Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 39051. |
The scalar and vector products of two vectors are 48sqrt(3) and 144 respectively. What is angle between the two vectors? |
|
Answer» `30^(@)` |
|
| 39052. |
In a gravity free surface, shape of large drop of liquid is |
|
Answer» SPERICAL |
|
| 39053. |
To hit a car a gun is positioned horizontally behind the car along a straight road. The car is moving on theroadwith auniform velocity of 72 km*h^(-1) . If the gun is fired at an angle of 45^@ with thehorizontal , at a distance of 500 m from the car,find the distance of thecar from the gun just when the bullet hits the car. Given, g=10 m/s^2. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39054. |
A car moving with a velocity of 72 KMPH stops engine just before ascending an inclined road. If 25% of energy is wasted in overcoming friction, the car rises to a height of (g=10ms^(-2)) |
|
Answer» 6m |
|
| 39055. |
Which oner of the following relationships between the acceleration a and displacement x of a particle involve SHM. |
|
Answer» a=5x |
|
| 39056. |
An adult weighting 600 N raises the centre of gravity of his body by 0.25 m while taking each step of 1 m length in jogging. If he jog for 6 km, calculate the energy utillised by him in jogging assuming that there is no energy loss due to friction of ground and air. Assuming that the body of the adult is capable of converting 10% of energy intake in the form of food. calculate the energy equivalents of food that would required to compensate energy utilised for jogging. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :W = mg = 600 N h = 0.25 m l = 1 m d = 6 km = 6000 m ` :. ` Total number of STEPS= `(6000)/1 = 6000` Total energyutilisedin jogging ` = n xx mgh` ` = n xx mgh ` ` = 6000 xx 600 xx0.25 `J `= 9 xx10^(5)J` Since, 10 % intake ENERGY is utilised in jogging ` :. `Total intake energy ` = 10 xx 9 xx 10^(5)J` ` = 9xx10^(6)J` |
|
| 39057. |
Explain Shear Modulus. |
|
Answer» Solution :The ratio of shearing tres to be coresponding shearing strain is called the SHEAR modulus of the material and is represented by G. It is also called the modulus of rigidity. `G = ("Shering stress"(sigma _(s)))/("Shearing strain"(theta))` `(F//A)/(Delta L) = (FL)/(ADeltax)` But for shear strain `(Delta X)/(L) = tan theta =theta` `G = ((F //A))/(theta) = (F)/(A theta)` The shearing stress `sigma _(s)` can also be expressed as `sigma _(s) = G xx theta` SI unit of shear modulus is `Nm^(-2) or Pa` The shear moduli (G) of a few common materials : 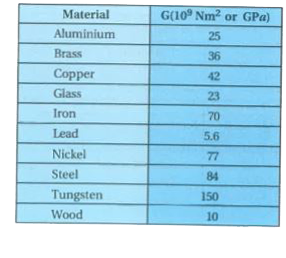 The shear moduli of a few common materials are given in table. It can be SEEN that shear modulus (or modulus of rigidity) is generally less than Young.s modulus. For most materials `G ~~ (Y)/(3).` |
|
| 39058. |
Twoballs are dropped to the ground from different height . One ball is dropped 2.0s after the other, but both strike the ground at the same time 5.0 s after the 1 st is dropped. a) What is the different in the heights from which they were dropped ? b) From what height was the firstball dropped ? |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 39059. |
The atmosphere is held to the earth by |
|
Answer» The ROTATION of the earth |
|
| 39060. |
A butterfly and stone (mass of later is greater than earlier ) is moving with same velocity . Momentum of the stone is . . . . . Than the momentum of butterfly . |
|
Answer» equal |
|
| 39061. |
During the propagation of one progressive harmonic wave having amplitude 10 m, displacements and particles at 2 m and 16 m at respectively 2s and 8 s are5 mand 5sqrt3 m respectively. Find angular frequency and wave vector for this wave. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`(i) y _(1) = A sin (omega t _(1) - kx _(1))` `therefore 5 = 10 sin (2 omega -2k)` `therefore sin (2 omega -2k) =1/2 = sin ""(pi)/(6)` `therefore 2 omega - 2k = (pi)/(6)` `therefore 12 omega - 12k =pi ""...(1)` `(ii) y _(2) = A sin (omega t _(2) - kx _(2))` `therefore 5 sqrt3 = 10 sin (8 omega -16K)` `therefore sin (8 omega - 16k ) = (sqrt3)/( 2) = sin ""(pi)/(3)` `therefore 8 omega - 16 K = (pi)/(3)` `therefore 24 omega - 48 k =pi ""...(2)` Multiplying equation (1) by `(-2)` we GET, `-24 omega + 24 k =- 2pi` Adding equation (2) and (3), `- 24 k =- pi` `therefore k = (pi)/(24) (rad)/(m) ""...(4),` From (1) and (4), `12 omega -12 ((pi)/(24)) = pi` `therefore 12 omega -(pi)/(2) =pi` `therefore 12 omega = (3pi)/(2)` `therefore omega = (pi)/(8) (rad)/(s) ""...(5)` |
