Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 44501. |
Show that the magnetic field at any point on the axis of the solenoid having n turns per unit length is B =(1)/(2) mu_(0) n I (cos theta_(1) - cos theta_(2)). |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Consider a solenoid havingradius R consistsof n NUMBER of TURNS PER unit length . Let P be the pointat a distance. Xformthe origin of thesolenoid. The current carrying element dx ata distance. xfromorigin andthe distance r from point p . ` r = sqrt(R^(2) + (x'- x)^(2))` The magnetic field due to current carryingcircular coil along its axis is `dB = mu_(0)/2 . (IR^(2))/r^(2) xx N ` where ` N= ndx ` then ` dB = mu_(0)/2.(nIR^(2))/r^(3) . dx ` `sin theta= R/ r ` ` r = R cosec phi ` .....(1) `tan phi = R/ (x' - x) ` ` x - x= R cotphi ` ` (dx)/(d phi) = R cosec^(2) phi ` ` dx = R cosec^(2) phi d phi ` .....(2) from above equation , `dB = mu_(0)/ 2 . (nIR^(2).R cosec ^(2) phi .d phi )/(R^(3) cosec ^(3) phi ) ` `dB = mu_(0)/2 . nI sin phi d phi ` Total magnetic field can be obtained by INTEGRATING `B= (mu_(0) nI)/2 underset(phi_(1))overset(phi_(2)) int sin phi d phi ` ` B = ( mu_(0)nI)/2 [ - cos phi ]_(phi_(1))^(phi_(2))` `B = (mu_(0)nI)/2 ( cos phi_(1) - cos phi_(2))` |
|
| 44502. |
A coil having an area 2 m^(2) is placed in a magnetic field which changes from 1 Wb m^(2)" to "4 Wb m^(2) in an interval of 2 s. The induced emf in the coil will be |
|
Answer» 4V `|EPSI|=(phi_(2)-phi_(1))/t=(8-2)/2=3V` |
|
| 44503. |
A charge Q is placed at each of the opposite corners of square. A chargeqis placed at each of the other two corners. If the net electrical force on Q is zero , then Q/q equals. |
|
Answer» `-1` As force `oversetto (F_(AC))` is repulsive HENCE for equilibrium `oversetto (F_(AB)) and oversetto (F_(AD))` must be attractive i.e.,q must be negative As force`oversetto (F_(AC) ) ` is repulsive, hence for equilibrium `oversetto (F_(AB)) "and" oversetto (F_(AD)) ` must be attractive i.e.,q must be negative ` ""|oversetto ( F_(AC)) | = ( kQ^(2))/((lsqrt2)^(2)) =(kQ^(2))/( 2L^(2)) and |oversetto (F_(AB))| = | oversetto (F_(AD)) |=(kQ .q)/(l^(2))` Then ` ""|oversetto(F_(AB)) +oversetto (F_(AD))| =sqrt(F_(AB) ^(2) +F_(AD)^(2) )= ( sqrt2kQq)/(l^(2)) ` ` (##U_LIK_SP_PHY_XII_C01_E04_014_S01.png" width="80%"> SINCE ` ""oversetto (F_(AC) ) +oversetto (F_(AB)) +oversetto (F_(AD)) =0, "hence" |oversetto (F_(AC)) | =- |oversetto (F_(AB))+oversetto (F_(AD)) | ` ` THEREFORE "" (kQ^(2))/( 2l^(2)) =-(sqrt2kQq)/(l^(2)) rArr (Q)/(q) =-2sqrt2` |
|
| 44504. |
Three identical, parallel conducting plates, A, B and C are placed as shwon. Switches S_(1) and S_(2) are open, and can connect A and C to earth when closed +Q charge is given to B. |
|
Answer» If `S_(1)` is closed with `S_(2)` OPEN a charge of amount `Q` will PASS THORUGH `S_(1)` |
|
| 44505. |
block of mass 0-1 kg is held against a wall by applying a horizontal force of 5 N on the block. If the coefficient of friction between the block and the mass is 0.5, the magnitude of the frictional force acting on the block is : |
|
Answer» 0.98 N `F_(f)= muR = 0.5 xx 5 = 2.5 N` ` wt. of block = mg = 0.1 xx 9.8 = 0.98N` As weight is less than limiting friction ::. block does not move :. FRICTIONAL force = wt. of block = 0.98 N  Hence correct CHOICE is (a). |
|
| 44506. |
A : If white light is used is Young.s experimened the central bright fringe is white and the fringe closest on either side of the central white fringe is red. R : When white light is used in Y.D.S.E for a point .P. for which S_(2)S-S_(1)P= (lambda_B)/(2), (lambda_(B)=" wavelength of blue ") the blue component will be absent and fringe will appear red in colour. |
