Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 2551. |
If MPC is 0.9. What is the value of multiplier? How much investment is needed to increase national income by 5000 crore ? Calculate. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :500 CRORE | |
| 2552. |
As a result of increase in price by 20%, the quantity demanded decreases by 40%. Comment on PED. |
|
Answer» Solution :`PED=("Percentage change in Quantity demanded")/("Percentage change in Price")=(-40%)/(20%)=[-]2` Negative Sign of ED INDICATES that inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. PED = 2[More than UNITARY elastic demand or Elastic demand]. |
|
| 2554. |
The government has started promoting foreign capital. What is its economic value in the context of Production Possibilities Frontier? |
|
Answer» Solution :The inflow of foreign capital is EXPECTED to increase the availability of the RESOURCES in an economy, which will THEREBY shift the production possibility FRONTIER to the right. Value: Economic Growthwith increase in resources |
|
| 2555. |
What is deficiet demand? Explain diagrammatically. (b) RBI refers bank rate to control dificient demand. In your opinion when will rate be an effective measure? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :REFERS to section 9.2 of Chapter 9. RBI refers bank rate to control dificient DEMAND. In your opinion when will rate be an effective MEASURE? |
|
| 2556. |
If supply curve passes through origin, elasticity of supply is greater than one ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FALSE : When SUPPLY CURVE passes through origin, Elasticity of supply is always UNITY. | |
| 2557. |
Define capital formation . OR Define investment . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2558. |
Explain forestryrelated factors responsiblefor land degradationin India. |
|
Answer» Solution :(1) There has been large scale DEFORESTATION causing loss of vegetationon account of cutting of trees. (2) There is EXCESS fuelwood and fodder extraction. (3) Forest areas are converted into habitation byencroaching them. (4) There are forest FIRES and overgrazingcausing DAMAGE to forest areas. |
|
| 2559. |
Can an economy be in equilibrium when there is unemployment in the economy. Explain. |
| Answer» Solution :As LONG as the demand = the supply , the economy will be in EQUILIBRIUM. If the demand is met by employing LESS number of people than the number of people willing to work, then OFCOURSE the economy is at equilibrium with unemployment STILL present in it. | |
| 2560. |
A soap manufacturing company wishes to pay compesation to its employeesto its employees in the form of soaps. Howerver , employees want compensation in the form of money. Why compensation is more convenient in term of money than in soaps ? |
| Answer» Solution :Soap lack general acceptability, while enjoys MERIT of general acceptability. EMPLOYEES can purchase any goods and services with the help of money at any point of TIME and there is no problem of lack of DOUBLE coincidence of wants. | |
| 2562. |
APS can never be zero |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2563. |
How can an increase in foreign direct investment affect the price of foreign exchange ? |
| Answer» Solution :An increase in foreign direct investment INCREASES supply of foreign CURRENCY. This will lead landing to FALL in PRICE of foreign EXCHANGE. | |
| 2564. |
If demand is elastic, how will an increase in price affect the total revenue ? Explain. |
| Answer» Solution :If DEMAND is ELASTIC, an INCREASE in price reduces the total revenue. In elastic demand, the QUANTITY demanded falls by a greater percentage than the price rises , As the result of, total revenue DECLINES. | |
| 2565. |
