Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 39001. |
A boy and a man carry a uniform pole of length 8 m and of mass 60 kg by supporting it on their shoulders. They are located at the ends of the pole. Where should a load of 90 kg be suspended from boy.s end so that boy carroes only one - third of the total load ? |
Answer» Solution :The mas of pole acts from its centre .C.. Let the load placed at a distance .x. from the BOY.s end. If `N_(1), N_(2)` are the normal REACTIONS on man and boy respectivelt then `N_(1)=(2)/(3)(60+90)g=100 g N` `N_(2)=(1)/(3)(60+90)g=50g N` TAKING turning effects about boy.s end .B., we have. `N_(1)xx8-60g xx 4-90g xx x=0` or `100 g xx 8-60g xx 4-90g xx x =0` on solving x = 6.22 m. |
|
| 39002. |
. Two spheres Pand Qmoving in opposite directions with velocities v_(1)and v_(2) collide with each other. If .e. is the coefficient of restitution, what is their distance of separation at time .t. after collision ? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39003. |
Which of the following pairs of physical quantities have same dimension? |
|
Answer» THRUST and linear MOMENTUM |
|
| 39004. |
The pressure of air in a constant volume thermometer is 90 cm and 110 cm at 0^@Cand 100^@Crespectively . When the bulb is kept in hot liquids, pressure is 105 cm . Find the temperature of hot liquid. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39005. |
A cylindrical container contains water. A cubical block is floating in water with its lower surface connected to a spring. (a) Suppose that the spring is in relaxed state. Now, if the whole contaienr is accelerated vertically upwards. Will the spring get compressed? (b) Suppose that the spring is initially compressed. Now, what will happen to the state of the spring when the container is accelerated upwards? (c) Assume that mass of the block is 1 kg and initially the spring (force constant k=100 N/m) is compressed by 5cm. when the container is accelerated up by an acceleration of 5m//s^(2), the spring has a total compression of 6cm. Calculate the chnag ein volume of block submerged inside water when the container gets accelerated. Density of water is 10^(3) kg//m^(3). |
|
Answer» (b) SPRING will GET compressed more (C) `100CM^(3)` |
|
| 39006. |
Identify the periodic functions and their time periods, if any from the following (i) sin 2t , (ii) sin 3t , (iii) sint + cos t , (iv) sin t + sin 3t (v) e^(-1) |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :If can be written as `sin 2T = sin (2t + 2pi) = sin 2(t+ pi)` Comparing with equation 5.1, time period of given function is `pi` units. (ii) `sin 3t = sin (3t + 2pi) sin 3 (t+ (2pi)/(3)) therefore ` Time period , `T= (2pi)/(3)` (iii) After trigonometric transformations, the given functions can be written as `sin t + COS t = sqrt2 sin [omega t + pi/4]` , Since it is a sine function , its time period is also `2pi` Note that the linear combination of time and COSINE functions , such as `f(t) = A sint + B cost ` is also periodic of time period `2pi` (IV) The time period of sin t and sin 3t are `2pi and 2pi//3` as already discussed in above examples . Since the given function can repeat it self only after a time of `2pi` , its time period is `2pi` . (v)The plot of `e^(-1)` vs t is an shown From the graph , it is easy to say that the given function is not periodic . 