|
Answer» Both A and R are true and R is the CORRECT explanation of A |
|
| 44507. |
A transformer is used to light a 100 W 110V lamp from a 220 V mains. If the main current is 0.5A, the effciency of the transfomer is approximately |
|
Answer» 0.1 |
|
| 44508. |
Describewith suitableblock diagrams,action of pn-junctiondioide under forwardand reversebias conditions . Also draw I-V characteristics . |
Answer» Solution :FORWARD Bias :When a battery is connectedacross the junctionsuch that p side is connectedto the positiveterminaland n sideto thenegativeterminalof the source,the p-n junctionis said to be forwardbiased . The appliedvoltageopposesthe junctionp.d. and forvalues of the applied voltage GREATER than the junctionand constitutesa currentin an externalcircuit.This currentriseslinearlywith the appliedvoltagebeyondthe knee voltage . Thus a forward biasedp-n junctionoffers a low resistance.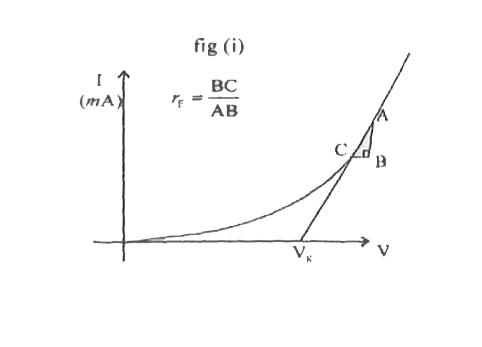 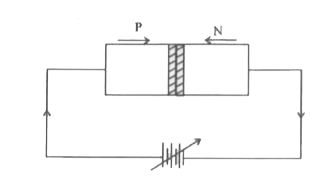 Reverse bias : When batteryis connected acrossthe junctionsuch that p side is connectedto the negative terminaland n side to the positive terminal , the p-n junction is said to be reverse biased In this case , the appliedvoltage adds to the EFFECT of junction p.d.and hencemajority carrierscannot cross the junction.The currentthroughthe circuit is practically zero.Thus ,reveres bias offersa very highresistancebut small CURRENT of the order of a few mA flowsthrough the circuit due to the minoritycarriersin the p and nregions. As the appliedvoltageis graduallyincreaseda very large currentresultsat a particularvoltage . This voltage is CALLED thebreak down or cut-in voltage. 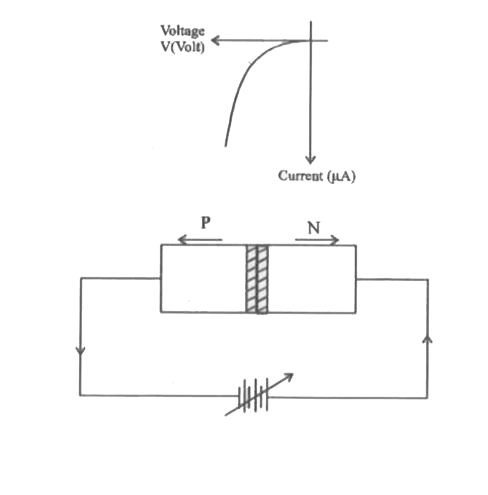
|
|
| 44509. |
For a medium with permittivity and permeability mu, the velocity of light is given by : |
|
Answer» `SQRT(mu/EPSILON)` |
|
| 44510. |
Find the effective capacitance between the terminals a and b shown in figure. |
|
Answer» `(8C )/(27)` |
|
| 44511. |
Find the effective capacitance between the terminals a and b shown in figure. |
|
Answer» `(4C )/(3) ` |
|
| 44512. |
The head lights of a jeep are 1.2 m apart. If the pupil of the eye of an observer has a diameter of 2 mm and light of wavelength 5896 Å, is used, what should be the maximum distance of the jeep from the observer if the two head lights are just separated ? |
|
Answer» `33.4` KM D= Diameter of lens, d = Separation between sources or `x=((2xx10^(-3))xx1.2)/(1.22xx5896xx10^(-10))m=3.34xx10^(3)m=3.34"km"` |
|
| 44513. |
In the electrical network, shown in the diagram R_(1)=5Omega,R_(2)=2Omega,R_(3)=3Omega and E_(1)=2E_(2)=10V, sources have negligible internal resistance. For this network, |
|
Answer» The power generated in `R_(1)` is `6.4J//s`  (A). Power generated P is `R_(1)` is `i_(1)^(2)R_(1)` now `i_(1)=(V)/(R_(1))` where V is the potential at `P`, ASSUMING that the negatives of the BATTERIES are earthed. Simple application of Kirchhoff's junction and loop laws yields `i_(3)=(45)/(31)A,i_(2)=-(10)/(31)A` `i_(1)=i_(2)+i_(3)=(35)/(31)A` `V=R_(1)i_(1)=(175)/(31)=5.7V` When `R_(1)=5Omega,R_(2)=2Omega,R_(3)=3Omega` Hence `P=(V^(2))/(R_(1))=((5.7)^(2))/(5)=6.4(J)/(s)` (B). CURRENT in `R_(1)` will be different if the sources of emf `E_(1)` and `E_(2)` are interchanged. (C). Current in `R_(1)` will be reversed in direction but numerically be the same hence P is not changed (D). Ratio of powers in `R_(2)` and `R_(3)` is given by `(P_(2))/(P_(3))=((V-5)^(2)//R_(2))/((10-V)^(2)//R_(3))=((0.7)^(2)//2)/((4.3)^(2)//3)APPROX(1)/(30)` |