Explain in briefhow the following tools can be used for creditcontrol by the central bank in an economy : (a) Open Market Operations (b) Margin Requirements |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Open Market OPERATIONS (OMO) refers to the sale and purchase of governmentsecurities in the open market by the Central Bank (RBI) . By selling such securities theCentral Bank SOAKS liquidityfrom the economyand by purchasingthe government securities,Central Bank releases liquidity. This is an important method of regulating the money supply (liquidity ) in themarket. (ii)The Margin Requirement of loanrefersto the differencebetween thecurrent value of the securityofferedand amount of loan granted. When margin requirement is lowered by the Central Bank, theborrowers are able to secure LARGER amount of funds from the bankswhich will increase the money supply in the economy. Conversely,a RISE in the marginrequirements will contractthesupply ofcredit in the economy. |
|
| 2566. |
Currency is issued by the central bank, yet we say that commerical banks create money. Explain. How is this money creation by commerical banks likely to affect the national income? Explain. |
| Answer» Solution :We know that RBI prints new money, while on the other hand, commerical banks multiplies money supplied by the RBI through the process of credit CREATION. People deposit money in their respective bank accounts. As PER the CENTRAL bank guidelines, the commerical banks are required to maintain a portion of total deposits in form of cash reserves. With the help of the past experiences, the commerical banks know that not all the depositors will turn-up for withdrawal at the same day. Consequently, the commerical banks lends the remaining portion (left after MAINTAINING cash reserves) of the total deposits to the general public in form of credit, loans and advances. It is the second portion of the total deposits that is responsible for the credit creation (credit money). The process of creation fo credit money begins as soon as the commercial banks start the lending process. The amount of the credit money increases as the banks lend loans to more and more number of people in the economy. The deposit of money by the people in the banks and the subsequent lending of loans by the commerical banks is a recurring process. This lending process of the commerical banks increases the rate of investment and production in the economy, which in turn helps in improving the national income in the economy. | |
| 2567. |
With a given supply curve a decrease in demand causes ............ . |
|
Answer» an overall DECREASE in price but a INCREASE in EQUILIBRIUM QUANTITY. |
|
| 2568. |
If Marginal Rate of Substitution is constant throughout, the Indifference curve will be : (choose the correct alternative) |
|
Answer» PARALLEL to the x-axis |
|
| 2569. |
Differentiatebetween NormalGoods and inferior Goods. |
Answer» SOLUTION :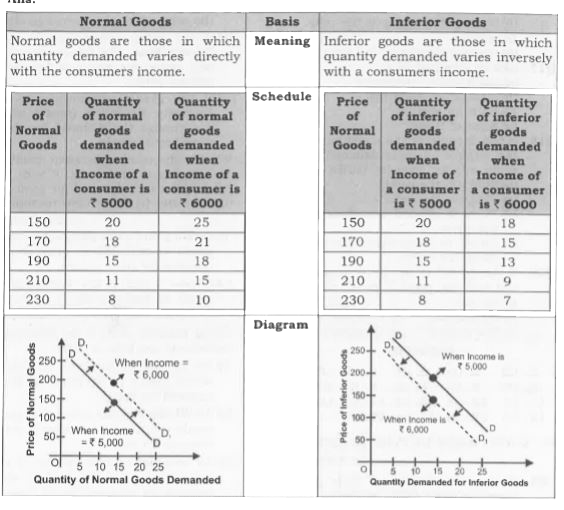
|
|
| 2570. |
Other things remaining the same, when in a country the market price of foreign currency falls, national income is likely: (Choose the correct alternative) |
| Answer» Solution :to fall | |
| 2571. |
A farmer in Punjab transports wheat from the farm to a flour mill. Is this activity considered as production? Why? |
|
Answer» Solution :Yes, It adds to the UTILITY and generates income. VALUE: CRITICAL THINKING |
|
| 2572. |
What is a central bank? |
| Answer» Solution :Central Bnk is an APEX institution that controlsand regulates banking OPERATIONS and money supply of a COUNTRY (RBI in INDIA) | |
| 2573. |
The ReserverBank of India aims to makethe creditcostly for thegeneralpublicin orderto reducethe availabiltyofcredit . What shouldbe done ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The RESERVEBANK of INDIA should Increase the reporate. Anincrease in repo rate increases thecostsofborrowing from the central bank. It forcesthe commercial BANKS to increase theirlending rates, whichdiscourage borrowers from taking loans. It makes the creditcostlyforthecredit costlyfor thegeneralpublicand reducesthe AVAILABILITY of credit. | |
| 2574. |
