Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 43901. |
When 6 identical cells of no internal resistance are connected in series in the secondarycircuit of a potentio meter, the balancing lengths is .l., balancing length becomes 1/3 when some cells are connected wrongly, the number of cells connected wrongly are |
|
Answer» 1 |
|
| 43902. |
Radius of spherical shell is 0.5 m. It is charged. Now imagine spherical surface of radius 2 m and 3 m concentric with spherical shell of 0.5 m radius. If electric field on these surfaces are E_(1)and E_2 respectively, then |
|
Answer» `E_(1) = 3/2E_(2)` `THEREFORE` For a point-out SIDE shell. `E = (sigmaR^(2))/(epsilon_(0)r^(2))` `therefore E PROP 1/r^(2)` `E_(1)/E_(2) = 9/4` `therefore E_(1) = 9/4E_(2)` |
|
| 43903. |
A force of 750 N is applied to a block of 100 kg to prevent it from sliding down an inclined plane of 30^(@) inclination. If coefficients of static and kinetic friction are 0.4 and 0.2, the frictional force acting is : |
|
Answer» 750 N `= 0.4 XX 100 xx 10 xx(sqrt2)/(2)` `= 200 xx 1.732 = 3.464 xx 10^(2)` `= 350 N ("nearly") ` (c) is the CHOICE. |
|
| 43904. |
In a car race,car A takes time t less than car B and passes the finishing point with a velocity v more than the velocity with which car B passes the point.Assuming that the cars start from rest and travel with Constant acceleration a_(1) and a_(2),show that (v)/(t)=sqrt(a_(1)a_(2)). |
|
Answer» Solution :Let s be the distance covered b y each car.Let the times taken by the two cars to complete the journey be `t_(1)` and `t_(2)` , and their velocity at the finishing point be `v_(1)` and `v_(2)` respectively. According to the given problem. `v_(1)-v_(2)=v` and `t_(2)-t_(1)=t` Now,`(v)/(t)=(v_(1)-v_(2))/(t_(2)-t_(1))=(SQRT(2a_(1)s)-sqrt(2a_(2)s))/(sqrt(2S)/(a_(2))-sqrt(2s)/(a_(1)))=(sqrt(a_(1))-sqrt(a_(1)))/(sqrt(1)/(a_(2))-sqrt(1)/(a_(1)))` |
|
| 43905. |
Two concentric circular coils of ten turns each are situated in the same plane. Their radii are 20 and 40 cm and they carry respectively 0.2 and 0.3 ampere current in opposite direction. The magnetic field in weber/m^(2) at the centre is: |
|
Answer» `(35)/(4)mu_(0)` |
|
| 43906. |
Photo electric emission is observed from a metallic surface for frequencies v_(1) and v_(2) of the incident light rays (v_(1)gtv_(2)). If the maximum values of kinetic energy of the photo elections emitted in the two cases are in the ratio of 1:K, then the threshold frequency f the metallic surface is |
|
Answer» `(v_(2)-v_(1))/(K-1)` |
|
| 43907. |
When the energy of the incident radiation is increased by 20% ,the kinetic a metal surface increased from 0.5 eV to 0.8 eV.The work function of the metal is ….. |
|
Answer» 0.65 EV `therefore` In first condition 0.5 eV=hf-`phi`…(1) and By increasing energy 0.8 eV=1.2 hf-`phi`…..(2) multiplying EQUATION (1) by 1.2, 0.6 eV=1.2 hf-1.2 `phi` 0.8 eV=1.2 hf-`phi` `(--+)/(-0.2 eV=-0.2 phi)` `therefore phi=1.0 eV` |
|
| 43908. |
Rain is falling vertically downward with a velocity of 4 km/hr. A person moves on a straigth road whit velocity 3 km/hr. then, the apparent velocity of the train with respect to person is |
|
Answer» 7 km/hr |
|
| 43909. |