|
| 44514. |
It is observed that only 0.39% of the originalradioactive sample remains undecayed after eight hours. Select the correct options. |
|
Answer» The HALF-life of that SUBSTANCE is 1 hour. As `N=N_0 e^(-lambdat)` [ Law of radioactive decay] `rArr N/N_0=e^(-lambdat) rArr 0.0039 =e^(-lambda8)` `rArr e^(8lambda)=1/0.0039 = 256` or `e^(8lambda)=2^8` Taking natural logarithm on both sides , we get `8 lambda = 8 ln2` `lambda` = ln2 per hour Again, half life `=T_(1//2)=(ln2)/lambda`=1 hour Mean time, `tau =1/lambda=1/(ln2)` hour `therefore N=(10)^8 (1/2)^(1//2)=1/sqrt2xx10^8` or `N=5sqrt2xx10^7` . |
|
| 44515. |
One mole of a gas at standard temperatureand pressure (STP corresponds to 7=273 K and rho= 1.01 xx 10^5 Pa) occupies a volume of 22.5 /. Suppose the container is in the shape of a cube, (a) Determine the length of the cube edge, (b) What force is exerted by the gas on each face ofthe container ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) 0.282 m, (B) 8.03 KN | |
| 44516. |
Same current l is flowing through 3 infinite long thin wires along+ve x,y,z axes. Find the net magnetic induction at a point (0,0,-a) such that yz plane is in the plane of the paper (i,jk are the unit vectors along x,y and z axes respectively) |
|
Answer» Solution :B due to conductor along Z-axis = 0 B due to conductor along y axis `vecB_(y)=(mu_(0))/(2PI)l/a(-HATI)` B due to conductor along X-axis `vecB_(x)=(mu_(0))/(2pi)I/a(hatj)` `(vecB("NET"))_(P)=vecB_(x)+vecB_(y)+vecB_(z)` `=(mu_(0))/(2pi)I/a(-hati+hatj)` 
|
|
| 44517. |
A parallel beamof light falls successively on a thin convex lens of focal length 40 cm and then ono a thini convex lens of focal length 10cm as shown in figure. In figure, the second lens is an equiconcave lens of focal length 10cm and made of a material of refractive index 1.5. In both the cases, the second lens has an aperture equal to 1cm. Q. Now, a liquid of refractive index mu is filled to the right of the second lens in case B such that the area illuminated in both the cases is the same. Determing the refractive index of the liquid. |
|
Answer» 1 `A_(1)=pi(1)^(2)=picm^(2)` In case (b), let x be the diameter of the area illuminated. Then, `(x)/(45)=(1)/(5)rArr x=9cm` `A_(2)=pi((9)/(2))^(2)=(81)/(4)picm^(2)` `(A_(2))/(A_(1))=(81)/(4)` When liquid of refractive index `mu` is filled to the right of this lens, the first surface of the lens (radius of curvature `=10cm)` forms the imag at the OBJECT only. Considering the refraction at the second surface. `(mu)/(oo)-(1.5)/(-10)=(mu-1.5)/(10)` (therefore, same area `rArr upsilonrarroo)` `rArr mu=3` 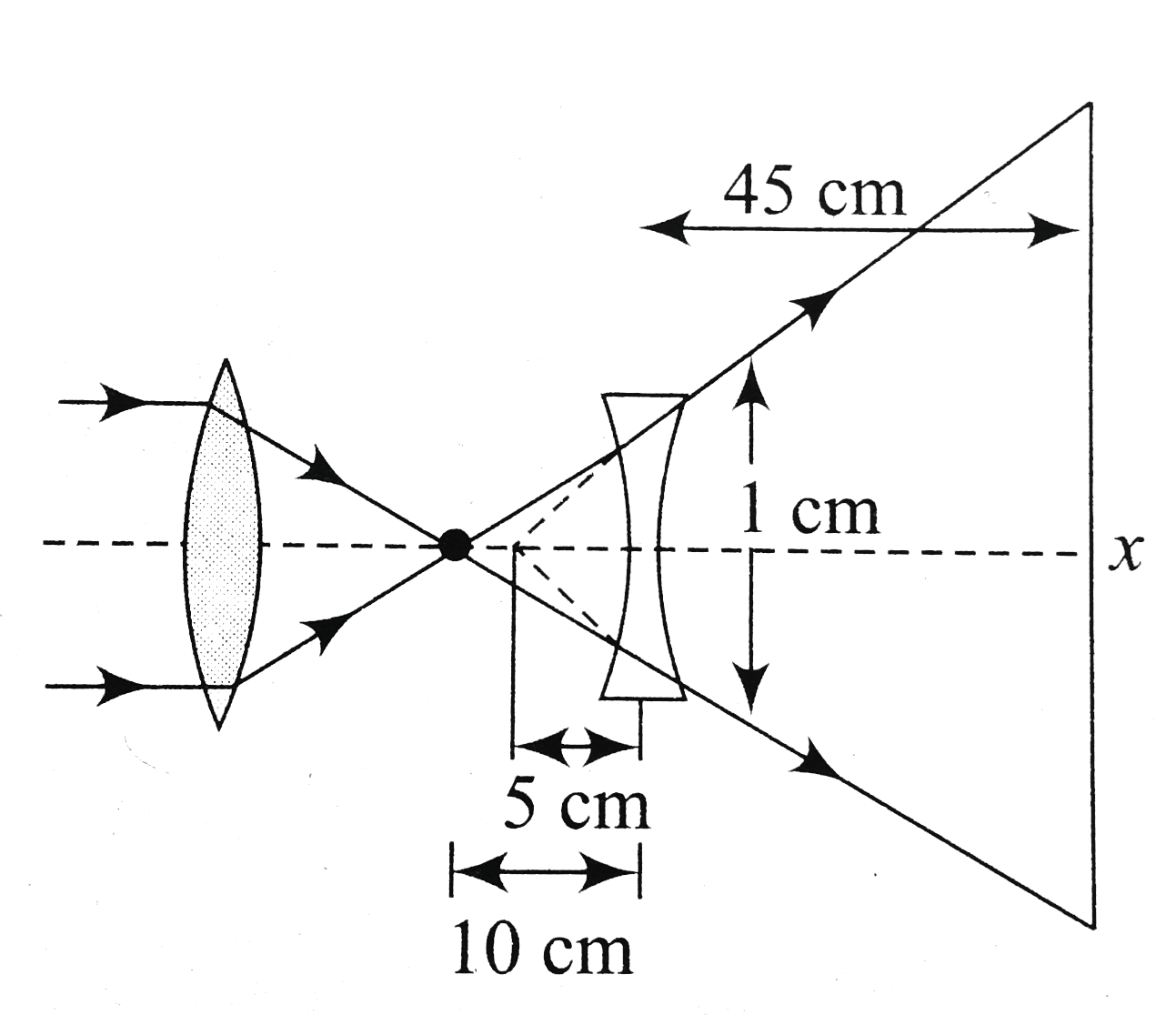
|
|
| 44518. |
A parallel beamof light falls successively on a thin convex lens of focal length 40 cm and then ono a thini convex lens of focal length 10cm as shown in figure. In figure, the second lens is an equiconcave lens of focal length 10cm and made of a material of refractive index 1.5. In both the cases, the second lens has an aperture equal to 1cm. Q. Compare the area illuminatedby the beam of light on the screen, which passes through the second lens in the two cases. The ratio (A_(2)//A_(1))will be |
|
Answer» `72//5` `A_(1)=pi(1)^(2)=picm^(2)` In case (b), let X be the diameter of the area illuminated. Then, `(x)/(45)=(1)/(5)rArr x=9cm` `A_(2)=pi((9)/(2))^(2)=(81)/(4)picm^(2)` `(A_(2))/(A_(1))=(81)/(4)` When liquid of refractive index `mu` is FILLED to the right of this lens, the first surface of the lens (radius of curvature `=10cm)` forms the IMAG at the OBJECT only. Considering the refraction at the second surface. `(mu)/(oo)-(1.5)/(-10)=(mu-1.5)/(10)` (therefore, same area `rArr upsilonrarroo)` `rArr mu=3` 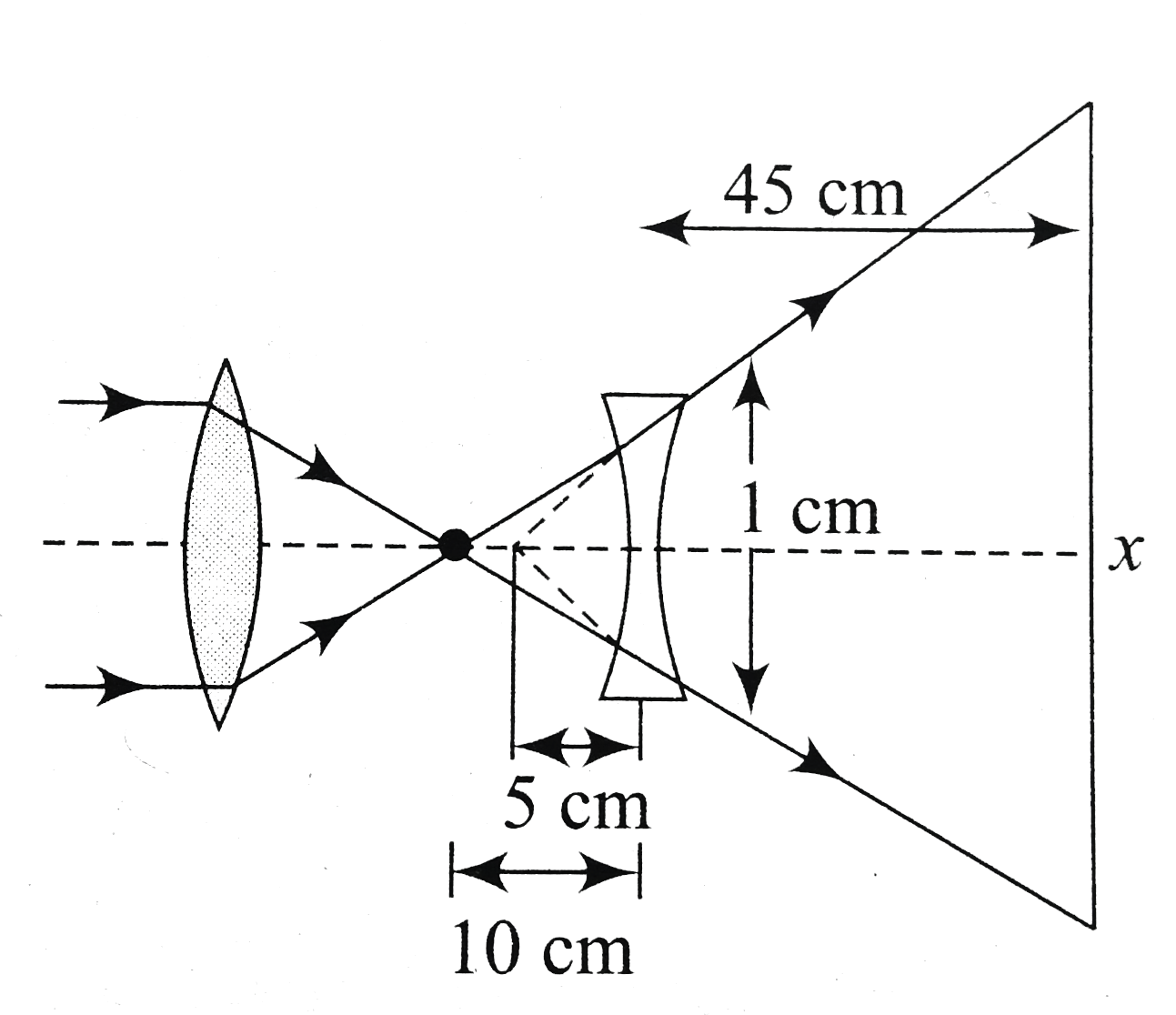
