Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 43951. |
Give their possible range of valves |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`alpha=0.9`to0.099beta=20`to200 | |
| 43952. |
Two moles of helium gas are taken over the cycle ABCDA, as shown in the P-T diagram The net work done on the gas in the cycle ABCDA is |
|
Answer» zero |
|
| 43953. |
A straight wire carrying current I is truned intocircular loopif the magnitude of magnetic moment associated with it in is m thelength of wire will be |
|
Answer» `4piimn` `r=15xx10^(-2) m` `OP=sqrt(225-25)=sqrt(200)` cm since at the neutral pointmagnetic field DUE to the magnet equal to `B_(H)` `B_(H)=(mu_(0))/(4pi).(M)/(OP^(2)+AO^(2))^(3//2)` `0.4xx10^(3)xx10^(-6)(225)^(3//2)=M` `M=1.35 A-m` |
|
| 43954. |
Two masses 5 kg and 3 kg are suspended from the ends of an unstretchable light string passing over a frictionless pulley. When the masses are released, the thrust on the pulley is (g = 10 ms^(-2)) |
| Answer» ANSWER :D | |
| 43955. |
A charge Q has been divided on two concentric conducting spheres of radii R_(1) and R_(2)(R_(1) gt R_(1)) such that the surface charge densities on both the spheres are equal. The potential at their common centre is |
|
Answer» `(1)/(4PI epsilon_(0))(Q(R_(1)^(2) + R_(2)^(2)))/((R_(1) + R_(2)))` |
|
| 43956. |
How will the interference pattern in Youngs double slit experiment change, whendistance between the slits S_1 and S_2 are reduced |
|
Answer» Solution :Fringe WIDTH `BETA=(LAMDA D)/d` If d decreases, fringe width `β ALPHA1 /d` INCREASES |
|
| 43957. |
A moving coil sensitive galvanometer gives at once much more deflection. To control its speed of deflection |
|
Answer» A high resistance is to be CONNECTED ACROSS its terminals |
|
| 43958. |
In an experiment of photoelectric emission for incident light of 4000Å, the stopping potential is 2V. If the wavelength of incident light is made 3000Å, then stopping potential will be : |
|
Answer» less than 2 VOLT `(hc)/(lambda_(2))-(phi_(0))/(e)=V_(0_(2)) ""...(2)` From eqs (2)-(1) `rArr V_(0_(2))-V_(0_(1))=(hc)/(elambda_(2))-(hc)/(elambda_(1))""...(3)` `lambda_(1)=400xx10^(-10)m` `lambda_(2)=3000xx10^(-10)m""...(4)` `V_(0_(1))=2` volt `V_(0_(2))=?` From eqs (3) and (4), `V_(0_(2))2+(6.62xx10^(-34)xx3xx10^(8))/(1*6xx10^(-19)) xx[(1)/(3xx10^(-7))-(1)/(4XX10^(-7))]` `V_(0_(2))=2+1=3` volts. |
|
| 43959. |
We call the conductors which have very low conductivity as ? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43960. |
Prove that the force acting on one plate due to the other in a parallel plate capacitor isF =(1)/(2) (CV^(2))/(d) . |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The electric field due to ONE PLATE is `E_(1) = (sigma)/(2 epsilon_(0))` A second plate having CHARGE AA is present in the above electric field. `:.` The force acting on second plate `F= F_(1) (sigmaA)` Substituting the value of `E_(1)` from (1) we get `F = (sigma^(2)A)/(2 epsilon_(0))` but `sigma= (Q)/(A)` `:.F =((Q^(2))/(A^(2)).A)/(2epsilon_(0))=(Q^(2))/(2epsilon_(0)A)=((Q^(2))/(d))/(2epsilon_(0)(A)/(d))=(Q^(2))/(2dC)` `[because (epsilon_(0)A)/(d) =C]` `:. F =(1)/(2) (CV^(2))/(d ) "" ( because Q = CV)` |
