Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 44251. |
Electric potential in a region is varying according to the relation V = (3x^(2))/(2) - (y^(2))/(4), where x and y are in metre and V is volt, Electric field intensity (in N/C) at a point (1 m, 2 m ) is |
|
Answer» `3 hat(i) - hat(J)` |
|
| 44252. |
Einstein's photoelectric equation is |
|
Answer» `W + hv = (1)/(2) mV_("MASS")^(2)` |
|
| 44253. |
Consider a potentiometer circuit, Primary cell is ideal. The length of potentiometer wire is 1 m and the resistance per unit length of potentiometer wire varies with length as lamda=2xOmega//m. Where x is distace from end A. Resistance of Rheostat varies with time as R=I^(2)Omega Null deflection point for secondary cell is obataied at x=1/2 m and at t=1 sec. If emf of secondary cell is 1/gamma times of emf of primary cell, find gamma. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 44254. |
In young's double slit experiment the n^(th) red bright band coincides with (n+1)^(th) blue bright band. If the wavelength of red and blue lights are 7500 A^(@) and 5000 A^(@), the value of 'n' is |
| Answer» ANSWER :B | |
| 44255. |
If Fig. 5-48, a chain consisting of five links, each of mass 0.100 kg, is lifted vertically with constant acceleration of magnitude a=2.50" m"//"s"^(2). Find the magnitudes of (a) the force on link 1 from link 2, (b) the force on link 2 from link 3, (c) the force on link 3 from link 4, and (d) the force on link 4 from link 5. Then find the magnitudes of (e) the force vec(F) on the top link from the person lifting the chain and (f) the net force accelerating each link. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) 1.23 N, (B) 2.46 N, ( c ) 3.69 N, (d) 4.92 N, (e) 6.15 N, (F) 0.250 N | |
| 44256. |
What is ohmic device? Give one example. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Devices which OBEY ohn.s law are called ohmic devices. Example : VOLTMETER. Ammeter, GALVANOMETER. | |
| 44257. |
In a Young's double slit experiment, a monochromatic source of wavelength lambda is used to illuminate the two slits S_(1) and S_(2). The slits S_(1) and S_(2) are identical and source S is placed symmetrical as shown. Interference pattern is observed on a screen at a distance D from the centre of slit. The distance between the slits is d. If the size of slit S_(1) is slightly decreased, then |
|
Answer» Intensity at central maxima will REMAIN same |
|
| 44258. |
What is meant electric current? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :RATE of flow of CHARGE is called CURRENT I = dq/dt | |
| 44259. |
Calculate the percentage of error in the determination of g=4pi^2l//_t2 when l and t are measured with _-^+2% and _-^+3% errors respectively. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Here `G=4pi^2l//r^2 therefore(DELTA G)/g=_-^+((Delta)/lxx100+2(DELTAT)/txx100)` |
|
