuit is Charge on PLATE 2 `C_(eq)=(2C)/(3)=(2epsilon_(0)A)/(3d)` `q_(0)=((2C)/(3))(2V)=(4CV)/(3)` Charge on plate 1 Where switch `Sw_(2)` is OPENED, circuit is  `[((x-V))/(-2V)]C+(x-2V)C+xC=0` or `x=(5)/(3)V` Charge on plate 4 is `-(5)/(3)CV=(-5epsilon_(0)AV)/(2d)` ALTERNATIVE method `(-q_(1))/(C)+V+(q_(2))/(C)=0` or `-q_(1)+q_(2)=-CV` `(-q_(1))/(C)-((q_(1)+q_(2)))/(C)+2V=0` or `q_(1)+2q_(2)=2CV` `q_(1)=(4CV)/(3),q_(2)=(CV)/(3)` |
|
| 44111. |
In n-type semiconductors, majority charge carriers are |
|
Answer» HOLES |
|
| 44112. |
Figure-4.50 shows a thermal network of two metal rods of same cross section area. If the heat current from the ends A and B is 130 W, find the heat current through the curved metal rod. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 44113. |
Figure shows four plates each of plate area A and separated between plates is d. Two switches S_(w_1) and S_(w_2) can activate two batteries in the circuit. Switch S_(w_1) and S_(w_2) are closed, What is the charge on plate 2? |
|
Answer» `3/2 (epsilon_0AV)/(D)`  When both the switches are closed, CIRCUIT is Charge on plate 2 `C_(eq)=(2C)/(3)=(2epsilon_(0)A)/(3d)` `q_(0)=((2C)/(3))(2V)=(4CV)/(3)` Charge on plate 1 Where switch `Sw_(2)` is opened, circuit is  `[((x-V))/(-2V)]C+(x-2V)C+xC=0` or `x=(5)/(3)V` Charge on plate 4 is `-(5)/(3)CV=(-5epsilon_(0)AV)/(2d)` Alternative method `(-q_(1))/(C)+V+(q_(2))/(C)=0` or `-q_(1)+q_(2)=-CV` `(-q_(1))/(C)-((q_(1)+q_(2)))/(C)+2V=0` or `q_(1)+2q_(2)=2CV` `q_(1)=(4CV)/(3),q_(2)=(CV)/(3)` |
|
| 44114. |
As shown in figure a two slit arrangement with a source (S) which emits unpolarised light. I_(0) is the intensity of principle maxima when no polariseer is present. Now a polarised 'P' is placed as shown with its axis whose direstion is not given. Then |
|
Answer» the intensity PRINCIPAL MAXIMA is `(5)/(8)I_(0)` `A=A_(_|_)+A_(11)` `A_(_|_)=A_(_|_)^(1)+A_(_|_)^(2)=sin(kx-omega t)` `+A_(_|_)^(@)sin(kx-omega t+phi), A_(11)=A_(11)^((1))+A_(11)^((2))` `A_(11)=A_(11)^(@)[sin(kx-theta t)+sin(kx-omega t+phi)]` where `A_(_|_)^(@), A_(11)^(@)` care the amplitudes of either of the beam in `_|_` and 11 polarizations. `:. "Intensity" =` `= = {|A_(_|_)^(0)|^(2) + |A_(11)^(@)|^(2)}` `[sin^(2)(kx-omega t)(1+cos^(2)phi+2sin phi)` `+sin^(2)(kx-omega)sin^(2)phi]_("average")` `={|A_(_|_)^(0)|^(2) + |A_(11)^(@)|^(2)} ((1)/(2)).2(1+cos phi)` `=2|A_(_|_)^(@)|^(2).(1+cos phi)since |A_(_|_)^(@)|_("average") = |A_(11)^(@)|_("average")` With P: Assume `A_(_|_)^(2)` is blocked: Intensity `= (A_(11)^(1)+A_(11)^(2))+(A_(_|_)^(1))^(2)` `= |A_(_|_)^(@)|^(2) (1+cos phi) + |A_(_|_)^(@)|^(2). (1)/(2)` Given: `I_(0) = 4|A_(_|_)^(@)|^(2)` = intensity wityhout polariser at principal maxima. intensity principal maxima with polariser `= |A_(_|_)^(@)|^(2) (2+(1)/(2))` `= (5)/(8)I_(0)` Intensity at first minima with polariser `= |A_(_|_)^(@)|^(2) (1-1)+(|A_(_|_)^(@)|^(2))/(2) = (I_(0))/(8)` . |
|
| 44115. |
Initially conditions of L-C oscillator circuit ………. |
|
Answer» Q=0 , I=0 and t=0 |
|
| 44116. |
When load is applied to a wire the extension is 3 mm, the extension in the wire of same material, length but half the radius by the same load is : |
|
