Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 44201. |
A T.V tower is 150 m tall. If the area around the tower has a population density of 750 km^(2), then the population covered by the broadcasting tower is about : (Re = 6400 km) |
|
Answer» `4.5 XX 10^(6)` |
|
| 44202. |
Calculate the mass defect, binding energy and binding energy per nucleon of an alpha particle ? (An alpha- particle is nothing but helium nucleus. Hence its symbol is ._2He^4. It contains 2 protons, 2 neutrons with a mass number 4. Mass of hydrogen atom m_H= 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron m_n = 1.008665 u, Atomic number of helium Z = 2, Mass number of helium A = 4, Mass of helium atom m_n = 4.00260 u.) |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Mass defect , `DELTAM=Zm_H+(A-Z)m_n-m_a` [(2)(1.007825)+(4-2)(1.008665)-4.00260]u `=(2xx1.007825+2xx1.008665-4.00260)u` Mass defect, `Deltam`=0.03038 u `THEREFORE` Binding energy of the nucleus =`(Deltam)C^2` `=(0.03038)uxxC^2` `=0.03038xx931.5` MEV (`because 1uxxC^2` = 931.5 MeV) =28.3 MeV Binding Energy per NUCLEON = `28.3/4` MeV Binding energy per nucleon = 7.075 MeV |
|
| 44203. |
A motor car running at the rate of 7 m/s can be stopped by it's brakes in 10 meters. Prove that the total resistance to car's motion, when the brakes are on is one quarter of the weight of the car. |
|
Answer» F = w/4 |
|
| 44204. |
Two short bar magnets are placed at the distance along the same axis with their south poles facing each other. These magnets will repel with a force which varies inversely as : |
|
Answer» `d^4` |
|
| 44205. |
Electric field at centre of quarter circular ring having charge density lambda is _____ |
|
Answer» `(sqrt(2)LAMBDA)/(4piepsilon_(0)R)` |
|
| 44206. |
Two waves of light in air, of wavelength lambda= 600.0 nm, are initially in phase. They then both travel through a layer of plastic as shown in Figure, with L_(1)= 4.00 mu m, L_(2)= 3.50 mu m, n_(1) = 1.42, and n_(2) = 1.60. (a) What multiple of lambda gives their phase difference after they both have emerged from the layers? (b) If the waves later arrive at some common point with the same amplitude, is their interference fully constructive, fully destructive, interme- diate but closer to fully constructive, or intermediate but closer to fully destructive? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) 0.700, (B) intermediate CLOSER to FULLY destructive | |
| 44207. |
When we consider a point charge q moving with a velocity vecv at a given time in presence of magnetic field vecB, the charged particle experiences a magnetic force vecF_m = q[vecv xx vecB]. The force was first given by H.A. Lorentz and is called the Lorentz magnetic force. The force depends on q, vecv and vecB and involves a vector product of vecv and vecB. The force acts in a side ways direction perpendicular to both the velocity and magnetic field and the direction is given by right hand thumb rule for vector product. Obviously force on a negative charge is opposite to that on a positive charge. When will a moving charge experience maximum force due to a magnetic field? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The moving CHARGE EXPERIENCES maximum force `F = q vB` when `VECV` and `vecB` are in MUTUALLY perpendicular directions. | |
| 44208. |