|
| 43961. |
Pitch of a musical note depends on |
|
Answer» Its harmonics only |
|
| 43962. |
A mixture of salt reach with conc. H_(2)SO_(4) to give Reddish-Brown coloured gas. Which Pass in water then water become coloured then the radical jis - |
|
Answer» Nitrate `2HBr+H_(2)SO_(4)rarrunderset(("reddish-BROWN"))(Br_(2)(g))` `H_(2)O + Br_(2) rarr` Brown colour WATER |
|
| 43963. |
A positively charged glass rod is brought near an uncharged pith ball pendulum. What happens to the pith ball ? |
|
Answer» The PITH ball is repelled by the rod |
|
| 43964. |
The susceptibility of diamagnetic materials has a ................ . Value. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43965. |
Show that the density of nucleus over a wide range of nuclei is constant independent of mass number. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :We have `R=R_(0) A^(1//3)` `therefore`DENSITY, `rho = (mA)/( (4)/(3) pi (R_(0)A^(1//3))^(3))` `= (m)/( (4)/(3) pi R_(0)^(3)` Hence `rho` is independent of A (Here `m` is the mass of the nucleus.) |
|
| 43966. |
When a current I is set up in a wire of radius r, the drift speed is v_d. If the same current is set up through a wire of radius 2r, then the drift speed will be |
|
Answer» `v_d/4` |
|
| 43967. |
Obtain the equation of electric field by dipole at a point on equator of dipole. |
|
Answer» Solution :Distance of point P from `+q` and `-q` are same. `r_(+) = r_(-) = sqrt(r^(2) + a^(2))` where, r = distance of P from 0. 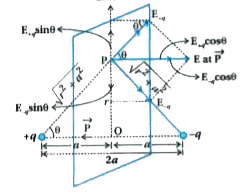 The magnitudes of the electric fields due to the two charges `+q` and `-q` are EQUAL. `vec(E_(+q)) = q/(4pi epsilon_(0)).1/(r^(2) + a^(2)) = (KQ)/(r^(2) + a^(2))`..........(1) `vecE_(-q) =q/(4pi epsilon_(0)).1/(r^(2) + a^(2)) = (kq)/(r^(2) + a^(2))`............(2) The distance of `vecE_(+q)` and `vecE_(-q)` are as shown in figure. The sine components will cancel each other. The total electric field at P. `therefore VECE =-(E_(+q) + E_(-q)) cos thetahatp = -(2kq)/(r^(2) + a^(2)). cos theta hatp`.............(3) (`therefore` from equation (1) and (2)) Perpendicular components to dipole axis of `vecE_(+q)` and `vecE_(-q)` at P are `E_(+q) sin theta` and `E_(-q) sin theta`. They are equal in magnitude and opposite ir direction, so they will cancel the effects of each other. But parallel components to dipole axis of `vecE_(+q)` and `vecE_(-q)`at P are `E_(+q) cos theta`and `E_(-q cos theta)`. And they are in same direction, so they will be added and resultant `vecE` will be in opposite to `hatp` `therefore vecE = -(E_(+q) cos theta + E_(-q).cos theta).hatp` `=-2E_(+q) cos theta hatp``(therefore E_(+q) = E_(-q))` `vecE = -(2kq)/(r^(2) + a^(2)) xx cos theta.hatp`...........