overline(x)andoverline(y)be two variable vectors satisfying simultaneous vector equationoverline(x)+overline(c)xxoverline(y)=overline(a)overline(y)+overline(c)xxoverline(x)=overline(b)where overline ( c) is a non zero vector . Then the value ofoverline(x)andoverline(y) is given by |
|
Answer» `overline(X)=(overline(a)+(overline(a).overline(C))overline(c)+overline(b)xxoverline(c))/(1+|c|^(2))` |
|
| 43910. |
Antistokes lines is Raman Scattering are the lines of ..... frequency and ......wavelength. |
|
Answer» LOW, HIGH |
|
| 43911. |
(a) Write Einstein's photoelectric equation and mention which important features in photo-electric effect can be explained with the help of this equation. (b) The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons gets doubled when the wavelength of light incident on the surface changes from lamda_(1) to lamda_(2). Derive the expressions for the threshold wavelength lamda_(0) and work function fo rthe metal surface. |
|
Answer» Solution :(B) In terms of wavelength `LAMDA`, the photoelectric wavelength. As per question for incident LIGHT of wavelength `lamda_(1), K_(max)=K(say)` and for light of wavelength `lamda_(2),K_(max)=2K.` hence, we have `hc((1)/(lamda_(1))-(1)/(lamda_(0)))=K and hc((1)/(lamda_(2))-(1)/(lamda_(0)))=2K ` `implies 2((1)/(lamda_(1))-(1)/(lamda_(0)))=(1)/(lamda_(2))-(1)/(lamda_(0))implies (1)/(lamda_(0))=(2)/(lamda_(1))-(1)/(lamda_(2)) implies lamda_(0)=(lamda_(1)lamda_(2))/((2lamda_(2)-lamda_(1)))` and work function of the metal `phi_(0)=(hc)/(lamda_(0))=(hc(2lamda_(2)-lamda_(1)))/(lamda_(1)lamda_(2))`. |
|
| 43912. |
Each quarter of a vessel of depth H is filled with liquids of the refractive indices n_(1),n_(2),n_(3) and n_(4) from the bottom respectively. The apparent depth of the vessel when looked normally is |
|
Answer» `(H(n_(1)+n_(2)+n_(3)+n_(4)))/(4)` `=(H//4)/(mu_(1))+(H//4)/(mu_(2))+(H//4)/(mu_(3))+(H//4)/(mu_(4))` `(H)/(4)((1)/(mu_(2))+(1)/(mu_(2))+(1)/(mu_(3))+(1)/(mu_(4))).` |
|
| 43913. |
Two charges q_1 and q_2 are placed on the X-axis at pointx=-a and x =+a respectively. a. How must q_1 and q_2 be related for the net electrostatic force on a charge Q at x=+(a)/(2)to be zero? b. Repeat (a) but with +Q at x =+(3a)/( 2) |
|
Answer» Solution :Data supplied ` (##JYT_AJP_AIO_PHY_XII_C01_SLV_014_S01.png" width="80%"> Net force at Q is zero Here force due to `q_1` acts towards left and that due to` q_2` towards right . Hence the RESULTANT forceon Q is `F_(Qq_1) -F_(Qq_2) =0` i.e., `F_(Qq_1) = F_(Qq_2) ` `(1)/( 4PI in _0) (Qq_1)/( (a+(a)/(2)))=(1)/( 4pi in _0) .(Qq_2)/( (a)/(2)^(2)) =( q_1)/(( 9a^(2))/( 4)) =(q^(2))/( (a^(2))/( 4)) ` ` (q_1)/( 9) =q_2"" therefore q_1 =9q_2` b.` (##JYT_AJP_AIO_PHY_XII_C01_SLV_014_S02.png" width="80%"> Here force due to `q_1 and q_2` both act towards right. Hence the resultant force on Q is `F_(Qq_1) +F_(Qq_2) =0` ` F_(Qq_1) =-F_(Qq_2) ` ` (1)/( 4pi in _0).( Qq_1)/( (a+(3a)/(2))^(2)) =(1)/( 4pi in _0) .(Qq_2)/( (a)/(2))^(2) =( q_1)/((25a^(2))/( 4)) =(-q_2)/( (a^(2))/( 4))` ` (q,)/( 25) =q_2 "" q_1 =-25 q_2` |
|
| 43914. |
