Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 2651. |
Then main source of foregin capital in India is : |
|
Answer» Loans from ABROAD |
|
| 2652. |
Define final goods. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2653. |
Tax rates on higher income groups have been increased. Which economic value does it reflect ? Explain |
| Answer» Solution :This will reduce the INEQUALITIES of income as the DIFFERENCE between DISPOSABLE incomes of higher income and LOWER income groups will fall. This will also provide more resource to the government for spending on welfare of the poor. | |
| 2654. |
What does the area under marginal cost curve show? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Area under marginal COST curve SHOWS TOTAL variable cost. | |
| 2655. |
Define intermediate goods. |
| Answer» Solution :INTERMEDIATE goods REFER to those goods which are used EITHER for RESALE or for further production. | |
| 2656. |
Identify the correct flowchart depicting the nature of Capital Expenditure . |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 2657. |
What is meant by economising of resources? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Economising of resources means that resources are to be used in such a manner that MAXIMUM output is realised per unit of input. It also means OPTIMUM utilisation of resources. | |
| 2658. |
Explain how the allocation of resources can be influenced in the government budget through taxes , expenditure and subsidies . |
|
Answer» Solution :Government can influence allocation of resource through taxes , subsidies and expenditure. `*` By IMPOSING taxes at higher rates , it can discourage those occupations which are not beneficial to society. `*` By giving subsidies , it can ENCOURAGE certain industries which are beneficial to people . `*` By openingpublic undertakings in FIELDS where the private sector is SHY of investing , it can promote PUBLIC utility services. |
|
| 2659. |
A Monopolist is a price: |
|
Answer» Maker |
|
| 2660. |
What is the inflationary gap? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Inflationary gap shows the gap by which actutal AD EXCEEDS the AD required to maintain full EMPOLYMENT EQUILIBRIUM. It is equal to excess demand. | |
| 2661. |
Explain how changes in prices of inputs influence the supply of a product. |
Answer» SOLUTION :Case I- When price of INPUT rises : Due to rise in price of input the cost of production of a firm increases, which will thereby decrease the supply curve to the left as shown in the given figure.  Case II- When price of input falls : Due to FALL in price of input the cost of production of a firm decreases which will thereby increase the supply curve to the RIGHT as shown in the given figure. 
|
|
| 2662. |
Write short notes on : (i) Budgetary deficit (ii) Revenue deficit (iii) Fiscal deficit(iv) Primary deficit . |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Budgetary deficit is the excess of all EXPENDITURE on both revenue and capital accounts , over all RECEIPTS on revenue and capital accounts INCLUDING borrowings by the central government . Budgetary deficit = TE - TR where TE `gt` TR , TR = Total receipts , TE = Total expenditure . (ii) Revenue deficit is the excess of revenue expenditure over revenue receipts Revenue deficit = RE - RR where `RE gt R R` , where RE = Revenue expenditure and RR = Revenue receipts . (iii) Fiscal deficit is the excess of total expenditure (both on revenue and capital accounts ) over revenue receipts and capital receipts excluding borrowings. Fiscal deficit = Total Expenditure- Total Receipts excluding borrowings (iv) Primary deficit is the DIFFERENCE between fiscal deficit andinterest payments . Primary deficit = Fiscal deficit = INTEREST payments . |
|
| 2663. |
Which one of the following is the fixed cost for a firm? (i) Rent paid in advance for 3 months. (ii) Hourly wage to be paid to labour every month. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) It is the FIXED cost. It cannot be RECOVERED if the firm closes down the operations. Value: Critical Thinking |
|
| 2664. |
What is balance of payment (BOP)? |
| Answer» Solution :BOP is the DIFFERENCE between a NATION's total payment of foreign exchange and total receipt from them. | |
| 2665. |
What is meant by the term "pricetaker' in the context of a firm? |
| Answer» Solution : A firm is said to be a price-taker if it has to ACCEPT the price, as determined by the market FORCES of DEMAND and supply. | |
| 2666. |
Demand curve facing a monopoly firm is a constraint for the monopolist." Comment. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) A monopoly firm has market power and is itself a price-maker. It can choose any price, it likes. (ii) Unlike perfect competition where as output increases, price remains unchanged. (III) In monopoly as output increases or decreases, price changes ACCORDING to what consumers are willing to pay along the demand curve. It produces and supplies product to satisfy the ENTIRE market. (iv) It is because a monopoly faces the entire demand of the market, that market demand curve is said to be a constraint FACING a monopoly firm. |