|
|
| 39007. |
Is it possible far a body to be accelerated without speeding up or slowing down? If so, give an example |
| Answer» Solution :Yes. An object in UNIFORM circular MOTION is ACCELERATING but its speed NEITHER decreases nor INCREASES. (In one dimensional motion it is not possible.) | |
| 39008. |
The whirling motion of a stone attached to a string is a .............. motion. |
|
Answer» linear |
|
| 39009. |
A polyatomic gas with six degrees of freedom does 25J of work when it is expanded at constant pressure. The heat given to the gas is |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 39010. |
Obtain an expression for the excess of pressure inside a (i) liquid drop (ii) liquid bubble (iii) air bubble. |
Answer» Solution :(i) Liquid drop:Let us consider a liquid drop of radius R and the surface tension of the liquid is T. The various forces acting on the liquid drop are, (a) Force due to surface tension `F_(T)=2piRT` towards right (b) Force due to outside PRESSURE,`F_(P_1)=P_(1)piR^(2)` towards right (c) Force due to inside pressure, `F_(P_2)=P_(2)piR^(2)` towards left As the drop is in equilibrium, `F_(P_2)=F_(T)+F_(P_1)` `P_(2)piR^(2)=2piRT+P_(1)piR^(2)` `rArr(P_(2)-P_(1))piR^(2)=2piRT` Excess pressure is `DeltaP=P_(2)-P_(1)=(2T)/(R)` (ii) Liquid bubble:A soap bubble of radius R and the surface tension of the soap bubble be T is as shown in Figure. A soap bubble has two liquid SURFACES in CONTACT with air, one inside the bubble and other outside the bubble. Hence, the force on the soap bubble due to surface tension is `2xx2piRT`. The various forces acting on the soap bubble are,  (a) Force due to surface tension `F_(T)=4piRT` towards right (b) Force due to outside pressure, `F_(P_1)=P_(1)piR^(2)` towards right (c) Force due to inside pressure, `F_(P_2)=P_(2)piR^(2)` towards left As the bubble is in equilibrium, `F_(P_2)=F_(T)+F_(P_1)` `P_(2)piR^(2)=4piRT+P_(1)piR^(2)` `rArr(P_(2)-P_(1))piR^(2)=4piRT` Excess pressure is `DeltaP=P_(2)-P_(1)=(4T)/(R)` (iii) Air bubble:Let us consider an air bubble of radius R inside a liquid having surface tension T as shown in Figure. Let `P_(1)andP_(2)` be the pressures outside and inside the air bubble, respectively. Now, the excess pressure inside the air bubble is `DeltaP=P_(1)-P_(2)`.  In ORDER to find the excess pressure inside the air bubble, let us consider the forces acting on the air bubble. For the hemispherical portion of the bubble, considering the forces acting on it, we get, (a) The force due to surface tension acting towards right around the rim of length `2piR` is `F_(T)=2piRT` (b) The force due to outside pressure `P_(1)` is to the right acting across a cross sectional area of `piR^(2)` is `F_(P_1)=P_(1)piR^(2)` (c) The force due to pressure `P_(2)` inside the bubble, acting to the left is `F_(P_2)=F_(T)+F_(P_1)` `P_(2)piR^(2)=2piRT+P_(1)piR^(2)` `rArr(P_(2)-P_(1))piR^(2)=2piRT` Excess pressure is `DeltaP=P_(2)-P_(1)=(2T)/(R)` |
|
| 39011. |
SI unit of Stefan-Boltzmaan constant is. . .. . . . |
|
Answer» `WM^(-2)K^(-4)` `W-A e sigma T^(4)e=1` (EMISSIVITY- unitless) `:.(W)/(AT^(4)t)= sigma` `:.` UNITS of `sigma=(J)/(m^(2)K^(4)s)` `=(W)/(m^(2)K^(-4))` |
|
| 39012. |
The center of mass is located at position i EX.5.4. Locate the center of mass of a uniform rod of mass M and length |
|
Answer» Solution :Consider a uniform ROD of mass M and length / whose one END coincides with the origin as shown in Figure. The rod is kept along the x AXIS. To find the CENTER of mass of this rod, we choose an infinitesimally small mass dm of elemental length dr at a DISTANCE from the origin `lambda`is the linear mass density (ie, mass per unit length) of the rod. `lambda=(M)/(l)` The mass of small element (dm) is `dm, (M)/(l)dx` Now, we can write the center of mass equation for this mass distribution as, `X_(CM)=(int x dxm)/( int dm)` `X_(CM)=( overset(1) underset(0) intx((M)/(l)dx))/(M)=(1)/(l)overset(1) underset(0) intxdx=(1)/(l)[(x^(2))/(2)]_(0)^(l)=(1)/(l)=((t^(2))/(2))` `X_(CM)=(l)/(2)` As the `(l)/(2)` position is the geometric center of the rod, it is concluded that the center of mass 
|
|
| 39013. |