Answer» 0.75 mm or `Deltalprop1/(R^(2))` `therefore(Deltal_(2))/(Deltal_(1))=(r_(1)^(2))/(r_(2)^(2))=(2/1)^(2)=4` `rArrDeltal_(2)=4Deltal_(1)=4xx3=12mm` So, the correct CHOICE is (d). |
|
| 44117. |
The radioactivity of a sample is .X. at time .t_1. . and .Y. at a time .t_2. . If the mean life time of the specimen is .t. , the number of atoms that have disintegrated in the time interval (t_(1) -t_(2))is |
|
Answer» `Xt_(1) - Yt_(2)` |
|
| 44118. |
The rate of disintegration of a radioactive sample is R and the number of atoms presentat any time t is N. When R/N is taken along Y-axis and t is taken along X-axis, the correct graphs is |
|
Answer»
 `(dN)/DT = -lambda N ` where,`(dN)/dt=` rate of disintegration So, `R = -lambda N RARR R/N = - lambda =` constant where, `lambda= ` decay constant So, the graph `R/N` VERSUS t is as, So the CORRECT graph shown in option (d). |
|
| 44119. |
Tworesistorsalongwitherrorsare kownas R_(1)= (30 +-3) OmegaR_(2) = (60+- 3 ) Omega column- Ilistsfouralagebraticfunctions ofR_(1) R_(2)column-IIlistscorrespondingerrorswhereas column-IIIlisitstheabsoluteerrors pickthe correctoptionparallelcombinationof R1 and R2 |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 44120. |
In a car race, car A takes time t less than car B and passes the finishing point with a velocity v more than the velocity with which car B passes the point. Assuming that the cars start from rest and travel with constant accelerations a_1 and a_2 show that v/t=sqrt(a_1a_2) . |
|
Answer» Solution :The distance covered by both the cars is the same .THUS ,`s_(1)=s_(2)=s.` If the cars TAKE time `t_(1)` and `t_(2)` for the race and their velocities at the FINISH be `v_(1)` and `v_(2)` ,then it is given that `(v_(1))/(2)t_(1)`=s……….(1) and `(v_(2))/(2)t_(2)=s`.........(2) `therefore (v_(1))/(t_(2))=(v_(2))/(t_(1))=(v_(1)-v_(2))/(t_(2)-t_(1))=(v)/(t)` ............(3) `((v)/(t))^(2)=(v_(1)v_(2))/(t_(2)t_(1))=(v_(1))/(t_(1)).(v_(2))/(t_(2))`..........(4) `therefore(v)/(t)=sqrt(a_(1)a_(2))impliesv=t sqrt(a_(1)a_(2))` |
|
| 44121. |
Consider a point charge +q placed at the origin and another point charge -2p placed at a distance of 9 m from the charge +q . Determine the point between the two charges at which electric potential is zero. |
|
Answer» Solution :According to the superposition PRINCIPLE the total electric potential at a point is equal to the sum of the potentials DUE to each charge at that point. Consider at a distance x from the charge +Q as shown in the figure The toatal electric potential at P is zero. 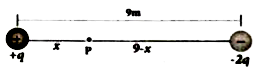 `V_("tot")=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))((q)/(x)-(2q)/((9-x)))=0` which gives `(q)/(x) =(2q)/((9-x))` or `(1)/(x)=(2)/((9-x))` Hence x =3 n |
|
| 44122. |
Orbital acceleration of an electron is ……….. |
|
Answer» `(pi^(2)N^(2)h^(2))/(2m^(2)r^(3))` `MVR=(nh)/(2pi)` `:.V=(nh)/(2pimr)` `:.(v^(2))/(r)=(n^(2)h^(2))/(4pi^(2)m^(2)r^(3))` `:.a_(C)=(n^(2)h^(2))/(4pi^(2)m^(2)r^(3))` [ `:.(v^(2))/(r)=` centripetal acceleration `a_(c)` ] |
|
| 44123. |
Tworesistorsalongwitherrorsare kownas R_(1)= (30 +-3) OmegaR_(2) = (60+- 3 ) Omega column- Ilistsfouralagebraticfunctions ofR_(1) R_(2)column-IIlistscorrespondingerrorswhereas column-IIIlisitstheabsoluteerrors pickthe correctoptionforseriescombinationof R1 and R2 . |