| 44260. |
In a Young's double slit experiment, a monochromatic source of wavelength lambda is used to illuminate the two slits S_(1) and S_(2). The slits S_(1) and S_(2) are identical and source S is placed symmetrical as shown. Interference pattern is observed on a screen at a distance D from the centre of slit. The distance between the slits is d. if the source is moved by up by a very small distance y_(0), the central maxima will shift |
|
Answer» Up by `(y_(0)d)/(x_(0))` |
|
| 44261. |
A planet of mass m moves around the Sum along an elliptical path with a period of revolution T. During the motion, the planet's maximum and minimum distance from Sum is R and (R)/(3) respectively. If T^(2)=alphaR^(3), then the magnitude of constant alpha will be |
|
Answer» `(10)/(9).(PI)/(Gm)` Maximum and minimum distance of the planet from Sum is R and `(R)/(3)`, respectively. `:.` Semi-major AXIS of elliptcal path of planet around the Sum, `a=(R+(R)/(3))/(2)=(2R)/(3)` `:.` Time period of planet is given by `T=2pisqrt((a^(3))/(Gm))=2pisqrt((((2R)/(3)))/(Gm))^(3)` `T=2pisqrt((8R^(3))/(27G m))` Square on the both sides we get `T^(2)=4pi^(2).(8R^(3))/(27Gm)` `T^(2)=(32pi^(2))/(27Gm).R^(3)=alphaR^(2)` `:.alpha=(32pi^(2))/(27Gm)` HENCE, the MAGNITUDE of constant `alpha` will be `(32)/(27).(pi^(2))/(Gm)` |
|
| 44262. |
In the given circuit in which case will the ammeter reading not change when R_2 is varied? |
|
Answer» `R_1= R` containing `R_1` REMAINS UNCHANGED, so the ammeter reading does not change. |
|
| 44263. |
Resistance of a wire is, measured using a meter bridge and the balancing length for the unknown resistance of 10omega in the right gap is 48 cm. Find the value of the resistance. If the end corrections are 0.6 cm and 0.4 cm respectively for the left and right ends, find the corrected value of the unknown resistance. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 44264. |
Derive an expression for electrostatic potential due to an electric dipole. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) AB be the electric dipole ( -q at A tna +q at B). 2a be the distance between -q and +q. .r. be the distance between the point .p. and mid point .O. of AB. `.theta.` be the angle between OP and OB. 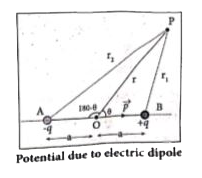 (ii) Let `r_1` be the distance of point P from +q and `r_2` be the distance of point P from -q. Potential at P due to charge +q `= 1/(4 pi epsi_0)q/r_1` Potential at P due to charge -q `=-1/(4piepsi_(0))q/r_2` Total potential at the point p, `V = 1/(4 pi epsi_0 ) q (1/r_1 - 1/r_2)"....(1)"` (iii) By the cosine LAW for triangle BOP. `r_1^2 = r^2 +a^2 - 2ra costheta` `r_1^2 = r^2 (1+a^2/r^2 - (2a)/r cos theta)` Since a a`ltlt`r, term `a^2/r^2` is very small and can be neglected. Therefore `r_1^2=r^2 (1-2a(cos theta)/r)` (or) `r_1 = r(1-(2a)/rcos theta)^(1/2)` `1/r_1 =1/r (1-(2a)/r cos theta)^(1/2)` (iv)Using binamial theorem we get. `1/r_1 = 1/r (1+a/rcostheta)"...