Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 2601. |
Explain the feature of firms mutually interdependent in an oligopoly market. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Interdependence means that actions of one firm affects the actions of other firms. (ii) SINCE the number of sellers is small, each firm has to take into consideration the POSSIBLE reaction of its competitors, when making decisions. (iii) The business decision of a single seller will have a substantial impact on the product price, output and profits of the rival firms. (IV) For example the "National Newspapers" market, when the "Economic Times" introduced invitation pricing policy-they offered the newspaper at a price of Rs.1.50 on WEEKDAYS. The Hindustan Times was forced to reduce its prices from Rs.2.50 per copy to Rs.1.50 per copy on weekdays. When Hindustan Times was celebrating its 75 YEARS of service, they offered the newspaper at Rs.1/- weekdays. The Times of India responded by matching the price cut. |
|
| 2602. |
Givemeaningof involuntaryunemployment . |
| Answer» SOLUTION : if REFERS OT a situationin whichall ablepersonswhoare workatprevailingwageratedo notgetwork. | |
| 2603. |
In which phase of Law of Variable Proportions a rational firm aims to operate? |
| Answer» Solution :Diminishing returns to a FACTOR (PHASE 2). | |
| 2604. |
If diminishing marginal returns will set in after the very first unit of labour is employed? What do the average product, and marginal product curves look like in this case ? |
Answer» Solution :The marginal and average PRODUCT CURVES will fall because diminishing marginal returns means that total product INCREASES at diminishing rate that MAKES the average and marginal product to fall. It can be explained with the help of the given diagram.
|
|
| 2605. |
The demand for life saving drugs is inelastic and hence prices will tend to be high. How can this problem be tackled ? |
|
Answer» Solution :In the case of life saving drugs, either the government should DIRECTLY CONTROL the prices of life saving drugs or the government should GIVE SUBSIDY to firms manufacturing such ITEMS so that they may charge less pricefrom the population. Value : Critical Thinking |
|
| 2606. |
How is the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity of a normal commodity affected by an increase in the income of its buyers? Explain with the help of a diagram. Or Explain the effect of increase in income of buyers of a normal' commodity on its equilibrium price. |
|
Answer» Solution :As, we know normal goods are those whose quantity demanded varies positively with the change in income. As given in the examination problem if income of a consumer rises and goods consumed is normal goods equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity both rise. It can be shown with the help of the given figure. In the given figure, price of normal goods is measured on vertical axis and quantity demanded and supplied are measured on horizontal axis. INITIALLY, the equilibrium price is OP and equilibrium quantity is OQ. But as given in the question when income of a consumer rises the demand of normal goods increases shifting the demand curve to the right from DD to `D_(1)D_(1)`. With new demand curve `D_(1)D_(1)` there is EXCESS demand at initial price OP because at price OP demand is PB and supply is PA, so there is excess demand of AB at price OP. Due to this excess demand, competition among the consumer will raise the price. With the rise in price there is upward movement along the demand curve (contraction in demand) from B to C and similarly, there is upward movement along the Supply curve fexpansion in supply) from A toC. So, finally, equilibrium price rises from OP to `OP_(1)` and equilibrium quantity ALSO rises from OQ to `OQ_(1)` . Conclusion Due to increase in income of a buyer for normal goods, (i) Equilibrium price rises from OP to `QP_(1)`. (ii) Equilibrium quantity also rises from OQ to `OQ_(1)` . ` (##FM_M_ECO_XII_P1_C12_E02_043_S01.png" width="80%"> |
|
| 2608. |
Define average propensity to save. |
