Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 38001. |
(A) : The value of dimensionless constants or proportionality constants cannot be found by dimensional methods. (B) : The equations containing trigonometrical, exponential and logarithmic functions cannot be analysed by dimensional methods. |
|
Answer» Both A & B are true |
|
| 38002. |
The potential energy of a particle varies with distance x from a fixed origin as V = (Asqrt(x))/(x+B) where A and B are constants. The dinmensions of ABare |
|
Answer» `M^1L^(5//2)T^(-2)` |
|
| 38003. |
A drunkard is walking along a straight road. He takes 5 steps forward and 3 steps backward and so on. Each step is 1 m long and takes 1 s. There is a pit 11m away. The drunkard will fall into the pit after |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 38004. |
What is perfectly black body? What is its absorbing power and emissivity ? |
| Answer» Solution :A BODY which absorbs all the radiation INCIDENT on it is CALLED a block boby. The absorbing power and also emissivity of it is unity. | |
| 38005. |
An equiconvex lens with radii of curvature of magnitude r each, is put over a liquid layer poured on top of a plane mirror. A small needle with its tip on the principle axis of the lens if moved along the axis intil its inverted real image coincides with the needle itself, Fig. The distance of needle from lens is measured to be a. On removing the liquid layer and repeating the experiment, the distance isn found to be b. Given that two values of distances measured represent that real length values in the two cases, obtain a formula for refractive index of the liquid. . |
|
Answer» Solution :Here, combined focal length of GLASS lens and liquid lens, `F = a`, and Focal length of CONVEX lens, `f_1 = b` If `f_2` is focal length of liquid lens, then `(1)/(f_1)+(1)/(f_2)=(1)/(F)` `(1)/(f_2)=(1)/(F)-(1)/(f_1) = ((1)/(a) - (1)/(b))` The liquid lens is plano CONCAVE lens for which `R_1 = -r, R_2 = oo` From `(1)/(f_2)=(MU -1) ((1)/(R_1) - (1)/(R_2))` `((1)/(a) - (1)/(b)) = (mu - 1) ((1)/(-r) - (1)/(- oo))` `:. (mu - 1) = (r)/(b) - (r)/(a)` `mu = 1 + (r)/(b) - (r)/(a)`. |
|
| 38006. |
An object of mass m is raised from the surface of the earth to a height equal to the radius of the earth, that is, taken from a distance R to 2R from the centre of the earth. What is the gain in its potential energy ? |
Answer» Solution : Potential energy of the OBJECT at the surface of the earth = `-(GMM)/R` PE of the object at a height EQUAL to the radiusof the earth `=-(GMm)/(2R)` `:.` Gain in PE of the object `=(-GMm)/(2R) -(-(GMm)/R)` `=(-GMm+2GMm)/(2R) = +(GMm)/(2R)` `= (gR^2xxm)/(2R) = 1/2 mgR "" ( :. g = (GM)/(R^2))` |
|
| 38007. |
The spring balance A read 2 kg. with ab block m suspended from it. A balance B reads 5 kg. When a beaker with liquid is put on the pan of the balance. The two balances are now so arranged that the hanging mass is inside the liquid in the beaker as shown in fig. In tis situation. |