Government has started spending moreonproviding free services like education and health to the poor. Explain the economic value it reflects |
| Answer» Solution :Spending on free SERVICES to the poor raises their standard of living and at the same time helps in reduction in INCOME inequalities. It also helps in raising production POTENTIAL of the country by raising the efficiency LEVEL of the WORKING class among the poor. | |
| 2575. |
The price elasticity of supply of commodity X and Y are equal. The price of X falls from 10rs to 8rs per unit and its quantity supplied falls by 16 per cent. The price of Y rises by 10 per cent. Calcualte the percentage increase in its supply. |
Answer» Solution :PES of X is EQUAL to the PES of Y.  Percentage change in price`=(DELTAP)/(P)xx100=(2)/(10)xx100=20%` PES = `("Percentage change in quantity supplied")/("Percentage change in price")=(16%)/(20%)=0.8` As, PES of X= PES of Y [given]. [So, PES of Y =0.8]  PES = `("Percentage change in quantity supplied")/("Percentage change in price")` `0.8=("quantity supplied")/(20%)` As, price is increasing by `10%` then quantity supplied also INCREASES by `8%` as per LAW of supply. [So, Percentage change in quantity supplied of commodity `Y=8%`] |
|
| 2576. |
Deficiency in demand has no effect on the country's output and prices. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :False, DEFICIENCY in demand leads to FALL in country's OUTPUT and prices. | |
| 2577. |
Accommodating transactions are undertaken to maintain balance in BOP account. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :True because these items being capital transactions are UNDERTAKEN to correct DISEQUILIBRIUM in AUTONOMOUS items of BOP. | |
| 2578. |
The interest payments as per the government budget duringa year are ₹ 1, 40 , 000 crores . If total borrowing requirements of the government are estimated at ₹2, 70 , 000 crores , then how much is primary deficit. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Total borrowing requirements of the government are ESTIMATED at ₹ 2 , 70 ,000 crores . It means , Fiscal Deficit = ₹2 , 70 , 000 crores. PRIMARY Deficit = Fiscal Deficit - Interest Payment Primary Deficit = ₹2, 70 , 000 crores - ₹1 , 40 , 000 crores = ₹ 1 , 30 , 000 crores. |
|
| 2579. |
Briefly describe how the government budget contributes to the process of growth and stability. |
|
Answer» Solution :The government BUDGET contributes to growth, because a significant percentage of BUDGETARY expenditure is committed to the growth and expansion of public sector enterprises. The government also OFFERS subsidies to the PRODUCERS to maintain high level of production of the essential goods. Stabilityis promoted by combating inflation through fiscal DISCIPLINE and combating deflation through liberal spending by the government. Fiscal discipline aims at lowering AD during inflation. Liberal spending promotes AD during deflation. |
|
| 2580. |
whatis investment multiplier |
| Answer» SOLUTION :investmentmultiplier(K)is therationis theincreaseinincome`( DELTA Y)`DUETO increasein INVESTMENT`(Delta I) `symolically`:K=DeltaY //Detla I.` | |
| 2581. |
How are equilibrium price and quantity affected when income of the consumers (i) Increase? (i) Decrease? |
|
Answer» Solution :As,m we know normal goods are those whose quantity demanded varies positively with the change in income. As income of a consumer rises and goods consumed is normal goods consumed is normal goods equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity both rise . It can be shown with the help of the given figure. (b) In the given figure, price of normal goods is measured on vertical axis and quantity demanded and supplied are measured on horizontal axis. Initially, the equilibrium quantity is OQ. (c) But as given in the exmination problem when income of a consumer rises the demand of normal goods increases shifting the demand curve to the right from DD to `D_(1) D_(1)` . (d) With new demand