Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 39151. |
Two capillaries of same diameter are dipped into liquids of specific gravity 0.4 and 0.8 respectively. If their surace tensions are in the ratio 6:5 then the ratio of heights of liquids in them will be |
|
Answer» `12:5` |
|
| 39152. |
A particle is found to be at rest when seen from a frame S_(1) and moving with a constant velocity when seen from another frame S_(2)(a) Both the frames are inertial(b) Both the frames are non inertial(c ) S_(1) is inertial and S_(2) is non inertial(d) S_(1) is non inertial and S_(2) is inertial |
|
Answer» a, B are TRUE |
|
| 39153. |
A shell of mass 200 gm is ejected from a gun of mass 4 kg by an explosion that generates 1.05 kJ of energy. Calculate the initial velocity of the shell |
|
Answer» Solution :GIVEN Data: m= 200 gm = 0.2 kg , M=4 kg, `"Energy GENERATED" 1.05 KJ =1.05 xx 10^(3) J` According to LAW of Conservation of linear momentum `mv=Mv^(.)` `:. v^(.)=((m)/(M))v` Total K.E of the GUN and bullet `=(1)/(2)Mv^(.2)+(1)/(2)mv^(2)` `=(1)/(2)M((m)/(M)v)^(2)+(1)/(2)mv^(2)` `=(1)/(2)(m^(2)v^(2))/(M)+(1)/(2)mv^(2)` `=(1)/(2)mv^(2)[(m)/(M)+1]` `(1)/(2) xx 0.2 xx v^(2)[1+(0.2)/(4)]=1.05 xx 10^(3)J` `:. v^(2)=(4 xx 1.05 xx 1000)/(0.1 xx 4.2)=100^(2)` `v=100 m // s` |
|
| 39154. |
Give the expression for the fundamental frequency in the case of an open pipe system. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`f_(0) =(v )/( 2L)` where `v -` velocity of SOUND in air and L-length ofthe pipe Note `:` with END correction `f_(o) = ( v)/(4( L + E ))` |
|
| 39155. |
A disc of mass .m. and radius R has a concentric hole of radius .r.. Its M.I. about an axis through centre and normal to its plane is |
|
Answer» `(m)/(2)(R-r)^(2)` |
|
| 39156. |
A rope of negligible mass is wound round a hollow cylinder of mass 3 kg and radius 40 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder if the rope is pulled with a force of 30 N ? What is the linear acceleration of the rope ? Assume that there is no slipping. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`25 s^(-2),10 m s^(-2)` | |
| 39157. |
Average speed of a particle moving with different speed is average of different speed. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39158. |
Find the components of vector vecA=2hati+3hatj along the directions of hati+hatj and hati-hatj. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39159. |
While during a carpet, we give a sudden jerk or beat it with a stick. Why? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Because inertia of rest keeps the DUST in its position and the dust gets removed as the carpet MOVES away. | |
| 39160. |
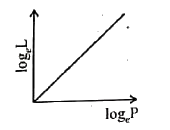
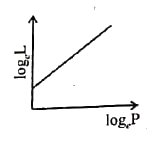
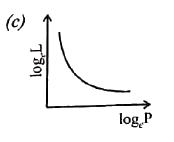
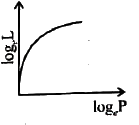
The curve betwee log_(e)L and log_(e)P is (L is the angular momentum and P is the linear momentum): |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 39161. |
Energy of a diatomic molecule at high temperature is _________ |
|
Answer» `(7)/(3)RT` |
|
| 39162. |
What is compressibility ? Write its formula, unit and dimensional formula. |
|
Answer» Solution :The reciprocal of the bulk modulus is called compressibility. It is DENOTED by k. It is also DEFINED as the fractional chanage in volume per unit increase in PRESSURE. `k = ((1)/(B)) = (-1)/(Delta p) XX ((Delta V)/(V)) =- (Delta V//V)/( Delta p ) ` Its unit is `N^(-1) m ^(2) or Pa ^(-1)` and dimensional formula `[M^(-1) L ^(1) T ^(2)]` |
|
| 39163. |
Explain the variation of 'g' with altitude. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Variation of g with altitude: Consider an object of mass m at a height h from the SURFACE of the Earth. Acceleration experienced by the object due to Earth is `g' = (GM)/((R_(E) + h)^(2))` `R_(E) to` Radius of Earth `g' = (GM)/(R_(E)^(2)(1 + h/(R_E))^(2)) = (GM)/(R_E^2) (1 + h/(R_E))^(-2)` If `h < < R_(E)` We can use Binomial expansion. Taking the terms UPTO first order `g' = (GM)/(R_E^2) (1-2h/(R_E)) = g(1-2 h/(R_E))` We find TAT `g' < g`. This means that as altitude h increases, the acceleration due to gravity g decreases.  . .