When we consider a point charge q moving with a velocity vecv at a given time in presence of magnetic field vecB, the charged particle experiences a magnetic force vecF_m = q[vecv xx vecB]. The force was first given by H.A. Lorentz and is called the Lorentz magnetic force. The force depends on q, vecv and vecB and involves a vector product of vecv and vecB. The force acts in a side ways direction perpendicular to both the velocity and magnetic field and the direction is given by right hand thumb rule for vector product. Obviously force on a negative charge is opposite to that on a positive charge. Under what condition does a moving charge experience minimum force due to a magnetic field present there? |
| Answer» Solution :A MOVING charge EXPERIENCES no (minimum) FORCE when `vecv` is either parallel or antiparallel to `VECB`. | |
| 44209. |
Kinetic energy of electron in nth orbit is given by |
|
Answer» `(RHC)/(2N^(2))` |
|
| 44210. |
When we consider a point charge q moving with a velocity vecv at a given time in presence of magnetic field vecB, the charged particle experiences a magnetic force vecF_m = q[vecv xx vecB]. The force was first given by H.A. Lorentz and is called the Lorentz magnetic force. The force depends on q, vecv and vecB and involves a vector product of vecv and vecB. The force acts in a side ways direction perpendicular to both the velocity and magnetic field and the direction is given by right hand thumb rule for vector product. Obviously force on a negative charge is opposite to that on a positive charge. Define SI unit of magnetic field on the basis of Lorentz force. |
| Answer» Solution :In the relation `vecF_m = q[vecv xx vecB] ` if `q = 1 C, vecv = 1 ms^(-1), vecB = 1 T and vecv and vecB` are in MUTUALLY perpendicular directions, then `F_B = 1N`. Hence we define one unit field in SI system as the field in which a particle having a charge of 1C moving with ALONG direction perpendicular to the direction of negative field with a constant VELOCITY of `1 ms^(-1)` experiences a force of 1 N . This unit of magnetic field is called TESLA (T). | |
| 44211. |
The intensity of an electric field depends only on the co-ordinates x, y and z as follows: vecE=a((xhati+yhatj+zhatk))/((x^2+y^2+z^2)^(3//2))unit. The electrostatic energy stored between two imaginary concentric spherical shells of radii R and 2R with centre at origin is |
|
Answer» `(4piepsilon_0a^2)/R` |
|
| 44212. |
When we consider a point charge q moving with a velocity vecv at a given time in presence of magnetic field vecB, the charged particle experiences a magnetic force vecF_m = q[vecv xx vecB]. The force was first given by H.A. Lorentz and is called the Lorentz magnetic force. The force depends on q, vecv and vecB and involves a vector product of vecv and vecB. The force acts in a side ways direction perpendicular to both the velocity and magnetic field and the direction is given by right hand thumb rule for vector product. Obviously force on a negative charge is opposite to that on a positive charge. An electron enters a given region moving with an initial velocity vecv = 12.5 hati m s^(-1) where a unifomr magnetic field vecB = B_0 hatj is also applied. What is the direction of force experienced by electron due to the magnetic field? |
| Answer» Solution :As per RIGHT HAND thumb RULEOF vector product FORCE is along -ve direction of z-axis. | |
| 44213. |
Rain is falling vertically downwards with a speed of 4 km h^(-1) . A girl moves on a straight road with a velocity of 3 km h^(-1) . The apparent velocity of rain with respect to the girl is : |
|
Answer» 3 km `H^(-1)` `:.|vec(V_(rg))=sqrt(V_(r)^(2) + V_(g)^(2))` `=sqrt(16 +9)` 5km/h 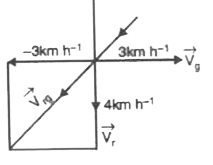
|
|
| 44214. |
If the momentum of certain body be increased by 50%, it's K.E. will increase by |
| Answer» ANSWER :D | |
| 44215. |
An element Delta l= Delta x hat i is placed at origin and carries a current I=10A. IF Delta x=1cm magnetic field at point P is….. T. |