|
|
| 44519. |
The magnifying power of an astronomical telescope in the normal adjustment position is 100. The distance between the objective and the eyepiece is 101 cm. Calculate the focal length of the objective and the eyepiece. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Here, `|m| =f_(0)/f_(e) = 100rArr f_(0) = 100 f_(e)` and `f_(0) + f_(e) =101 cm` or `100f_(e) + f_(e) = 101 f_(e) = 101 cm` `RARR f_(e)= 1CM` and `f_(0) = 100 cm = 1 cm` |
|
| 44520. |
A light ray is normally incident on one face of equilateral glass prism of refractive index sqrt2. Thedeviation of light ray is |
| Answer» ANSWER :C | |
| 44521. |
When n-P-n transistor is used as an amplifier |
|
Answer» ELECTRONS move from EMITTER to COLLECTOR |
|
| 44522. |
A ray of light is incident at 50^(@) on the middle of one of the two mirros arranged at an angle of 60^(@) between them. The ray then touches the second mirror, making an angle of incidence of |
|
Answer» `50^(@)`  From geometry of FIGURE In `Delta ABC , alpha = 180^(@) - (60^(@) + 40^(@)) = 80^(@)` `rArr beta = 90^(@) - 80^(@) = 10^(@)` In `Delta ABD , angle A = 60^(@), angle B = (alpha = 2 beta)` `=(80 + 2 xx 10) = 100^(@) and angle D = (90^(@) - theta)` `therefore angleA + angle B + angle D = 180^(@) rArr 60^(@) + 100^(@) + (90^(@) - theta)` ` = 180^(@) rArr theta = 70^(@)`. |
|
| 44523. |
When two waves of interfering with each other have amplitudes aplha_1 and alpha_2 and the phase difference of 3pi, the resultant amplitude is : |
|
Answer» `a_1-a_2` |
|
| 44524. |
Derive the law of reflection of light on the basis of Huygens wave theory. |
|
Answer» Solution :Law of REFLECTION : (i) The incident wavefront AB, the reflected wavefront CD and the reflecting surface XY all the in the same plane. (ii) Angle of INCIDENCE `i=/_PAN=90^(@)-/_NAB=/_BAC` Angle of reflection `r=/_NAD=90^(@)-/_DAC=/_DCA` In right angled TRIANGLES ABC and ADC `/_B=/_D=90^(@)`  `BC=AD` and AC is common `:.` The TWO triangles are congruent `:./_BAC=/_DCA` i.e., `i=r` THUS the angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection. |
|
| 44525. |
The correct functinal group X and the reagent/reaction conditions Y in the following scheme are : Condenasation polymer formed Nylon-66 |
|
Answer» `X=COOCH_(3), Y=H_(2)//NI//"heat"` 
|
|
| 44526. |
The energy band gap between valence band and conduction band is maximum in |
|
Answer» METALS. |
|
| 44527. |
Electromagnetic waves propagate through free space or a medium as transverse waves. The electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular to each other as well as perpendicular to the direction of propagation of waves at each point. In the direction of wave propagation, electric field vecE and magnetic field vecB form a right-handed cartesian coordinate system. During the propagation of electromagnetic wave, total energy of electromagnetic wave is distributed equally between electric and magnetic fields. Since in_0 and mu_0 are permittivity and permeability of free space, the velocity of electromagnetic wave, c=(in_0 mu_0)^(-1//2). Energy density i.e., energy in unit volume due to electric field at any point, u_E=1/2in_0E^2 Similarly, energy density due to magnetic field , u_M=1/(2mu_0)B^2. If the electromagnetic wave propagates along x-direction, then the equations of electric and magnetic field are