|
|
| 39164. |
A faulty barometer tube is 90 cm long and it contains some air above mercury. The reading is 74.5 cm when the true atmospheric pressure is 76 cm. What will be the true atmopsheric pressure if the reading on this barometer is 74 cm? (H = 10m of water column) |
|
Answer» 73.25 cm |
|
| 39165. |
In the question number 62, if the lift starts moving up with a uniform speed of 5 m s^(-1) and the girl again throws the ball up with the same speed, how much does the ball take to return to her hands? |
|
Answer» 5 s |
|
| 39166. |
A body of mass 2 kg is allowed to slide down along a quadrant of a circle from the horizontal position. In reaching to the bottom, Its velocity is 6m/sec. The work done in overcoming the friction is 10J. The radius of circle is (g=10 ms^(-2)) |
|
Answer» 2 mgl |
|
| 39167. |
Two ships are 10 km apart on a line running south to north. The one farther north is streaming west at 40 km per hr, the other ship is streaming towards north with the same speed. The time after which the two ships are at closed distance is |
|
Answer» 7.5 min |
|
| 39168. |
A foolball at 25^(@)C has 0.5 mole air molecules . calculate the internal energy of air in the ball. |
|
Answer» Solution :The INTERNAL energy of ideal GAS `=3/2` NkT. The number of air molecules is given in terms of number of moles so, rewrite the EXPRESSION as follows: `U=3/2muRT` Since `Nk=muR. "Here"mu` is number of moles. Gas CONSTANT `R=8.31 J/("MOL")K` Temperature`T=273+27^(@)C=300K` `U3/2xx0.5xx8.31xx300=1869.75J` This is approximately equivalent to the kinetic energy of a man of 57 kg runinf with a speed of 8 `ms^(-1)` |
|
| 39169. |
The horizontal acceleration that should be given to a smooth inclined plane of angle sin^(-1)((1)/(l)) to keep an object stationary on the plane, relative to the inclined plane is |
|
Answer» `(G)/(SQRT(l^(2)-1))` At equilibrium `mg sin theta=ma cos theta` |
|
| 39170. |
Three bodies each of mass.m. are placed at the three corners of a square of side .a.. The gravitational force on unit mass kept at the fourth corner is: |
|
Answer» `(GM)/(3a^(2))` |
|
| 39171. |
H calories of heat is required to increase thetemperature of one mole of monoatomic gas from 20^(@)C to 30^(@)C at const. volume. The quantity of heat required to increase the temperature of 2 moles of a diatomic gas from 20^(@)C to 25^(@)C is at constant volume is |
|
Answer» `(4H)/(3)` |
|
| 39172. |
Explain why simple harmonic motion is called so ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :No. Because it is not to and FRO. | |
| 39173. |
A heavy small sized sphere is suspended by a string of length 2. The sphere is rotated uniformly in a horizontal circle with the string making an angle theta with the vertical. The time period of this conical pendulum is |
|
Answer» `2 pisqrt((L tantheta)/( g))` |
|
| 39174. |
A uniform flexible chain of mass m and length 2 hangs in equilibrium over a smooth horizontal pin of negligible diameter. One end of the chain is given a small vertical displacement so that the chain slips over the pin. The speed of chain when it leaves pin is- |
|
Answer» `SQRT(2gl)` |
|
| 39175. |
A black body of mass 34.38 gm and surface area 19.2" cm"^(2) is at an initial temperature of 400K. It is allowed to cool inside an evacuated enclosure kept at constant temperature 300K. The rate of cooling is 0.04^(0)C per second. The specific heat of the body in J kg^(-1)K^(-1) is approximately |
|
Answer» 2800 |
|
| 39176. |
The blades of a wind mill sweep out a circle of area A. What is the K.E. of the air? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`K.E=(1)/(2)mv^(2)=(1)/(2)xx360xx(36xx(5)/(18))^(2)=18000Js^(-1)` | |
| 39177. |
A platinum resistance thermometer reads 0^(0)C when its resistance is 80 Omega and 100^(0) C when its resistance is 90 Omega. Find the temperature at the platinum scale at which the resistance is 86 Omega |
|
Answer» `30^(0)` C |
|
| 39178. |
A rod of length 2m and mass 0.5kg is fixed at one end and allowed to hang vertically from a rigid support. Find the work done in raising the other end of the rod until it makes an angle of 60^(@) with the vertical. (g = 10 ms^(-2)) |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`m= 0.5kg, l= 2M, theta = 60^(@)` WORD done `W= mg (l)/(2) (1- cos theta)` `=0.5 xx 10 xx(2)/(2) (1- cos 60^(@))` `=5 xx (1 - (1)/(2))= 5 xx (1)/(2) = 2.5J` |