|
Answer» Solution :`|DB| = (mu_0)/(4pi) (Idl sin theta)/(r^2) ` `dl = Delta x = 10^(-2) m , I = 10 A , r = 0.5m = y , mu_0 // 4pi = 10^(-7) (TM)/(A)` ` theta = 90^@ , sin theta = 1` `|dB| = (10^(-7) XX 10 xx 10^(-2))/(25 xx 10^(-2) ) = 4 xx 10^(-8) T` The direction of the field is in the +z-direction. This is so since, `dl xx r = Delta x hati xx y hatj = y Delta x (hati xx hatj) = y Delta x hatk` We REMIND you of the following cyclic property of cross-products `hati xx hatj = hatk , hatj xx hatk = hati , hatk xx hati = hatj` Note that the field is small in magnitude. |
|
| 44216. |
What is the difference between Nano materials and Bulk materials? |
|
Answer» Solution :• The solids are made up of particles. Each of the particle has a definite number of atoms, which MIGHT differ from material to material. If the particle of a SOLID is of SIZE less than 100 nm, it is said to be a .nano solid. • When the particle size exceeds 100 nm, it is a .bulk solid.. It is to be NOTED that nano and bulk solids may be of the same chemical composition. • For example, ZnO can be both in bulk and nano form. • Though chemical composition is the same, nano form of the material shows strikingly DIFFERENT properties when compared to its bulk counterpart. |
|
| 44217. |
Earth is moving towards a stationary star with a velocity 100 kms^(-1) . If the wavelength of light emitted by the star is 5000Å, then the apparent change in wavelength observed by the observer on earth will be |
|
Answer» 0.67Å |
|
| 44218. |
One mole of O_2 gas is heated at constant pressure starting at 27^@C. How much energy must be added to the gas as heat to double its volume? |
|
Answer» 750R |
|
| 44219. |
The displacement of a particle is given by x=(t-2)^(2)where x is in meters and in seconds. The distance covered by the particle in first 4 seconds is : |
|
Answer» 4m `x=(t-2)^(2)` Now whent=0 `x_0 =4 m` This means the PARTICLE has an INITIAL displacement of 4 m. The displacement in first 4 second with be `x_4 =(4-2)^(2)=4m` `:.` Total displacement in first 4 seconds will be `x=x_0 +x_4 =8m` |
|
| 44220. |
Earth receives 1400 W m ^-2 of solar power. If all the solar energy falling on lens of area 0.2m^-2 is focussed on to a block of ice of mass 280 g , then what is the time (in min) taken by the ice to melt completely ? [L_("fusion")=3.3xx105 J kg ^-1] |
|
Answer» |
|
| 44221. |
The focal length of a biconvex lens of refractive index 1.5 is 0.06m. Radii of curvature are in the ratio 1:2. Then radii of curvature of two lens surfaces are |
|
Answer» `0.045 m, 0.09m` |
|
| 44222. |
Statement-1 : A planet moves in a elliptical orbit around the sun. Its angular momentum remains constant. Statement-2 : Gravitational force is a central force. Therefore, no torque acts on the planet with respect to the sun. As a result angular momentum remains conserved. |
|
Answer» Statement-1 is FALSE, Statement-2 is TRUE. |
|
| 44223. |
If an electron and a photon propagate in the form of waves having same wavelength, it implies they have the same |
|
Answer» Energy |
|
| 44225. |
Derive the expression for torque on an electric dipole placed in a uniformelectric field. |
Answer» Solution :Consider an electric dipole of dipole moment `p= q xx 2A` in a uniform electric field. where `q to ` MAGNITUDE of EITHER charge and `2a to ` distance between the charges. LET `. theta’` be the angle made by the axis of the dipole with the direction of E and `F=qE `by the magnitude of the force experienced by either charge. The magnitude of the torque is given by Torque = Magnitude of either force `xx` PERPENDICULAR distance between the forces. 