|
Answer» The balance A will read read more than 2 KG |
|
| 38008. |
Consider the followig statements: Statement-1: Work done by friction is always negative. Statement-2 : If frictional force acts on a body its K.E. may decrease Statement 3: A rigid disc rolls without slipping on a fixed rough horizontal surface with uniform angular velocity.Then the acceleration of lowest point on the disc is zero. Statements-4: Consider an isolated sun planet system in which the planet moves in elliptical path around the fixed sun. Kinetic energy of the planet changes with time but its angular momentum with respect to centre of the sun remains constants. STatement-5: Net electric field inside the material of a conductor must always be zero Then, the number of incorrect statements is |
|
Answer» 2 |
|
| 38009. |
A sky lab of mass 2xx10^3 kg is first launched from the surface of earth in a circular orbit of radius 2R (from the centre of earth ) and then it is shifted from this circular orbit to another circular orbit of radius 3R . Calculate the minimum energy required (a) to place the lab in the first orbit (b) to shift the lab form first orbit to the second orbit . Given , R = 6400 Km and g = 10m//s^2 |
|
Answer» Solution :The energy of the sky lab on the SURFACE of EARTH `E_(s)=KE +PE=0+(-(GMm)/R)=-(GMm)/R` And the energy of the sky lab in an orbit of radius r `E=1/2mv_(0)^(2)+[-(GMm)/r]=(-GMm)/(2r)[ " as" v_(0) = sqrt((GM)/r)]` (a) So the energy required to place the lab from the surface of earth to the orbit of radius 2R, `E_(1)-E_(s)=-(GMm)/(2(2R))-[-(GMm)/(R)]=3/4(GMm)/R` i.e `DeltaE=3/4m/RxxgR^(2)=3/4mgR"" ["asg" =(GM)/R^2]` i.e. `DeltaE=3/4(2xx10^(3)xx10xx6.4xx10^6)=` `3/4(12.8xx10^(10))=9.6xx10^(10)J` (b) As for II orbit `r = 3R , E_(11)=-(GMm)/(2(3R))=-(GMm)/(6R)` `:. E_(11)-E_(1)=-(GMm)/(6R)-(-(GMm)/(4R))=1/12 (GMm)/R` But as `g=(Gm//R^2), ` i.e. `GM=gR^2` or `DeltaE=1/2mgR=1/12(12.8xx10^(10))=1.1xx10^(10)J` |
|
| 38010. |
The thrust developed by a rocket-motor is given by F= mv + A(P_1 -P_2)where m is the mass of the gas ejected per unit time, v is velocity of the gas, A is area of cross-section of the nozzle, P_1 and P_2are the pressures of the exhaust gas and surrounding atmosphere. The formula is dimensionally |
|
Answer» CORRECT |
|
| 38011. |
A horizontal force of 150N produces an acceleration of 2m//s^(2) on a body placed on a horizontal surface. A horizontal force of 200N produces an acceleration of 3m//s^(2). Find the mass of the body and the coefficient of kinetic friction (g=10ms^(-2)) |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :50KG, 0.1 |
|
| 38012. |
Pressure depends on distance as P =(alpha)/(beta) "exp" (-(alphaz)/(ktheta)) where alpha betaare constants z is distance k is Boltzmann is constant and theta is temperature. The dimension of beta are |
|
Answer» `M^(0)L^(0)T^(0)` |
|
| 38013. |
Give some practical applications of Stoke's law. |
|