|
| 39062. |
A particle starts from the origin at t=0 s with a velocity of 10.0hatjm//s andmoves in the x-y plane with a constant acceleration of (8.0hati+2.0hatj) " m s"^(-2) (a)At what time is the x - coordinate of thespeed of the particle at the time ? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39063. |
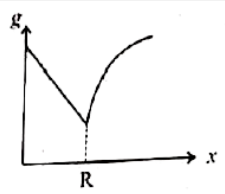
Variation of acceleration due to gravity (g) with distance x from the centre of the Earth is best represented by (R to Radius of the Earth) |
|
Answer»
`g={{:((GM)/(R^3)x," "xltR),((GM)/(x^2)," "xgeR):}` |
|
| 39064. |
Calculate the coefficient of performance of an ideal refrigerator working between -13 ^(@)C and 27^(@)C ? |
|
Answer» Solution :`T_(1) = 27 + 273 = 300 K, T_(2) = - 132 73 = 260 K` Coefficient of porformance `= (T_(2))/( T _(1) - T_(2)) = (260)/( 300 - 260 ) = (260)/( 40) = 6.5` |
|
| 39065. |
When the angle between two vectors of equal magnitudes is 2/3, prove that the magnitude of the resultant is equal to either. |
| Answer» Solution :`R=(P^(2)+Q^(2)+2PQcostheta)^(1//2)=(p^(2)+p^(2)+2P.pcos""(2PI)/(3))^(1//2)=[2p^(2)+2p^(2)((-1)/(2))]^(1//2)=p` | |
| 39066. |
In the above problem the final angular velocity of the small cylinder is |
|
Answer» `(omega_(0))/(4)` |
|
| 39067. |
A spherica ball of radius R and mass m collides with a plank of mass M kept on a smooth horizontal surface Just before impact the centre of the ball has a velocity V_(0) and angular velocity omega_(0) as shown in the figure. After the impact, the normal velocity is reversed with same magnitude and the ball stops rotating after the impact. The coefficient of friction between the and the plank is mu. Assume that the plank is larger enough. The distance on the plank between first two impacts of the ball is (4V_(0)Romega_(0))/(betag)(1+(m)/(M)) Find the value of beta |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39068. |
If vectors vecA and vecB are 3i -4j + 5k and 2i + 3j - 4k respectively then find the unit vector parallel to vecA + vecB |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`((5i-j+k))/SQRT(27)` | |
| 39069. |
The diameter of a brass rod is 4 mm and Young's modulus of brass is 9 xx 10 ^(9) Nm ^(-2),What will be the force required to stretch by 0.1% of its length ? |
|
Answer» `36pi N` Now `Y= (F)/(A) xx (l)/(Delta l )` `=F = YA xx (Deltal )/(l)` `= 9 xx 10 ^(9) xx pi R ^(2) xx 1 xx 10 ^(-3)` `= 0 xx 10 ^(9) xx pi xx(2 xx 10 ^(-3)) ^(2) xx 1 xx 10 ^(-3)` `= 36 pi xx 10 ^(0)` `= 36 pi N` |
|
| 39070. |
The value of resistance is 10.845Omega and the urrent is 3.23Ã…. On multiplying, we get the potential difference is 35.02935 V. the value of potential difference in terms of significant figures would be |
|
Answer» 35V |
|
| 39071. |
When an observer is standing on earth, the trees and houses appear stationary to him .However , when he is sitting in a moving train, all these objects appear to move in backward direction. Why ? |
| Answer» Solution :For the stationary observer, the relative velocity of TREES and houses is zero. for the observe sitting in the moving train, the relative velocity of houses and trees is NEGATIVE . So these OBJECTS appear to move in BACKWARD direction . | |
| 39072. |
Two particles of masses 2 kg and 4 kg are approaching towards each other with ccelerations 1m//s^(2) and 2m//s^(2), respectively, on a smooth horizontal suface. Then find the acceleration of centre of mass of the system and direction of acceleration of CM. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The acceleration of CM of the SYSTEM is given by `a_(CM)=(m_(1)a_(1)+m_(2)a_(2))/(m_(2)+m_(2))impliesa_(CM)=(2xx1+4(-2))/(2+4)=-1m//s^(2)` Negative sign indicates that aceleratioin of CM will be in the direction of acceleration of `4 kg` mass. |