curve `D_(1) D_(1)` . there is excess demand at iniial price is PB and SUPPLY is PA, so there is excess demand of AB at price OP. (E) DUE to this excess demand competition among the consumer will raise the price. With the rise in price there is upward movementalong the demand curve (contraction in demand ) from B to C and SIMILARLY, there is supply curve (expansion in supply) from A to C. So, finally, equilibrium price rises from OP to `OP_(1)` , and equilibrium quantity also rises from OQ to `OQ_(1)` . Conclusion Due to increases in income of a buyer for normal goods, (a) Equilibrium price rises from OP to `OP_(1)` . (b) Equilibrium quantity also rises from OQ to `OQ_(1)` . ` (##FM_M_ECO_XII_P1_C12_E01_005_S01.png" width="80%"> (ii)Decrease in income: When income decreases, demand curve will shift to leftward in case of Normal good as shown below: (a) As we know that normal goods are those whose quantity demanded varies positively with the change in income. As given in the examination problem if income of a consumer FALLS and goods consumed is normal goods, then both equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity fall. It can be shown with the help of the given figure. (b) In the given figure price of normal goods is measured on vertical axis and quantity demanded and supplied is measured on horizontal axis. Initially, the equilibrium price is OP and equilibrium quantity is OQ. (c) But as given in the examination problem when income of a consumer falls the demand of normal goods also falls shifting the demand curve to the left from DD to `D_(1) D_(1)` . (d)With new demand curve `D_(1) D_(1) `there is excess supply at initial price OP because at price OP demand is PB and supply is PA, so there is excess supply of AB at price OP. (e) Due to this excess supply competition among the producer will fall the price. Due to fall in price there is downward movement along the demand curve (Expansion in demand) from B to C and similarly, there is downward movement along the supply curve (Contraction in supply) from A to C. So, finally, the equilibrium price falls from OP to `OP_(1)`, and equilibrium quantity also falls from OQ to`OQ_(1)`. Conclusion Due to decrease in income of a buyer for normal goods, (a) Equilibrium price falls from OP to `OP_(1)` (b) Equilibrium quantity also falls from OQ to `OQ_(1)` . ` (##FM_M_ECO_XII_P1_C12_E01_005_S02.png" width="80%"> |
|
| 2582. |
Give the meaning of forwardexchange rate |
| Answer» SOLUTION : The exchange ratequoted in forward TRANSACTION is knownas the forward exchange RATE | |
| 2583. |
The objective of self-reliance means reducing dependence on : |
|
Answer» FOREIGN TRADE |
|
| 2584. |
In an economy C=500+0.9 Y and I=1,000 (where C= consumption, Y= income, I= investment). Calculate the following : (i) Equilibrium level of income. (ii) Consumption expenditure at equilibrium level of income. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :GIVEN `Y=C+I` (i) `Y=500+0.9 Y+1000` `Y=1500+0.9 Y` or `0.1 Y=1,500` `Y=` RS. `15,000` (II) `C=Y-I=15,000-1,000=` Rs. `14,000`. |
|
| 2585. |
A manager of zoo wants to increase the revenue, which measure is more appropriate when, ED gt 1 (i) Increase the entry fee (ii) Decrease the entry fee. Explain ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :By REDUCING the entry fee the number of visitors may increase and TOTAL REVENUE will increase, but if the entry fee is INCREASED, number of visitors may decrease and total revenue will fall. Value : Problem solving | |
| 2586. |
Which of the can be referred to as 'point of satiety ? |
|
Answer» MARGINAL UTILITY is negative |
|
| 2587. |
State and explain the condition of consumer equilibrium in case of two commodities through Utility approach. |
|