(2)"` Similarly applying the cosne law for triangle AOP, `r_2^2 = r^2 -a^2-2racos (180 - theta)` Since cos (`180 - theta`) = `-cos theta` we get `r_2^2 = r^2 + a^2 + 2ra cos theta` Neglecting `a^2/r^2` ( because `r gt gt a` ) `a_2^2 = r^2(1+(2a cos theta)/r)` `r_2 = r(1+(2a cos theta)/r)^(1/2)` Using Binomial theorem we get `1/r_2 = 1/r (1-a (cos theta)/r)"...(3)"` Substituting equation (3) and (2) in equation (1), `V=1/(4piepsi_(0))q(1/r(1+a(cos theta)/r)-1/r (1-a(cos theta)/r))` `V = q/(4piepsi_(0))(1/r(1+a(costheta)/r)-1/r (1-a(cos theta)/r))` `V=1/(4 piepsi_(0))(2aq)/r^2 cos theta` (v) But the electric dipole MOMENT p = 2qa and we get, `V = 1/(4pi epsi_0)((pcos theta)/r^2)` If p `cos theta = vec p * hatr,` where `hatr` is the unit vector from the point O to point P. then `V = 1/(4piepsi_0)(vecp*hatr)/r^2""(r gtgta)"...(4)"` Spacial cases Case (i) If the point P lies on the axial line then `theta = 0`, then `v = 1/(4 pi epsi_(0)) p/r^2 "...(5)"` Case (ii) If the point P lien on the axial line then `theta = 180^@`, then `V = 1/ (4 pi epsi_(0)) p/r^2 "...(6)"` Case (iii) If the point P lies on the equatorial line, then `theta = 90^@`. Hence V = 0...(7) |
|
| 44265. |
A piece of copper and another of germanium are cooled from room temperature to 77 K. The resistance of |
|
Answer» each of these DECREASES |
|
| 44266. |
Who discovered spin quantum number |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 44267. |
Water is more elastic than air. why ? |
| Answer» Solution :We know that volume ELASTICITY is reciprocal of COMPRESSIBILITY. Further , air is more COMPRESSIBLE than water.so , water is more ELASTIC than air . | |
| 44268. |
"When electric current is passed through a resis tance wire, it get heated up" . Name the law associated with this phenomenon. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :JOULES LAW of HEATING | |
| 44269. |
A spring of constant 5xx10^(3) N/m is stretched initially by 5 cm from the unstretched position. Then the work required to stretch it further by another 5 cm is : |
|
Answer» 12.50 N m |
|
| 44270. |
A series circuit consists of two capacitors, a resistors, and an ideal voltage source. The circuit is initially at steady state. Now a conducting wire is shorted across the capacitor C as shown by dotted line. After shorting the wire, select the correct statement// statements. |
|