(A): Always |(d vecv)/(dt)|=(d)/(dt) |vecv|, where vecv has its usual meaning. (R) : Acceleration is rate of change of speed. |
|
Answer» Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the CORRECT explanation of (A) |
|
| 39015. |
Three particles A,B,C of mass m each are joined to each other by massless rigid rods to form an equilateral triangle of side a. Another particle of mass m hits B with a velocity v_(0) directed along BC as shown. The colliding particle stops immediately after impact.n The time required by the triangle ABC to complete half revoution in its subsequent motion is (xapi)/(sqrt(3)V_(0)) where 'x' is |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39016. |
The gravitational force is always attractive whereas electrostatic force is attractive as well as repulsive. The ratio of electrostatic force and gravitational force between two protons is |
|
Answer» `10^-19` |
|
| 39017. |
A rigid body rotates with an angular momentum L. If its kinetic energy is halved, the angular momentum becomes, |
|
Answer» L If `E_(K)` is halved `E_(K).= (E_(K))/(2)` New angular momentum, `L.= sqrt(2ME._(K))= sqrt((2mE_(K))/(2))` `L.= (L)/(2)` |
|
| 39018. |
An electric kettle can heat certain quantity of water from 19°C to 100°C in 6 minutes, time it takes to boil the same quantity of water into steam at 100°C in (minutes) ( L_("steam") = 540 "cal/gm") |
|
Answer» 40 |
|
| 39019. |
Two projectiles thrown from the same point at angles60^(@)and 30^(@)with the horizontal attain the same height . Which of the following statements is a correct statement ? |
|
Answer» The ratio of their initial velocityies is`sqrt(3)` `h_("max")`is same in both the cases . `u_(1)^(2) sin^(2)30^(@)` `(u_(1))/(u_(2)) = (sin 30^(@))/(sin 60^(@))` `= (1)/(2) XX (2)/(sqrt(3)) = (1)/(sqrt(3))` |
|
| 39020. |
A small block of wood of specific gravity 0.5 is subnerged at a depth of 1.2 m in a vessel filled with water. The vessel is accelerated upwards with an acceleration a_(0) = (g)/(2). Time taken by the block to reach the surface, if it is released with zero initial velocity is (g = 10 m//s^(2)) |
|
Answer» 0.6 s |
|
| 39021. |
A particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude which is always perpendicular to the velocity of the particle. The motion of the particle takes place in a plane. It follows |
|
Answer» its VELOCITY is CONSTANT |
|
| 39022. |
A particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude which is always perpendicular to the velocity of the particle. The motion of the particle takes place in a plane. It follows that |
|
Answer» the KINETIC energy of the particle changes with time |
|
| 39023. |
Whichof the diagrams in figure correctly shows the change in kinetic energy of an iron sphere falling freely in a lake having sufficient depth to impart it a terminal velocity ? |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 39024. |
Find the depth at which g becomes 4% less than value at surface |
|
Answer» 0.2 R |
|
| 39025. |
Find the area of the triangle formed by the tips of the vectors vec(a) = hat(i) - hat(j) - 3hat(k), vec(b) = 4hat(i) - 3hat(j) + hat(k) and vec(c ) = 3hat(i) - hat(j) + 2hat(k) |
|
Answer» 3.2 sq.units |
|
| 39026. |
Prove that DeltaL=10log_(10)[(I_(1))/(I_(0))] decibel, from Weber-Fechner's law. |
|
Answer» Solution :According to Weber-Fechner's law, ''loudness (L) is proportional to the logarithm of the actual intensity (I) measured with an accurate non-human instrument''. It is meant that `LproplnI` `L=klnI` The difference between two loudnesses, `L_(1)andL_(0)` MEASURES the relative loudness between two precisely measured intensities and is called as sound intensity level. Mathematically, sound intensity level is `DeltaL=L_(1)-L_(0)=klnI_(1)-klnI_(0)` `=KLN[(I_(1))/(I_(0))]` If k=1, then sound intensity level is measured in bel, in HONOUR of Alexander Graham Bell. `:.DeltaL=ln[(I_(1))/(I_(0))]`bel However, this is practically a bigger unit, so we use a convenient smaller unit, called DECIBEL. Thus, decibel `=(1)/(10)bel`. Hence, by multiplying and dividing by 10 we get `DeltaL=10(ln[(I_(1))/(I_(0))])(1)/(10)bel` `DeltaL=10ln[(I_(1))/(I_(0))]` decibel with k=10 For practical purposes, we use logarithm to base 10 instead of natural logarithm, `DeltaL=10log_(10)[(I_(1))/(I_(0))]` decibel. |