Answer» Solution :The viscous force F acting on a spherical body of RADIUS r depends directly on: (i) radius (r) of the sphere (ii) velocity (v) of the sphere and (iii) coefficient of viscosity n of the liquid Therefore `F propeta^(x)r^(y)r^(y) = F k eta^(x)v^2 `where k is a dimensionless constant. . Using dimensions, the above equation can be written as `[MLT^(-2)]=K [ML^(-1)T^(-1) ] ^(z )xx [L]^(y) xx [LT^(-1) ]^(x)` On solving, we get x = 1, y = 1 and z = 1. Therefore, F = `k eta rv ` Experimentally, Stoke found that the value of `k = 6 pi` ` f= 6 pietar v ` This relation is KNOWN as Stoke.s law., Practical applications of Stoke.s law Since the raindrops are smaller in size and their terminal velocities are small, REMAIN suspended in air in the form of clouds. As they grow up in size, their terminal velocities increase and they start falling in the form of rain. This law explains the following: (a) Floatation of clouds (b) Larger raindrops hurt us more than the smaller ones (c) A man COMING down with the HELP of a parachute acquires constant terminal velocity. |
|
| 38014. |
A simple pendulum of length 1 m is oscillated at a place where g=9.8m//s^(2). Find the maximum velocity of the bob of the simple pendulum if the amplitude of oscillation is 3 cm. |
|
Answer» `5.219cms^(-1)` |
|
| 38015. |
The work done in time t on a body of mass m which is accelerated from rest to a speed v in time t_1 as a function of time t is given by |
|
Answer» `1/2 m (v)/(t_1) t^2` `:. A = (v)/(t_1) "" ….(i)` Force, `F = ma = (mv)/(t_1) ` DISTANCE travelled by the body in time t is `s = UT + 1/2 at^2 = 0 + 1/2 (vt^2)/(t_1) = (vt^2)/(2t_1) "(Using (i))"` `:. W = F xx s = (mv)/(t_1) (vt^2)/(2t_1) = 1/2 (mv^2 t^2)/(t_1^2)` |
|
| 38016. |
Under the influence of which force the oscillation of a pendulum gradually dies out? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :RESISTIVE FORCE | |
| 38017. |
The angle of friction between two surface in contact is 60^(@) What is the cofficient of friction between them . |
| Answer» Solution :`mu = TAN theta = tan 60^(@) = sqrt3` . | |
| 38018. |
Four small objects each of mass m are fixed at the corners of a rectangular wire-frame of negligible mass and of sides a and b (a gt b). If the wire frame is now rotated about an axis passing along the side of length b, then the moment of inertia of the system for this axis of rotation is |
|
Answer» `2ma^2` 
|
|
| 38019. |
A cylinder of ideal gas is closed by an 8 kg movable piston of area 60cm^2. The atmospheric pressure is 100 kPa. When the gas is heated from 30^@ C to 100^@ C the piston rises 20 cms. The piston is then fastened in the place and the gas is cooled back to 30^@ C. IfDelta Q_1 is the heat added to gas during heating and Delta Q_2 is the heat lost during cooling, find the difference. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`32.5cal` | |
| 38021. |
If the direction of the torque is inward the paper then the rotation is |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 38022. |