|
| 39179. |
Two particles which are initially at rest, move towards each other under the action of their internal attraction. if their speeds are v and 2v at any instant , then the speed of the centre of mass of the system will be |
|
Answer» 2v |
|
| 39180. |
A sphere of density d is allowed to fall in a liquid of density d/4. The acceleration of the body will be |
|
Answer» `G//4` |
|
| 39181. |
Why can't we make any conversaton on the surface of Moon ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Because SOND waves are mechanical which compulasrily NEED atmosphere. But Moon does not have any atmosphere and so we can not MAKE any conversatin on Moon. | |
| 39182. |
Identify the increasing order of the angular velocities of the following 1. Earth rotating about its own axis 2. Hour's hand of a clock 3. Second's hand of a clock 4. Flywheel of radius 2 m making 300 rpm |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 39183. |
A mass of 1 kg is suspended by means of a thread. The system is lifted up with an acceleration of 4.9 m//s^(2) |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :TENSION while lifting the mass, `T_(1) = G + a = g + (g)/(2) = (3g)/(2) [ because a = (g)/(2)]` |
|
| 39184. |
A ballistic pendulum is a device that was used to measure the speeds of bullets before the development of electronic tiring, devices. The device consists of a large block of wood of mass M, hanging from two long cords. A bullet of mass m is fired into the block. the bullet comes quickly into rest and the block + bullet rises to a vertical distance h before the pendulum comes momentarily to rest as the ends of the arc. ltbr. In the process. the linear momentum is conserved. In such a collision. some kinetic energy is dissipated as heat: so mechanical energy is not conserved. When there is a loss in mechanical energy, the collision is said to be inelastic. Further when two bodies coalesce, the collision is said to be perfectly inelastic. The energy dissipated as heat in the collision is |
|
Answer» `1/2"MU"^(2)-mgh` `=` initial energy `-` FINAL energy `=1/2"mu"^(2)-(m+M)gh` |
|
| 39185. |
A ballistic pendulum is a device that was used to measure the speeds of bullets before the development of electronic tiring, devices. The device consists of a large block of wood of mass M, hanging from two long cords. A bullet of mass m is fired into the block. the bullet comes quickly into rest and the block + bullet rises to a vertical distance h before the pendulum comes momentarily to rest as the ends of the arc. ltbr. In the process. the linear momentum is conserved. In such a collision. some kinetic energy is dissipated as heat: so mechanical energy is not conserved. When there is a loss in mechanical energy, the collision is said to be inelastic. Further when two bodies coalesce, the collision is said to be perfectly inelastic. The collision of block-bullet system is |
|
Answer» PERFECTLY elastic |
|
| 39186. |
A ballistic pendulum is a device that was used to measure the speeds of bullets before the development of electronic tiring, devices. The device consists of a large block of wood of mass M, hanging from two long cords. A bullet of mass m is fired into the block. the bullet comes quickly into rest and the block + bullet rises to a vertical distance h before the pendulum comes momentarily to rest as the ends of the arc. ltbr. In the process. the linear momentum is conserved. In such a collision. some kinetic energy is dissipated as heat: so mechanical energy is not conserved. When there is a loss in mechanical energy, the collision is said to be inelastic. Further when two bodies coalesce, the collision is said to be perfectly inelastic. What is the initial speed of the bullet in terms of heighth? |
|
Answer» `m/Msqrt(2gh)` `1/2(M+m)V^(2)=(m+M)gh` `V^(2)=2ghimplies[("mu")/((M+m))]^(2)=2h` `U^(2)=((M+m)/m)^(2)2gh` `impliesu=([M+m])/m sqrt(2gh)` |
|
| 39187. |