(4) (From equation (3)) Now, from figure, `cos theta = a/(r^(2) + a^(2))^(2)`.............(5) `cos theta = a/(r^(2) + a^(2))^(1/2)` `therefore` From equation (4) and (5), `vecE = (-2kq)/(r^(2) + a^(2)) xx a/(r^(2) + a^(2))^(2) hatp`. `therefore vecE =-(2kqa)/(r^(2) + a^(2))^(2).hatp` If `r gt gt a`, then `a^(2)` can be neglected. `therefore vecE = -(2kqa)/r^(3).hatp` But `2qa =p` `vecE = -(kq)/r^(3)hatp` or `vecE =-p/(4piepsilon_(0)r^(3)).hatp` |
|
| 43968. |
The energy contained in a small volume through which an electromagnetic wave is passing oscillates with: |
|
Answer» DOUBLE the FREQUENCY of the wave |
|
| 43969. |
A solid sphere rolls up a plane inclined at 45^(@)to the horizontal. If the speed of its centre of mass at the bottom of the plane is 5 m/s , find how far the sphere travels up the plane. |
|
Answer» Solution :Data : V= 5 m/s ,` theta= 45^(@) , g= 9.8 ` m/`s^(2)` The total energy of the sphere at the bottom of the inclined plane is `E = 7/10 Mv^(2)` Where M is the mass of the sphere. In ROLLING up the plane through a vertical height h, it TRAVELS a distance L along the plane. Then. ` h - L SIN 45^(@) = L /sqrt2` By conservation of energy , Mgh = E ` Mg = L/sqrt2 = 7/10 Mv^(2)` ` L = (7sqrt2)/10 . v^(2)/g = ( 7 xx 1.414)/1 . ((5)^(2))/9.8 = ( 4.949 xx 5)/ 9.8` = `24.75/(0.8) = 2.526 m` The sphere travels 2.526 m up the inclined plane. |
|
| 43970. |
When ordinary light strike the tourmaline crystal of certain thickness at right angles to the optic axes, then |
|
Answer» O-ray is completly ABSORBED and E-ray is PARTIALLY absorbed |
|
| 43971. |
The shape of the wavefront due to a light source situated at infinity is |
|
Answer» spherical |
|
| 43972. |
The unit of thrust is |
|
Answer» pascal |
|
| 43973. |
A point object O is kept at a distance of 30cm from a convex lenx of power +4 D towards its left. It is observed that when a convex mirror is kept on the right side at a distance of 50cm from the convexlens, theimage of the object O formed by the lens-mirror combination coincides with the object itself. Calculate the focal length of the convex mirror. |
|
Answer» Solution :Focal length of the CONVEX lens `= ( 1)/( P) m` `f = ( 1)/( 4) m = 25 cm` Let v be the position of the imae, I, of the object formed by the convex lens alone . We then have `(1)/( v) - ( 1)/( ( -U)) = ( 1)/( f)` `rArr (1)/(v) = ( 1)/( 25) - ( 1)/( 30) = ( 6-5)/( 150) = ( 1)/( 150)` `rArrv = 150 cm` HENCE the distance of the image (formed by the convex lens alone ) from the convex mirror would be ( 150-150) cm, i.e., 100cm. This distance is equal to the radius of the curvature of the convex mirror. Hence focal length of the convex mirror equals `100 //2`. i.e., 50 cm. `:.` Radius of the curvature of the convex mirror, `R = LI - LM ` 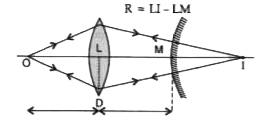
|
|
| 43974. |
When the wave of hydrogen atom comes from infinity into the first orbit then the value of wave number is |