In the following question, a statement of Assertion is followed by a statement of Reason. Assertion: When a body moves along a circular path, the work done by a centripetal force is zero. Reason: The centripetal force is utilised in moving the body along the circular path and hence the work is done. Choose one of the following statements is correct? |
|
Answer» Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct EXPLANATION of the assertion |
|
| 38023. |
A train standing in a station-yard, blows a whistle of frequency 400Hz in still air. The wind starts blowing in the direction from the yard to the station with a speed of 10 ms^(-1). What are the frequency wavelength and speed of sound for an observer standing on the station.s platform? Is the situation exactly identical the case when the air is still and the observer runs towards the yard at a speed of 10 ms^(-1) ? The speed of sound in still air can be taken as 340 ms^(-1) |
| Answer» Solution :400Hz, 0.875m, `350ms^(-1)`. No, because in this CASE, with respect to the MEDIUM both the OBSERVER and the source are in MOTION. | |
| 38024. |
The escape velocity of a body on the earth's surface is v_e. A body is thrown up with a speed of sqrt(5)V_e. Assuming that the sun and planets to not influence the motion of the body, then the velocity of the body at the infinite distance is |
| Answer» ANSWER :D | |
| 38025. |
Which of the following is an example of forced vibrations ? |
|
Answer» Vibration of the DIAPHRAGM of MICROPHONE |
|
| 38026. |
From a single source, two wave trains are sent in two different string. The two wave equations are ((area of corss-section and tension of both string are same y_(1)= A sin (w_(1)t-k_(1)x)and y_(2) = 2A sin (w_(1)t -k_(2)z)Suppose u = energy density , P = power trasmitted and I = intensity of the wave, then match the following. |
|
Answer» <P> |
|
| 38027. |
From a circular disc of radius R and mass 9M, a small disc of radius R/3 is removed as shown in figure. The moment of inertia of the remaining disc about an axis perpendicular to the plane of the disc andpassing through O is |
|
Answer» `4 MR^(2)` `=(9M)/(piR^(2))` Mass of REMOVED portion of disc `=(9M)/(piR^(2)) xx pi(R/3)^(3) = M` MOMENT of INERTIA of removed portion about an AXIS passing through center of disc and perpendicular to the plane of disc, using theorem of parallel axes is `I_(1)=M/2(R/3)^(2)+1/2(MR^(2))=4MR^(2)` 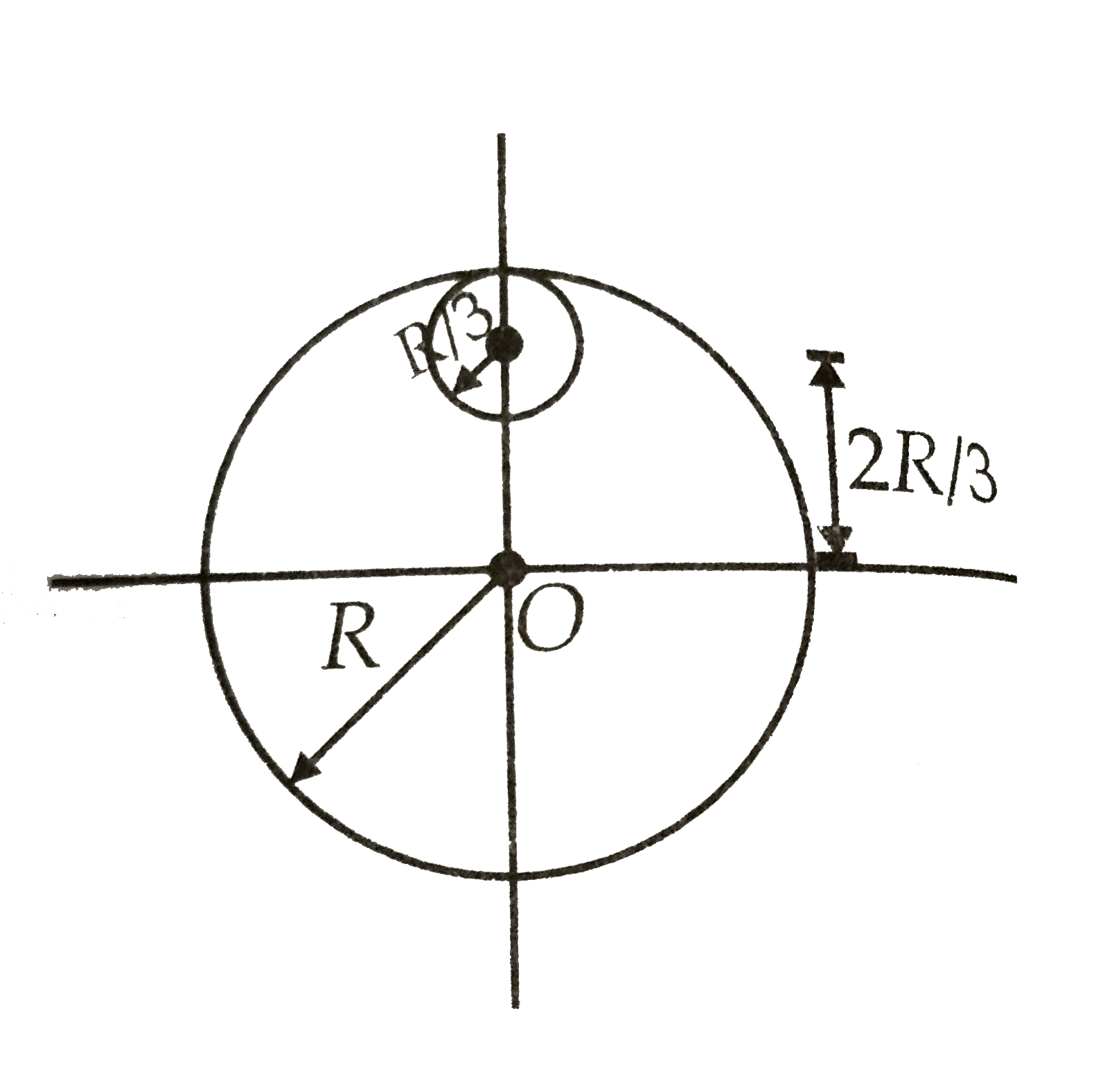
|
|
| 38028. |
Show that for a particle in linear SHM the average kinetic energy over a period of oscillation equals the average potential energy over the same period. |
| Answer» Solution :HINT: Average K.E. `=1/Tint_(0)^(T)1/2mv^(2)DT,` Average P.E. `=1/Tint_(0)^(T)1/2kx^(2)dt` | |
| 38029. |
A particle is fired vertically upwards from the surface of earth and reaches a height 6400 km. Find the initial velocity of the particle if R = 6400 km and g at the surface of earth is 10 m//s^(2). |
|