| Answer» Solution :average propensity to save (APS), ALSO known as the savings RATIO, is the proportion of INCOME which is SAVED, usually expressed for household savings as a FRACTION of total household disposable income | |
| 2609. |
Show diagrammatically the conditions for consumer's equilibrium in Hicksian analysis of demand . |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) To define consumer equilibrium, we use Interference Curve map and the budget line . Two conditions for consumer Equilibrium (a) NECESSARY Condition Marginal Rate of Substitution = Market Rate of Exchange `[(P_x)/(P_y)]` Or , `MRS_(x,y)=P_x//P_y` MRS ( Market Rate of Exchange ) MRE Or `MRS_(x,y) =MRE[(P_x)/P_y]` `"*" ` If `MRS_(x,y) gt MRE [(P_x)/(P_y)]` , At point T in figure It means the consumer.s willingness to pay for commodity X is higher than what makes VALUES for commodity X. So, the consumer should buy more of X and less of Y to get MRS `=P_x/P_y` 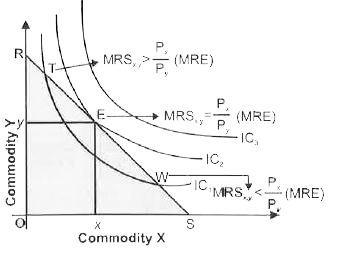 `"*"` If `MRS_(x,y) lt MRE [(P_x)/(P_y)]`, At point W in figure, It means the consumer willingness to pay for commodity X is lesser than what market value for commodity X ,So, consumer should buy less of X and more Y to get MRS = `p_x/p_y` (b) Sufficient Condition `MRS_(x,y)` Diminishing (Convex) at a point of equilibrium i.e., when `MRS_(xy)=MRE[P_x/P_y]` (ii) The consumer will reach equilibrium when the budget line is tangential to the higher POSSIBLE Indifference Curve, i.e. ., where necessary and sufficient condition SATISFY . In the above diagram , the consumer will reach equilibrium at point E where budget line RS is tangential to the higher possible `IC_2` (iii) The consumer cannot move to Indifference Curve , i.e. ., `IC _3`as this is beyond this money income. (iv) Even on `IC_2` all the other points except E are beyond his means . (v) Hence , at point E, the consumer is in equilibrium where his satisfaction maximizes, given his income and prices of goods X and Y . In equilibrium at E , the slope of Budget line = the slope of Indifference Curve. THEREFORE `MRS_(xy)`is equal to the ratio of the price bof two goods `[(P_x)/(P_y)]` . |
|
| 2610. |
Explain any two uses ofinfrastructuralfacilities. |
|
Answer» Solution :(1) Qualityof life improves by the facilitiesconcerning health, EDUCATION, housing,sanitation, etc.These facilitiesenable people to better EMPLOYMENT opportunities and raisestandard of living. (2) HELP in raisingproductivity. Goodhealth and education help in ACQUIRING better skills and raise EFFICIENCY. Power, transport telecommunications, etc.create conditions for carrying out economic activities. (3) Help in expansionof trade and industry.Roads, power, telecommunication, etc.lead to free movement of capital, goods and people and help in markets tospread over the countryand the world. Also help large scale production. |
|
| 2611. |
Explain the 'bank of issue' function of the central bank. OR Explain 'Government's Bank' function of central bank. |
|
Answer» Solution :Bank of issue function of central bank implies that the central bank of a country has the exclusive authority to issue the currency (notes + COINS). The currency issued by the central bank is known as 'legal tender money' i.e. the value of such currency is backed by the central bank. However, the currency issued by the central bank is its monetary liability. In other words, the central bank is obliged to back the currency issued by it by assets such as GOLD coins and bullions, foreign exchange. In ADDITION to issuing currency to the general public, the central government of the country. That is, the central government if required, can sell its securities to the central bank and in return gets the required cash currency. OR Central bank acts as a banker and financial advisor to the government. As a banker to the government, it performs the following functions. (a) It manages the account of the government. (b) It accepts receipts from the government and makes payment on behalf of it. (c ) It GRANTS short-term loans and credit to the government. (d) It performs the task of managing the public debt. (e) The central bank ADVISES the government on all the banking and financial related matters. |
