Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 2451. |
Explain the meaning of Managed floating. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Managed floating is a tool employed by the Central Bank to RESTORE the value of the country's currency (in relation to other currencies) within the desired limits. It is in essence a floating exchange RATE DETERMINED by market FORCES but called managed floating rate because of intervention by the Central Bank | |
| 2452. |
Fiscal deficit in the economy will be zero if there is no provision for borrowing in the budget. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2453. |
A consumer buys 14 units of a good at a price of Rs. 8 per unit. At price Rs. 7 per unit he spends Rs. 98 on the good. Calculate price elasticity of demand by the percentage method. Comment upon the shape of demand curve based on this information. |
|
Answer» Solution :`{:("INITIAL Price (P) = 8","Initial Expenditure = 112","Initial Quantity (Q) = 14"),("New Price "(P_(1))=7,"New Expenditure = 98","New Quantity "(Q_(1))),(,,=("EXP.")/("Price")=(98)/(7)=14),(Delta P=(-)1,,Delta Q=0):}` `PED=(Delta Q)/(Delta P)xx(P)/(Q)=(0)/((-)1)xx(8)/(14)=0` ED is perfectly inelastic as quantity DEMANDED does not CHANGE at all in response to change in price. Thus, its demand curve will be vertical/parallel to y-axis. |
|
| 2454. |
How the efficiency may increase if two firms merge? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Suppose that initially there are two firms in an industry and both are same but inefficient. (ii) Their MC curves are at a high level and consequently they charge a higher price and produce less. (iii) They realize, however, that if they merge with each other - and thereby become a monopoly-they can reduce their cost. (iv) For instance, one FIRM may have excellent technical MANPOWER but may not have good marketing SKILLS, whereas the other may not have good technical manpower but possesses superior marketing knowledge by merging the resulting monopoly firms MC CURVE will be at a lower level and thus it will be more efficient firm. (v) This, by itself will induce the monopoly to charge a price which is less and produce a quantity which is greater than when both firms were competing with each other. |
|
| 2455. |
Why PPC is concave to the point of origin? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Because of INCREASING MARGINAL OPPORTUNITY COST. | |
| 2456. |
Distinguish between current account and capital account of the balance of payments account on the basis of its components. |
|
Answer» On the other HAND, Capital Account records: BORROWINGS from and to abroad, Investments from and to abroad and Decrease and INCREASE in foreign exchange reserves. |
|
| 2457. |
Explain the process of money creation by commerical banks with the help of numerical example. |
| Answer» | |
| 2458. |
Explain the process of credit creation by commercial banks. |
|
Answer» Solution :SUPPOSE you deposit RS. 10,000 in a bank A, which is the primary deposit of the bank. The cash reserve requirement of the central bank is 10%. In such a case, bank A would keep Rs. 1000 as reserve with the central bank and would use remaining Rs. 9000 for LENDING purposes. The bank lends Rs. 9000 to Mr. X by opening an account in his name, known as demand deposit account. However, this is not ACTUALLY paid out to Mr. X. The bank has issued a check-book to Mr. X to withdraw money. Now, Mr. X writes a check of Rs. 9000 in favor of Mr. Y to settle his earlier debts. The check is now deposited by Mr. Y in bank B. Suppose the cash reserve requirement of the central bank for bank B is 5%. Thus, Rs. 450 (5% of 9000) will be kept as reserve and the remaining balance, which is Rs. 8550, would be used for lending purposes by bank B. Thus, this process of DEPOSITS and credit creation continues till the reserves with commercial banks reduce to zero. |
|
| 2459. |
When AC curve slopes downwards, what will be the position of MC curve? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :MC CURVE is below AC curve. | |
| 2460. |
Commodities X and Y have equal price elasticity of supply. The supply of X rises from 400 units to 500 units due to a 20 per cent rise in its price. Calculate the percentage fall in supply of Y if its price falls by 8 per cent. |
Answer» Solution :In the given example, FIRST we will calculate Price ELASTICITY of Good X.  Percentage change in supply `=(DELTAQ)/(Q)xx100=(100)/(400)xx100=25%` ES=`("Percentage change in quantity SUPPLIED")/("Percentage change in price ")=(25%)/(20%)=1.25` Now, Price Elasticity of Good `Y=1.25` (as both X and Y have the same price elasticity.) Let us now calculate `%` FALL in Supply for Y.  ES `=("Percentage Change in supply")/("Percentage Change in Price")` `1.25=("Percentgae Change in supply")/(8)` Percentage fall in supply `=10%` Supply for Good Y will fall by `10%` |
|
| 2461. |
Borrowing by government from World Bank to finance the BOP deficit will be recorded in the capital account. |
| Answer» Solution :TRUE. It will be recorded in the capital ACCOUNT as it relates to CLAIMS and liabilities of financial NATURE. | |