Answer» Heat developed in the circuit is `2 CV^2//3` Before SHORTING the wire at steady STATE the charges on each capacitors will be EQUAL to 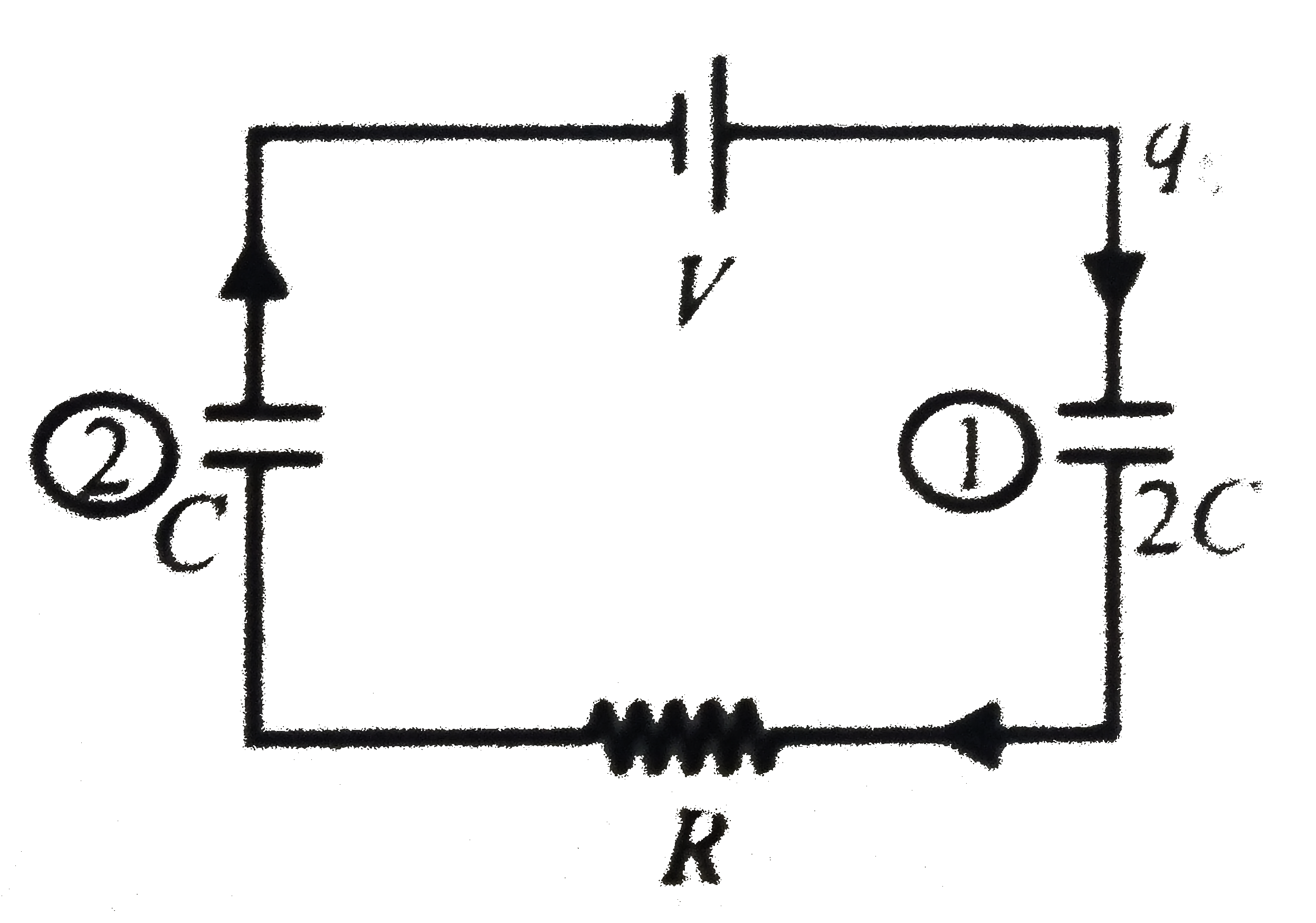 `q_0 = q_1 = q_2 = (2C)/3 V` After shorting the capacitor marked (2) will be useless in circuit. Hence `q'_1 = 2CV = q_f and q'_2 = 0` The charge supplied by battery after shorting 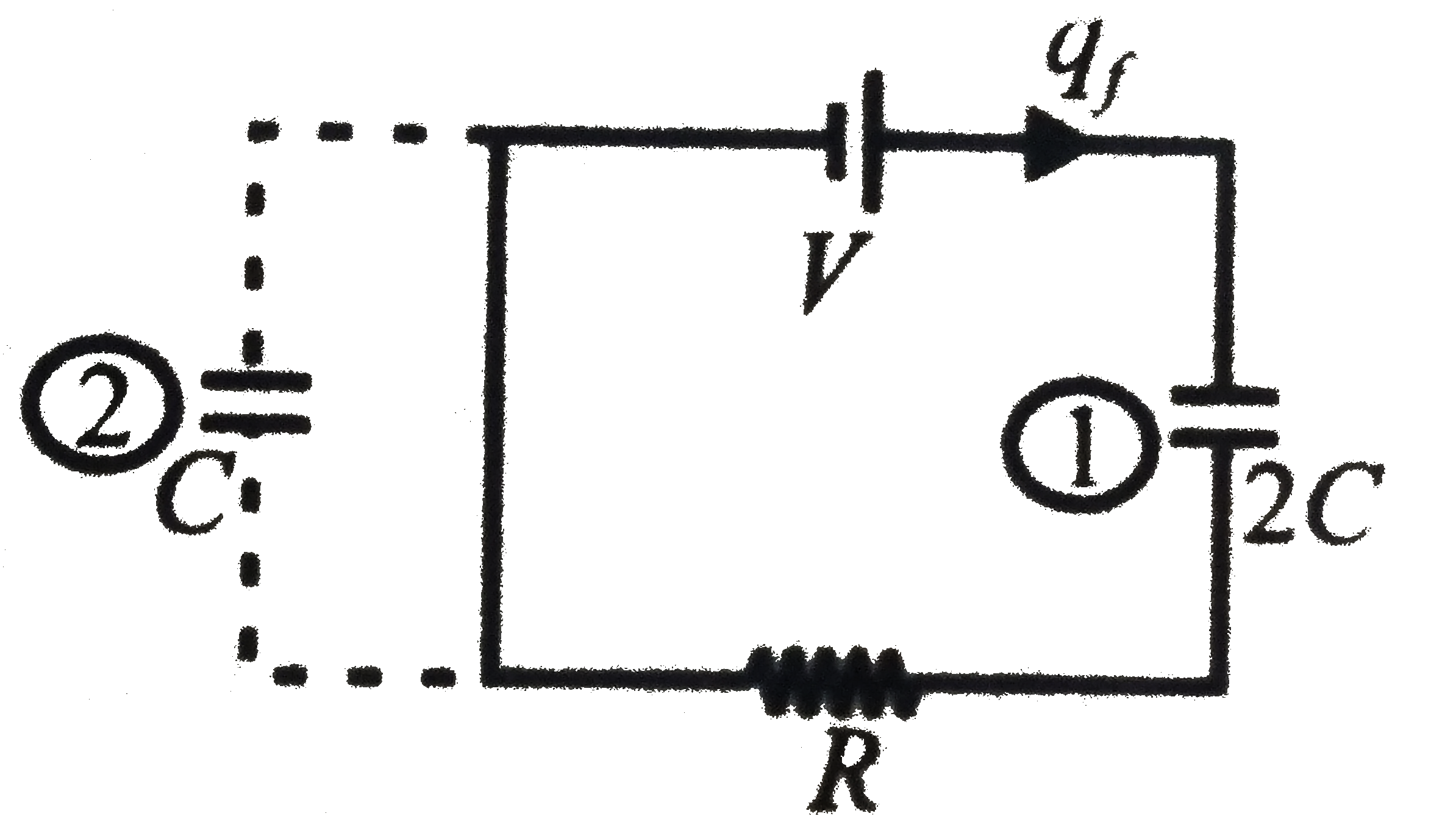 `Deltaq = q_(f) - q_0 = 2CV - (2CV)/3 = (4CV)/3` Hence work done by battery `W = Deltaq V = (4CV^2)/3` Initial potential energy of system. `V_0 = 1/2 (2/3C) V^2 = 1/3 CV^2` Final potential energy of system `U_(f) = 1/2 (2C)V^2 = CV^2` Hence change in PE `DeltaU = U_(f) - U_(i)` or `DeltaU = CV^2 - 1/3 CV^2 = 2/3 CV^2` Work done by battery `W = DeltaU + Heat` Heat developed `H = W-DeltaU` or `H = 4/3CV^2 - 2/3 CV^2 = 2/3CV^2` . |
|
| 44271. |
Fig. shows a 2.0 V potentiometer used for the determination of internal resistance of a 1.5 V cell. The balance point of the cell in open circuit is 76.3 cm. When a resistor of 9.5Omegais used in the external circuit of the cell, the balance point shifts to 64.8 cm length of the potentiometer wire. Determine the internal resistance of the cell. |
|
Answer» Solution :Here balancing length of potentiometer wire in opencircuit of given cell `l_1`= 76.3 cm. The balancing length in closed circuit `l_2`= 64.8 cm and external RESISTANCE JOINED with cell R = 9.5 `OMEGA` ` THEREFORE ` Internal resistance of the given cell `r = (l_1 - l_2)/(l_2) R = (76.3 - 64.8)/(64.8) xx 9.5 = 1.7 Omega` |
|
| 44272. |
For the arrangement shown, a cylinder of mass m with cross-sectional area A, initially in equilibrium poisition, is displaced slightly inside the liquid of density p. Prove that the motion is simple harmonic and also find its time-period. |
|
Answer» Solution : `T=kx_(0)` and `T+Vrhog=mg` `rArr kx_(0)+Vrhog=mg` when `m` is displaced by `DELTAX` downwards `ma=T'-k(x_(0)+Deltax)` `rArr ma=mg-(v+Adeltax)rhog-T'` Adding `2ma=mg-k(x_(0)+Deltax)-(v+ADeltax)rhog` `=-[k+Arhog]Deltax`, using equation (`3`) `rArr a=-([k+Arhog])/(2m)Deltax` `:. T=(2PI)/(OMEGA)=2pisqrt((2m)/([k+Arhog]))` 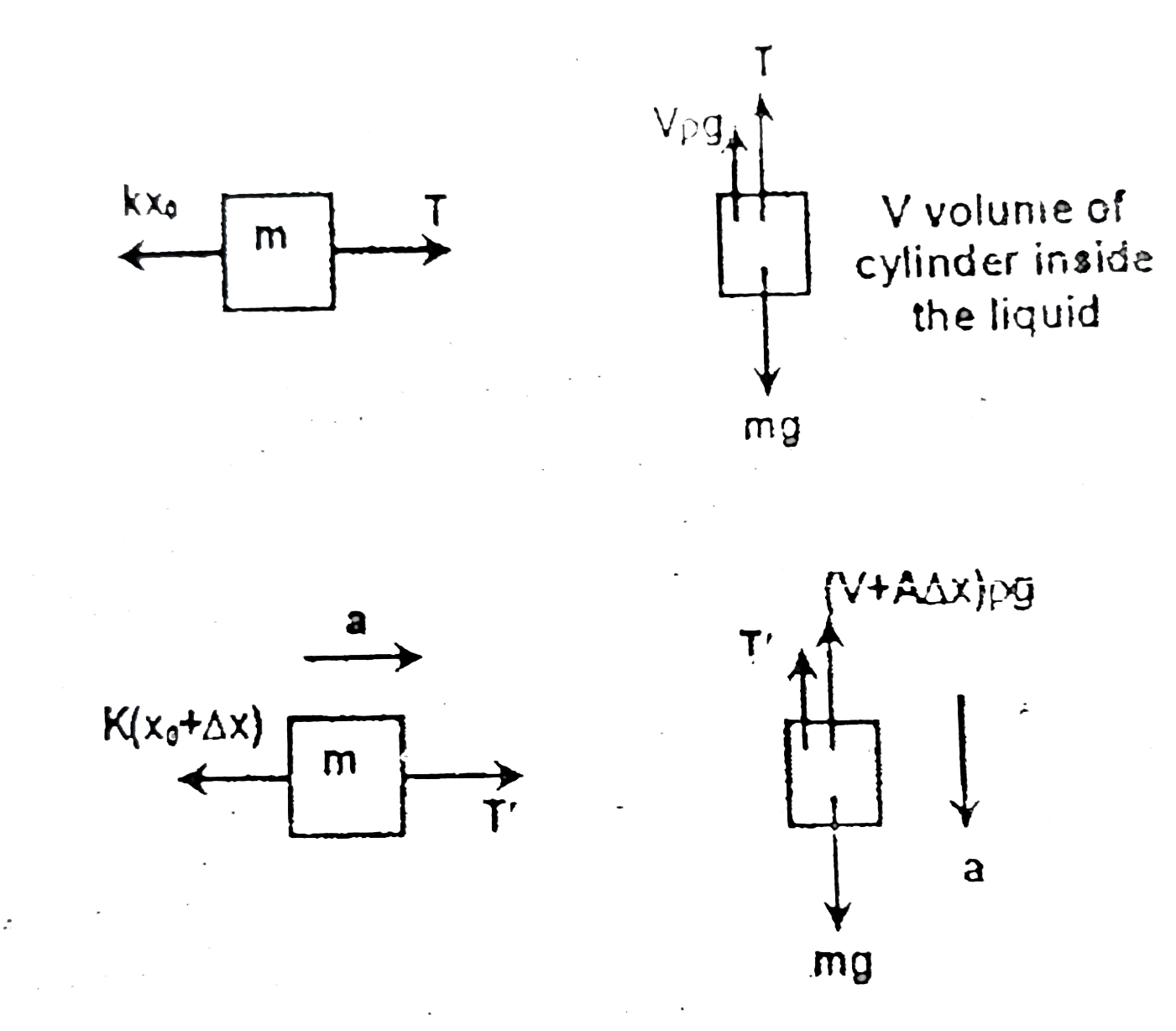
|
|
| 44273. |
A biconvex thin lens is prepared from glass of refractive index mu_2 = 3/2. The two conducting surfaceshave equal radii of 20cm each. One of the surface is silvered from outside to make it reflecting. It is placed in a medium of refractive index mu_1 = 5/3 . It acts as a |
|
Answer» converting MIRROR |
|
| 44274. |
Define capacitance . Give its unit. |
|
Answer» Solution :The capacitance of a capacitor is defined as the ratio of the magnitude of charge on either of the CONDUCTOR plates to the potential difference EXISTING between the conductors. `C=(Q)/(V)` or `QpropV`.The SI unit of capacitance is COULOMB per volt or farad (F). |
|
| 44275. |
A current of 1//4pi amp is flowing in a long straight conductor. The line integral of magnetic induction around a closed path enclosing the current carrying conductor is |
|
Answer» `10^(-7)` weber PER METER |
|
| 44276. |
Answer the following questions: (c) Magnifying power of a simple microscope is inversely proportional to the focal length of the lens. What then stops us from using a convex lens of smaller and smaller focal length and achieving greater and greater magnifying power? |