Point 'A' moves uniformly with speed V_(1)(=20 m//sec) so that vector vecv_(1) is continuously 'aimed at point B which in turn moves rectilinearly and uniformly with velocity v_(2) (=10 m//s) along the path PtoQ as shown in the figure if the time (in sec) when the points A and B converge is(3k)/(7) Then, find the value of k? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43915. |
Using Biot Savart's law, derive the expressionfor the magnetic field at a point on theaxis of a circularcurrent loop. |
Answer» Solution :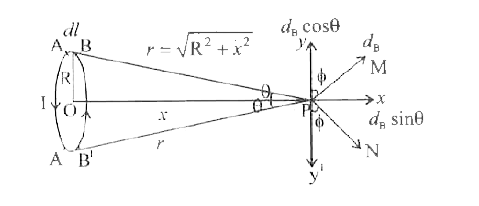 CONSIDER a circular loop of radius R carrying a currentI. Let P be a point at a distancex fromthe centrethe , of the loop on axis.AB is currentelement of lengthdl. The distanceof the pointP from currentelement is r. `therefore` From figure `r=sqrt(R^2+x^2) sin theta=R/r` According to Biot-Savart.s law, magnetic fieldat the PONT P due to the current element AB is `dB =mu_0/(4pi)(Idl)/r^2 "sin"phi` Since `phi=90^@` `dB=mu_0/(4pi)(Idl)/r^2` sin `90^@`( `because ` sin `90^@=1`) `dB=mu_0/(4pi)(I dl)/r^2 ` along PM dB due to the current elementA.B. at the point P is `dB=mu_0/(4pi)(I dl)/r^2` along PN. The magnetic field dB along PM can be resolved into two rectangular components dB cos `phi` along Py and dB sin `phi` along PX. Similarly the magnetic field `d_B` along PN can be resolved into two components . If we consider more smallelementscos `theta`componentscancel each other out . `SigmadB cos phi=0 "" alphaSigmad_B cos theta # 0` `B=intdB sin phi` `B=intmu_0/(4pi)(Idl)/r^2 sin phi` Substituting the values of `r=sqrt(R^2+x^2)`and sin `phi=R/r`in the equation , we get `B=intmu_0/(4pi)(Idl)/(R^2+x^2) R/r = int mu_0/(4pi) (I dl)/(R^2+x^2) R/sqrt(R^2+x^2) =mu_0/(4pi) (IR)/((R^2+x^2)^(3//2)) int dl` But `intdl=2piR to` CIRCUMFERENCEOF the loop `therefore B=(mu_0IR)/(4pi(x^2+R^2)^(3//2))xx2piR` `therefore B=mu_0/(4pi)(2piIR^2)/((x^2+R^2)^(3//2))` |
|
| 43916. |
In the net work of resistors shown in the adjoining figure, the equivalent resistance between A and B is: |
|
Answer» 54 ohm |
|
| 43917. |
(A): The method of dimensions cannot be used to obtain the dependence of work done by a force when the force is incli- ned to the direction of displacement. (R): All trigonometric functions are dimensionless. |
|
Answer» Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of (A) |
|
| 43918. |
How many number of energy bands are there in solids ? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43919. |
A 100 Hz a.c. is flowing in a coil of inductance 10 mH. What is the reactance of the coil ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Here `L = 10 MH = 10 xx 10^(-3) H = 10^(-2)H` `v = 100 Hz` USING `X_(L) = L omega = L xx 2pi v`, we GET `X_(L) = 10^(-2) xx 2 xx 3.14 xx 100 = 6.28 Omega`. |
|
| 43920. |
Using the law of conservation of energy. |
|
Answer» `Deltax=a_(x)t^2//2,v_(x)=alpha_xt, Deltat^2//2v_(y)=a_yt` According to the law of conservation of energy, the decrease in the potential energy of the rod as it sinks is equal to the increase in the kinetic energies of the rod and of the wedge: `m_2gDeltay=(m_2v_y^2)/2+(m_1v_x^2)/(2)` Substituting the VALUES of the displacements and the velocities we obtain `m_2ga_y=m_2a_y^2+m_1a_x^2,a_y=a_xtanalpha` from which we get `a_x=(m_a"g" tanalpha)/(m_1+m_2tan^2alpha),a_y=(m_2"g"tan^2alpha)/(m_1+m_2tan^2alpha)` The reaction is `Q=(m_1alpha_x)/(sinalpha)=(m_1m_2gcosalpha)/(m_1cos^2alpha+m_2sin^2alpha)` |