|
|
| 44226. |
An electric field is uniform and in the positive x direction for positive x and uniform with the same magnitude but in the negative x direction for negative x. It is given that E = 200 hati N//Cand E = - 200 hatiN/C for x lt0. A right circular cylinder of length 20 cm and radius 5 cm has its centre at the origin and its axis along the *-axis so that one face is at jc = + 10 cm and the other is at x = - 10 cm as shown in figure, (a) What is the net outward flux through each flat face ? (b) What is the flux through the side of the cylinder ? (c) What is the net outward flux through the cylinder ? (d) What is the net charge inside the cylinder ? |
|
Answer» Solution :`A_(1) = A_(2) = pir^(2)` `=(3.14) (0.05)^(2)` `=7.85 xx 10^(-3) m^(2)` (a) ELECTRIC flux linked with face-1 is, `phi_(1) =A_(1)E_(1) cos theta_(1)` `=(7.85 xx 10^(-3)) (200) cos0^(@)` `therefore phi_(1) = 1.57 (Nm^(2))/C` Electric flux linked with face-2 is, `ph_(2) = A_(2)E_(2) cos theta_(2)` `=(7.85 xx 10^(-3)) (200) cos 0^(@)` `therefore phi_(2) = 1.57 (Nm^(2))/C` (b) Here curved surface of given cylinder is parallel to electric field and so no electric flux PASSES through this curved surface. Hence, `phi_(3)=0` (c) NET electric flux passing through given cylinder is, `phi= phi_(1) + phi_(2) + phi_(3)` `=1.57 + 1.57 + 0` `therefore phi = 3.14 (Nm^(2))/C` (d) If q is the net charge enclosed by above cylinder then according to Gauss theorem, `phi = q/(epsilon_(0))` `therefore q = phi epsilon_(0)` `=(3.14)(8.85 xx 10^(-12))` `therefore q = 2.779 xx 10^(-11) C` |
|
| 44227. |
(a) A parallel beam of monochromatic light of wavelength 500 nm is incident normally on a perfectly absorbing surface. The power through any cross section of the beam is 10 W. Find (i) the number of photons absorbed per second by the surface and the force exerted by the lilght beam on the surface. (a) Radiation of wavelength 200 nm, propagating in the form of a parallel beam, fall normally on a plane metallic surface. The intensity of the beam is 5 mW and its cross-sectional area is 1.0 mm^(2). Find the pressure exerted by the radiation on the metallic surface if the radiation is completeley reflected. (c) A parallel beam of monochromatic light of wavelength 663 nm is incident on a totally reflecting plane mirror. The angle of incidence is 60^(@) and the number of photons striking the mirror per second is 1.0xx10^(19) . Calculate the force exerted by the light beam on the mirror. (d) A beam of white light is incident normally on a plane surface absorbing 70%) of the light and reflecting the rest. If the incident beam carries 10 W of power, find the force exerted by it on the surface. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) (i) `P =n(hc)/(lambda)` `n=(P lambda)/(hc) =(10xx500xx10^(-9))/(6.6xx10^(-34)xx3xx10^(8)) =2.52xx10^(19)` (ii) `F= (P)/(c) =(10)/(3xx10^(8)) =3.3xx10^(-8) N` (b) `I= (P)/(A) =(5XX10^(-3))/(1xx10^(-6)) =5xx10^(3) W//m^(2)` `p =(2I)/(c) =(2xx5xx10^(3))/(3xx10^(8)) =3.3xx10^(-5) N//m^(2)` (c) 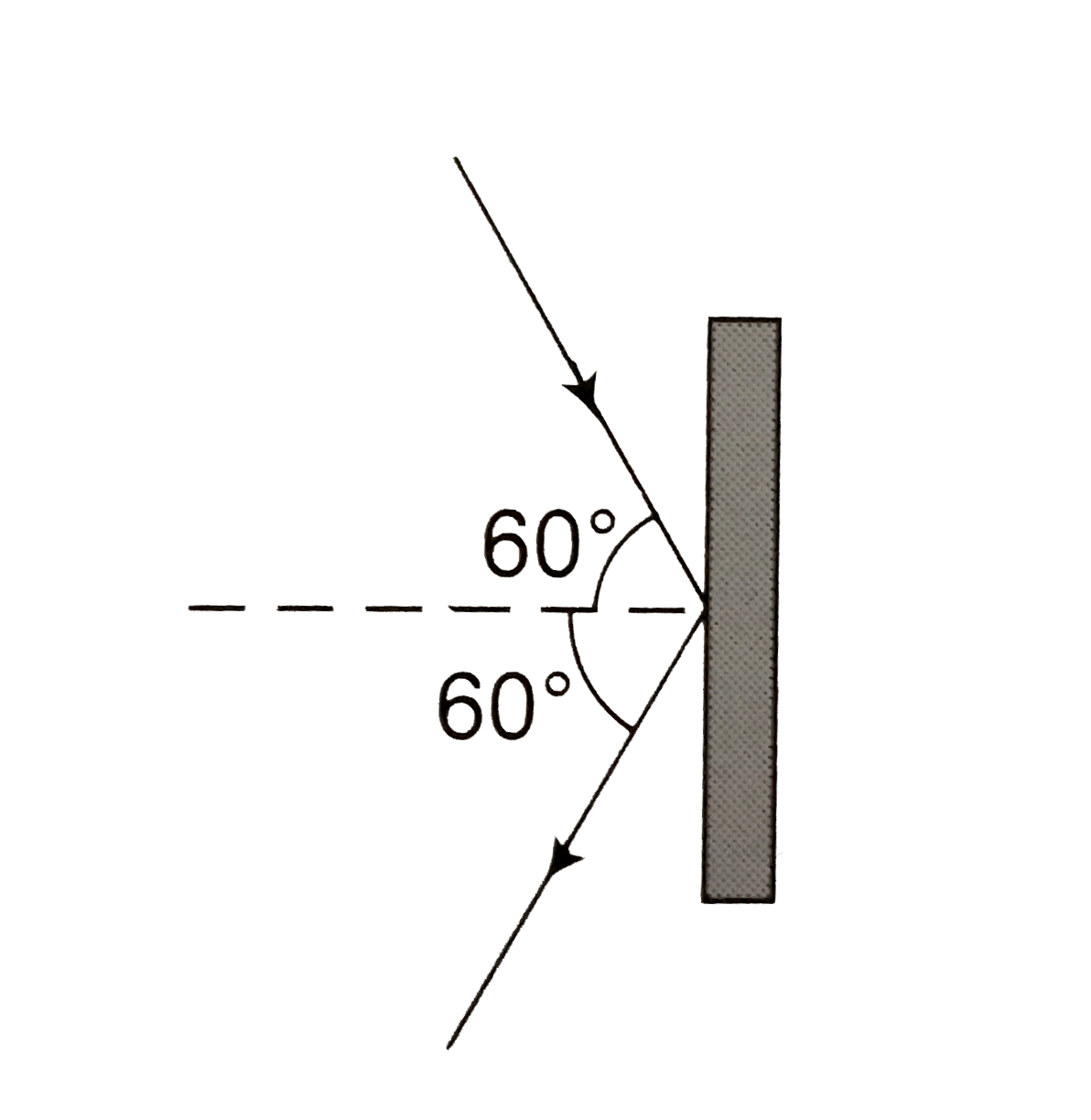 `F =(2P cos 60^(@))/(c)` `=(2xxn(hc)/(lambda)cos 60^(@))/(c)` `=(10^(19)xx6.6xx10^(-34))/(663xx10^(-9)) =10^(-8) N` (d) `F =2 P//c` , if light is completely reflected `F =P//c` , if light is completely absorbed Here, in this problem, `70%` light is absorbed and `30%` is reflected. `F =(70)/(100)xx(P)/(c)+(30)/(100)xx(2P)/(c) =13 (P)/(c) =(1.3xx10)/(3xx10^(8))` `=4.3xx10^(-8) N` |
|
| 44228. |
A parallel beam of light of wavelength 500 nm falls on a narrow slit and the resulting diffraction pattern is observed on a screen 1 m away. It is observed that the first minimum is at a distance of 2.5 mm from the centre of the screen. Find the width of the slit. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Here wavelength of light `l=500nm=5xx10^(-7)m`, Distance of screen from the slit `D=1m` and distance of FIRST minimum on the screen from the central maxima `x_(1)=2.5mm=2.5xx10^(-3)m` `therefore` Diffraction ANGLE for first minima `theta_(1)=(x_(1))/(D)=(2.5xx10^(-3))/(1)=2.5xx10^(-3)rad` We know that for first diffraction minima `a sintheta_(1)=lamdaimpliesa=(lamda)/(sintheta_(1))=(lamda)/(theta_(1))` `therefore` Slit width `a=(lamda)/(theta_(1))=(5xx10^(-7))/(2.5xx10^(-3))=2xx10^(-4)m=0.2mm`. |
|
| 44229. |
The resistance of an R-L A.C. circuit is 10 Omega. An emf E_0 applied across the circuit at omega=20 rad/s . If the current in the circuit is I_0/sqrt2 what is the value of L ? |
|
Answer» 0.55 H `omega`=20 rad/s `I=I_0/sqrt2` `rArr` Impedence of series connection of R-L `|Z|=sqrt(R^2+(omegaL)^2)` Current in CIRCUIT `I=E_0/"|Z|"` `I_0/sqrt2=E_0/(R(sqrt(1+((omegaL)/R)^2)))` `I_0/sqrt2=I_0/sqrt(1+((omegaL)/R)^2)[because E_0/R=I_0]` `therefore 1/sqrt2=1/sqrt(1+((omegaL)/R)^2)` `therefore 2=1+((omegaL)/R)^2` `therefore 1=((omegaL)/R)^2` `therefore 1=(omegaL)/R` `therefore L=R/omega` `therefore L=10/20` `therefore` L=0.5 H |
|
| 44230. |
A potentiometer wire of length 1 m has a resistance of 5Omega. It is connected to a 8 V battery in series with a resistance of 15Omega. Determine the emf of the primary cell which gives a balance point at 60 cm. |
|
Answer» Solution : CURRENT flowing in the potentiometer `I=V/(R_1+R_2)` `=8/(5+15)A=8/20A`=0.4 A Potential drop across the potentiometer wire V=IR =0.4 x 5 =2 V Potential gradient `K=V/t` `=2/1=2Vm^(-1)` `THEREFORE`Unknown EMF of the CELL = kl’ = 2 × 0.6 V = 1.2 V |
|
| 44231. |