| Answer» Solution :(C) First, grinding lens of very small focal length is not easy. More important, if you decrease focal length, aberrations (both spherical and chromatic ) become more pronounced. So, in PRACTICE, you cannot get a MAGNIFYING power of more than 3 or so with a simple CONVEX lens. However, using an aberration corrected lens system, one can increase this limit by a FACTOR of 10 or so. | |
| 44277. |
The magnetic field of Earth can be modelled by that of a point dipole placed at the centre of the Earth. The dipole axis makes an angle of 11.3° with the axis of Earth. At Mumbai, declination is nearly zero. Then, |
|
Answer» the declination VARIES between 11.3° W to 11.3° E. Magnetic field obtain similar DUE to a HYPOTHETICAL magnetic dipole located at the magnetic fields. centre of the earth. This axis of dipole makes an angle of 11.3° to the axis of rotation of earth. As a result two possibilities arise as shown in the figure below.  So the declination varies from 11.3° (West) to 11.3° (East). |
|
| 44278. |
A sinusoidal wave travelling in the positive direction on a stretched string has amplitude 2.0 cm, wavelength 1.0 m and wave velocity 5.0 m/s. Ar x = 0 and t = 0, it is given that y=0 and (deltay)/(deltat)lt 0. Find the dr wave function y(x, t). |
|
Answer» Solution :We start with a general form for a RIGHTWARD MOVING wave. `y(x,t) =A sin (kx - omegat + phi)`. The amplitude given is A= 2.0 cm=0.02 m. The wavelength is given as, `lambda`= 1.0m `:.` Wave number `k =(2pi)/lambda = 2pi m^(-1)` Angular frequency `omega =vk = 10pi` red /s `:. y (x,t) =(0.02) sin[2pi(x - 5.0t) +phi]` We are told that for x = 0, t = 0, Y= 0 and `(deltay)/(deltat) lt 0` From these conditions, we may conclude that `phi = 2 N pi` where n=0, 2, 4, 6, ....... THEREFORE, `y(x,t) = (0.02m) sin[(2pi m^(-1) ) x - (10pi s^(-1))t ] m` |
|
| 44279. |
The AT/GC ratio in human beings is (where A=adenine, T=thymine, G=guanine, C=cytosine) |
|
Answer» 1 |
|
| 44280. |
An electron and a proton are released from rest in a uniform electric field E and are found to take time t_e and t_p respectively to cover a distance x. Calculate the ratio of time taken by them. If both the particles are allowed to fall under gravity in vacuum,then calculate the ratio of time taken by them to cover a distance x starting from rest. |
|
Answer» Solution :We know , `X=ut+1/2at^2` As both the particles are released from rest, u=0, `rArr x=1/2 at^2` or `t=sqrt((2x)/a)` For electron : ACCELERATION , `a_e=F/m =(EE)/m_e` TIME taken by electron to cover a distance x , `t_e=sqrt((2x)/a_e)` For PROTON : Acceleration `a_p=F/m=(eE)/m_p` `therefore t_p=sqrt((2x)/a_p)` The required ratio of time period , will be `t_e/t_p=sqrt((2x)/a_e)xxsqrt(a_p/(2x))=sqrt(a_p/a_e)` `rArr sqrt((eE)/m_p xx m_e/(eE))=sqrt(m_e/m_p)` `=sqrt((9.1xx10^(-31))/(1.67xx10^(-27))` `=2.3xx10^(-2)` When the particles fall under gravity in vacuum, the time of fall is independent of mass of body . Therefore , both the electron and proton will take the same time to cover a distance x . Thus we conclude `t_e/t_p=1` |