|
| 43921. |
In 1959 Lyttleton and Bondi suggested that the expansion of the Universe could be explained il matter carried a net charge. Suppose that the Universe is made up of hydrogen atoms with a number density N, which is maintained a constant. Let the charge on the proton be : e_(p) =-(1+y)ewhere e is the electronic charge. (a) Find the critical value of y such that expansion may start. (b) Show that the velocity of expansion is proportional to the distance from the centre. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Let the Universe have a radius R. Assume that the hydrogen atoms are uniformly distributed. The expansion of the universe will start if the COULOMB REPULSION on a hydrogen atom at R is larger that the gravitational attraction. The hydrogen atom CONTAINS one proton and one electron, charge on each hydrogen atom. `e_(1p) = e_(p) + e =(-1 +y)e +e` `=-e + ye + e` = ye Let E be electric field intensity at distance R, on the surface of the sphere, then according to Gauss. theorem, `oint vecE.dvecS = q/epsilon_(0)` `therefore E(4piR^(2)) = 4/3 (piR^(3)N|ye)/epsilon_(0)`......(1) Let us suppose the mass of each hydrogen atom = `m_p` = mass of a proton and `G_R` = gravitational field at distance R on the sphere. Then `=-4piR^(2)G_(R) = 4piGm_(p)(4/3piR^(3))N` `therefore G_(B) =-4/3piGm_(p).NR`........(2) Gravitational force on this atom is, `F_(G) =m_(p) xx G_(R) = (-4pi)/3 Gm_(p)^(2)NR`......(3) Coulomb force on hydrogen atom at R is, `F_( C) = (ye)E = 1/3(y^(2)e^(2)NR)/epsilon_(0)` [From eqns (1)] Now to expansion `F_(C) gt F_(G)` and critical value of Y to start expansion would be when `F_( C) = F_(G)` `therefore 1/3 (Ny^(2)e^(2)R)/epsilon_(0) = (4pi)/3 Gm_(p)^(2)NR` `therefore y^(2) = (4piepsilon_(0))G xx (m_(p)/e)^(2)` `therefore y = sqrt(79.8 xx 10^(-38)) = 8.9 xx 10^(-19) = 10^(-18)` Hence, `10^(-18)`is the required critical value of y corresponding to which expansion of universe would start, (b) Net force experience by the hydrogen atom is given by, `F = F_( C) - F_(G) = 1/3 (Ny^(2)e^(2)R)/epsilon_(0) -(4pi)/3 Gm_(p)^(2)NR` Because of this net force, the hydrogen atom experience an acceleration such that, `m_(p) xx (d^(2)R)/(dt^(2)) = F = 1/3 (Ny^(2) e^(2)R)/epsilon_(0) - (4pi)/3 Gm_(p)^(2)NR` `therefore (d^(2)R)/(dt^(2)) = alpha^(2)R`......(4) where, `alpha^(2) =1/m_(p) (1/3 (Ny^(2)e^(2))/epsilon_(0) -(4pi)/3 Gm_(p)^(2)N)` The solution of equation (4) is given by,`R = Ae^(alphat) + Be^(-alphat)`. We are looking for expansion, here so B = 0 and `R = Ae^(alphat)` Velocity of expansion, `v= (dR)/(dt) = d/(dT) (Ae^(alphat))` `therefore v prop R` Velocity of expansion is proportional to the distance from the CENTRE. |
|
| 43922. |
An ac generator G with adjustable frequency of oscillation is used in the circuit, as shown, Current drawn from the ac source will be maximum if its angular frequency is |
|
Answer» `10^(5) rad/s` |
|
| 43923. |
A radio can tune into any station in the 7.5 MHz to 12MHz band. Wha t is the corresponding wavelength band ? |
|
Answer» Solution :`lambda_(1)=(3xx10^(8))/(7.5xx10^(6))=40 m` `lambda_(2)=(3xx10^(8))/(12XX10^(6))=25 m` THUS WAVELENGTH band is 40 m to 25 m. |