When we consider a point charge q moving with a velocity vecv at a given time in presence of magnetic field vecB, the charged particle experiences a magnetic force vecF_m = q[vecv xx vecB]. The force was first given by H.A. Lorentz and is called the Lorentz magnetic force. The force depends on q, vecv and vecB and involves a vector product of vecv and vecB. The force acts in a side ways direction perpendicular to both the velocity and magnetic field and the direction is given by right hand thumb rule for vector product. Obviously force on a negative charge is opposite to that on a positive charge. A charged particle is placed at rest at a point P whose coordinates are (2,3,0) and a magnetic field vecB = 5 xx 10^(-3) hatk is present here. What is the magnetic force experienced by the charge ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :MAGNETIC force on the CHARGE is zero because it is at rest i.e, its velocity `VECV` is zero. | |
| 44232. |
Consider two conducting spheres of radii R_(1) and R_(2) with R_(1) gt R_(2). If the two are at the same potential, the larger sphere has more charge than the smaller sphere. State whetehr the charge density of the smaller sphere is more or less than that of the larger oe. |
|
Answer» Solution :SINCE, the two SPHERES are at the same potential, therefore ltbr `(kq_(1))/(R_(1))=(kq_(2))/(R_(2))implies(kq_(1)R_(1))/(4piR_1^(2))=(kq_(2)R_(2))/(4piR_(2)^(2))`. or `sigma_(1)R_(1)=sigma_(1)R_(1)=sigma_(2)R_(2)implies(sigma_(1))/(sigma_(2))=(R_(2))/(R_(1))` `R_(2) gt R_(1)` This imply that `sigma_(1) gt sigma_(2)` The charge density of the SMALLER sphere is more than that of the LARGER one. |
|
| 44233. |
वर्ग समीकरण ax^2+bx+c=0 का विवेचक D=b^2-4ac है । |
|
Answer» वास्तविक एवं भिन्न होंगें यदि DGT0 है। |
|
| 44234. |
A conducting ring of radius 1 meter is placed in an uniform magnetic field B of 0.01 tesla coscilliating with frequency 100Hz with its plane at right anglesto B. What will be the induced electric field. |
|
Answer» `pivolt//m` i.e., `T=1//100s`, in time `T//2` FLUX links with coil changes from `BA` to zero. :. Induced emf `=("CHANGE in flux")/("time")` `=(BA)/(T//2)=(2BA)/(T)` `=2Bxxpir^(2))/(T)` `(2xx0.01xxpixx1^(2))/(1//100)=4piV` induced electric field along the circle, using maxwell equatiion `ointE.dl=-(dphi)/(dt)=A(DB)/(dt)=e` :. `E=(1)/(2pir)xx(pir^(2)xx(dB)/(dt))=(e)/(2pir)=(4pi)/(2pir)=2V//m` |
|
| 44235. |
Can we use a gas in place of liquid in a hydraulic press |
|
Answer» we can use |
|
| 44236. |