|
| 2612. |
PED of X is known to be thrice that of Y. If price of the commodity X increases by 20% and price of the commodity Y decreases by 40%, calculate percentage change in demand in both the cases. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Suppose PED of Y = 1 PED X = 3Y `=3xx1=3` `{:("Commodity X", "Commodity Y"),(PED=3,PED=1),(PED=("Percentage change in Quantity demanded")/("Percentage change in Price"),PED=("Percentage change in Quantity demanded")/("Percentage change in Price")),(3=("Percentage change in Quantity demanded")/(20%),1=("Percentage change in Quantity demanded")/([-]40%)),("As price of commodity X INCREASE by","As price of commodity Y increase by"),("20%, then quantity demanded must","40%, then quantity demanded must"),("decrease by 60% as per law of demand.","increase by 40% as per law of demand."):}` |
|
| 2613. |
How can surplus budget be used during inflation? |
| Answer» Solution :Surplus budget refers to a budget where estimated TOTAL receipts are more than estimated total expenditure . In case of surplus budget, government TAKES more money from the economy than it injects into it. It RESULTS a fall in aggregate DEMAND and price level in the economy and helps to combat inflationary situations. | |
| 2614. |
Underflexible exchange rate system, exchange rate is determined ____ |
|
Answer» by the government |
|
| 2615. |
What is transaction demand for money? How is it related to the value of transactions over a specthed Period of time? |
| Answer» Solution :Hint: Discuss “Transaction Motive’ GIVEN in Power BOOSTER SECTION | |
| 2616. |
Suppose a ban is imposed on consumption of tobacco. Examine its likely effects on : (a) gross domestic product, and (b) welfare. |
| Answer» Solution :(a) Ban on consumption of TOBACCO will bring down PRODUCTION of tobacco. SINCE it is counted in GDP, GDP will fall. (b) The ban will IMPROVE the health in GENERAL. It will thus increase welfare. | |
| 2617. |
How will a rich household's demand for low - quality rice respond to an increase in income of the household ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :It will DECREASE. | |
| 2618. |
What does the area under the marginal utility curve depict ? |
|
Answer» Average UTILITY |
|
| 2619. |
In an economy, investment increases from 300 to 500. As a result of this equilibrium level of income increase by 2000. Calculate the marginal prepensity to consume. |
|
Answer» Solution :`""Delta I= 500-300=200` `""K = (Delta Y)/(Delta I)= (2000)/(200) = 10 ""RARR K = (1)/(1- MPC)` `""10 = (1)/(1-MPC)` `""10-10 MPC= 1` `""- 10 MPC = 1 - 10` `""MPC= (9)/(10)= 0.9` |
|
| 2620. |
Give two examples of fixed cost. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) RENT of the BUILDING. (II) Salary of permanent employees. |
|
| 2621. |
Bharat is living in his own house. So, rent of his house should not be included in national income. |
| Answer» Solution :False. Bharat ALSO enjoys the HOUSING services similar to those PEOPLE who stay in rented HOUSES. So, imputed rent of his house will be INCLUDED in national income. | |
| 2622. |
What is deficit in balance of payments? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :It REFERS to a SITUATION when OUTFLOW of foreign exchange is more than inflow of foreign exchange. | |
| 2623. |
Indian rupee is appreciated in terms of British pound because of |
|
Answer» FALLING demand of pounds |
|
| 2624. |
Mention the two components of aggregate supply. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(i) CONSUMPTION, (II) SAVING. | |
| 2625. |
In an economy , investmentis increased bu Rs. 300 crore If marginalpropensityto consumeis ⅔calculate increase in national income,(set 1)Suppose marginal propensityto consumeis 0.8 . How muchincrease in inestmentis required to increase to increasenational incomeby Rs. 2,000 crore? Calculate .(set 2) In an economyan increase in investmentby Rs. 100 croreledto 'increase' in nationalincomeby Rs. 1,000croreFind marginal propensityto consume ,(set 3) |