|
| 2667. |
APC rises with increase in income |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2668. |
A consumer wants to consume two goods . The prices of the two goods are Rs 4 and Rs 5 respectively. The consumer's income is Rs 20. (i) Write down the equation of the budget line. (ii) How much quantity of good 1 can the consumer consume if she spends her entire income on that good ? (iii) How much of good 2 can she consume if the spends her entire income on that good ? (iv) What is the slope of the budget line ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Let the two quantities of GOODS be X and Y. We are given `P_x` = RS 4, `P_y` = Rs5, Consumer.s income (M) = Rs 20 . Budget line equation is , `P_(x^(.))X+P_(y^(.))Y=M" or "=4X+5Y=20` (II) If quantity consumed of good y = 0 , Budget equation becomes, `P_(x^(.))X+ZERO = M = 4.X = 20 = X = 20//4=5` UNITS . (iii) If quantity consumed of good X = 0 , Budget equation becomes, Zero , `+p_.Y=M` or = 5Y= 20 = Y = 20/5 = 4 units . (iv) Slope of budget line `=P_x//P_y = 4//5 = 0.8` |
|
| 2669. |
If the quantity supplied does not change at all as price changes, what will be the elasticity of spply ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :PERFECTLY INELASTIC SUPPLY (ES=0) | |
| 2670. |
Distinguish between balance of trade and balance of payments. |
| Answer» Solution :Balance of trade can be calculated by deducting the value of imports of GOODS from the value of exports of goods. Balance of payments, on the other hand, can be calculated by ADDING balance of payments at current account and balance of payments at capital account or by FINDING out the net balance between INFLOW of foreign exchange and outflow of foreign exchange.Balance of trade portrays a partial picture of foreign exchange. Balance of payments, on the other hand, provides a holistic picture.The net effect of balance of trade can be positive, negative, or zero. The net effect of balance of payments would always be zero.Capital and unilateral transfers are not INCLUDED in the balance of trade. Capital and unilateral transfers are major parts of balance of payments.Balance of trade is a sub-set of balance of payments. Without computing balance of trade, we would not be able to see the net effect of export and import in the balance of payments. | |
| 2671. |
In perfect competition, a firm independently determines price. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FALSE: In PERFECT competition, a firm is only price taker and industry is price MAKER. | |
| 2672. |
According to _________ theory, an economy may function at less than full employment level. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2673. |
What change in TR will result in a decrease in MR ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :When TR INCREASES at a DIMINISHING RATE. | |
| 2674. |
The marginal product of a variable input is best described as: |
|
Answer» Total product divided by the number of units of variable input. |
|
| 2675. |
Lack of double coincidence of wants exists in barter exchange as all commondities are not of equal value. |
| Answer» Solution :FALSE. It exists under barter exchanges because of difficulty in simultaneous fulfillment of mutual wants of BUYERS and SELLERS. | |
| 2676. |
What are the measures to correct excess demand? |
|
Answer» Solution :Measure to control excess demand are: (i) DECREASE in government spending. In this fiscal measure, central government reduces its expenditure in order to decrease level of aggreagate demand. (ii) Increase in government revenue. I.e.increase in taxes, increase in public debt, decrease in deficit financing. (iii) Decrease in availability of credit. Central bank aims to reduce availability of credit through 'Monetary policy'. It includes: (a) Increase in bank rate. (b) Sale of securities (c ).Increase in lega reserve REQUIREMENTS(CRR& SLR). QUALITATIVE INSTRUMENTS: (a) Increase in margin instrument (b) Moral suasion (to discourage lending) (c ).Selective credit CONTROLS (credit rationing). |
|
| 2677. |
Where is 'borrowings from abroad' recorded in BOP accounts? Give reason. |
| Answer» Solution :Borrowings from abroad is recorded in capital account of BOP as it INCREASES LIABILITY. It is entered on the credit side of capital account as it corresponds to INFLOW of foreign EXCHANGE. | |
| 2678. |
Do you consider a commerical bank creator of money in the economy? |
| Answer» | |
| 2679. |
In microeconomics, there exists : |
|
Answer» LIMITED aggregation |
|
| 2680. |