| 2462. |
Explain the inverse relationship betweenthe price of a commodity and its demand. |
|
Answer» Solution :The inverse relationship between price of the COMMODITY and quantity demanded for that commodity is because of the following reasons: (i) Income effect : (a) Quantity demanded of a commodity changes due to change in purchasing power (real income), caused by change in price of a commodity is called Income Effect. (b) Any change in the price of a commodity affects the purchasing power or real income of the consumers although his money income remains the same. (c ) When price of a commodity rise more has to be spent on purchase of the same quantity of that commodity. Thus, rise in price of commodity LEADS to fall in real income, which will thereby reduce quantity demanded is known as Income effect. (ii) Substitution effect : (a) It refers to substitution of one commodity in place of another commodity when it becomes relatively cheaper. (b) A rise in price of the commodity let coke, also means that price of its substitute, let pepsi, has fallen in relation to that of coke, even though the price of pepsi remains unchanged. So, people will buy more of pepsi and less of coke when price of coke rises. (c ) In other words, consumers will I substitute pepsi for coke. This is called Substitution effect. Price effect = Income effect+ Substitution effect (iii) Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility: (a) This law states that when a consumer consumes more and more units of a commodity,every additional UNIT of a commodity giveslesser and lesser satisfaction and marginal utilitydecreases. (b) The consumer consumes a commodity till marginal utility (benefit) he gets equals to the price (cost) they pay, i.e., where benefit = cost. (c ) For example, a THIRSTY man gets the maximum satisfaction (utility) from the first glass of water. Lesser utility from the 2nd glass of water, still lesser from the 3rd glass of water and so on. Clearly, if a consumer wants to buy more units of the commodity, he would like to do so at a lower price. Since, the utility derived from additional unit is lower. (IV) Additional consumer: (a) When price of a commodity falls, two effects are quite possible: New consumers, that is , consumers that were not able to afford a commodity previously, starts demanding it at a lower price. Old consumers of the commodity starts demanding more of the same commodity by spending the same amount of money. (b) As the result of old and new buyers push up the demand for a commodity when price falls. |
|
| 2463. |
Define Marginal Rate of Transformation (MRT). |
| Answer» Solution :Marginal rate of transformation is the ratio of a NUMBER of UNITS of a GOOD sacrificed to produce an ADDITIONAL UNIT of another commodity. | |
| 2464. |
What are non-debt creating capital receipts ?Give two examples such receipts . |
|
Answer» Solution :Capital receipts are those receipts of GOVERNMENT which either create liabilities or reduce assets. Capital receipts EXCLUDING BORROWINGS are KNOWN as non-deptcreating capital receipts . Examples : DISINVESTMENT, Recovery of loans. |
|
| 2465. |
Under perfect competition, all the units of a good produced can be heterogeneous. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :False: Under perfect COMPETITION, all the units of a GOOD produced are homogeneous. | |
| 2466. |
How does the budget line change if the consumer's income increase to Rs 40 but the prices remain unchanged ? |
Answer» Solution :If consumer.s INCOME INCREASES to RS40 ,the consumercan buy more pieces/quantities of both the goods X and Y . There will be PARALLEL rightward shift in the budget LINE AB to `A_1B_1` . 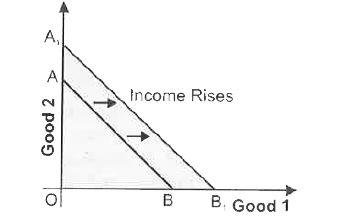
|
|
| 2467. |
A soft Drinkscompany purchases 20 Truksfor thetranksfor thetransportationof softdrinks fromthefactoryto the wholesale agents . Whether thetrukspurchased will betreasted as finalgoodor intermediategoods? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :TRUCKS PURCHASED by thecompanyare finalgoodsas theyarepurchased forinvestment. | |
| 2468. |
The supply for a good rises to 1000 units in response to rise in price by 1rs. If the original supply was 800 units at the price of 10rs , calculate price elasticity of supply. |
Answer» SOLUTION : Price Elasticity of Supply (ES) `=(DeltaQ)/(DeltaP)XX(P)/(Q) =(200)/(1)xx(10)/(800)=2.5` ES=2.5(Supply is highly elastic as ES gt 1) ES is always POSITIVE DUE to direct relationship between price and QUANTITY supplied. |
|
| 2469. |
What happens when (i) credit is made costlier (ii) Credit is made cheaper. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :When credit is made COSTLIER, it leads to contraction of credit and it CORRECTS EXCESS demand or inflationary gap. (II) When credit is made cheaper, it leads to extension of credit, and it corrects deficient demand or deflationary gap. |
|
| 2470. |
What is full employment equilibrium ? |
| Answer» Solution :Full employment equilibrium REFERS to a situation when aggregate demand is EQUAL to the aggregate SUPPLY at full employment level ie., AD = AS. | |