Consider two conducting spheres of radii R_(1) and R_(2) with R_(1) gt R_(2).If the two are at the same potential, the larger sphere bas more charge than the smaller sphere. State whether the charge density of the smaller sphere is more or less than that of the larger one. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Both spheres have same POTENTIAL `:. V_(1) = V_(2)` `:. (kq_(1))/(R_(1))=(kq_(2))/(R_(2))` `:. (q_(1)R_(1))/(4piR_(1)^(2))= (q_(2)R_(2))/(4piR_(2)^(2))` (` because ` Dividing by 4 pi on both SIDES ) `sigma_(1) R_(1) = sigma_(2) R_(2) [ because sigma= (q)/(4piR^(2))]` Now `R_(1) gt R_(2)` `sigm_(1) lt sigma_(2)` SECOND Method : Charge on larger sphere is more than charge on smaller sphere Now `(kq_(1))/(R_(1)) = (kq_(2))/(R_(2))` `[becauseq = sigmaA] ` and `k = (1)/(4piin_(0))` `(sigma_(1)A_(1))/(4piin_(0)R_(1))=(sigma_(2)A_(2))/(4piin_(0)R_(2))` `:. (sigma_(1)xx4piR_(1)^(2))/(4piin_(0)R_(1))=(sigma_(2)xx4piR_(2)^(2))/(4piin_(0)R_(2))` `:. (sigma_(1)R_(1))/(in_(0))= (sigma_(2)R_(2))/(in_(0))` `:. (sigma_(1))/(sigma_(2))=(R_(2))/(R_(1))` but `R_(1) gt R_(2) implies 1 gt (R_(2))/(R_(1))` `(sigma_(1))/(sigma_(2)) lt 1` `:. sigma_(1) lt sigma_(2)` `:.` Charge DENSITY of smaller sphere is less than that of larger sphere . |
|
| 44237. |
An object A is moving with 5 m/s and B is moving with 20 m/s in the same direction. (Positive x-axis). Find a) velocity of Brelative to A. |
|
Answer» Solution :`VEC v_(B)=20 hatim/s, vecV_(A)=5 hatim//s` `vecV_(B)-vecV_(A)=15 I hatim//s` (b) `vecV_(B)=20 hatim//s, vecV_(A)=-5 hati m//s` |
|
| 44238. |
What is the condition for the error in measuring resistance on a Wheatstone bridge to be a minimum? How can it be achieved? |
|
Answer» Hence the error is at its MINIMUM when the EXPRESSION y=l (L-l) is at its maximum. But `y=IL-l^2=(L^2)/4-L^2/4+2l L/2-l^2=(L^2)/4-(l-L/2)^2` is at its maximum when l=L/2. i.e, when the slide is in hte middle of the scale. This will be the CASE, if the calibrating resistance is choosen as close tot the resistance being measured as possible. |
|
| 44239. |
Smallest odd composite number is - |
|
Answer» 3 |
|
| 44240. |
Paschen series of atomic spectrum of hydrogen gas lies in |
|
Answer» INFRARED REGION. |
|
| 44241. |
A metal ball immersed in alcohol weights W_(1)" at "0^(@)C and W_(2)" at "59^(@)C. The coefficient of cubic expansion of metal is less than that of alcohol. If the density of the mnetal is large compared to that of alcohol then: |
|
Answer» `W_(1)=W_(2)` `therefore` Upthrust at temperature T is GIVEN by `U_(T)=V_(T)P_(T)g" where "P_(T)` is density of ALCOHOL at temperature T. Since `V_(T)=V_(0)(1+gamma T) and P_(T) =(P_(0))/(1+gamma T)` `therefore U_(T) =V_(0) (1+ gamma T) xx (P_(0))/(1+gamma T) CDOT g =V_(0) P_(0)g` `U_(T)=U_(0)" where "U_(0)` is thrust at `0^(@)C`. Since upthrust is independent of temperature `therefore W_(1)=W_(2)` THUS, correct choice is (a). |
|
| 44242. |
A beat needs one-third of the time to go a certain distance downstream that it takes upstream. Then number of times the velocity of boat is greater than that of current is: |
|
Answer» FOUR TIMES |
|
| 44243. |
The waves used by artificial satellites for communication purpose are : |