|
| 43924. |
Suppose that you release a small ball from rest at a depth of 0.400 m below the surface in a pool of water. If the density of the ball is 0.450 that of water and if the drag force on the ball from the water is negligible, how high above the water surface will the ball shoot as it emerges from the water? (Neglect any transfer of energy to the splashing and waves produced by the emerging ball.) |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`0.489` m | |
| 43925. |
The distance x travelled by the car in above problem in time t is given by - |
|
Answer» `X = (t^(2))/(2) ((ALPHABETA)/(alpha - BETA))` |
|
| 43926. |
The band gap of the semiconductor of the LED that produces the visual light is at least …… |
| Answer» ANSWER :D | |
| 43927. |
Discuss the spectral series of hydrogen atom. |
|
Answer» Solution :The spectral lines of hydrogen are grouped in separate series. In each series, the distance of separation between the CONSECUTIVE wavelengths decreases from higher wavelength to the lower wavelength, and also wavelength in each series approach a limiting value known as the . series limit. These series are named as LYMAN series, Balmer series, Paschen series, Brackett series, Pfiind series, etc. The wavelengths of these spectral lines perfectly agree with the equation derived from Bohr atom model. `1/lambda = R(1/n^(2) - 1/m^(2)) =barv` where `barv` is known as wave number which is inverse of wavelength, R is known as Rydberg constant whose value is `1.09737 XX 10^(7) m^(-1)` and m and n are positive INTEGERS such that m > n . The various spectral series are discussed below: (a) Lyman series : Put n = 1 and m=2,3,4.....in equation (I). The wave number or wavelength of spcctra lines of Lyman scries which lies in ultra-violet REGION is `barv = 1/lambda = R(1/l^(2) -1/m^(2))` (b) Balmer series: Put n = 2 and m = 3,4,5......in equation (1). The wave number or wavelength of spectral lines of Balmer series which lies in visible region is `barv = 1/lambda = R(1/2^(2) -1/m^(2))` (c ) Paschen series: Put n - 3 and m = 4,5,6......in equation (1). The wave number or wavelength of spectral lines of Paschen scries which lies in infra-red region (near IR) is `barv =1/lambda = R (1/3^(2) -1/m^(2))` (d) Brackett series: Put h = 4 and m = 5,6,7.......in equation (1). The wave number or wavelength of spectral lines of Brackett scries which lies in infra-red region (middle IR) is `barv =1/lambda =R(1/4^(2) -1/m^(2))` ( e) Pfund series: Put n=5 and m=6,7,8,.... in equation (1). The wave number or wavelength of spectral lines of Pfund series which lies in infra-red region (far IR) is `barv = 1/lambda = R(1/5^(2) -1/m^(2))` |
|
| 43928. |
In the circuit in figure, find the amount of heat genrated when switch s is closed. |
|
Answer» Applying loop law  `5-(q)/(2) +10 -(q)/(4) = 0` `(3q)/(4) = 15` `q = 20muC` FINAL distribution of charge  By closing switch only `30muC` charge flow through BATTERY of `10V`. `W_("battery") = 10xx 30muC = 300muJ` `U_(3muF) = (1)/(2)CV^(2) = (1)/(2)xx3muF = (10V)^(2) = 150muJ` Heat generated `= 300muJ - 150muJ - 150muJ` |
|
| 43929. |