|
Answer» (III)(ii)(P ) |
|
| 44124. |
Tworesistorsalongwitherrorsare kownas R_(1)= (30 +-3) OmegaR_(2) = (60+- 3 ) Omega column- Ilistsfouralagebraticfunctions ofR_(1) R_(2)column-IIlistscorrespondingerrorswhereas column-IIIlisitstheabsoluteerrors pickthe correctoption |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 44125. |
A mark on the surface of a glass spehre (mu=1.5) is viewed from a diametrically opposite position. It appears to be at a distance 10 cm from its actual position. The radius of the sphere is |
|
Answer» 5 cm |
|
| 44126. |
An alternating voltage of frequency f is applied across a series LCR circuit. Let f_r be the resonance frequency for the circuit. Will the current in the circuit lag, lead or remain in phase with the applied voltage when (i) f gt f_r(ii) fltf_r (iii) f=f_r? Explain your answer in each case. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Current will LAG because. `V_(L) lt V_( C)` HENCE `V_(L) - V_(C) gt O` (ii) Current will lead, because. `V_(L) lt V_( C)` Hence `V_(L) - V_( C) lt O` (III) In phase |
|
| 44127. |
In an experiment to find focal length of a concave mirror a graph is drawn. The graph looks like ........... |
|
Answer»
OBJECT distance u, image distance v and focal length f `u=(ALPHA)` when v=f u=2f(object on centre of CURVATURE) v=2f and when u=f then v=`infty` (infinite) |
|
| 44128. |
The energy band gap is maximum in |
|
Answer» metals |
|
| 44129. |
How manystereoisomers arepossiblefor - |
Answer» Solution :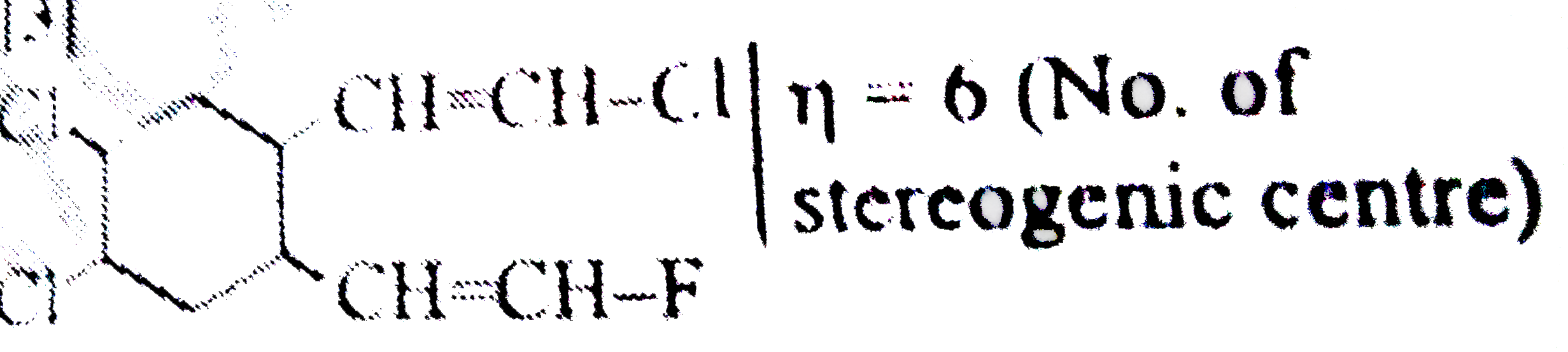 it isunsymetricmoleculeand no. of stereoimers `=2^(n)=2^(6)` |
|
| 44130. |
When a silver foil (Z = 47) was used in an alpharay scattering experiment , the number of alpha-particlesscattered at 30^(@) was found to be 200 per minute. If the silver foil is replaced by alumninium (z = 13) foil of same thickness, the number of alpha-particles scattered per minute at 30^(@) is nearly equal to |
|
Answer» 15 |
|
| 44131. |
Define electric resistance and write it's SI unit. How does the reisitance of a conductor vary if (a) conductor is stretched to 4 times of it's length (b) Temperature of a conductor is increased. |
|
Answer» Solution :Electric (R ) : The resistance offered by a flow of electrons in a CONDUCTOR is called electric resistance. S.I unit of resistance is ohm `(OMEGA)` The resistance of a conductor `R = (rho l)/(A) = (rho l^(2))/(V) implies R PROP l^(2)` (a) In first CASE, `R_(1) = R, l_(1) = l` (b) In second case, `l_(2) = 4l, R_(2) = ?` `(R_(2))/(R_(1)) = (l_(2)^(2))/(l_(1)^(2)) implies (R_(2))/(R) = ((4I)/(I))^(2) :. R_(2) = 16 R` (b) Variation of resistance with temperature is given by `R_(t) = R_(0) (1 + alpha t)` If temperature increases, resistance also increases. |
|
| 44132. |
A galvanometer of100Omega resistance gives full scale deflection when 10mA of current is passed.To convert it into 10 A range ammeter, the resistance of the shunt required will be : |
|
Answer» `10 OMEGA` |
|
| 44133. |
