Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 37901. |
A glass flask of volume 1000cm. is completely filled with mercury at 0^(@)C. The coefficient of cubical expansion of mercury is 182 xx 10 ^(4) // ^(@)Cand that of glass is 30 xx 10 ^(-4) //^(@)C. If the flask is now placed in boiling water at 100°C, how much mercury will over flow? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`15.2 CM ^(3)` | |
| 37902. |
A cylinderical wooden block of cross-section 15.0 cm^(2) and 250 gram attached to its bottom. The cylinder floats vertically. From the state of equilibrium, it is slightly depressed and released. If the specific gravity of wood is 0.3 and g=9.8 ms^(-2), deduce the frequency of oscillation of the block. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Here, `(250+30)980=15.0xxlxxlxx980` or `l=56//3 cm.` USE the relation `T=2pisqrt(l//g)` and put the VALUES. |
|
| 37903. |
A metal rod of Young's modulus and coefficient of thermal expansion alpha is held at its two ends such that its length remains invariant. If its temperature is raised by t^(@)C, the linear stress developed it its is ..... |
|
Answer» `(alpha t )/(F)` `therefore (Delta l )/(l) = alpha Delta T ""...(1)` YOUNG modulus `Y = ("stress" SIGMA _(l))/("STRAIN" G_(l))` `therefore epsi _(l ) = (sigma _(l))/(Y)` `therefore (Delta l )/(l) = (sigma _(l))/( Y) ""...(2)` From equation (1) and (2) `(sigma _(1))/(Y) = alpha Delta T` `therefore sigma _(l) = Y prop Delta T` `therefore sigma _(l) = Y prop T` (where `Delta T =l ^(@)C)` |
|
| 37904. |
A circular ring of mass m and radius r is rotating in a horizontal plane about an axis vertical to its plane. What will its rotational kinetic energy? (Angular speed of ring is w) |
|
Answer» `(1)/(2)MR^(2)w^(2)` `I=mr^(2)` `=(1)/(2)mr^(2)omega^(2)` |
|
| 37905. |
A thermodynamic process is shown in figure. In process ab, 600 J of heat is added, and in process bd 200 J of heat is added. The total heat added in process acd is |
|
Answer» 550 J `W = P(V_(2) - V_(1)) = (8 xx 10^(4) Pa)(5 xx 10^(-3)m^(3) - 2 xx 10^(-3) m^(3)) = 240 J` Thus the total work for abd is W = 240 J and the total heat for abd is Q = 800 J. `:. Delta U = Q - W = 800 J - 240 J = 560 J` Because `Delta U` is independent of path, the INTERNAL energy change is the same for the path acd as for abd, that is, 560 J. The total work for path acd is `W = (3 xx 10^(4) Pa)(5 xx 10^(-3)m^(3) - 2 xx 10^(-3) m^(3)) = 90 J` `:.` Total heat added in the path acd is `Q = Delta U + W = 560 J + 90 J = 650 J` |
|
| 37906. |
When F = 2 N , the frictional force between 5 kg block and ground is : |
|
Answer» 2N  If F = 2N `f_(1) = F = 2N` `f_(2) = f_(1)` 
|
|
| 37907. |
At a metro station, a girl walks up a stationary escalator in time. t _(1),If she remains stationary on the escalator, then the escalator take her up in time t_(2). The time taken by her to walk up on the moving escalator will be |
|
Answer» `(t_(1) +t_(2)) //2` Let displacemtn is L, then velocity of girl `v _(g) = (L)/(t _(1)) ` velocity of escaltoor `v _(e) = (L)/(t _(2))` Net velocity of the girl, `v =v _(g) + v _(e) = (L)/(t_(1)) + (L)/(t_(2)) ...(i)` If t is total time taken in covering distance L, then `v = L/t` Using in (i) `L/t = (L)/(t _(1)) + (L)/(t _(2)) IMPLIES t = (t_(1) t_(2))/(t _(1) + t _(2))` |
|
| 37908. |
A stone is allowed to fall from a top of a tower 100 m high and at the same time another stone is projected vertically upwards from the ground with a velocity of 25 m/s.The two stones will melt after : |
|
Answer» 40s ` s = ut - (1)/(2) g t^(2)` `100 - x = 25 t - (1)/(2) g t^(2) "". . . (2)` Adding (1) and(2) we get , 100 = 25 t `:. t = (100)/(25) = 4s` |
|
| 37909. |
The reading of centigrade thermometer coincides with that of Fahrenheit thermometer in a liquid. The temperature of the liquid is |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 37910. |
The ratio of the distance travelled in the third and fourth second by a particle moving over a straight path with constant acceleration is ...... |
|
Answer» `7/5` `THEREFORE S _(3) = 9/2 (5)` `therefore S_(4) = 9/2 (7)` `therefore (S_(3))/(S _(4)) = (5)/(7)` |
|
| 37911. |
Draw the stationary wave pattern in the fundamental mode for the following cases: (i) an open organ pipe (ii) resonance column apparatus (iii) a rigid metallic rod clamped in the middle, the rod is hit with a stick at one of its free ends . |
|
Answer» Solution :Fig. 4.24 (a) : Two antinodes at the two open ENDS and a node between them . (II)Fig . 4 . 24 (B) : An antinode at the open end and the nearest node at thetop of the liquid surface . (iii)fig . 4.24 (c) : twoantinodes at the free ends and only one node between them at the clamped mid-point. In Fig. 4 . 24 (a) and 4 . 24 (b) , it is to be notedthat sound waves are ALWAYS longitudinal waves.For convenience only they have been drawn as trans-verse waves . 