|
| 39027. |
The density of mercury in egs system is 13.6 g cm^(3). Its value in SI is |
|
Answer» `136 kg//m^(3)` |
|
| 39028. |
A metal rod of length 'L' and maws 'm' is pivoted at one end A thin disc of mass 'M' and radius 'R' ( |
|
Answer» Restoring torque in case A = Restoring torque in case B In case A disc is not free to rotate about itscentre hence it has to change its orientation during the oscillation and its moment of inertia as a disc will be counted. But in second case disc will oscillate without changing its orientation andit will be just like a POINT mass attached at theend of rod. We can understand that moment of inertia in case A will be more than in case B. Frequency is INVERSELY proportional to square root of moment of inertia, hence we can understand that option (d) is ALSO correct. |
|
| 39029. |
Can the sum of three vectors, i.e.,their resultant, be equal to zero ? Explain. |
|
Answer» Solution :Yes, if the resultant of any TWO of the vectors is EQUAL andoppositeto the THIRD one , the resultant of the three vectors will be zero. Let `VECA,vecb,VECC` bethree vectors related as `veca+vecb=-vecc`.Then `veca+vecb+vecc=0` |
|
| 39030. |
The dimensions of 1/2 epsilon E^2. Where epsilon_0 is permittivity of free space and E is electric field is |
|
Answer» `[ML^(2) T^(-2) ]` |
|
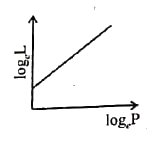
| 39031. |
The curve between log_(e) L and log_(e) P is (L is the angular momentum and P is the linear momentum). |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 39032. |
A person sitting in a chair in a satellite feels weightless because |
|
Answer» the CARTH does not attract the objects in a satellite |
|
| 39033. |
If the earth was a homogeneous sphere and a straight hole was bored through its centre, show that a body dropped into this hole will execute shm. Calculate the time period if the radius of the earth is 6400 km and g = 9.8 ms^(-2) |
|
Answer» `T=2pisqrt((R-x))//g.=2pisqrt(R//g)=2pisqrt(6.4xx10^6//9.8)=5079.6`SECOND |
|
| 39034. |
If orbit velocity of planet is given by v = G^(a)M^(b)R^(c), then |
|
Answer» `a = (1)/(3),b=(1)/(3),c=-(1)/(3)` |
|
| 39035. |
The work done by pressure in forcing 2m^(3) of water through a pipe of radius 1 cm, if the pressure difference across a pipe is 10^(5)Pa is |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 39036. |
If a raindrop with a mass of 0.05 g falls with constant velocity, the retarding force of atmospheric frictionis (neglect density of air) …………… . |
|
Answer» zero |
|
| 39037. |
The length of each rail is 10m. The linear expansion of steel is 12xx10^(-6)//""^(@)C and range of variation of temperature at the given place is 15^(@)C. The gap to be left between the rails is |
|
Answer» 0.0018 m |
|
| 39038. |
The position of an object moving along x-axis is given by x=a+bt^(2) where a=8.5m, b=2.5ms^(-2) and t is measured in seconds. Then which of the following is true? |
|
Answer» VELOCITY at `t=2` SEC is zero |
|
| 39039. |
A grass hopper can jump maximum distance of 1.6m It spends negligible time on the ground. How far can it go in 10 seconds? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`(U^(2))/(G)=1.6u^(2)=16rArru=`4m/s `4costheta=4xx(1)/(sqrt(2))=2sqrt(2)//s` `S=4costheta.t = 2sqrt(2)xx10""S=20sqrt(2)m` |
|
| 39040. |
(A): If vecr_(1) and vecr_(2) be the initial and final displacement in time vecv_("avg")=(vecr_(2)-vecr_(1))/(t) (R) : The average velocity of a particle having initial and final velocity vecv and vecv_(2) is (vecv_(1)+vecv_(2))/(2), for uniform accelertion |
|
Answer» Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of (A) |
|
| 39041. |
An explosion breaks a rock into three parts in a horizontal plane. Two of them go off at right angles to each other. The first part of mass 1 kg moves with a speed of 12 ms^(-1) and the second part of mass 2 kg moves with 8 ms^(-1) speed. If the third part flies off with 4 ms^(-1) speed, then its mass is |
|