|
| 44281. |
The time of reverberation of a room a is one seond. What will be the time of reverberation of room having all the dimensions double of those of room A : |
|
Answer» 1 s Where `alpha` is average absorption coefficient and S is surface area. `RARR T prop `V/S `THEREFORE (T_(1))/(T_(2)) = (V_(1))/(V_(2)) XX (S_(2))/(S_(1)) = (V)/(8V) xx (4S)/(S) = (1)/(2) ` `rArr T_(2) = 2T_(1) = 2xx 1 = 2s` correct choice is (b). |
|
| 44282. |
Two rods with lengths 12.32 lcm and 10.3 cm and placed side by side. The difference in theirlengths is |
|
Answer» `2.02` CM |
|
| 44283. |
Find the relationship between angle of incidence and angle of emergence of light in the adjacent figure. Are angle of incidence and angle of emergence equal? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`sin^2 theta_1 + sin^2theta_3 = mu^2 ,No` | |
| 44284. |
An intrinsic semi conductor has 10^(18) //m^3 free electron and is doped with pentavalent impurity of 10^(24) //m^3. Then the free electrons density order increase by |
|
Answer» 4 |
|
| 44285. |
Howis thepoweroflensrelatedtoitsfocallength ? |
|
Answer» <P> SOLUTION : INVERSELY PROPORTIONAL[Or] P = 1/f |
|
| 44286. |
When a nucleus in an atom undergoes a radioactive decay, the electronic energy levels of the atom |
|
Answer» do not change for any type of RADIOACTIVITY |
|
| 44287. |
Light travelling through tranparent oil enters in to glass of refractive index 1.5. If the refractive index of glass with repectto the oil is 1.25, what is the refractive index of the oil? |
|
Answer» Solution :GIVE: `n_(go) = 1.25 and n_(g) = 1.5` Refractive index of GLASS with respect to oil, `n_(GN) = (n_(g))/(n_(o))` Refracting for refractive index of oil, `n_(o) = (n_(g))/(n_(gu))=(1.5)/(1.25)=1.2` The refractive index oil is `n_(o)` = 1.2 |
|
| 44288. |
The resultant of vectors vecP and vecQ is vecR. The resultant becomes 2vecR when vecP is either doubled or reversed in V its direction. |
|
Answer» The value of P : Q is `sqrt(3) : sqrt(5)` When P is reversed one gets `P^(2)+Q^(2)-2PQ cos theta= 4R^(2)` From eqn (i) and (ii) one get `-4PQ cos theta=3R^(3)implies PQ cos theta=-(3)/(4) R^(2)` When P is doubled , `4P^(2)+Q^(2)+4PQ cos theta=4R^(2)` `4P^(2)+4Q^(2)-8PQ cos theta= 16R^(2)` `(4 xx`eqn. (ii)) From eqn. (iii) and (iv) `(3Q^(2)-12PQ cos theta= 12R^(2)` `3Q^(2)=12R^(2)+12PQcostheta=12R^(2)+12(-(3)/(4))R^(2)` `=12R^(2)-9R^(2)=3R^(2)` `:. Q= R` Substituting in eqn (i) `P^(2) +R^(2)+2PQ cos theta=R^(2)` `:.P^(2) = -2PQ cos theta=-2 -2(-(3)/(4)R^(2))=(3)/(2)R^(2)implies P=sqrt((3)/(2))`R `:. P: Q = sqrt(3) :sqrt(2)`. |