Answer» Solution :`(1)/(2) mv^(2) = (mgh)/([1+(h//R)])` here h = R = 6400 KM and `G = 10 m//s^(2)` so `v^(2) = gh`, i.e., `v = sqrt(10 xx 6400 xx 10^(3)) = 8 km//s` |
|
| 38030. |
Two metal spheres of same material and each of radius r are in contact with each other. The gravitational force of attraction between the spheres is proportional to |
|
Answer» `1/R^(2)` |
|
| 38031. |
A sphere and a cube both made of copper have equal volumes and are blackened. These are heated to same temperature and are allowed to cool under same surroundings. The ratio of their rates of loss of heat is |
|
Answer» `1:1` |
|
| 38032. |
Draw a graph showing the variation of K.E and P.E with respect to displacement for a spring mass system. |
|
Answer» Solution :Let us consider the nature of a compressed or extended spring. A compressed or extended spring will transfer its STORED potential ENERGY into kinetic energy of the mass attached to the spring. The potential energy-displacement graph is shown in the figure. It SHOWS variation of potential energy with respect to displacement. In a frictionless environment, the energy gets transferred from kinetic to potential and potential to kinetic repeatedly in such a way that the total energy of the system remains CONSTANT. At the MEAN position, `DeltaKE=DeltaU` i.e., change in kinetic energy = Change in potential energy. 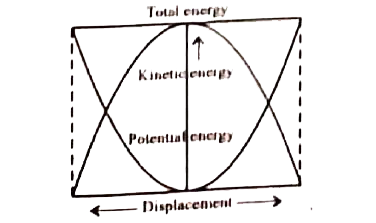
|
|
| 38033. |
A stone is released from an elevator going up with an acceleration 'a'. The acceleration of the stone after the release is |
|
Answer» a UPWARD |
|
| 38034. |
What is meant by reverberation time? |
| Answer» Solution :The PERSISTENCE of audible SOUND after the SOURCE has CEASED to EMIT sound is called reverberation . | |
| 38035. |
A steel wire 0.72 m long has a mass of 5.0 xx 10^(-3) kg. If the wire is under a tension of 60 N. What is the speed of transverse waves on the wire ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Mass PER unit length of the wire, `mu = (5.0 x 10^(-3) kg)/(0.72 m)` `= 6.9 xx 10^(-3) kg m^(-1)` Tension, T = 60 N The SPEED of wave on the wire is GIVEN by `V = sqrt((T)/(mu)) = sqrt((60 N)/(6.9 xx 10^(-3) kg m^(-1))) = 93 s^(-1)` |
|
| 38036. |
The breaking stress of a wire depends upon …………. . |
|
Answer» lengthof a wire |
|
| 38037. |
(A) : A body is momentarily at rest at the instant it reverses the direction. ( R) : A body cannot have acceleration if its velocity is zero at a given instant of time. |
|
Answer» Both (A) and ( R) are TURE and ( R) is the correct explanation of (A) |
|
| 38038. |
A hiker stands on the edge of cliff 490 m above the ground and throws a stone horizontally with an initial speed of 15 "m s "^(-1) Neglecting airresistance , find the time taken by the stone to reach the ground , and the speed with which it hits the ground . (Take g=9.8 " m s"^(2)). |
|