|
| 39073. |
Two sitar strings A and B playing the note .Dha. are slightly out of tune and produce beats of frequency 5 Hz. The tension of the string B is slightly increased and the beat frequency is found to decrease to 3 Hz. What is the original frequency of B if the frequency of A is 427 Hz ? |
| Answer» Solution :Increase in the tension of a string increases its frequency. If the original frequency of B (`v_(B)`) were GREATER than that of A (`v_(A)`), further increase in `v_(B)` should have resulted in an increase in the BEAT frequency. But the beat frequency is FOUND to decrease. this shows that `v_(B) lt v_(A)`. since `v_(A) - v_(B) = 5 Hz`, and `v_(A) = 427 Hz`, we get `v_(B) = 422 Hz`. | |
| 39074. |
Two small satellites move in circular orbits around the earth, at distances r and r+ triangle r from the centre of the earth. Their time periods of rotation are T and T= triangle T.(triangle r lt lt r, triangle T lt lt T). |
|
Answer» `TRIANGLE T= (3)/(2)T (triangle R)/(r )` |
|
| 39075. |
A force F is applied on the top of a ring of mass M and radius R placed on a rough horizontal surface. Friction is sufficient to prevent slipping. Find the frictional force acting on the ring. |
|
Answer» Solution :`:.alpha=(TAU)/(I)=(F(2R))/(2MR^(2))=(F)/(MR)` Now `F+f=Ma=Mralpha=F` or `f=0` 
|
|
| 39076. |
Tie a small piece of stone to one end of a string and whirl it in a circle with your hand The centripetal force required by the stone is being supplied by your hand through the string If the string breaks suddenly you observe that the stone flies off along the tangent to the circle at that instant . Read the above passage and answer the followingquestions: (i) Why does the stone fly off along the tangent to the circle at the instant the string breaks (ii) What lessons of life do you learn from this study ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) At the instant the string breaks the centripetal force is no LONGER provided to the stone Therefore the stone is not being forced to move along the circle On account of inertia of DIRECTION the stone flies off along the tangent to the circle that intant. (ii) To change the straight line path of stone to circular path a continous force (= centripetal) is needed The moment this force ceases the stone reverts to its natural st line path The same is true in day to life Continuous motivation and efforts are needed to KEEP the young kids on the desired path The moment we STOP motivating kids may revert to the path of their choice . |
|
| 39077. |
Define universal gravitational constant (G). |
|
Answer» Solution :In `F = (Gm_(1) ,m_(2))/r^2`taking `m_1 = m_2 = 1 kg, r = 1 m F = G` The FORCE of attraction between two BODIES each of UNIT MASS placed at unit distance apart is known as universal gravitational constant. |
|
| 39078. |
A machine gun fires 360 bullets per minute. Each bullet moves with a velocity of 600ms^(-1). If the power of the gun is 5.4 kw, the mass of each bullet is |
|
Answer» 5 kg |
|
| 39079. |
The focal length of the objective and the eye piece of a compound microscope are 2.0cm and 3.0 respectively. The distance between the objective and the eyepiece is 15.0cm, The final image formed by the eyepiece is at infinity. The two lenses are thin. The distance, in cm, of the object and the image produced by the objective, measured from the objective lens, are respectively, |
|
Answer» Solution :The eyepiece forms the final image at infinity.Its object should therefore lie at its FOCUS. F denotes focus of eyepiece. I denotes image formed by the OBJECTIVE lens which serves as object for eyepiece. IT should be at 3CM from eyepiece. `therefore v_0` for objective lens =15-3=12 cm (1) `therefore 1/v_2-1/u_0=1/f_0` or `1/12-1/mu_0=1/2` `1/mu_0=1/12-1/2=-5 /12` `1/mu_0=1/12-1/2= -5/12 ` or `mu_0=-2.4cm` From objective lens `mu_0=2.4cm `(to left) `v_0=12 cm` (to right) 