|
Answer» `109700 cm^(-1)` `and n_(1)=1 rArr vecv =R= 1.097 XX 10^(7) m^(-1) =109700 cm^(-1)` |
|
| 43975. |
The liquid drop of density rho , radius r and surface tension sigmaoscillates with time period T. Which of the following expression for T^(2)is correct. |
|
Answer» `RHOR^(3)//sigma` |
|
| 43976. |
On increasing the temperature the specific resistance of a semiconductor :– |
|
Answer» increases |
|
| 43977. |
If the light from an ordinary sodium lamp, having an intensity I, passes through a polaroid sheet, the intensity of emergent light is _____. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`(I)/(2)` | |
| 43978. |
A metallic ring is attached with the wall of a room. When the north pole of a magnet is brought near to it, the induced current in the ring will be |
|
Answer» FIRST CLOCKWISE then ANTI clockwise |
|
| 43979. |
A ball is projected with speed u at an angle of projection 30^@ has range R. Is there any other angle of projection at which the range with same initial speed u is R ? |
| Answer» Solution :YES,` 60^@` the RANGE is same for two angle `theta_1=90^@-theta_1` | |
| 43980. |
Unit of Bolar magneton is………….. |
|
Answer» Am |
|
| 43981. |
A radioactive nucleus (initial mass number A and atomic number Z) emits 2alpha and 2 positrons. The ratio of number of neutrons to that of proton in the final nucleus will be |
|
Answer» `(A-Z-4)/(Z-2)` |
|
| 43982. |
Magnetic flux linked with one closed conducting loop is phi=t^2+3t-7. Then graph of epsilon to t would be a ..... (All the values are in SI units) |
|
Answer» circle `therefore (dphi)/(dt)=2t+3` `therefore epsilon=-(dphi)/(dt)=(-2)t+(-3)` Above equation is of the FORM y = MX + c which is equation of a straight line. |
|
| 43983. |
Repulsion is the sure test of electrostatics than attraction. Why? |
|
Answer» Solution :If a positively CHARGED BODY is brought near a NEGATIVELY charged body or an uncharged body, there exist a force of attraction. So the attraction is DUE to oppositvely charged body or chargeless body. If a positively charged body is brought near a positively charged body there exist a force of repulsion. Thus repulsion is the sure test of elecrification. |
|
| 43984. |
A person wants to roll a solid non-conducting spherical ball of mass m and radius r on a surface whose coefficient of static friction is mu. He placed the ball on the surface wrapped with n turns of closely packed conducting coils of negligible mass at the diameter. By some arrangement he is able to pass a current i through the coils in anti-clockwise direction when viewed downwards from point P. A constant horizontal magnetic field vecB is present throughout the space along the positive x direction as shown in the figure. (Assume mu is large enough to help pure rolling motion and initially the plane of the coils is perpendicular to the y-axs) The angular velocity of the ball when it is has rotated through an angle theta is (thetalt180^(@)) |