Answer» Solution :We choose the ORIGIN of the x - and y-axis at the EDGE of the cliff and t =0 s at the instant the stone is THROWN . Choose the positive direction of x-axis to be along the initial velocity and the positivedirection of axis to be the VERTICALLY upward direction The x- , and y- COMPONENTS of the motion can be treated independently . Theequations of motion are : `x(t)=x_(@)+v_(@x)t` `y(t)=y_(@)+v_(@y)t+(1//2)a_(y)t^(2)` Here , `x_(@)=y_(@)=0,v_(@y)=0,a_(y)=-r=-9.8 " m s "^(-2),v_(@x)=15 " m s"^(-1)`. The stone hits the ground when y(t) =- 490 m. `-490m=-(1//2)(9.8)t^(2)`. This gives `t=10s`. The velocity components are `v_(x)=v_(@x)andv_(y)=v_(@y)- gt` so that when the stonehits the ground : `v_(@y)=15 " m s"^(-1)` `v_(@y)=0-9.8xx10=-98 " m s"^(-1)` Therefore , the speed of the stone is `sqrt(v_(x)^(2)+v_(y)^(2))=sqrt(15^(2)+98^(2))=99 " m s"^(-1)` |
|
| 38039. |
One rod vibrates with frequency 200 Hz. It produces a sound which travels in air with velocity 340 m/s. Find wavelength of this wave |
|
Answer» `1.7cm` `therefore lamda = (340)/(200) =1.7 m` |
|
| 38040. |
Is it possible to have apparent expansion equal to real expansion? |
| Answer» Solution :YES, if the EXPANSION of the container is compensated by introducing a CERTAIN amount of MERCURY whose expansion is just equal to that of the container used, | |
| 38041. |
An air bubble starts rising from the bottom of a lake. Its diameter is 3.6 mm at the bottom and 4 mm at the surface. The depth of the lake is 2.5 m and the temperature at the surface is 40^(@)C. What is the temperatue at the bottom of the lake ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Let `P_(1), V_(1), T_(1)" and "P_(2), V_(2), T_(2)` are the parameters of the air bubble at the bottom and surface of the lake respectively. `P_(1)=` ATM/PRESSURE + Pressure of water at the bottom `""=(76 times 13.6 times 980)+(250 times 1 times 980)=1283.6 times 980" dyne "cm^(-2)` `P_(2)="Atm. pressure"=76 times 13.6 times 980=1033.6 times 980" dyne "cm^(-2)` `V_(1)=4/3pi(0.36/2)^(3)=0.007776 times PI cm^(3) rArr V_(2)=4/3pi(0.4/2)^(3)=0.01067 times picm^(3)` `T_(2)=273+40=313K` From the equation, `(P_(1)V_(1))/T_(1)=(P_(2)V_(2))/T_(2)` `rArr T_(1)=P_(1)/P_(2) times V_(1)/V_(2) times T_(2)=(1283.6 times 980)/(1033.6 times 980) times (0.00776pi)/(0.01067pi) times 313=1.242 times 0.7288 times 313=283.3K` Temperature at the bottom of the lake = 283.3 - 273 = `10.3^(@)C` |
|
| 38042. |
A bob of mass m is attached to one end of the rod of negligible mass and length r, the other end of which is pivoted freely at a fixed centre O as shown in the figure. What initial speed must be given to the object to reach the top of the circle? (Hint: Use law of conservation of energy). Is this speed less or greater than speed obtained in the section 4.2.9? |
Answer» Solution :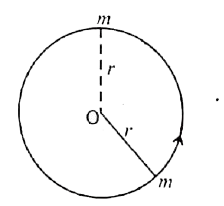 ACCORDING to law of conservation of energy `(1)/(2)mv_(0)^(2)+0=0+mg(2r)` `v_(0)=sqrt(4gr)ms^(-1)` This VALUE is less than `v_(1)=sqrt(5gr)` and GREATER than `v_(2)=sqrt(gr)` |
|
| 38043. |