Answer» Solution :According to the TWO commodity consumer equilibrium or law of Equimarginal utility , a consumer gets maximum satisfaction , when ratios of MU of two commodities and their respective prices are equal. Conditions of Consumer.s Equilibrium in case of two commodities (i) Necessary Condition Necessary Condition MARGINAL utility of last rupee SPEND on each commodity is same. Suppose there are two commodities, X and Y respectively . So , for commodity X, the condition is Marginal Utility of Money = price of X Or `{:("Marginal Utility of a Product in Utile " [MU_x])/("Marginal Utility of One Rupee "[MU_R])` = Price of X Or `(MU_x)/P_x=MU_R""....(1)` Similarly , for commodityY , the condition is , `(MU_x)/(P_y)=MU_R""....(2)` Putting equation (2) in (1) , we get `(MU_x)/(P_x) = (MU_y)/(P_y)` (a) If, `(MU_x)/(P_x) gt (MU_y)/(P_y)` : It means, marginal utility from last rupee SPENT on commodity X is more than marginal utility from the last rupee spent on commodity Y. So, to attain the equilibrium consumer MUST increase the quantity of X, which decrease the `MU_x` and decrease the quantity of Y which will increase the `MU_y` . Increase in quantity of X and decrease in quantity of X and decrease in quantity of Y continue till `(MU_x)/P_x = (MU_y)/(P_y)` . (b) If, `(MU_x)/P_x lt (MU_x)/P_y` :It means , marginal utility from the last rupee spent on commodity X is less than marginal utility from the last rupee spent on commodity Y. So , to attain the equilibrium the consumer must decrease the quantity of X which will increase the `MU_x`and increase the quantity of Y , which will decrease the `MU_y`Decrease in quantity of X and increase in quantity of Y continues till`(MU_x)/(P_x) = (MU_y)/P_y` (ii) Sufficient Condition Expenditure on commodity X+ Expenditure on commodity Y = Money Income . In other words Marginal Utility falls as more units of a commodity are consumed. This condition must be satisfied to attain the necessary condition , i.e., `(MU_x)/(P_x)=(MU_y)/(P_y) `. If. MU does not falls as Consumption of a commodity increases, the consumer will spend all his income on one commodity, which is highly unrealistic. |
|
| 2588. |
Calculate : |
Answer» SOLUTION :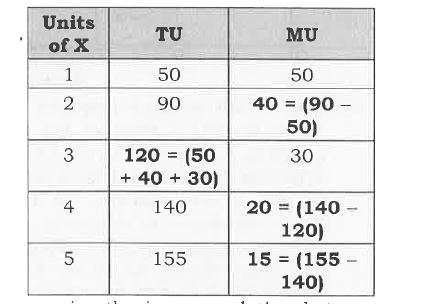
|
|
| 2589. |
Why is the equality between marginal cost and marginal revenue necessary for a firm to be in equilibrium? Is it sufficient to ensure equilibrium? Explain. |
Answer» Solution :The conditions must hold if a PROFIT maximizing firm produces positive output in a competitive market when price is CONSTANT under MR/MC approach is determined where (i) MR = MC (ii) MC must be rising  According to Table, both the conditions of equilibrium are satisfied at 4 units of output. MC is equal to MR and MC is rising. MC is more than MR when output is produced after 4 units of output. So, Producer.s Equilibrium will be achieved at 4 units of output. However, MR is equal to MC at 2 units of output ALSO. But, second condition is not fulfilled here. Let us understand the determination of equilibrium with the help of a diagram:  Producer.s Equilibrium is determined at OQ level of output corresponding to point E as at this point, MC = MR and MC curve CUTS MR curve from below. In Figure, output is shown on the horizontal axis and revenue and costs on the vertical axis. Producer.s equilibrium will be determined at OQ level of output corresponding to point E because at this, the following two conditions are met: (i) MC=MR (ii) MC curve cuts the MR curve from below. When `MR gt MC`, then producer will continue to produce as long as MR becomes equal to MC. It is so because firm will find it profitable to raise the output level. When `MRgtMC`, then producer will cut down the production as long as MR becomes equal to MC. It is so because firm will find it unprofitable to produce an extra UNIT. So, it starts reducing the level of output till MR = MC. |
|
| 2590. |
A cloth mill wishes to pay compensation to its employees in the form of its product i.e., cloths. But employees want their compensation in cash, not in kind. Why is the compensation more convenient in the form of money (cash) than in cloth ? |