|
|
| 37913. |
In an n type silicon, which of the following statements is true: |
|
Answer»
`therefore v ^(2) = 2as` `thereforfe s to v` has PARABOLA SHAPE. |
|
| 37914. |
Two seconds after projection, a projectile is moving at 30^(@) above the horizontal. After one more second it is moving horizontally. If g = 10ms^(-2), the velocity of projection is |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 37915. |
From a disc of radius R and mass M, a circular hole of diameter R, whose rim passes through the centre is cut. What is the moment of inertia of the remaining part of the disc about a perpendicular axis, passing through the centre ? |
|
Answer» `13MR^(2)//32` |
|
| 37916. |
A string of mass 2.50kg is under a tension of 200N. The length of the stretched string is 20.0m. If the transverse jerk is struck at one end of the string, how long does the disturbance take to reach the other end? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 37917. |
A player throws a ball upwards with an initial speed of 29.4 ms^(-1) (a) What is the direction of acceleration during the upward motion of the ball ? (b) What are the velocity and acceleration of the ball at the highest point of its motion ?(c) Choose the x = 0 m and t=0 s to be the location and time of the ball at its highest point vertically downward direction to be the positive direction of x-axis and give the signs of position, velocity and acceleration of the ball during its upward and downward motion. (d) To what height does the ball rise and after how long does the ball return to the player's hands ? (Take g = 9.8 ms^(-2) and neglect air resistance). |
| Answer» Solution :(a) Vertically downwards, (b) ZERO velocity, ACCELERATION of `9.8 MS^(-2)` downwards, (c ) `X gt 0` (upward and downward motion), `UPSILON lt 0` (upward), `upsilon gt 0` (downward), `a gt 0` throughout, (d) 44.1 m, 6 s. | |
| 37918. |
The stress- strain graphs for two materials A and B are shown in Fig. (The graphs are to the same scale). (i)Which of the materials has greater Young.s modulus ? (ii) Which of the two is the stronger material ? |
|
Answer» Solution : i) Young.s modulus= stress/strain = SLOPE of the straight portion of the stress-strain GRAPH. Since `TAN theta_A gt tan theta_B` , slope of OP > slope of `OP^1` . Y for material-A > Y for material B. ii) Strength of a material is determined by the highest point on the stress-strain curve. The stress corresponding to this point is called the ultimate strength `(S_u)`. Since this point(C) for material-B is higher than corresponding point`(C^1)`for material-A, `(S_u)_B gt (S_u)_A`.Hence, material B is stronger than material-A. |
|
| 37919. |
A train is moving along a straight line with a constant acceleration 'a' . A boy standing in the train throws a ball forward with a speed of 10 m//s , at an angle of 60(@) to the horizontal. The boy has to move forward by 1.15 minside the train to catch the ball back at the initial height . the acceleration of the train , in m//s^(2) , is |
|
Answer» 3 m `s^(-2)` `:.u_(x)=ucostheta=10xxcos60^(@)=5MS^(-1)` and `u_(y)=usintheta=10xxsin60^(@)=5sqrt3ms^(-1)` `:.t=(2u_(y))/(G)=(2xx5sqrt3)/(10)=sqrt(3)s` and `1.15=u_(x)t-(1)/(2)at^(2),` where a is the acceleration of train `1.15=5xxsqrt(3)-(1)/(2)xxaxx(sqrt(3))^(2)` `(3a)/(2)=5sqrt(3)-1.15=8.65-1.15-7.5` `a=7.5xx(2)/(3)=5ms^(-2)` |
|
| 37920. |
Calculate the stress developed inside a tooth cavity that filled with copper. When hot tea at temperature 57^(@)C is drunk. You can take body (tooth) temperature to be 37^(@)C and alpha = 1.7 xx 10^(-5//""^(@))C bulk modules for copper = 140 xx 10^(9) Nm^(–2). |
|