|
Answer» `sqrt(10/7 (piniB)/m SIN THETA)` |
|
| 43985. |
In one dimensional motion, instantaneous speed V satisfies 0 le V lt V_0 |
|
Answer» The displacement in TIME T must always TAKE NONNEGATIVE values. |
|
| 43986. |
A person wants to roll a solid non-conducting spherical ball of mass m and radius r on a surface whose coefficient of static friction is mu. He placed the ball on the surface wrapped with n turns of closely packed conducting coils of negligible mass at the diameter. By some arrangement he is able to pass a current i through the coils in anti-clockwise direction when viewed downwards from point P. A constant horizontal magnetic field vecB is present throughout the space along the positive x direction as shown in the figure. (Assume mu is large enough to help pure rolling motion and initially the plane of the coils is perpendicular to the y-axs) If current i is passed through the coil then |
|
Answer» maximum torque in the coils is `-pinir^(2)Bhatk` |
|
| 43987. |
Derivethe expressionformotionalemfinducedin acondctormovingin auniformmegneticfield . |
|
Answer» Solution :Let .PQ. representa conductormovingwithaspeed.V.atrightanglesto themagnetic fluxdensity.B.pointingperpendicularto thesheetof paperandpointingtowardsthepaper.LetRQ= xbethe distancecoveredby theconductor.Magneticflux` phi_(B )= B //x .` Induced emf`=- (d{PHI _(E )))/(dt )=-(d )/(dt )(b//x )` ` i,e.,e=- Bl (dx)/(dt)` 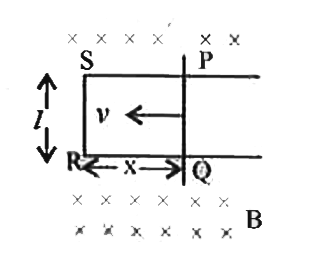 But, ` (-dx )/(dt) = v ` ` thereforee= B/v ` Note : TheLorentzforceactsonachargein aconductorand acts alongPQ. Workdonein movinga charge .Q.fromP TOQ is W= (Lorentzforce)(displacement of thecharge .q. ). i.e.,W= (Bqv )L Bydefinitionelectricp.d `=(W)/(q)=(Bqvl)/(q)=Bvl` Equation(1) and (2)areidentical . |
|
| 43988. |
A parallel beam of light 500 nm is incident at an angle 30^(@) with the normal to the slit plane in a young.s double slit experiment .The intensity due to each slit is Io. Point O is equidistant from S_(1) and S_(2) .The distance between slits is 1 mm . |
|
Answer» the INTENSITY at O is 4Io |
|
| 43989. |
A bar magnet M is dropped so that is falls vertically through the coil C. The graph obtained for voltage produced across the coil Vs time is shown in figure. (i) Explain the shape of the graph. (ii) Why is the negative peak longer than the positive peak ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) When the bar magnet moves towards the coil magnetic flux passing through the coil INCREASES as velocity of magnet increases in downward DIRECTION, e.m.f. induced also increases, DUE to formation of similar pole repulsive FORCE decreases the rate of increase of flux. (ii) once the magnet has passed through the coil, flux decreases in downward direction but `(d phi)/(dt)` increases as self induced e.m.f. in the coil maintains its flux in the same direction. Thus due to the addition of self induced e.m.f. in same direction according to LENZ’s law. |