In a series resonant L-C-R circuit, the capacitance is changed from C to 3C. For the same resonant frequency, the inductance should be chenged from : |
|
Answer» L to 3L |
|
| 43930. |
A hydrogen atom moving at a speed v absorbs a photon of wavelength 122 nm and stops. Find the value of v. Mass of a hydrogen atom =1.67 xx (10^-27)kg. |
|
Answer» Solution : The linear momentum of the PHOTON ` = H/ lambda = (6.63 xx (10^-34)Js/ 122 xx (10^-9)m) = 5.43 xx (10^-27)KG m (s^-1)` ` or, V = (5.43 xx (10^27)/ 1.67 xx (10^27))m (s^-1)= 3.25 m (s^-1). |
|
| 43931. |
As a wave propagates |
|
Answer» the wave intensity REMAINS constant for a PLANE wave |
|
| 43932. |
In the above question what is the angular velocity of cylinder after the masses fall down from height 'h'? |
|
Answer» `sqrt((8mgh//M+4m)/(R ))` `a=(4T)/(M)=(4Mmg)/(M(M+4m))` `=(4mg)/(M+4m)` Now `omega=(V)/(R)" but "v^(2)=2ah` `therefore omega=((2ah)^(1/2))/(R)` PUTTING for .a. or `omega=(((2xx4mgh)/(M+4m))^(1//2))/(R)` `=(((8mgh)/(M+4m))^(1//2))/(R)` |
|
| 43933. |
A monochromatic light source of frequency villuminates a metallic surface and ejects photoelectron. The electron with maximum energy are just able to ionize the hydrogen atom in the ground state. When the whole experiment is repeated with an incident radiation of frequency 5/6 v, the photoelectrons so emitted are able to excite the hydrogen atom beam which then emits a radiation of the wavelength 1215Å. Find the work function of the metal : |
|
Answer» 6.875 eV `hv=W+(1)/(2)mv_(1)^(2)=w+` Ionization energy Now, ionisation potential =13.6V `:.hv=w+1.6xx10^(-19)xx13.6` `=w21.+76xx10^(-19) ""...(1)` In second case `h.(5)/(6)=w+(1)/(2) mv_(2)^(2)=w+(HC)/(lambda)` `=w+(6.6xx10^(-34)xx3xx10^(8))/(1215xx10^(-10))` `=w+16.3xx10^(-19) ""....(2)` Dividing (1) by (2), `(6)/(5)=(w+21.76xx10^(19))/(w+16.3xx10^(-19))` or `w=11xx10^(-19)J=6.875eV` |
|
| 43934. |
What is the (a) momentum, (b) speed, and (c) de-Broglie wavelength of an electro with kinetic energy energy of 120 eV. |
|
Answer» Solution :Kinetic energy of electron `K=120eV=120xx1.6xx10^(-19)J=1.92xx10^(-17)J` (a) `THEREFORE `Momentum of electron `p=sqrt(2mK)=sqrt(2xx9.11xx10^(-31)xx1.92xx10^(-17))=5.92xx10^(-24)kg" ms"^(-1)` (b) Speed of electron `v=(p)/(m)=(5.92xx10^(-24))/(9.11xx10^(-31))=6.50xx10^(6)ms^(-1)` (C) de-Broglie wavelength of electron `lamda=(h)/(p)=(6.63xx10^(-34))/(5.92xx10^(-24))=1.12xx10^(-10)m=0.112nm`. |
|
| 43935. |
Two identical small metallic sphere having arbitrary charges are separated by a distance ' r ' in air. They are then touched by two more identical metal spheres respectivelyand seperated After- wards A and B are brought to r/(2)distance. Show that initial interaction is same as final interaction- |
|
Answer» Solution :`F=( 1)/( 4piin _0) (q_1q_2)/( r^(2) ) `where, `q_1` and `q_2`are the arbitary charges in A and Brespectively . As and A and B are touched by identical spherethe charges are RESPECTIVELY reduced by ` (q_1)/( 2 ) and ( q_2)/( 2 ) ` Since they are then placed at `(r)/(2) `the new FORCE is ` F.=(1)/( 4pi in _0) ((q_1)/(2) xx (q_2)/( 2) )/( (r)/(2) ^(2)) = (1)/( 4pi in _0) (q_1q_2)/( r^(2)) ((1//4)/(1//4)) ` ` =(1)/( 4pi in _0) (q_1q_2)/( r^(2))` F, hence result. |
|
| 43936. |