| Answer» Solution :Cloth lack general ACCEPTABILITY whereas money is commonly accepted as a medium of exchange. With the USE of money, the employess can purchase any good and service at any POINT of time. MOREOVER,money SOLVES the barter's problem of lack of double coincidence of wants. That is why employees want compensation in cash , not in kind. | |
| 2591. |
Categorise the following into direct tax or indirect tax Interest received on loans . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2592. |
Define Ex-post savings |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Ex-post savings refers to the acutal SAVING in an ECONOMY during a YEAR. | |
| 2593. |
Explain that Higher IC provides higher level of satisfaction. |
Answer» Solution :(i) Higher IC lying above and to the right of another IC represents a higher level of satisfaction. All combinations of goods X and Y lying on the higher indifference curve `IC_2` have more satisfaction than lower indifference curve `"IC"_1` as shown in figure given here. 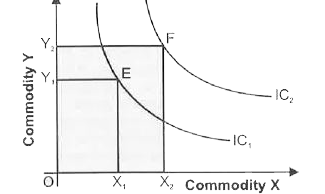 (II) This is because of monotonic preferences , as monotonic preferences state that we must have ATLEAST more of one good and no LESS that of other goods (means other goods can be equal or greater , but not less). The figure above shows that bundle `F("Ox"_2+"OY"_2)` is monotonicpreferred to bundle `F("Ox"_1+"OY"_1)`So , if bundle F is monotonic preferred to bundle E than F bundle gives more satisfaction than that of Bundle E. (iii) It can be seen from the above diagram that all combinations of `IC_2` contain a large quantity of both X and Y, than all combinations of `"IC"_1 ` . For, e.g. , point E lying on `"IC"_1` represents `"OX"_1` units of X and `"OY"_1` units of Y. Point F lying on `"IC"_2` represents more units of Y, i.e `"OY"_1` as well as more units of X, i.e. `"OX"_2` . The consumer gets greater satisfaction from a lager pieces of goods than from a smaller amount . Hence , point F shall be on a higher IC and Shall be more preferable to point E, lying on lower IC. |
|
| 2594. |
Dicuss howthe central bank plays the role of 'controller of credit' in an economy ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Thisis the mostcrucialfunctionplayedby any CENTRAL Bankin themodern times. Central Bank are supposedto regulate and controlthe volumeand directionof thecreditby using: (i) Quantitative Quantitative Techniques: These are these techniques which INFLUENCE the quantum of credit In the economy like open MARKET operations bank rate policy, rape and reverse repo rate policy, etc (ii)Qualitative Techniques or Selective Credit Control techniques are the ones which influence the direction of credit' In the economy, like margin requirements and MORAL suasion. |
|
| 2595. |
What one step can be taken through market to reduce the consumption of a product harmful for health ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :IMPOSITION of tax . It will increase the PRICE of the product and DISCOURAGE its consumption . | |
| 2596. |
Give meaning of managed floating exchange rate. |
| Answer» Solution :It REFERS ot the exchange rate which is DETERMINED by the MARKET FORCES and central bankinfluences it through intervention in the foreign exchange market . | |
| 2597. |
What causes a movement along the supply curve of a good ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Change (INCREASE or decrease) in price CAUSES a movement ALONG the supply curve. | |
| 2598. |
When aggregate demand is greater than aggregate supply, inventories. |
|
Answer» FALL |
|
| 2599. |
Cash and coins are known as bank money. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2600. |
A appreciation of India rupees will occur when Rs. 75 have to be paid to exchange one US$ instead of present rate Rs. 70//$ |
| Answer» SOLUTION : False. In case of appreciation, LESSER RUPEES have to be paid EXCHANGE one US dollar, i.e. less than `Rs. 70//$` | |