How many units of a commodity should a consumer buy to get its maximumutility ? Example with my help of a numerical example. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) When purchasing a unit of a commodity a consumer compares its price with the expanted utility from the utility obtained is the benefit, and the pricepayable is the cost , the consumer compares benefit and the cost. He will by the unit of commodity only if the benefit is is GREATER than or at latest equal to the cost. (ii) Equilibrium conditions for single commodity consumer Equilibrium . (a) Necessary Condition Marginal utility of Money = price `""...(1)` Or `(" Marginal Utility of a Product in Util " [MU_x])/("Marginal Utility of One Rupe "[MU_R]) " = Price of X"....(2)` In particular, the condition (1) saya that themarginal utility of a product in terms of Money should be equal to its price. Sometimes this is loosely stated as Marginal Utility is equal to price, i.e. ., MU = price . `"*"`If MU `gt`price `implies` As a rational consumer he willContinue to purchase an additional unit on a commodity as long as MU = price . `implies` MU `gt`Price impulse benefit is greater than cost and when ever benefit is greater than cost the consumer keeps on consuming additional unit of a commodity till MU = price . `implies` It is so because according to the law of diminishing marginal utility MU falls moreis purchased . As MU falls it is bound to become equal to the price at some point of purchase. `"*"` If MU `lt`Price `implies` As a rational consumer he will have to reduce the consumption of a commodity as long as MU = price . `implies MU lt`price implies when benefit is less than cost , never benefit is less than cost the dressing the additional unit of a commodity till MU = price. `implies` It is so because according to the law of diminishing marginal utility, MU RISES as less units are consumed. As MU rises , it is bound to become equal to the price at some point of purchase . (b) Sufficient condition: Total gain falls as more is purchased after equilibrium . it means that consumer continues to purchase so long as total gain is increasing or at least constant. (iii) It can be explained with the help of the following schedule : 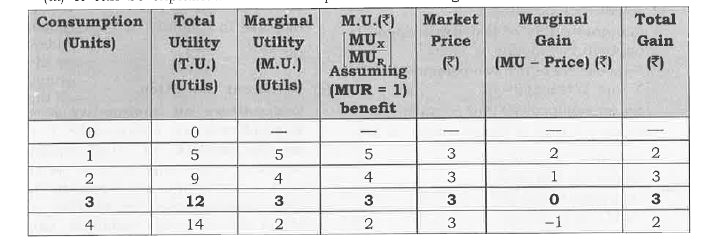 (a) Suppose , the price of commodity X in the market is Rs3 per unit .It means he has to pay Rs3 per unit for all the units he buys.Suppose, the unility obtained from the first unit is 5 utils(=Rs 5)The consumer will buy this unit because the utility of this unit is greater than the price and this PROCESS continues till Marginal utility = price as shown in the above schedule at quantity 3 . (b) Consumer will not buy the fourth unit utility of this unit is 2 unit because utility of this unit is 2 utils (= Rs 2)which is less than the price . It is not worth buying the fourth unit. The consumer will restrict his purchase to only 3 units. |
|
| 2681. |
Explain the following (i) Why are exports added while calculating GDP through the expenditure approach ? (ii) Why are subsidies added while calculating national income ? (iii) Why are intermediate cost deducted for arriving at GDP through the production approach ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Exports are added because these are produced within the economic (domestic) territory of the country. GDP is also defined in the same Way. (ii) SUBSIDIES are added because these are paid by government to production unit over and above the price paid by the BUYERS. As such these add to the factor payments paid by the production units. (iii) Intermediate COST is deducted to avoid double counting of the VALUE of the same product more than once. By doing so we arrived at the value of final products which counts value of a product only once |
|
| 2682. |
An economy is in equilibrium. Calculate national income from the following. Autonomous consumption=100 Marginal propensity to save = 0.2 Investment expenditure=200 |
|
Answer» Solution :Given AUTONOMOUS CONSUMPTION `(barC)`=100 MPS(s)=0.2 i.e. MPC (C )=1-MPS=1-0.2=0.8 1=200 y=?? We KNOW that at equilibrium, Y=C-I i.e. Y = `(barC)`+cY+I implies Y=100+0.8Y+200 implies Y=0.8Y+300 implies Y-0.8Y=300 implies0.2Y=300 so, Y=1,500 |
|
| 2683. |
Excess of foreign exchange receipts over foreign exchange payments on account of accommodating transactions equals deficit in the balance of payments. |
| Answer» Solution :False. EXCESS of foreign EXCHANGE PAYMENTS over foreign exchange receipts on account of autonomous transactions leads to DEFICIT in the BALANCE of payments. | |
| 2684. |
What is legal tender? |
| Answer» | |
| 2685. |
Direct taxes are _________. |
|
Answer» imposed on every MEMBER of the society |
|
| 2686. |
If the value of exports of a country is Rs 1,000 crores and the value of imports is Rs 600 crores, how much will be the trade balance? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2687. |
Compute NNP at market price {:("S.NO","Items","Amount (in Rs crore)"),((i),"Exports",155),((ii),"Government final consumption expenditure",2500),((iii),"Subsidies",120),((iv),"Gross domestic fixed capital formation",1190),((v),"Net factor income to abroad",125),((vi),"Net decrease in inventories (stocks)",100),((vii),"Ne Exports",(-) 420),((viii),"Net Indirect Taxes",470),((ix),"Net current transfer from capital",350),((x),"Consumption of fixed capital",145),(("xii"),"Private final consummption expenditure",2200):} OR Explain any two limitations of using GDP as a measure/index of welfare of a country. |