There is a branch hanging from a tree on the bank of a lake. It is at a height of h_(1) from the surface of water. A diver under water sees it at height of h_(2) . What is the relation between h_(1) and h_(2)? Given, mu_(w) = 1.33 |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :As the object is situated in a rarer medium and it is seen from the denser medium, `mu = (("apparent HEIGHER of the object")/("from the surface of water"))/(("real heigher of the object")/("from the surface of water")) = (h_(2))/(h_(1))` `or, " " 1.33 = (h_(2))/(h_(1)) or, h_(2) = 1.33 h_(1)` |
|
| 43937. |
A dics of mass 400gm is rolling in a horizontal surface with uniform velocity of 2m/s . calculate its total K.E. |
|
Answer» 2J |
|
| 43938. |
Howmany significat figures are there in 4077- |
|
Answer» 3 |
|
| 43939. |
Deduce and expression for Magnetic dipole moment of revolving electron around the nucleus in a circular orbit. |
Answer» Solution :Suppose an electron undergoes circular motion AROUND the nuleus as shown in Figure. The circulating electron in a loop is like current ina circular loop ( since flow of charge is known as current). The magnetic DIPOLE moment due to current carrying circular loop is `vecmu_(L) =I vecA`......(1) In magnitude , ` mu_(L) = I A` If T is the TIME period of an electron , the current due to circular motion of the electron is ` I = (-e)/T ` .....(2) where - e is the charge of an electron . If R is the radius of the circular orbit and v is the velocity of the electron in the circular orbit , then ` T = (2 pi R)/v ` ......(3) Using equation (2) and equation (3) in equation (1), we get `mu_(L)=- e/((2pi R)/v) pi R^(2) = ( evR)/2 ` .....(4) where ` A = pi R^(2)` is the area of the circular loop. By definition, angular momentum of the electron about O is ` vecL = vecr xx vecp` In magnitude, ` L = Rp = MV R` ......(5) Using equation (4) and equation (5) , we get , `mu_(L)/L = - ((evR)/2)/(mvR) = e/(2 m) rArrvecmu_(L) = - e/(2 m ) vecL ` ......(6) The negative sign indicates that the magnetic moment and angular momentum are in OPPOSITE direction. The ratio `mu_(L)/L ` is a constant and also known as gyro - magnetic ratio `(e/(2m)) ` . It must be noted that the gyro- magnetic ratio is a constant of proportionality which connects angular momentum of the electron and the magnetic moment of the electron. |
|
| 43940. |
A horizontal loop abcd is moved across the pole piece of a magnet as shown in the figure. Witha constant speed v. When the edge ab of the loop enters the pole pieces at time t=0 sec. Which one of the following graphs presents correctly the induced emf in the coil? |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 43941. |
A 100 kg piston encloses 32 g of oxygen gas at a temperature of 27^(@)C in a vertical cylinder of hose area of 4 dm^(2). The air pressure outside is 1xx10^(5)Pa. The axis of the cylinder is vertical, and the piston can moves in it without friction. How much heat is to be transferred to the gas to raise the piston by 20cm from rest . positon? ("Use" R=(25)/(3)J//"mol"-k) |
|
Answer» 3000J `V=(nRT)/(P)` `H=(V)/(A)=(2xx10^(-2))/(4xx10^(-2))=(1)/(2)m` `T_(2)-(T_(1))/(T_(1))=(DELTAH)/(h)` `DeltaQ=nC_(p)(T_(2)-T_(1))` |
|
| 43942. |