Is the source of magnetic field analogue to the source of electric field ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :No, the SOURCE of MAGNETIC field is not a magnetic charge, but in CASE of electric field the source of electric field is electric charge | |
| 44134. |
(A) : Dimensions of constant of proportionalities can be derived from dimensional method. (R): Numerical value of constant of proportionality can be found from experiments only.) |
|
Answer» Both (A) and (R) are TRUE and (R) is the CORRECT explanation of (A) |
|
| 44135. |
Atomic hydrogen is in thermodynamics equilibrium with its radiation. Find: (a) the ratio of probabilites of induced and spontaneous radiation of the atoms from the level 2P at a temperature T=3000K, (b) the temperature at which these probabilites become equal. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :ATOMIC hydrogen is in thermodynamics equilibrium with its radiation, Find: (a) the RATIO to probabilites of induced and SPONTANEOUS RADIATIONS of the atom from the level `2P` at a temperature `T=3000K`, (b) the temperature at which these probabilites become equal. |
|
| 44136. |
Figure 33.5 depicts the grid characteristics of a triode plotted at anode voltages of 450 V and 600 V. Find the triode's internal resistance R_(i) in the linear section of the characteristic and its amplification factor mu, i.e. the ration of the change in the anonde voltage to the change in the grid voltage which cauases a given change in the anode current. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 44137. |
In the circuit shown in Fig. 4.68, the cells epsilon_(1) " and " epsilon_(2) have emf's of 4 V and 8 V and internal resistances of 0.5 Omega and 1 Omega respectively. Calculate the current in each resistance. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 44138. |
What happens to the interference pattern if one of the slits in Young's double-slit experiment is closed ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The interference PATTERN DISAPPEARS and we observe diffraction pattern DUE to a single-slit. | |
| 44139. |
A pan filled with hot food cools form 94^(@)C to 86^(@)C in 2 minutes . When the roo temperature is 20^(@)C. How long will it cool from 74^(@)C to 66^(@)C ? |
|
Answer» 2 MINUTES In Case (i), `(94-86)/(2)prop((94+86)/(2)-20)` `IMPLIES (8)/(2)prop(90-20)` or `4prop70""….(1)` In Case (ii), `(74-66)/(t)prop((74+66)/(2)-20)` `(8)/(t)prop(70-20)` `(8)/(t)prop50""....(2)` Dividing (1) and (2) `(t)/(2)=(70)/(50)` `t=(14)/(5)` `t=2.8` minutes |
|
| 44140. |
A particle of mass 10 g is performing SHM. Its kinetic energies are 4.7 J and 4.6 J when the displacements are 4 cm and 6 cm , respectively. Compute the period of oscillation. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Data : m = 0.01 kg, `KE_(1) = 4.7 J, x_(1) = 4 xx 10^(-2) m, KE_(2) = 4.6 J ` ` x_(2) =6 xx 10^(-2) m` Since the total energy of a PARTICLE is SHM is CONSTANT . ` KE_(1) + PE_(1) = KE_(2) +PE_(2)` ` KE_(1) -KE_(2) = PE_(2) -PE_(1) = 1/2m omega^(2) (x_(2)^(2) -x_(1)^(2))` ` 1/2 m((4pi^(2))/(T^(2)) (x_(2)^(2) -x_(1)^(2)) "" (therefore omega = (2pi)/T)` ` T^(2) = 2mpi^(2) = ((x_(2)^(2)-x_(1)^(2)))/(KE_(1) -KE_(2))` ` = 2(0.01) pi^(2) ([(6^(2)-4^(2)) xx 10^(-4)])/(4.7 - 4.6)` ` = 0.2 pi^(2) xx 20 xx 10^(-4)= 4pi^(2) xx 10^(-4)` The period of oscillation of the particle. ` T= sqrt(4pi^(2) xx 10^(-4)) = 2pi xx10^(-2) = 6.284 xx 10^(-2)S` |