| Answer» | |
| 2688. |
Other things remaining unchanged, when in a country the price of domestic currency rises, national income is: |
|
Answer» LIKELY to RISE |
|
| 2689. |
Average revenue curve is also known as : |
|
Answer» PROFIT Curve |
|
| 2690. |
TU starts declining when MU starts declining. |
| Answer» Solution :False : Because TU STARTS declining only when DIMINISHING MU BECOMES negative. | |
| 2691. |
Assume that when price is 20rs the quantity demanded is 9 units and when price is 19rs, the quantity demanded is 10 units. Based on this information what is the marginal revenue resulting from an increase in output from 9 units to 10 units. |
| Answer» ANSWER :(C ) | |
| 2692. |
Distinguish between 'nominal income' and 'real income'. Explain why due to the presence of non-monetary production, real national income on its own cannot be treated as a true index of welfare. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Nominal income is what ONE gets in money terms. Real income is the amount of GOODS and service one can BUY from the nominal income. Non-monetary production means OUTPUT not obtained through the market, it consists of self-consumed output etc. Such output though should be included is left out of national income due to non-availability of data. But this output contributes to welfare. Leaving it out underestimates national income and thus economic welfare. |
|
| 2693. |
What does 'cost' mean in economics? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :COST of producing a good, in economics, is the SUM total of EXPLICIT cost, implicit cost and CERTAIN minimum profit (normal profit). | |
| 2694. |
In a economy , the actual level of income is Rs. 500 crores, whereas, the full employment level of income is Rs. 8000 crores. If one - fourth of additional income is saved, calculate increase in investment required to achieve full employment level of income. |
|
Answer» Multiplier (k) `=(1)/(MPS)=(1)/(0.25)=4` We also KNOW : k `=("Change in Income"(DeltaY))/("Change in INVESTMENT"(DELTAL))` Given : Change in Income `(DeltaY) = 800 -500 = Rs. 3000` crores i.e., 4`=(300)/("Change in Investment"(Deltal))` Hence ,Change in Investment required `= Rs. 75` crores |
|
| 2695. |
A consumer consumes two goods X and Y. What will happen if (MU_x)/(P_x)is greater than (MU_y)/(P_y) ? |
|
Answer» Solution :As, we know conditions for consumer equilibrium is , NECESSARY CONDITION Marginal UTILITY of last rupee spent on each commodity is same . Suppose there are two commodities, X and Y respectively. So , for commodity X, the condition is, Marginal Utility of Money = Price of X Or `(" Marginal in Util Product in Util " [MU_x])/( "Marginal Utility of One Rupee " [MU_R])` = Price of X or `(MU_x)/(P_x) = MU_R "".....(1)` Similarly, for commodity Y , the condition is, `(MU_y)/P_y=MU_R ""....(2)` Putting equation (2) in (1), we get `(MU_x)/(P_y)=(MU_y)/P_y` But as given in the question that the ratio of marginal utility to price in case of X is higher than that in case of Y, i.e., `(MU_x)/P_x gt (MU_y)/P_y` It means marginal utility from the last rupee spent on commodity X is more than marginal utility from the last rupee spent on commodity Y. So, to attain the equilibrium consumer must increase the quantity of X, which decreases the `MU_x` and decreases the quantity of Y, which will increase the `MU_y` Increase in quantity of X and DECREASE in quantity of Y continue TILL `(MU_x)/P_x = (MU_y)/P_y` . |
|
| 2696. |
When will there be a surplus in the Balance of Trade account? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2697. |
Can there be fiscal deficit without a revenue deficit ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Yes, it is possible (i) when revenue BUDGET is balanced but capital budget shows a deficit or (II) when revenue budget is in SURPLUS but deficit in capital budget is GREATER than the surplus of revenue budget. | |
| 2698. |
Explain the concept of real income. Explain why, due to the presence of externalities, real national income in itself cannot be treated as a true index of welfare. |
| Answer» Solution :Real income REFERS to the income of an individual or group after taking into CONSIDERATION the EFFECTS of INFLATION on purchasing power.due to presence of externalities,real income in itself cannot be treated as true index of welfare because an increase in the real income is associated with increased levels of pollution, accidents, disasters, shortage and depletion of natural resources, ETC. | |
| 2699. |
Describe four causes for disequilibrium in BOP. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Large imports DUE to large-scale development expenditure. (ii) High domestic prices which LEADS to imports. (iii) NEW sources of SUPPLY and new substitutes. (iv) CHANGES in taste, fashion and preferences. |
|
| 2700. |
Explain the role of government budget in influencing resource allocation |
| Answer» | |