| 2471. |
What are debit and credit in BOP account? |
| Answer» Solution :Any transaction resulting in a payment to foreigners is ENTERED as a DEBIT in BOP account whereas transactions resulting in receipts from foreigners is entered as a CREDIT in BOP account. | |
| 2472. |
If marginal product falls, average product must also fall. |
| Answer» Solution :False: There may be an intermediate STAGE when the marginal product may be falling, the AVERAGE product keeps rising or CONSTANT. This occurs when the fixed inputs are better UTILISED. | |
| 2473. |
Which point on PPF shows a "productively efficient" level of output? |
|
Answer» A |
|
| 2474. |
RBI' has reduced Bank Rate from 7.25% to 6.75% on 29th Sept. , 2015 . '(The Economic Times ) Analyse its economic value from viewpointof (i) Household , (ii) Investor and (iii) Economy . |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Impact on Households - A cut in bank rate FOLLOWED by marked rate of interest wil induce borrowings for purchase of consumer DURABLE LIKE houses, CARS and electical gadgets, etc. This implies direct monetary benefits to the household. (ii) Impacton Investors - Clearly a cut in market rate of interest will reduce the cost of borrowing money capital. As a result, investment is EXPECTED to increase thereby providing more scope for profits to the investors. (iii) Impact on Economy - Increase in consumption expenditure on consumer durables coupled with investment expenditure will increase aggregate demand. As a result, level of planned output will rise thereby raising the level of GDP. With rise in growth rate of GDP, the economy will get scope for further development. |
|
| 2475. |
Explain tax reforms under New EconomicPolicy (1971). |
| Answer» Solution :The rates of taxes before 1991 were quite high. High taxes resort PEOPLE to tax EVASION. Todiscouragetax evasion tax rates were gradually beingreduced. Also taxlaws and proceduresare being simplifiedto SIMPLIFY filing of tax returnsand MAKING payments. In 2016, GST law was passed. It has established a common national market ensuringsmooth flow of products from and part of country to another. | |
| 2476. |
Equilibrium price will not change if the decrease in demand meets with a proportionate decrease in supply. |
| Answer» Solution :True: Decrease in demand results in a fall in EQUILIBRIUM PRICE, decrease in supply, on the other hand, results in an increase in price. If both the changes are PROPORTIONATELY EQUAL, equilibrium price will not change. | |
| 2477. |
What is the major reason for rise in demand for foreign currency when its price falls? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :When PRICE of foreign exchange fall,s imports from that country becomes cheaper e.g, when exchange rate falls from Rs 50 to Rs 40 for one dollar, it mens less rupees are required to buy good worth 1 dollar from America, hence DEMAND RISES. | |
| 2478. |
How can money be defined ? |
| Answer» | |
| 2479. |
How is total utility deriveds from marginal utility ? |
| Answer» Solution :`"TU" = MU_(1) +"MU"_2 + "MU"_3 +..........+"MU"_N = sum"MU"` | |
| 2480. |
What is meant by aggregate supply ? |
| Answer» Solution :Aggregate supply, also KNOWN as total OUTPUT, is the total supply of goods and services produced within an ECONOMY at a given overall PRICE level in a given period. | |
| 2481. |
What will be the effect of a deficit budget on aggregate demand ? |
|
Answer» AD decreases |
|
| 2482. |
Which one of the following statements is an example of an "implicit cost"? |
|
Answer» Interest that could have been earned on retained earnings used by the firm to finance expansion. |
|
| 2483. |
Explain the role of Reserse RepoRatioin controllingcredit creation. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The rate at which Central Bank borrows money from the banks is termed as Reverse Repo Rate. The Central Bank uses this tool when it feels there is too much money floating in the banking system. In case of a rise in the Reverse Repo Rate, it becomes more profitable for the Commercial Banks to lend to Central Bank, since they will now GET higher amount against the amount lent. This IMPLIES higher the amount lent, higher are the returns. Thus, the Commercial Banks aim to transfer greater amount of funds to the Central Bank. This, in turn implies that the Commercial Banks are left with less surplus funds that they can lend to the general public. Hence, the lending capacity of the Commercial Banks reduces. This would further imply lesser amount of credit and money flowing WITHIN the economy, hence, lesser money supply. This results in the reduction in the credit creation capacity of Commercial Banks. A rise in reverse repo rate is desirable by the Central Bank if it aims at contracting monetary policy. However, on the contrary if the Central Bank aims at expansionary monetary policy, then it at FIRST instance reduces the Reverse Repo Rate, which in tum makes the lending unattractive and discourages the Commercial Banks to lend to the Central Bank. Thereby, a fall in the reverse repo rate restricts the flow of money and credit in an economy. | |