|
| 44289. |
One end of a long cylindrical bar is kept at 200^(@)C and the other end is matintained at 40^(@)C. In the steady state the graph of temperature of bar against distance from not end is shown here. From the graph which of the following statements can be concluded true? |
|
Answer» The equantity of HEAT ENTERING the hot cnd PER second is equal to that leaving the other end per second |
|
| 44290. |
"Ski wax” is an application of nano product in the field of |
|
Answer» Medicine |
|
| 44291. |
Two balls roll toward each other. The red ball has a mass of 0.5 kg and a speed of 4m/s just before impact. The green ball has a mass of 0.3 kg and a speed of 2 m/s. if the collision is perfectly inelastic, determine the velocity of the composite object after the collision. |
|
Answer» Solution :If the collision is perfectly inelastic, then, by DEFINITION, the masses STICK together after impact, moving with a velocity, v. applying CONSERVATION of linear momentum, we FIND total `p_("before")=`total `p_("after")` `m_(red)v_(red)+m_("green")v_("green")=(m_(red)+m_("green"))v'` `(0.5)(+4)+(0.3)(-2)=(0.5+0.3)v'` `v'=+1.8m//s` |
|
| 44292. |
In Fig 27-53, a voltmeter of resistance R_(v)=300 Omega and an ammeter of resistance R_A= 3.00 Omega are being used to measure a resistance R in. a circuit that also contains a resistance R_0= 100 Omega and an ideal battery of emf epsi= 28.5 V. Resistance R is given by R=V//i where V is the voltmeter reading and i is the current in resistance R. However, the ammeter reading is not i but rather i', which is i plus the current through the voltmeter. Thus, the ratio of the two meter readings is not R but only an apparent resistance R'=V/I'. If R=85.0 Omega what are (a) the ammeter reading. (b) the voltmeter reading, and (c) R' (d) If R_v is increased does the difference between R' and R increase, decrease or on the same? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 44293. |
In the case of interference, the maximum and minimum intensities are in the 16 : 9. Then |
|
Answer» the MAXIMUM and MINIMUM amplitudes will be in the RATIO 9 : 5 |
|
| 44294. |
An object moving at a speed of 5 m/s towards a concave mirror of local length f = 1 m is at a distance of 9 m. The average speed of the image is : |
|
Answer» `(1)/(5) m//s` `(1)/(V) + (1)/(u) = (1)/(f) or v = (fu)/(u-f)` When an object is at a distance of 9 m from the concave mirror `thereforeu=-9m,f=-1mrArrV=((-1)(-9))/(-9+1)=-(9)/(8)m` As the object moves at a constant SPEED of `5ms^(-1)`, after 1s the position of image is `u.=-9m+5m=-4mrArr V. = ((-1)(-4))/(-4+1)=-(4)/(3)m` The shift in the position of image in 1 s is `V-V.=(-9)/(8)+(4)/(3)=(-27+32)/(24)=(5)/(24)=(1)/(4.8)APPROX(1)/(5)` Average speed of the image `= (1)/(5) ms^(-1)`. |
|
| 44296. |
Explain the conduction process in a junction transistor with a neat labelled diagram. |