|
|
| 39080. |
A block of mass m is placed on a rough inclined plane. The coefficient of friction between the block and the plane is mu and the inclination of the plane is theta. Initially theat-0 and the block will certain stationary on the plane. Now the inclination theta is gradually increased. The block presses the inclined plane with a force mg cos theta. So welding strength between the block and inclined is mu mgcos theta, and the pulling forces is mg sin theta. As soon as the pulling force is greater than the welding strength, the welding breaks and the block starts sliding, the angle theta for which the block starts sliding is called angle of repose (lambda). During the contact, two contact forces are acting between the block and the inclined plane. The pressing reaction (Normal reaction) and the shear reaction ( frictional force) and the shear reaction(frictional force) . The net contact force will be resultant of both. If the entire system, were accelerated upward with acceleration 'a', the angle of repose , would : |
|
Answer» increases `m(g+a)sintheta'=F` `m(g+a)COS theta'=R` `:. (F)/(R)=TANTHETA'` `theta'=tan^(-1)((F)/(R))=alpha` Hence angle of repose does not change. |
|
| 39081. |
A hoop of radius r and mass m rotation with an angular velocity omega_(0) is placed on a rough horizontal surface. The initial velocity of the centre of the hoop is zero. What will be the velocity of the centre of the hoop when it ceases to slip ? |
|
Answer» `(romega_(0))/(4)` |
|
| 39082. |
(A): The specific heat of a given mass of a gas in an adiabatic process is zero and in an isothermal process is infinity. (R) : Specific heat of gas is directly proportional to change in heat of a system and directly proportional to change in its temperature. |
|
Answer» Both (A) and ( R) are true and (R ) is the correct explanation of (A) |
|
| 39083. |
Explain - “To hit sixer the cricketer hit the ball by whirling the bat”. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Whencricketwhirls the BAT TIMEOF contactbetweenbat andball increasehenceimpulse offorceincreasehencefinalvelocityof BALL INCREASE. | |
| 39084. |
A square Nickel slab of side 50 cm and thickness 10 cm is subject to a shearing force (on its narrow face) of 9.0 xx 10 ^(4) N.The lower edge is riveted to the floor. How much will the upper edge be displaced ? Shear modulus of Nickel G=77 xx 10 ^(9) Nm^(-2) |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Displacement of upper EDGE `DELTA X =0.012mm` | |
| 39085. |
The magnitudes of two vectors vec(P) and vec(Q) differ by 1. The magnitude of their resultant makes an angle of tan^(-1)(3//4) with P. The angle between P and Q is |
|
Answer» `45^(@)` |
|
| 39086. |
A rod of lengh l with thermally insulated lateral surface consists of material whose heat conductivity coefficient varies with temperature as x=alpha//T, where alpha is a constant. The end of the rod are kept at temperature T_(1) and T_(2). Find the heat flow density. |
|
Answer» `(ALPHA)/(l)log_(E)((T_(1))/(T_(2)))` |
|
| 39087. |
A water fountain on the ground sprinkles water all around it. If the speed of the water coming out of the fountain is v. Calculate the total area around the fountain that gets wet. |
|
Answer» `:.` Rang of the particle `(R_(max))=(V^(2))/(g)sin2theta=(v^(2))/(g)` here, `R_(max)` is radius of the area covered. `:.` area covered `pir^(2)=piR_(max)^(2)=PI((v^(2))/(g))" Area" (piv^(2))/(g^2)` |
|
| 39088. |
A rod of lengh l with thermally insulated lateral surface consists of material whose heat conductivity coefficient varies with temperature as x=alpha//T, where alpha is a constant. The end of the rod are kept at temperature T_(1) and T_(2). Find the function T(x), where x is the distance from the end whose temperature is T |
|
Answer» `T_(1)((T_(2))/(T_(1)))^(x//l)` |
|
| 39089. |