Answer» Solution :THERMAL stress = Kx strain = `(KDeltaV)/(V)` Now , `"" GAMMA= (DeltaV)/(VDeltaT) or (DeltaV)/(V)=gammaDeltaT` Thermal stress `=K gamma DeltaT= 3K alpha DeltaT "" [because gamma=3alpha]` `=3xx140xx10^(9)xx1.7xx10^(-5)xx20` `=1.428xx10^(8)Nm^(2)` |
|
| 37921. |
Is itpossibleif workis doneby theinternalforce, whatwillbe thechangein kineticenergy ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :YES . Thispossibleif WORKIS donebythe internalforcesthenkineticenergywillbeincreased.As ANEXAMPLE, whena bombexplodes, thecombinedkineticemergy of ALLTHE fragmentsis greaterthanthe initial energy. | |
| 37922. |
The temperature of a solid object is observed to rise in a period. In this period . |
|
Answer» HEAT is CERTAINLY supplied to it |
|
| 37923. |
Masses each 1 kg are placed at the verticies of an isosceles triangle ABC in which AC = BC = 5cm and AB = 8 cm. The distance of centre of mass of the system from the vertex C is |
|
Answer» 2 cm |
|
| 37924. |
The Kundt's tube experiment shows that the sound waves are |
|
Answer» LONGITUDINAL in nature |
|
| 37925. |
A ball moving with velocity 2m/s collides head on with another stationaryball of double the mass . If coefficient of restitution is 0.5 then their velocities after collision will be ………. ms^(-1) . |
|
Answer» 0,1 ` :. 0.5 = (v_(2)-v_(1))/2 ` ` :. V_(2) = 1 + v_(1) ""………(1)` From conservation of momentum `mv_(1)+2mv_(2)=mv_(1)+2mv_(2),v_(1)=2m//s ND v_(2) = 0 ` ` 2m = mv_(1) +2mv_(2) "".....(2)` From EQUATION (1) and (2) ` :. 2 = v_(1)+2(1+v_(1))` ` :. 2 =v_(1)+2+2v_(1)` ` :. 3v_(1)=0` ` :. v_(1)=0` From equation (1) `v_(2) =1 ` m/s . |
|
| 37926. |
A bus travels 6 km towards north at an angle of 45^(@)to the east and then travels 4 km towards north at an angle of 135^(@)to the east . How for is its final position , due east and due north ? How far is the point from the starting point ? What angle does the straight line joining its initial andfinal position makes with the east ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Net movement along x-direction (DUE east) `= (6 - 4) cos 45^(@)` `= 2 XX (1)/(sqrt(2)) = sqrt(2) km` Net movement along y-direction (due NORTH) `= ( 6 + 4) sin 45^(@)` `= 10 xx (1)/(sqrt(2)) = 5 sqrt(2) km` Netmovement from starting point = 6 + 4 = 10 km Angle which makes with the east direction `TAN theta = ("y-component")/("x-component") = (5 sqrt(2))/(sqrt(2))` `:. theta = tan^(-1) (5) `(or) `theta = 79^(@) `(approx). 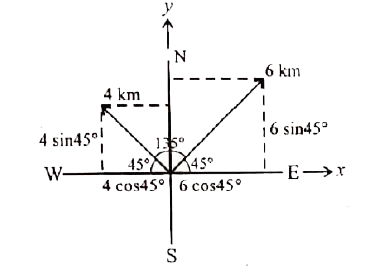
|
|
| 37927. |
Precise measurements of physical quantities are a need of science. For example, to ascertain the speed of an aircraft, one must have an accurate method to find its positions at closely separated instants of time. This was the actual motivation behind the discovery of radar in World War II. Think of different examples in modern science you can, give a quantitative idea of the precision needed. |
|
Answer» Solution :In modern science accurate measurement is necessary. For example in statellite LAUNCH system time of `1mus` accuracy is required. While dealing with LASER DISTANCE (LENGTH) `1Å(1Å=10^(-10)m)` measurement is required. Also in measurement of size of NUCLEUS accuracy of `10^(-15)m` is required. When mass of molecule is measured by using mass spectometer accuracy of `10^(-30)` kg is required. |
|
| 37928. |
The position of a particle moving along a straight line is given by x =2 - 5t + t ^(3). Find the acceleration of the particle at t =2 s. (x is metere). |
|
Answer» Solution :`X (t) = 2 - 5t + t ^(3)` is given, `therefore V = (dx)/(dt) = (d)/(dt) [2- 5t +t ^(3)]` `therefore v =-5 + 3T ^(2)` and ACCELERATION `a = (dv)/(dt) = (d)/(dt) [-5 + 3t ^(2) ] = 6t` acceleration at 2s, `a = 6 xx 2 =12 ms ^(-2)` |
|
| 37929. |