|
Answer» Solution :For normal operation of a junction transistor, the emitter-base junction is ALWAYS forward biased and the collector-base junction is always reverse biased. Consider the more common npn transistor. The emitter. base junction is forward biased by the battery `V_(BB)` While the collector-base junction is reverse biased by the battery `V_(C C)`. The base is common, so that the junction in opposite directions. This current is called the reverse curran npn transistor in common base configuration. neat labelled diagram. the circuit SHOWN is called the common-base configuration. The emitter is a very heavily doped n-type region. Hence, the current between emitter E and base B is almost entirely electron current from E into B across the forward biased emitter junction. The `rho`-type base is narrow and the hole density in the base is very low. Therefore, practically all the injected electrons diffuse right across the base to the collector junction without RECOMBINING with holes. Since thiscollector-base junction is reverse-baised, the electrons on reaching this junction are quickly swept into the n-type collector region, where they constitute the collector current `I_(C)`. In PRACTICE, about 1% to 5% of the holes from the emitter recombine with holes in the base year layer and cause a small current `I_(B)` to flow in the base lead. Therefore, the emitter current, `I_(E)=I_(B)+I_(C)` If a PNP transistor is used, the battery connections must be reversed for the correct bias. The conduction process is similar but takes place instead by migration of holes from the emitter to collector. 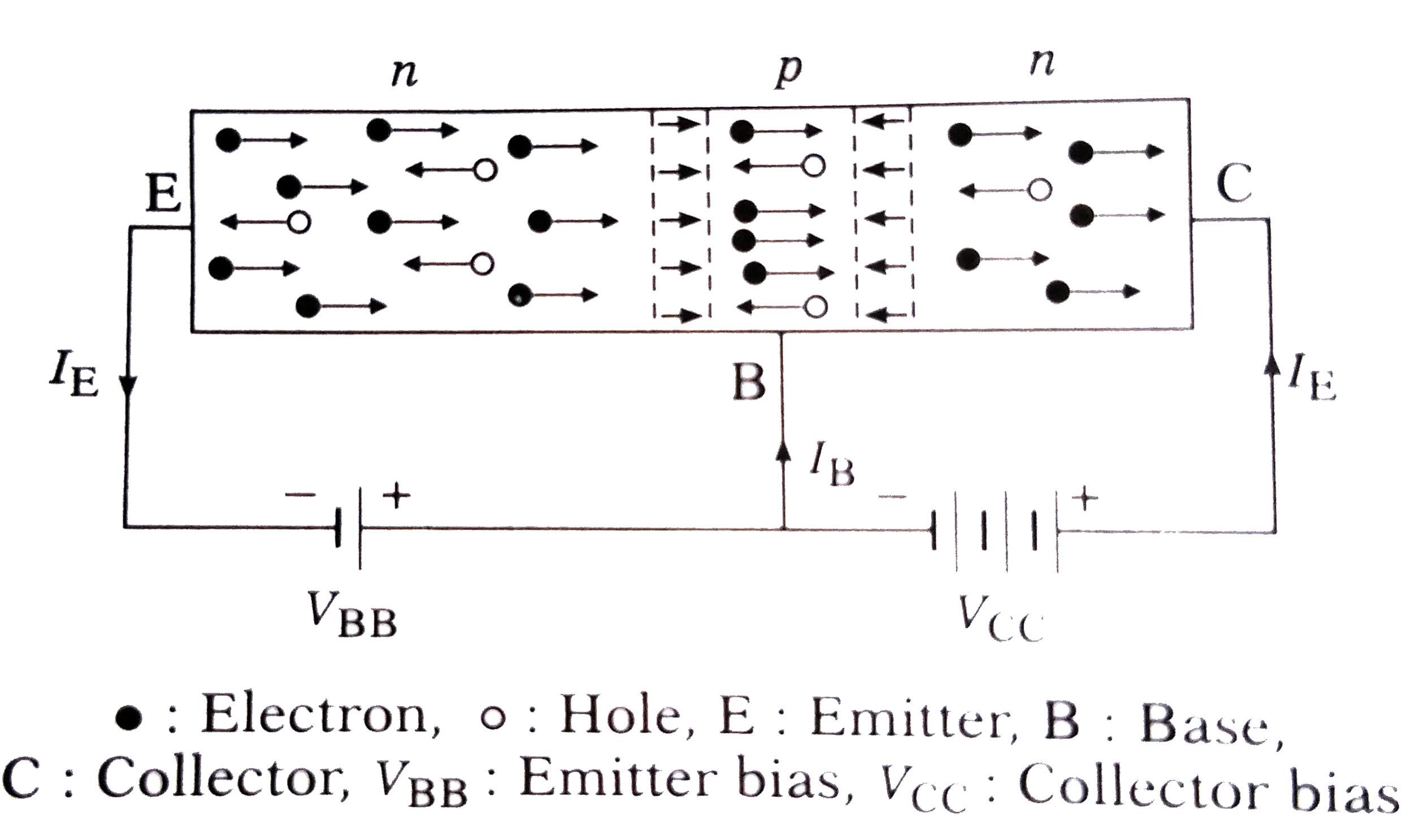
|
|
| 44297. |
A circular coil of area 8m^2and number of turns 20 is placed in a magnetic field of 2T with its plane perpendicular to it. It is rotated with an angular velocity of 20rev/s about its natural axis. The emf induced is |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 44298. |
A body is kept on the floor of a topless lift at rest. The lift starts descending at an acceleration 'a' then A) If a > g, the displacement of the body in a time 't'is1/2 g t^2w.r.t ground. B) If a < g, the displacement of the body in a time 't' is 1/2 a t^2w.t ground. |
|
Answer» Both A & B are TRUE |
|
| 44299. |
Three capacitors each of capacitance 9pF are connected in seris a. What is the total capacitance of the combination? (b). What is the potential difference across each capacitor if the combination is connected a 120V supply? |
|
Answer» Solution :C=9pF a. `C_("EFF")=C/3=3pF` (b). POTENTIAL difference `=(120)/(3)=40V` |
|
| 44300. |
An LC series circuit has an oscillation frequency f. Two isolated inductors, each with inductance L and two capacitors each with capacitance C, all are connected in series and circuit is completed. The oscillation frequency is |
|
Answer» `f/4` |
|