|
Answer» MICROWAVES |
|
| 44244. |
Raju found that capacity of a parallel plate air capacitor is 10mF. Find the capacity of it when he immersed the unit completely in a medium of dielectric constatn 2.5 |
| Answer» Solution :Area of this GRAPH gives ENERGY STORED in the CAPACITOR. | |
| 44245. |
A pole of height 4 m is kept in front of a vertical plane mirrorof length 2m. The lower end of the mirror is at a height of 6m form the grown .the horizontal distance betweem the mirror and the pole is 2m. Upto what minimum and maximum heights a man can see the image of top of the pole at a horizontal distance of 4m (from the mirror O standing on the same horizontal line which is passing through the pole and the horizontal point below the mirror? |
|
Answer» Solution :`PQ="Pole", MN="Image of pole" ` `(HG)/(GN)=(BD)/(BN)` `:. BD=((HG)(BN))/(GN)=((2)(6))/(2)` `=6 M` Minimum height required `=AD=BD+AB=10m` Further ,`(IG)/(GN)=(BE)/(BN)` `:. BE=((IG)(BN))/(GN)=((4)(6))/(2)=12 m` `:.` MAXIMUM height required `=AE` `=BE+AB=16 m`. 
|
|
| 44246. |
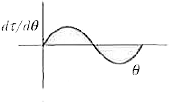
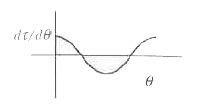
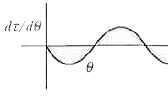
Correct plot of d tau//d theta.theta vs theta in case of an electric dipole placed in any uniform electric field is |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 44247. |
Light of wavelength 5000 Å falls on a plane reflecting surface. What are the wavelength and frequency of the reflected light ? For what angle of incidence is the reflected ray normal to the incident ray ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Here `lamda=5000` Å`=5000xx10^(-10)m=5xx10^(-7)m` `therefore` Wavelength of reflected LIGHT=Wavelength of incident light `lamda=5xx10^(-7)m` Frequency of reflected light `V=(c)/(lamda)=(3xx10^(8))/(5xx10^(-7))=6xx10^(14)Hz` As reflected ray is normal to incident ray, hence `anglei+angler=90^(@)` but `angler=anglei` `therefore anglei+anglei=2anglei=90^(@)impliesanglei=45^(@)`. |
|
| 44248. |
P and Q are two points on a uniform ring of resistance R. The equivalent resistance between P and Q is |
|
Answer» Solution :Resistance of SECTION PSQ `R_(1)=(R )/(2pir).r theta=(R theta)/(2PI)` Resistance of section PTQ  `R_(2)=(RR(2pi-theta))/(2pir)rArr (R(2pi-theta))/(2pi)` As `R_(1) and R_(2)` are in parallel `"So, "R_("eq")=(R_(1)R_(2))/(R_(1)+R_(2))=(Rtheta(2pi-theta))/(4pi^(2))` |
|
| 44249. |
A proton, a deuteron and an alphaparticle having same momentum enter a uniform magnetic field at right angles to the field. Then the ratio of their angular momenta during their motion in the magnetic field i |
|
Answer» `2:2:1` |
|
| 44250. |
Which of the following is not true for electomagnetic waves? |
|
Answer» it transport ENERGY |
|