N. m^(-1) is the S.I unit of |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 37930. |
A bullet of mass m strikes a pendulum bob of mass M with velocity u. It passes through and emerges out with a velocity u/2 from bob. The length of the pendulum is l. What should be the minimum value of u if the pendulum bob will swing through a complete circle? |
|
Answer» `(2M)/mxxsqrt(5gl)` |
|
| 37931. |
For the travelling harmonic wave y(x,t) = 2.0 cos 2 pi (10 t - 0.0080 x + 0.35) where x and y in cm and t in s. Calculate the phase difference between oscillatory motion of two points seperated by a distance of (a) 4 m, (b) 0.5 m, (c ) lamda//2, (d) 3lamda//4 |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) `6.4 PI` RAD (B) `0.8pi` rad (C ) `pi` rad (d) `(pi//2)` rad | |
| 37932. |
(A) : When an object is placed between two plane parallel mirror, then all the images found are of un equal intensity. (R ): In case of plane parallel mirrors, only two images are possible. |
|
Answer» Both A and R are true and R is the CORRECT explanation of A |
|
| 37933. |
Three particles each of mass.m. are located at the three vertices of an equilateral tirangle of side .a.. If the system is revolving in a uniform circle due to their mutual force of attraction, then the angular velocity of each particle is |
|
Answer» `sqrt((GM)/(3a^(3)))` |
|
| 37934. |
When temperature of a body made of brass sincreases its moment of inertia. |
|
Answer» increase |
|
| 37935. |
When some vehicle moves towards a stationary person, he finds difference in the frequency of horn by 2.5% of original frequency. If speed of sound is 320 m/s then, find speed of this vehicle. |
|
Answer» `8m//s`  We have, `(f _(L))/( V + v _(L)) = (f _(S))/( v + v _(S))` Here if `f _(S) = 100 Hz,` then `f _(L) = 102.5 Hz` `THEREFORE ( 102.5)/(320+0) = (100)/(320 -v _(S))` `therefore 320 -v _(S) = (32000)/(102.5)` `therefore 320 - (32000)/(102.5) =v _(S)` `therefore v _(S) = ((320 xx 102.5) - 32000)/(102.5)` `v _(S) = (800)/( 102.5) = 7.8 (m)/(s) ~~ 8 (m)/(s)` |
|
| 37936. |
If bodies at a latitude of 45^@of the earth are to be weightless, what should be earth.s time period of rotation? |
|
Answer» Solution : The acceleration due to gravity at latitude `phi`is `g_phi =g - R omega^2 cos^2 phi` For bodies to be WEIGHTLESS at a latitude of`45^@` then “ `g_phi` ” must be zero. ` rArr 0 = g - R omega^2 cos^2 45^@ rArr 0 = g - R omega^(2) 1/2 rArr R omega^2 = 2g rArr omega = sqrt((2g)/(R ))` We KNOW that , `omega = (2PI)/(T) rArr (2pi)/(T) = sqrt((2g)/(R ))rArr T = 2pi sqrt((R)/(2g)) " or " T = pi sqrt((2R)/(g))` |
|
| 37937. |
When a motor cyclist takes a U-turn in 4s what is the average angular velocity of the motor cyclist? |
|
Answer» 0.7855 |
|
| 37938. |
The surface energy of a liquid drop is E. It is sprayed into 1000 equal droplets. Then their surface energy is |
| Answer» ANSWER :D | |
| 37939. |
(x^(2))/("mass") has the dimensions of kinetic energy. Then x has the dimensions of |
|
Answer» Pressure |
|
| 37940. |
At t = 0, block B in figure starts moving with a velocity 15 cm/s and with a constant acceleration. It is observed that after blocks travels 24 cm to the right its velocity is 6cm/s. Find: (a) The accelerations of A and B, (b) The acceleration of point M of the string. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 37941. |
Pick out the only vector quantity in the following list : Temperature , pressure impulse , time, power , total path length , energy , gravitational potential , coefficient of friction , charge . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 37942. |