respectively. E=E_0sin(omegat-kx) and B=B_0sin(omegat-kx) Here, the frequency and the wavelength of oscillating electric and magnetic fields are f=omega/(2pi) and lambda=(2pi)/k respectively. Thus E_"rms"=E_0/sqrt2 and B_"rms"=B_0/sqrt2, where E_0/B_0=c. Therefore, average energy density baru_E=1/2in_0E_"rms"^2and baru_M=1/(2mu_0)B_"rms"^2. The intensity of the electromagnetic wave at a point, I=cbaru=c(baru_E+baru_B). To answer the following questions , we assume that in case of propagation of electromagnetic wave through free space, c=3xx10^8 m.s^(-1) and mu_0=4pixx10^(-7) H.m^(-1) If the electromagnetic wave propagates along x-axis, then the electric field vecE will be |
|
Answer» ALONG y-axis |
|
| 44528. |
What do you mean by internal resistance of a cell ? |
|
Answer» Solution :The resistance offered by the electrolyte of a CELL to the flow of current between its ELECTRODES is called INTERNAL resistance of the cell. An ideal battery has zero internal resistance and the potential difference across the batteryequals to its emf. But a real battery is made of electrodes and electrolyte, there is resistance to the flow of charges within the battery. A FRESHLY prepared cell has low internal resistance and it increases with AGEING. |
|
| 44529. |
A compass needle made of pure iron (with density 8000 kg//m^2) has a length 5 cm, width 1.0 mm and thickness 0.50 mm. The magnitude of magnetic dipole moment of an iron is mu_"Fe"=2 xx 10^(-23) J/T. If magnetisation of needle is equivalent to the alignment of 10% of the atoms in the needle, what is the magnitude of the neddle's magnetic dipole momentmu ? (mass of iron per mole =0.05 kg//"mole", N_A=6xx10^23) |
|
Answer» `2.4xx10^(-3)` J/T |
|
| 44530. |
One end of a long rope is tied to a fixed vertical pole. The rope is stretched horizontally with a tension 8 N. Let us consider the length of the rope to be along X-axis. A sample harmonic oscillator at x = 0 generates a transverse wave of frequency 100 Hz and amplitude 2 cm along the rope. Mass of a unit length of the rope is 20 gm/m. Ignoring the effect of gravity, answer the following questionsAssuming that the oscillator has its maximum negative displacement at t = 0, wave equation (function)for the wave can be expressed as |
|
Answer» `y = (0.02m) cos[ 8pi (RAD // m) x - 100pi (rad // s) t]` |
|
| 44531. |
Name the e.m. waves used for studying crystal structure of solids. What is its frequency range ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :X-rays. Frequency RANGE of X-rays is from `10^(16)Hz" to "10^(21)Hz`. | |
| 44532. |
One end of a long rope is tied to a fixed vertical pole. The rope is stretched horizontally with a tension 8 N. Let us consider the length of the rope to be along X-axis. A sample harmonic oscillator at x = 0 generates a transverse wave of frequency 100 Hz and amplitude 2 cm along the rope. Mass of a unit length of the rope is 20 gm/m. Ignoring the effect of gravity, answer the following questionsWavelength of the wave is |
|
Answer» 50cm |
|
| 44533. |
In a wheatstone's bridge arrangement we can interchange the cell and galvanometer without affecting the balance condition of the bridge. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :TRUE | |
| 44534. |
The current gain of an n-p-n transistor in common emitter configuration is 100. What will be the change in the emitter current, if the collector current changes by 1mA? |
|
Answer» `1.00mA` |
|
| 44535. |
Th equivalent resistance between points A and B of an infinite network of resistance each of 1Omegaconnected as shown is |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 44536. |