Force acting on a particle is (2 hat(i) + 3hat(j))N. Work done by this force is zero, when a particle is moved along the line 3y+ kx =5. Here the value of k is |
|
Answer» 2 |
|
| 39090. |
Under what condition will the distance and the displacement of a moving object have same magnitude? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :When the OBJECT moves ALONG a straight LINE in the same fixed direction. | |
| 39091. |
Figure. gives the x-t plot of a particle in one-dimensional motion. Three different equal intervals of time are shown. In which interval is the average speed greatest, and in which is it the least ? Give the sign of average velocity for each interval. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Greatest in 3, least in 2, `UPSILON gt 0` in 1 and 2, `upsilon lt 0` in 3. | |
| 39092. |
Mass of the moon is 1/81 of the earth but gravitational pull is 1/6 of the earth. It is due to the fact that |
|
Answer» RADIUS of the moon is `(81)/(6)` of the earth |
|
| 39093. |
The radius of gyration of a body about an axis at a distance of 4cm from its centre of mass is 5cm. The radius of gyration about a parallel axis through centre of mass is |
| Answer» ANSWER :D | |
| 39094. |
Consider a carnot's cycle operating between T_(1)=500 K and T_(2)=300K producing 1 kJ of mechanical work per cycle. Find the heat transferred to the engine by the reservoirs. |
|
Answer» Solution :`Q_(2)/Q_(1)=T_(2)/T_(1)=3/5, Q_(1)-Q_(2)=W=10^(3)J` `:. Q_(1)[1-Q_(2)/Q_(1)]=10^(3)J` `:. Q_(1)[1-3/5]=10^(3)J` `:. Q_(1)=5/2xx10^(3)=2500J`2 and `Q_(2)=Q_(1)3/5=1500J` |
|
| 39095. |
A small particle is tied by the help of two strings to vertical walls with the parameters as shown in the figure (g = pi^(2)). The time period of the small oscillations of the particle if it is displaced perpendicular to the plane of the paper slightly is x sec, the value of x is ____________ |
|
Answer» `T = 2pi sqrt((d)/(g_(eff)))` where `T =2pisqrt((d)/((gsqrt(3)/(2))))RARR d(sqrt(3))/(2)` `T = 2sec` |
|
| 39096. |
A lift is ascending with acceleration (g)/(3). Find the time period of simple pendulum of length L kept in lift. |
|
Answer» `2PI sqrt((3L)/(g))` `therefore T= 2pi sqrt((L)/(g_(eff)))= 2pi sqrt((L)/(2g"/"3))` `=2pi sqrt((3L)/(2g))`. |
|
| 39097. |
Suppose you keep your two hands on two bodies simultaneously and feel them equally cold or hot. What is your inference ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :They are at the same TEMPERATURE as your BODY (THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM). | |
| 39098. |
A string of length 20 cm and linear mass density 0.40 g cm^-1 is fixed at both ends and is kept under a tension of 16 N. A wave pulse is produced at t = 0 near an end as shown in figure, which travels towards the other end. (a) When will the string have the shape shown in the figure again ? (b) Sketch the shape of the string at a time half of that found in part (a). |
|
Answer» `v=SQRT((T/m))` `sqrt((16x1^5)/0.4)` `=2000cm/sec` `:. Time taken to reach to the other END `=20/2000=0.01sec` Time taken to see the PULSE again in the origiN/Al POSITION `=0.01xx2=0.02sec` b. At t=0.01s, then will be a trough atthe right end as it is reflected. |
|
| 39099. |
A pulley fixed to the ceiling carries a string with blocks of masses m and 3 m attached to its ends. The masses of string and pulley are negligible. When the system is released the acceleration of centre of mass will be |
|
Answer» ZERO |
|
| 39100. |
Read each statement below carefully and state with reasons , if it is true of false :(a) The magnitude of a vector is always a scalar , (b) each component of a vector is always a scalar , (c ) the total path length is always equal to the magnitude of the displacement vector of a particle . (d) theaverage speed of a either greater or equal to the magnitude of average velocity of the particle over the same interval of time , (e ) Three vectors not lying in a plane can never add up to give a null vector . |
|
Answer» |
|