A circular disc is made to rotate in horizontal plane about its centre at the rate of 2 rps. The greatest distance of a coin placed on the disc from its centre so that it does not skid is (mu is coefficient of friction) |
|
Answer» `(MU)/(6.2)m` |
|
| 37943. |
Choose the wrong option. |
|
Answer» Inertial MASS is a measure of difficulty of accelerating a body by an EXTERNAL force whereas the gravitational mass is RELEVANT in determining the gravitational force on it by an external mass |
|
| 37944. |
A wire stretched between two rigid supports vibrates in tits fndamental mode with a frequency of 45 Hz. The mass of the wire is 3.5 xx 10 ^(-2) kg andits inear mass density is 4.0 xx 10 ^(-2) kg m ^(-1). What is (a) the speed oa a transverse wave on the string, and (b) the tension in the string ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Fundamental frequency of stationary wave, `f _(1) = (V)/(2L) implies f _(1) =(v mu)/(2 xx M)` `(because mu = (M)/(L) implies L = (M)/(mu)) ` `THEREFORE v =(2f _(1) M )/( mu) = (2 xx 45 xx 0.035)/(0.04) = 78.75 (m)/(s)` (b) Wave speed of transverse wave, `v = sqrt ((T)/(mu))` `therefore v ^(2) = (T)/(mu) implies T = muv ^(2)` `therefore T = (0.04) (78,75)^(2) = 248.1 N` |
|
| 37945. |
A thin but large plank of mass 2m is placed on a horizontal smooth surface. A solid cylinder of mass m and radius r is given only translation velocity V_(0) and gently placed on the plank as shown in the figure. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the plank and the cylinder is mu. Match List - I with List - II and selected the correct answer using the codes given below the lists : {:("List-I","List-II"),("(A) Final Kinetic energy of the plant",(P)(14mv_(0)^(2))/(98)),("(B) Final kinetic energy of the cylinder",(Q)(mv_(0)^(2))/(49)),("(C) Magnitude of work done by kinetic frictionally till the cylinder starts",(R)(24mv_(0)^(2))/(98)),("(D) Final kinetic energy of the cylinder with respect to the plank",(S)(33)/(98)mv_(0)^(2)):} |
|
Answer» |
|
| 37946. |
The dimensions of (l)/(KA) are (l is the length of rod, K is the thermal conductivity of rod and A is the area of cross-section of rod) |
|
Answer» `[ML^(2)T^(-3)K^(-1)]` or `(l)/(KA)= (d theta)/(dQ//dt) :. [(l)/(KA)]= [(K)/(ML^(2)T^(-3))]= [M^(-1)L^(-2)T^(3)K]` |
|
| 37947. |
A man can jump to a height of 1.5 m on a planet A . What is the height he may be able to jump on another planet whose density and radius are, respectively, one-quarter and one-third that of planet A |
|
Answer» 1.5 m |
|
| 37948. |
A freely falling body travels _____ of total distance in 5th second |
|
Answer» 0.08 |
|
| 37949. |
In Exercise 14.9, let us take the position of mass when the spring is unstreched as x = 0, and the direction from left to right as the positive direction of x-axis. Give x as a function of time t for the oscillating mass if at the moment we start the stopwatch (t = 0), the mass is (a) at the mean position, (b) at the maximum stretched position, and (c) at the maximum compressed position. In what way do these functions for SHM differ from each other, in frequency, in amplitude or the initial phase? |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) X = 2 SIN 20t (b) x = 2 cos 20t (c) x = - 2 cos 20t where x is in cm. These functions differ NEITHER in amplitude nor frequency. They differ in initial phase. |
|
| 37950. |
A piece of iron having a square cross-section has a length of 30 cm, and it floats on mercury at 0^(@)C. If the temperature is raised to 100^(@)C, then what additional length of the piece will be immersed? Density of mercury at 0^(@)C=13.6g*cm^(-3), density of iron at 0^(@)C=7.6 g*cm^(-3), coefficient of real expansion of mercury =1.82 times 10^(-4@)C^(-1) and coefficient of volume expansion of iron =3.51 times 10^(-5@)C^(-1). |
|
Answer» |
|