Electromagnetic waves propagate through free space or a medium as transverse waves. The electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular to each other as well as perpendicular to the direction of propagation of waves at each point. In the direction of wave propagation, electric field vecE and magnetic field vecB form a right-handed cartesian coordinate system. During the propagation of electromagnetic wave, total energy of electromagnetic wave is distributed equally between electric and magnetic fields. Since in_0 and mu_0 are permittivity and permeability of free space, the velocity of electromagnetic wave, c=(in_0 mu_0)^(-1//2). Energy density i.e., energy in unit volume due to electric field at any point, u_E=1/2in_0E^2 Similarly, energy density due to magnetic field , u_M=1/(2mu_0)B^2. If the electromagnetic wave propagates along x-direction, then the equations of electric and magnetic field are respectively. E=E_0sin(omegat-kx) and B=B_0sin(omegat-kx) Here, the frequency and the wavelength of oscillating electric and magnetic fields are f=omega/(2pi) and lambda=(2pi)/k respectively. Thus E_"rms"=E_0/sqrt2 and B_"rms"=B_0/sqrt2, where E_0/B_0=c. Therefore, average energy density baru_E=1/2in_0E_"rms"^2and baru_M=1/(2mu_0)B_"rms"^2. The intensity of the electromagnetic wave at a point, I=cbaru=c(baru_E+baru_B). To answer the following questions , we assume that in case of propagation of electromagnetic wave through free space, c=3xx10^8 m.s^(-1) and mu_0=4pixx10^(-7) H.m^(-1) Average energy density (in J . m^(-3))of electromagnetic wave at that point |
|
Answer» `4.98xx10^(-9)` |
|
| 44537. |
An X-ray tube operates on 30 kV. The minimum wavelength emitted is h = 6.6 xx 10^(-34) Js, c = 3 xx 10^(8) m/s, e = 1.6 xx 10^(-19)C. |
|
Answer» 6.6 `Å` |
|
| 44538. |
Assertion If a glass slab is placed in front of one of the slits, then fringe width will decrease Reason Glass slab will produce an additional path difference. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 44539. |
Electromagnetic waves propagate through free space or a medium as transverse waves. The electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular to each other as well as perpendicular to the direction of propagation of waves at each point. In the direction of wave propagation, electric field vecE and magnetic field vecB form a right-handed cartesian coordinate system. During the propagation of electromagnetic wave, total energy of electromagnetic wave is distributed equally between electric and magnetic fields. Since in_0 and mu_0 are permittivity and permeability of free space, the velocity of electromagnetic wave, c=(in_0 mu_0)^(-1//2). Energy density i.e., energy in unit volume due to electric field at any point, u_E=1/2in_0E^2 Similarly, energy density due to magnetic field , u_M=1/(2mu_0)B^2. If the electromagnetic wave propagates along x-direction, then the equations of electric and magnetic field are respectively. E=E_0sin(omegat-kx) and B=B_0sin(omegat-kx) Here, the frequency and the wavelength of oscillating electric and magnetic fields are f=omega/(2pi) and lambda=(2pi)/k respectively. Thus E_"rms"=E_0/sqrt2 and B_"rms"=B_0/sqrt2, where E_0/B_0=c. Therefore, average energy density baru_E=1/2in_0E_"rms"^2and baru_M=1/(2mu_0)B_"rms"^2. The intensity of the electromagnetic wave at a point, I=cbaru=c(baru_E+baru_B). To answer the following questions , we assume that in case of propagation of electromagnetic wave through free space, c=3xx10^8 m.s^(-1) and mu_0=4pixx10^(-7) H.m^(-1) The peak value of magnetic field (in Wb . m^(-2)) at that point |