|
| 44141. |
माचिस की डिब्बी दर्शाती है |
|
Answer» घनीय ज्यामिति |
|
| 44142. |
The magnetism of magnet is due to |
|
Answer» the SPIN MOTION of electrons |
|
| 44143. |
Find unit vector in direction of friction force acting on block placed on plank 'p' (Given : bar(V)_(P)=7i - 2j,bar(V)_(B)=3hat(i)+hat(j)) |
|
Answer» `(4)/(5)hat(i)-(3)/(5)hat(j)` Here, `t_(0)` is the time when VELOCITY becomes zero. Since, the given time t = 5s is greater then `t_(0)`. The distance `d=|(u^(2))/(2a)|+|(1)/(2)a(t-t_(0))^(2)|=(144)/(2xx4)+(1)/(2)xx4xx4=18+8=26m` |
|
| 44144. |
In a series combination of two capacitances C and C (Cgt C) (as shown in the circuit), |
|
Answer» C' STORES more ENERGY than C |
|
| 44145. |
Potential at a point A is 3 volt and at a point B is 7 volt, an electron is moving towards A from B. |
|
Answer» It must have some K.E at B to REACH A |
|
| 44146. |
Answer the questions : In what way is diffraction from each slit related to the interference pattern in a doutler slit experiment ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The INTENSITY of interference fringes in a double SLIT ARRANGEMENT is modulated by diffraction PATTERN of each slit. | |
| 44147. |
Figure here gives the speed-time graph for a body. The distance travelled between I = 1.0 second and t = 7.0 second is nearest to: |
|
Answer» Solution :Here the AREAS from t=1 sec. to t =7 sec are From t=1 to t=2 `x_1=1xx2+(1)/(2)xx1xx2=3 m` From t=2 to t=3 `x_21xx4=4m` From t=3 to t=4 `x_3=(1)/(2)xx1xx4=2 m` From t4 to t=5 `x_4=(1)/(2)xx1xx-4= -2m` Net distance =3+4+2-2-4=3m. |
|
| 44148. |
Mention various (any four) energy losses in a transformer. |
|
Answer» Solution :Possible causes of energy losses in TRANSFORMERS are as FOLLOWS: (i) Flux leakage : There is always some leakage of magnetic flux. It can be reduced by WINDING the primary and secondary coils one over the other. (ii) Resistance of the windings : The wires used for the windings have some resistance and hence some energy is lost due to heat produced in wire. It can be minimised by taking thick insulated copper wire for windings. (iii) Eddy currents : The alternating magnetic flux INDUCES eddy currents in iron core, which results loss of electrical energy. To minimise it we use a laminated iron core. (iv) Hysteresis: As the magnetisation cycle of iron core is repeated again and again some loss of energy takes place due to magnetic hysteresis. To minimise it we prefer a SOFT iron core for which hysteresis loss is less. |
|
| 44149. |
An alternating current is given by i=(3sin omegat+4cos omegat)A. Find rms current. |
|
Answer» Solution :`i=3sin OMEGA t+4 cos omega t` `(int_(0)^(t)i^(2).dt)/(int_(0)^(t)dt)=(int_(0)^(T)(3sin OMEGAT+4cos omegat)^(2)dt)/(T)` `=(1)/(T)int_(0)^(T)(9sin^(2)omegat+16cos^(2)omegat+12sin 2omegat)dt` `=(25)/(2)""therefore i_("rms")=(5)/(sqrt2)A` |
|
| 44150. |
In the circuit diagram shown in figure, potential difference across 3Omega resistance is 20 V. Then, match the following two columns. |
|
Answer» |
|