A 10Omega resistance, 5mH inductor and 10muF capacitor are joined in series. When a suitable frequency of alternating current source is joined to this combination, the circuit resonates. If the resistance is halved, the resonance frequency …… |
|
Answer» is HALVED `therefore omega=1/sqrt(LC)` , where there is no TERM of resistance so on changing the VALUE of resistance there will no CHANGE of `omega`. |
|
| 43943. |
In an a.c. circuit, the instantaneous values of e.m.f. and current are : e = 100 sin300 tvolt and i= 2 sin (300 t + pi/3) Ampere The average power consumed in the circuit is : |
|
Answer» 100 W |
|
| 43944. |
The horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field at a certain place is 3.0 xx 10^(-5) T and the direction of the field is form the geographic south to the georgraphic north . A very long straihgt conductor is carrying a steady current of 1 . What is the force par unit length on it when it is placed on horizontal table and the direction of the current is (a) east to west , (b) south to north ? |
|
Answer» Solution :`F = 1L xx B` `F= I// B SIN theta` The FORCE per unit length is `f= (F)/(l)` = IB sin `theta` When the current is flowing fromeast to west, `theta = 90^(@)` Hence, `f= IB =1 xx 3 xx 10^(-5) = 3 xx 10^(-5) Nm^(-1)` The direction of the force is downwards. b. When the current is flowing from south to north `theta = 0^(@)` f=0 , Hence there is no force on the conductor. |
|
| 43945. |
A convex lens of focal length 10 cm. is used as a magnifying lens. What will be the magnification? |
Answer» Solution : `m=[(I)/(O)] =(v)/(u) =(-30)/(-7.5 )=4` image is ERECT, VIRTUAL and four times the size of object. |
|
| 43946. |
A particle of charge q and mass m moves in a circular orbit of radius r with angular speed omega. The ratio of the magnitude of its magnetic moment to that of its angular momentum depends on |
|
Answer» `omega` and Q which is a function of q and m only. This can be derived as follows `M=1A = (qupsilon)(pir^2)=(q)(omega/(2PI))(pir^2)=(qomegar^2)/2` `L=Iomega=(mr^2omega) THEREFORE M/L=(q omegar^2//2)/(mr^2omega)=q/(2m)` |
|
| 43947. |
A ball A of mass m moving along positive x-direction with kinetic energy K and momentum p undergoes elastic head on collision with a stationary ball B of mass M after collision the ball A moves along negative x-direction with kinetic energy K//9, final momentum of B is |
|
Answer» p `12MV_(1)^(2)=K/9` ` implies V_(1)= sqrt((2K)/(9M))` `K=1/2MV^(2)=1/2(MV^(2))/M=p^(2)/(2M)` `Mu_(1)=-MV_(1)+p_(B)` `M(u_(1)+V_(1))=p_(B)` `P_(B)=M[sqrt((2K)/M)+ sqrt((2K)/9K)]` `=sqrt(2MK) + sqrt(2MK)/K` `=p+p/3` `(4p)/3` |
|
| 43948. |
An electron is moving in a circle of radius r in a uniform magnetic field B. Suddenly the field is reduced to B/2. The radius of the circular path now becomes. |
|
Answer» `r/2` `r=(mv)/(qB)rArrrprop1/B` When B is REDUCED to `B/2`, r is doubled `therefore` NEW radius of circular path is 2r |
|
| 43949. |
What do you mean by Hygrometry ? |
| Answer» Solution :HYGROMETRY is the STUDY and MEASUREMENT of the quantity, of AQUEOUS VAPOUR in the atmosphere. | |
| 43950. |
A cube of side 1 is placed in a uniform field E, where E= E hat(i). The net electric flux through the cube is |
|
Answer» ZERO |
|