|
Answer» `5XX10^(-8)` |
|
| 44540. |
One end of a long rope is tied to a fixed vertical pole. The rope is stretched horizontally with a tension 8 N. Let us consider the length of the rope to be along X-axis. A sample harmonic oscillator at x = 0 generates a transverse wave of frequency 100 Hz and amplitude 2 cm along the rope. Mass of a unit length of the rope is 20 gm/m. Ignoring the effect of gravity, answer the following questionsTension in the given rope remaining the same, if a simple harmonic oscillator of frequency 200 Hzis used instead of the earlier oscillator of frequency 100 Hz, then |
|
Answer» speed of transverse WAVES in the rope will be doubled, wavelength will not change |
|
| 44541. |
Distinguish between 'Analog and Digital signals'. |
|
Answer» Solution :Analog Signal : The amplitude of the signal VARIES continuously with time. The value of the signal at any instant is REPRESENTED by its amplitude at that instant. For example, pressure variation in the SOUND waves can be converted into CORRESPONDING current or voltage variations with the help of a microphone. Digital Signal : In a digital signal, the amplitude of the signal is discontinuous with time. The amplitude of a digital signal has only two levels i.e., either low or high. Thus, a digital signal in the form of pulses usually uniformly speed in time. |
|
| 44542. |
Small drops of the same sizes are charged to V volt each. If x such drops coalesce to farm a single large drop, i^ potential will be: |
|
Answer» VN |
|
| 44543. |
The focal lengths of a thin lens for red and violetlight are 90.0 cm and 86.4cm respectively. Find the dispersive power of the material of the lens. Make appropriate assumptons. |
|
Answer» Solution :We have `(1)/(F) = (mu-1) ((1)/(R_1) - (1)/(R_2))` `or `mu - 1 = (1)/(f). (1)/((1)/(R_1) - (1)/(R_2)) = (K)/(f).` THUS, `mu_(upsilon) -1 = (K)/(f_(upsilon))` and `mu_r - 1=(K)/(f_r)` so that `mu_(upsilon) - mu_r = K((1)/(f_(upsilon)) - (1)/(f_r))` `=K[(1)/(85.4 cm) - (1)/(90CM)]=Kxx4.6 XX 10^(-4) cm^(-1)` Also, we can assume that `mu_y -1 = (mu_(upsilon) + mu_r)/(2) -1 = (mu_(upsilon) - 1)/(2) + (mu_(upsilon)-1)/(2)` `(K)/(2) ((1)/(f_(upsilon) + (1)/(f_r))` `=(K)/(2) [(1)/(86.4 cm) + (1)/(90cm)] = Kxx1.1xx10^(-2)cm^O(-1)` Thus, the dispervise power of the meterial of the lens `omega= (mu_(upsilon) - mu_r)/(mu_y - 1) = (4.6xx 10^(-4))/(1.1xx10^(-2)) = 0.042.` |
|
| 44544. |
(a) Calcualte the potential at a point P due to a charge of 4 xx 10^(-7) C located 9 cm away. (b) Hence obtain the work done in bringing a charge of 2 xx 10^(-9) C from infinity to the point P. Does the answer depend on the path along which the charge is brought? |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) `V= 1/(4piepsilon_(0)). Q/r = 9 xx 10^(9)Nm^(2)C^(-2) xx (4 xx 10^(-7) C)/(0.09m)` `=4 xx 10^(4)` V (B) `W = qV = 2 xx 10^(-9) C xx 4 xx 10^(4)` V `= 8 xx 10^(-5)` J No, work DONE will be path independent. Any arbitrary infinitesimal path can be resolved into two perpendicular displacements. One along r and another perpendicular to r. The work done corresponding to the later will be zero. |
|
| 44545. |
One end of a long rope is tied to a fixed vertical pole. The rope is stretched horizontally with a tension 8 N. Let us consider the length of the rope to be along X-axis. A sample harmonic oscillator at x = 0 generates a transverse wave of frequency 100 Hz and amplitude 2 cm along the rope. Mass of a unit length of the rope is 20 gm/m. Ignoring the effect of gravity, answer the following questionsMaximum magnitude of transverse acceleration of any point on the rope will be nearly |