|
Answer» Increase in investment =Rs. 400 CRORE Marginal propensity to CONSUME = 0.90 crore |
|
| 2626. |
Checking governement spending is a part of |
|
Answer» MONETARY policy |
|
| 2627. |
Estimate the value ofAggretate Demand in a economy if : (a)AutonomousInvestment (I)= 100 crores (b)Marginal Propenstiyto save= 0.2 (c)Levelof Income(Y)= 4,000 crores (d) Autonomous Consumption Expenditure(c) =50 crores. ORIn an economyC = 200 + 0.5 Y is thecompsumption functionwhereC is theconsumptionexpenditureand Y is thenationalincome. Investment expenditureis ₹ 400 crores . Is theeconomyin equilibriumat anincomelevel ₹ 1,500 crores ?Jusiftyyour answer. |
|
Answer» Solution :AggregateDemand (AD) functionis givenas: AD = C+ I AD = `{barC + B(Y)} + I` `barc = 50` (GIVEN) bor MPC = 1 - MPS= 1 -0.2 = 0.8 Substitutingthe values ofof `barC` andb inAD function, we get : AD = {50 + 0.8 ( 4,000)}+ 100 =₹ 3,350 CRORES OR No, theEconomyis notin astateof equilibrium at 1,500 crores Given : ConsumptionFunction, C= 200 + 0.5 Y InvestmentExpenditure (I)= 400 crores At the equilibrium level Y =C + I Substituting the value from the question: Y= { 200 + 0.25Y} + 400 Y-0.5 Y = 600 0.5 Y = 600 Y = 600/ 0.5 = ₹ 1,200 crores. The equilibrium levelof income is ₹ 1,200 crores. The given income ₹ crores is greater thanequilibrium levelof income . Therefore, the ECONOMY is notin equilibrium. |
|
| 2628. |
If economic subsidies are added to and indirect taxes are subtracted from the national income at market prices , then it will be equal to : |
|
Answer» Domestic Income |
|
| 2629. |
Money supply does not include money held by government and banking system. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2630. |
Can Marginal revenue be zero. |
| Answer» Solution :True : Marginal revenue is the ADDITION to the total revenue due to a unit increase in sales. If an additional unit sold at a LOWER PRICE does not add anything to total revenue, MR will be ZERO. This generally happens when demand for a commodity is equal to unit elastic. | |
| 2631. |
Explain Central Bank’s function as currency authority.ORExplain ‘bank of Issue’ function of central bank. |
| Answer» Solution :The central bank is given the sole monopoly of issuing currency in order to secure control over volume of currency and credit. These notes circulate throughout the country as legal tender money. It has to keep a reserve in the form of gold and foreign securities as per statutory rules against the notes issued by it.It may be noted that RBI issues all currency notes in India except one rupee note. Again, it is under the directions of RBI that one rupee notes and small coins are issued by government mints. REMEMBER, the central government of a country is usually authorised to borrow money from the central bank.When the central government expenditure exceeds government revenue and the government is unable to reduce its expenditure, then it borrows from the RBI. This is done by selling SECURITY bills to RBI which creates new currency notes for the purpose. This is CALLED monetisation of budget deficit or deficit financing. The government spends new currency and PUTS it into circulation to meet its expenditure. | |
| 2632. |
What is the significance of autonomous transactions of BOP? |
| Answer» Solution :The significance of AUTONOMOUS transactions is that SURPLUS or DEFICIT in BOP is DETERMINED only by autonomous transactions. | |
| 2633. |
Is the following revenue expenditure or capital expenditure in the context of government budget ? Give reason. (i) Expenditure on collection of taxes. (ii) Expenditure on purchasing computers. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :i) EXPENDITURE on collection of taxes It is a revenue expenditure, as it does not reduce any government liability nor increases government asset.(ii) Expenditure on purchasing computers It is a capital expenditure, as it creates PHYSICAL ASSETS for the government. | |
| 2634. |