A uniform metre scale of mass 2kg is suspended from one end. If it is displaced through an angle 60^(@) from the vertical, the increase in its potential energy is |
|
Answer» 4.9 J |
|
| 38044. |
Vessel A is filled with hydrogen while vessel B, whose volume is twice that of A, is filled with the same mass of oxygen at the same temperature. The ratio of the mean kinetic energies of hydrogen and oxygen is |
|
Answer» `16:1` |
|
| 38045. |
Does it matter if one uses gauge instead of absolute pressures in applying Bernoulli's equation Explain? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :No. unless the atmospheric PRESSURES at the two POINTS where Bernoulli.s equation is applied are significantly DIFFERENT. | |
| 38046. |
Two identical copper spheres are put in contact. The gravitational force of attraction between them is proportional to r^(x). Find the value of x |
|
Answer» |
|
| 38047. |
The refractive index of a lens material is 1.5 and focal length f. Due to some chemical changes in the material, its refractive index has increased by 2%. The percentage change in its focal length is |
|
Answer» `+4.5%` |
|
| 38048. |
Consider two cylindrical rods of identicaly dimensions, one of rubber and the other steel. Both the rods are fixed rigidly at one end to the roof. A mass M is attached to each of the free ends at the centre of the rods. Then |
|
Answer» Both the rods will elongate but there no PERCEPTIBLE change in the shape. |
|
| 38049. |
Find the angle between the vectors 2hati+3hatj-6hatk" "and 6hati-3hatj+2hatk |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The angle between the two vector is`90^@ . [ cos theta = (vecA.vecB)/(AB)]` | |
| 38050. |
An artificial satellite is describing an equatorial orbit at 1600 km above the surface earth. Calculate its orbital speed and the period of revolution. If satellite is travelling in the same direction as the rotation of the earth (i.e., from west to east), calculate the interval between two successive time at wich it will appear verically overhead to an observer at a fixed point on the equator. Radius of earth = 6400 km. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :We KNOW that period of the satellite is `T = (2pi)/(sqrt(GM))r^(3//2) = (2pi)/(sqrt(gR^(2)))r^(3//2)` Where `r = 6400+1600=8000xx10^(3)m`, `g = 9.8 m/sec^(2)` and `R = 6400xx10^(3)m` SUBSTITUTING values we get `T=2xx3.14[((8000xx10^(3))^(3))/(9.8xx(6400xx10^(3))^(2))]^(1//2)` `= 7096` FUTHER, orbital speed, `v = sqrt((GM)/(r )) = sqrt((gR^(2))/(r ))` or `v = sqrt(((9.8)/(8000xx10^(3))))xx(6400xx10^(3))` `= 7083.5 m//s` Let t be the time interval between two successive moments at which the satellite is overhead to an observer at fixed position on the equator. As both satelite and earth are moving in same direction with angular speed `omega_(S)` and `omega_(E )` respectively, we can write the time of separation as `t = (2pi)/(omega_(S)-omega_(E ))` Here `omega_(S)=(2pi)/(7096)` and `omega_(E )=(2pi)/(86400)` Thus we have `t = (86400xx7096)/(86400-7096)` `= 7731 s` |
|