|
| 43990. |
For a projectile the ratio of maximum height reached to the square of flight time is |
|
Answer» `5:4` |
|
| 43991. |
What does the author analyze in the story? |
|
Answer» RICH people |
|
| 43992. |
(A): No power loss associated with pure capacitor in ac circuit. (R) : No current is flowing in this circuit. |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are TRUE and 'R' is the correct explanation of 'A'. |
|
| 43993. |
For a short magnet with magnetic dipole moment overset(to)(m), its magnetic field at distance d from its centre on its equator is ...... |
|
Answer» `-(mu_0 m)/( 4 pi d^3)` |
|
| 43994. |
A particle of mass 100 g is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 5 m/s. The work done by the force of gravity during the time the particle goes up is: |
|
Answer» `-0.5 J` `W=1/2mv^2-1/2"mu"^2` `W=0-1/2xx(100)/(1000)xx25=-1.25 J` |
|
| 43995. |
the frequenct of sinusoidal wave, 0.40 cos (2000t + 0.80) would be |
|
Answer» `1000 PI HZ` |
|
| 43996. |
A parallel beam of rays of width 20 cm passing through a glass slab makes an angle phi=60^(@) with its plane surface. If the beam emerges into air from this surface then calculate the width of emergent beam. Refractive index of glass = 1.8. |
|
Answer» Solution :The width of the beam of parallel RAYS = AB = 20 CM and the width of the beam of emergent rays in AIR = CD. From Fig. 2.13, I = `30^(@)` `therefore "" g^(mu)a = (SIN30^(@))/(sinr)` `or, "" sinr = (1)/(2) * (1)/(g^(mu)a) = (a^(mu)g)/(2)` `(1.8)/(2) = 0.9` `"From the figure" , angleBAC = 30^(@) and angleACD = r` `Now, cos 30^(@) = (AB)/(AC), cosr = (CD)/(AC)` `(cos 30^(@))/(cosr) = (AB)/(AC)` `or, "" CD = (ABcosr)/(cos30^(@)) = (20sqrt(1-sin^(2)r))/(sqrt(3/2))= (40)/(sqrt3) sqrt(1-0.81)` `= (40)/(sqrt3) xx sqrt(0.19) = 10.064 cm` 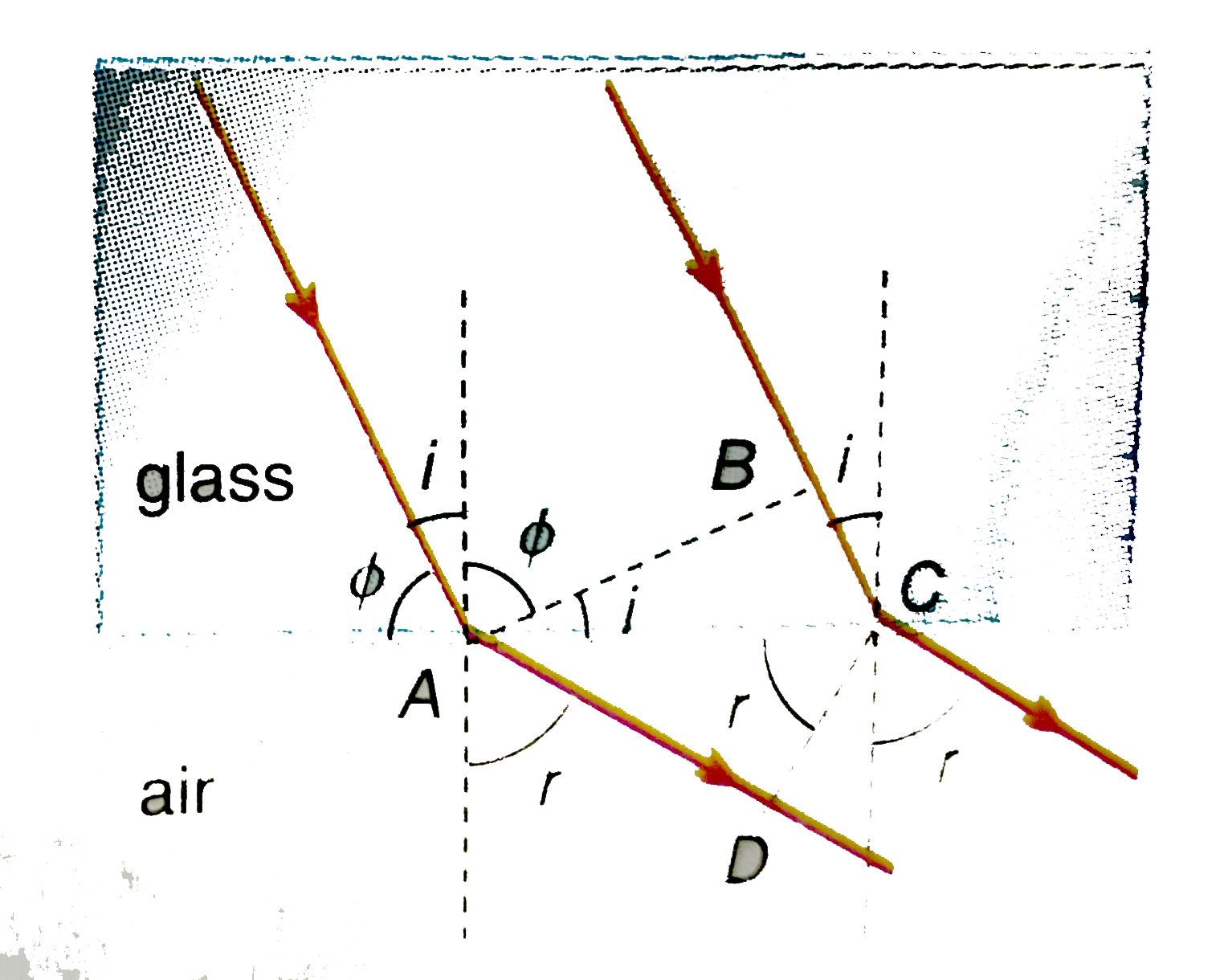
|
|
| 43997. |
A simple harmonic wave of amplitude 0.2 cm, frequency 1000 Hz and wavelength 0.31 m is travelling along the positivex-axis . Calculate the displacement of the particle at 3.1 m from the origin after 1.004 s. What would be the phase difference for two positions of the vibrating particle after an interval of 0.001 s ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Data : A= 0.2 cm = 0.002 m, n = 1000 Hz, ` lamda = 0.31m ,x = 3.1 m` ` t = 1.004 s, t_(2) -t_(1) = 0.001 s` (i) The displacement of the particle. ` y = A sin 2 pi (NT -x/lamda)` ` = 0.002 sin 2 pi(1000 xx 1.004 - (3.1)/(0.31))` ` = 0.002 sin 2 pi (1004 -10)` ` = 0.002 sin 2pi (994)` ` y = 0 [ or y =0` metre] `2 pi xx 1000 xx 0.001 = 2pi` radians |
|
| 43998. |
Assertion : Electric conduction in gases is possible at normal pressure. Reason : The electricconduction ingases depends only upon the potential difference between the electrodes. |
|
Answer» If both assertion and reason are ture and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion. |
|
| 43999. |