Answer» Solution :Thesituationis asshownin thefigureaccordingto lawofconservationoflinearmomemtum ` vecp_1 + vecp_2 + vecP_3=0 thereforevecP_3 =-vecP_1 + vecP_(2)` here` vecv_1= ( 1 kg) ( 12 ms^(-1)) HATI= 12 hati kgms^(-)` ` thereforevecP_3 = - (12hati+ 16hatj ) kg ms^(-1) ` Themagnitudeof `P_3` is ` P_3 = sqrt((12)^2 + (16)^2) = 20kg ms^(-1)` ` thereforem_3 = (p_3)/(v_3) =( 20 kg ms^(-1))/(4 ms^(-1)) =5kg ` 
|
|
| 39042. |
What is the slope of graph of stress to strain upto elastic limit? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :SLOPE EQUIVALENT to elastic MODULUS of material. | |
| 39043. |
Find the load on wire of cross section 16 mm to increase its length by 0.3%(Y=5xx10^(9)N//m^(2),g=10m//s^(2)) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39044. |
Two blocks of masses 10 kg and 30 kg are placed on x - aixs. The first mass is moved on the axis by a distance of 2 cm right. By what distance should the second mass be moved to keep the position of centre of mass unchanged. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :mass of the first block, `m_(1)=10 kg` mass of the second block, `m_(2)=30 kg` Let `x_(1)` and `x._(1)` are positions of `m_(1)` `x_(1)` and `x._(1)` are positions of `m_(2)` INITIALLY and later respectively  In this case of `.x_(cm).` is the POSITION of centre of centre of mass then `x_(cm)=(m_(1)x_(1)+m_(2)+x_(2))/(m_(1)+m_(2))` then the new position of CM when blocks are shifted `x._(cm)=(m_(1)x._(1)+m_(2)x._(2))/(m_(1)+m_(2))` subtracting the above equations `x._(cm)-x_(cm)=(m_(1)(x_(1).-x_(1))+m_(2)(x._(2)-x_(2)))/(m_(1)+m_(2))` `Delta x_(cm)=(m_(1)Delta x_(1)+m_(2)Delta x_(2))/(m_(1)+m_(2))` `0=(10xx2+30 Delta x_(2))/(40) "" therefore Delta x_(2)=-2//3` Therefore the second block should be moved left through a distance of 2/3 cm to keep the position of centre of mass UNCHANGED. |
|
| 39045. |
A shell projected from a level ground has a range R, if it did not explode. At the highest point, the shell explodes into two fragments having masses in the ratio 1 : 2 , with each fragment moving horizontal immediately after the explosion. If the lighter fragment falls at a distance R/2 from the point of projection, behind the point of projection, the distance at which the other fragments falls from the point of projection is |
|
Answer» R/2 |
|
| 39046. |
If the surface tension of solution of soap in water is 35 dyne/cm, calculate the work done to form an soap bubble of diameter 14 mm with that solution |
|
Answer» Solution :Surface tension `S=35` dynes `cm^(-1)=0.035Nm^(-1)` Radius of the bubble `(R )=(14mm)/(2)=7mm` `=7XX10^(-3)m` `W=A(S)=8pir^(2)S` `implies W=8xx(22)/(7)xx49xx10^(-6)xx0.035` `W=4.312xx10^(-6)J` |
|
| 39047. |
One end of a long string of linear mass density 8.0 xx 10^(-3) kg m^(-1) is connected to an electrically driven tuning fork of frequency 256Hz. The other end passes over a pulley and is tied to a pan containing a mass of 90kg. The pulley end absorbs all the incoming energy so that reflected waves at this end have negligible amplitude. At t=0, the left end (fork end) of the string x=0 has zero transverse displacement (y=0) and is moving along positive y-direction. The amplitude of the wave is 5.0 cm. Write down the transverse displacement y as function of x and t that describes the wave on the string. |
| Answer» Solution :`y= 0.05 sin (omega t- KX) " here " omega = 1.61 XX 10^(3) s^(-1), k= 4.84m^(-1), X and y` are in m | |
| 39048. |
The maximum fractional error in the difference of two quantities is………… |
|
Answer» Z = A + B |
|
| 39049. |
Answer the following questions based on the P-T phase diagram of carbon dioxide: At what temperature and pressure can the solid, liquid and vapour phases ofCO_(2)co-exist in equilibrum ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :At the TRIPLE POINT temperature ` = - 56.6 ^(@) C`and pressure = `5.11` atm. | |
| 39050. |
A vertical glass tube closed at the bottom contains mercury to height of 50 cm at 20^(@)C. What will be the height of mercury column at 40^(@)C? (gamma _(Hg (R ))= 18.5 xx 10 ^(-5) //^(@)C and alpha _(g) = 8 xx 10 ^(-6) //^(@)C) |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`50.20 CM` | |