Classify the following as factor income or transfer income Financial help to victims of Uttrakhand tragedy. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :TRANSFER INCOME | |
| 2635. |
If the total cost curve is parallel to X-axis, marginal cost will: |
|
Answer» increase |
|
| 2636. |
Why would a compensation in form of money and not in florm of foodgrains for a worker working in an agrobased processing unit be more convenient ? Why does noney assume more importance than commodities as a medium of exchange? |
| Answer» Solution :Money is the commonly accited MEASURE of value.If worker is paid in FORM of commodities ,he will not be able to use these TOMAKE PAYMENT for the other commodities he needs to consume .Money being the medium of exchange gives him freedom of choice in BUYING goods and serivices | |
| 2637. |
Findingthe milk price high,government decides to reduce market price by giving subsidiesto producers of milk. Analyseits effects on (a) GDP and (b) welfare. |
|
Answer» Solution :Reducingmarket price of MILK will encourage households toconsume more milk . This in turn will raise productionof milk. As a result GDP will RISE. Increase in consumptionof milk will have POSITIVE effect on health of thepeople. This will raise efficiencyandin turn welfare. |
|
| 2638. |
The amount of loans offered by the commercial banks are equal to the deposits received by them. Do you agree with the given statement ? |
| Answer» Solution :No, I do not agree with the given statement. Through the function of money creations, commercial banks are able to offer LOANS ( or CREATES CREDIT), which are in far excess of deposits RECEIVED. | |
| 2639. |
What is a barter system? What are its drawbacks? |
| Answer» | |
| 2640. |
Explain how government budget can be helpful in bringing economic stabilization in the economy. |
| Answer» Solution :The government CONTROLS the FLUCTUATION in the prices and brings price stability through taxes, SUBSIDIES and expenditure. This is the method through which government can bring price STABILISATION. In case of inflation, government reduces its expenditures and in case of deflation or depression government reduces the taxes. The government provides subsidies for producing necessary goods like wheat, rice and sugar which RESULTS in the shift of resources from the production of luxury goods to the production of necessary goods. This brings economic stabilisation in the economy. | |
| 2641. |
How are following treated in the estimation of national income ? Services rendered by family members to each other. |
| Answer» Solution :No, it will not be included in the NATIONAL income as it is difficult to determine the value of services provided by FAMILY MEMBERS to each other. | |
| 2642. |
Which of the following is a source of demand for foreign currency? |
|
Answer» Foreign TOURISTS visiting India |
|
| 2643. |
When government imposes more unit tax, supply of the concerned good increases ? |
| Answer» Solution :False : If GOVERNMENT imposes more UNIT TAX, then COST of PRODUCTION increase, which will thereby shifts the supply curve leftward. | |
| 2644. |
Define the following terms : (i) GDP_(MP) , (ii) NDP_(FC) , (iii) NNP_(MP) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2645. |
The term 'market' refers to a…………. |
|
Answer» place where BUYER and SELLER bargain a product or service for a PRICE |
|
| 2646. |
What aggregate do we get, when we add up the gross value added of all the producing sectors of an economy ? |
| Answer» Solution :GROSS DOMESTIC product at MARKET PRICE. | |
| 2647. |
Define money supply. |
| Answer» | |
| 2648. |
Which one of the following cost curves is never 'U' shaped? |
|
Answer» Average COST curve. |
|
| 2649. |
Gifts and remittances to abroad are recorded on the: |
|
Answer» CREDIT SIDE of CURRENT Account |
|
| 2650. |
Why is the AD curve also known as 'C'+I' curve? |
| Answer» Solution :AD(Aggregate DEMAND) curve is also known 'C+I` curve as it gives the VALUE of final demand in an economy which is nothing but a SUM total of consumption demand (C ) and investment demad (I)HENCE, AD=C+I | |