Draw the diagram of a switch which enables a parallel connection of a capacitor battery to be changed to a series one and vice versa. |
Answer» Solution :A possible CIRCUIT DIAGRAM is shown in FIG. 24.12 for the case of a five-capacitor system. It follows from the diagram that a tenposition SWITCH is required. When the knob is in the upper position,  the capacitors are connected in parallel: when the knob is in the lower position, they are connected in series. |
|
| 44000. |
Derive the equation for refraction at single spherical surface. |
Answer» Solution :Let us consider two transparent media having refractive indices `n_(1)` and `n_(2)`are separated by a spherical surface. Let C be the centre of curvature of the spherical surface. Let a point object O be in the medium nr The line OC cuts the spherical surface at the pole P of the surface. As the rays considered are paraxial rays, the perpendicular dropped for the point of incidence to the principal axis is very close to the pole or passes through the pole itself. 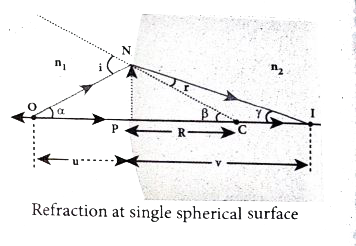 Light from O falls on the refracting surface at N. The normal drawn at the point of incidence passes through the centre of curvature C. As `n_(2) gt n_(1)`,light in the denser medium DEVIATES towards the normal and meets the principal axis at I where the IMAGE is formed. Snell.s law in product form for the refraction at the point N could be WRITTEN as, `n_(1) sin i = n_(2) sin r` As the angles are small, sin of the angle could be approximated to the angle itself. `n_(1)i = n_(2)r`............. (2) Let the angles, `angleNOP =alpha, angleNCP = beta, angleNIP =gamma` `tan alpha =(PN)/(PO), tan beta =(PN)/(PC), tan gamma = (PN)/(PI)` As these angles are small,tan of the angle could be approximated to the angle itself. `alpha = (PN)/(PO), beta = (PN)/(PC), gamma =(PN)/(PI)`.............(3) For the triangle, `triangleONC`, `i = alpha + beta` .............(4) For the triangle, `triangleINC` `beta = r + gamma` (or) `r = beta - gamma`.........(5) Substituting for i and r from equations (4) and (5) in the equation, (2). `n_(1)(alpha + beta) = n_(2) (beta - gamma)` Rearranging, `n_(1)alpha + n_(2)gamma = (n_(2)-n_(1))beta` Substituting for `alpha, beta` and `gamma` from equation (3) `n_(1)(PN)/(PO) + n_(2)(PN)/(PI) = (n_(2)-n_(1)) (PN)/(PC)` Further simplying by cancelling PN, `n_(1)/(PO) + n_(2)/(PI) = (n_(2)-n_(1))/(PC)` Following sign conventions,PO =- u, PI = +v and PC =-R in equation (6), `n_(1)/-u + n_(2)/v = (n_(2)-n_(1))/R` After rearranging, finally we get `n_(2)/v - n_(1)/u =(n_(2)-n_(1))/R`...........(7) Equation (7) gives the relation among the object distance u, image distance v, refractive indices of the two mediaand the radius of curvature R of the spherical surface. It holds for any spherical surface. If the first medium is air then, `n_(1) = 1` and the SECOND medium is taken just as `n_(2)=n`, then the equation is reduced to, `n/v - 1/u = (n-1)/R`................. (8) |
|