A ballistic pendulum is a device that was used to measure the speeds of bullets before the development of electronic tiring, devices. The device consists of a large block of wood of mass M, hanging from two long cords. A bullet of mass m is fired into the block. the bullet comes quickly into rest and the block + bullet rises to a vertical distance h before the pendulum comes momentarily to rest as the ends of the arc. ltbr. In the process. the linear momentum is conserved. In such a collision. some kinetic energy is dissipated as heat: so mechanical energy is not conserved. When there is a loss in mechanical energy, the collision is said to be inelastic. Further when two bodies coalesce, the collision is said to be perfectly inelastic. After collision what is the combined velocity of the bullet + block system? |
|
Answer» `m/Mu` `mu=(m+M)Vimplies V("mu")/((M+m))` |
|
| 39188. |
A cylindrical drum open at the top contains 30 liters of water. It drains out through a small opening at the bottom. 10 litres of water comes out in first 10%, the next 10 litres in a further time t_(2) and the last 10 litres in a further time t_(3). Then |
|
Answer» `t_(1)=t_(2)=t_(3)` |
|
| 39189. |
Random error can also be called as ............. |
|
Answer» PERSONAL error |
|
| 39190. |
A lead shot of 1 mm diameter falls through a long colummn of glycerine. The variation of the velocity v with distance covered (s) is represented by |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 39191. |
A hydrogen balloon released on the moon |
|
Answer» climbs up with an ACCELERATION of `6 xx 9.8 ms^(-2)` |
|
| 39192. |
A ring of radius R made of lead wire of breaking strength rho and density delta, is rotated about a stationary vertical axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to its plane. Calculate the number of rotation per second at which the ring ruptures |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39193. |
10 gm of ice at - 10^@Cis mixed with 100 gm of water at 50^@Ccontained in a calorimeter weighing 50gm. (Specific heat of water = 1 "cal gm"^(-1).""^(@)C^(-1) Latent heat of ice = 80 cal/gm, specific heat of ice = 0.5 "cal/gm"^(0)Cand specific heat of copper = 0.09 "cal/gm/"^(@)C ). The final temperature reached by the mixtures is |
|
Answer» `25.5^@C` |
|
| 39194. |
Find the moment of inertia of a uniform rod about an axis which is perpendicular to the rod and touches any one end of the rod. |
Answer» Solution :The concepts to form the integrand to find the moment of inertia are to be followed. Now, the ORIGIN is fixed to the LEFT end of the rod and LIMITS are to be taken from 0 to `l`.  `I=(M)/(l)int_(0)^(l)x^(2)dx=(M)/(l)[(x^(3))/(3)]_(0)^(l)=(M)/(l)[(l^(3))/(3)] I=(1)/(3)Ml^(2)` |
|
| 39195. |
A body falls freely from a height of 125m(g=10m//s^(2)) after 2 sec gravity ceases to act Find the time taken by it to reach the ground? |
|
Answer» Solution :Distance covered in 2s under GRAVITY `s_(1)=(1)/(2)g t^(2)=(1)/(2)(10)2^(2)=20M` velocity at the end of 2s `V=g t=(10)2=20m//s`. Now at this instant gravity CEASES to act implies velocity by here after BECOMES constant. The remaining distance which is `125-20=105m` is covered by the body with constant velocity of `20m//s`. Time taken to cover `105m` with constant velocity is given by, `t_(1)=(S)/(V)impliest_(1)=(105)/(20)=5.25s` Hence total time taken to reach the ground `=2+5.25=7.25s` |
|
| 39196. |
A simple pendulum from earth is shifted to moon (g_(m) = g_(g)//6). Foreign minute on earth, the time on the moon as measured by the pendulum is (For same number of oscillations) |
|
Answer» 24.5 SEC |
|
| 39197. |
During an adiabatic change, specific heat of a gas is |
|
Answer» Zero |
|
| 39198. |
A particle of mass m is moving yz-plane with a uniform velocity v with its trajectory running parallel to +ve y-axis and intersecting z-axis at z=a. The change in its angular momentum about the origin as it bounces elastically from a wall at y= constant is |
|
Answer» `mvabari` |
|
| 39199. |
In case of superposition of waves (atx=0), y_(1)=4sin(1026pit) and y_(2)=2sin(1014pit) (a) the frequency of resulting wave is 510Hz (b) the amplitude of resulting wave varies at frequency 3Hz (c ) the frequency of beats is 6 per second (d) the ratio of maximum to minimum intensity is 9 The correct statements are |
|
Answer» `a,d` |
|
| 39200. |
For the equation FpropA^(a)v^(b)d^©, where F is the force, A is the area V is the velocity and d is the density, the values of a,b and c are, respectively. |
|
Answer» `1,2,1` Comparing powers of `M,L` and `T` on both sides, we GET `c=1, 2a+b-3c=1, -b=-2` or `b=2` Also `2a+2-3(1)=1implies2a=2` or `a=1` `:.` This 1,2,1 |
|