| 2484. |
When is value of output equal to value added ? |
| Answer» Solution :VALUE of output is EQUAL to value ADDED if there are no INTERMEDIATE costs. | |
| 2485. |
Government provides essential items of food grains almost free to the families below the poverty line . Which objective the government is trying to fulfil through the government budget and how ? Explain. |
| Answer» Solution :By providing essential items of food grains almost free to the families below the poverty LINE , government is TRYING to reduce the gap between the rich and the poor. Government taxes the rich and SPENDS the amount on the poor . This reduces DISPOSABLE income of the rich and INCREASES the disposable income of the poor. | |
| 2486. |
Price elasticity of demand of a good is -0.75. Calculate the percentage fall in its price that will results in 15 per cent rise in its demand. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Elasticity of demand `= ("PERCENTAGE change in quantity DEMANDED")/("Percentage change in price")` or `= 0.75 = (15)/(x)`...[Let x be the percentage change in price] or `-0.75x = 15 x = 15 xx (100)/(-0.75) x = - 20` Price will fall by 20% |
|
| 2487. |
RBI produces money while commercial banks increase the supply of money. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2488. |
Final goods refer to those goods which are used either for "______" or for "________". |
|
Answer» CONSUMPTION , INVESTMENT |
|
| 2489. |
Does public debt impose a burden ? Explain. |
| Answer» Solution :Public debt can IMPOSE a burden in the following cases : (i) When government has imposed new taxes or raised the existencetax rates to redeem the debt, (ii) When debt is to be REDEEMED through PRINTING of new currency . In such case , it would CAUSE INFLATIONARY trends in the economy , (iii) When public debt is taken for war purpose or debt is used in an unplanned manner. | |
| 2490. |
What is the relation between good x and good y in each case, if with a fall in price of x demand for good y (i) rises and (ii) falls? Give reason. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i)GOODS X and y are complementary goods as with fall in PRICE of x, demand for good y RISES. (ii)Goods x and y are SUBSTITUTE goods as with the fall in price of x, demand for good y also falls. |
|
| 2491. |
The central bankcan increase availability of credit by: (Choose the correct alternative) |
|
Answer» Raising REPO rate |
|
| 2492. |
What is noney multiplier ? How will you determine its value? What ratios play an important role in the determination of the value of the money multiplier? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Money MULTIPLIER =`(1)/(LRR)` Lower the LRR, higher is the value of money multiplier and VICE versa (REFER to 6.2.1) |
|
| 2493. |
In a perfectly competitive market the buyers treat products of all the firms as homogeneous. Explain the significance of this feature. |
|
Answer» Solution :In a perfectly COMPETITIVE market, the buyers treat products of all the firms as homogeneous. This implies that all the firms in perfect competitive market produces homogeneous product. This further implies that the product of each and every firm in the market is perfect substitute to other product in terms of quantity, quality, colour, size, features, etc. This indicates that the buyers are INDIFFERENT between the products of different firms. Due to HOMOGENEITY of the products, existence of uniform price is guaranteed. Implication : The products of different firms are qualitatively and QUANTITATIVELY homogeneous. |
|
| 2494. |
What is meant by capital expenditure? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :CAPITAL EXPENDITURE refers to the expenditure which either creates an asset or causes a reduction in the LIABILITIES of the government . | |
| 2495. |
To increase themoneysupplyin theeconomy, central bankreducesthe marginerequirements. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :TRUE : Fall in MARGIN requirementsenhances theborrowingcapacityof PUBLIC, whichraisethe money supplyin theeconomy. | |
| 2496. |
Balance of Payments 'deficit' is the excess of |
|
Answer» Current account PAYMENTS over current account receipts |
|
| 2497. |
Identify the following as Normal Residents of India : Indian workers employed in power projects of Nepal on daily wages and crossing into Indian territory every week. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :NORMAL RESIDENTS. | |
| 2498. |
What is meant by capital account? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2499. |
Distinguish between revenue receipts and capital receipts. Give an example of each |
Answer» SOLUTION :
|
|
| 2500. |
The ratio ottotal deposits that a commercial bank has to keep with Keserve Bank ot India is ca lled: (choose the correct alternative) (a) Statutory liquidity rado (b) Deposit ratio (c) Cash reserve ratio (d) Legal reserve ratio |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(C) CASH RESERVE RATIO | |