|
Answer» `7888 m//s^2` |
|
| 44546. |
One end of a long rope is tied to a fixed vertical pole. The rope is stretched horizontally with a tension 8 N. Let us consider the length of the rope to be along X-axis. A sample harmonic oscillator at x = 0 generates a transverse wave of frequency 100 Hz and amplitude 2 cm along the rope. Mass of a unit length of the rope is 20 gm/m. Ignoring the effect of gravity, answer the following questionsWhich of the following is correct ? |
|
Answer» The wave propagates with a fixed and any PARTICLE of the MEDIUM vibrates with the same fixed SPEED |
|
| 44547. |
Electromagnetic waves propagate through free space or a medium as transverse waves. The electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular to each other as well as perpendicular to the direction of propagation of waves at each point. In the direction of wave propagation, electric field vecE and magnetic field vecB form a right-handed cartesian coordinate system. During the propagation of electromagnetic wave, total energy of electromagnetic wave is distributed equally between electric and magnetic fields. Since in_0 and mu_0 are permittivity and permeability of free space, the velocity of electromagnetic wave, c=(in_0 mu_0)^(-1//2). Energy density i.e., energy in unit volume due to electric field at any point, u_E=1/2in_0E^2 Similarly, energy density due to magnetic field , u_M=1/(2mu_0)B^2. If the electromagnetic wave propagates along x-direction, then the equations of electric and magnetic field are respectively. E=E_0sin(omegat-kx) and B=B_0sin(omegat-kx) Here, the frequency and the wavelength of oscillating electric and magnetic fields are f=omega/(2pi) and lambda=(2pi)/k respectively. Thus E_"rms"=E_0/sqrt2 and B_"rms"=B_0/sqrt2, where E_0/B_0=c. Therefore, average energy density baru_E=1/2in_0E_"rms"^2and baru_M=1/(2mu_0)B_"rms"^2. The intensity of the electromagnetic wave at a point, I=cbaru=c(baru_E+baru_B). To answer the following questions , we assume that in case of propagation of electromagnetic wave through free space, c=3xx10^8 m.s^(-1) and mu_0=4pixx10^(-7) H.m^(-1) Intensity (in W . m^(-2)) of electromagnetic wave at that point is almost |
|
Answer» 0.15 |
|
| 44548. |
Two identical conducting spheres, fixed in place, attract each other with an electrostatic force of 0.108 N when their center-to-center separation is 50.0 cm. The spheres are then connected by a thin conducting wire. When the wire is removed, the spheres repel each other with an electrostatic force of 0.144 N. Of the initial charges on the spheres, with a positive net charge, what was (a) the negative charge on one of them and (b) the positive charge on the other ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) `-0.646 MU C`, (B) `4.65 mu C` | |
| 44549. |
How are rainbows formed? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) Rainbow is due to dispersion of sunlight through droplets of water during rainy days. (ii) When sunlight FALLS on the water drop suspended in air, it splits (or dispersed) into its CONSTITUENT seven colours. Thus, water drop suspended in air behaves as a glass prism. (iii) Primary rainbow is FORMED when light entering the drop undergoes one total internal reflection inside the drop before coming out from the drop. (iv) The angle of view for violet to red in primary rainbow is `40^@`to `42^@`. A secondary rainbow appears outside of a primary rainbow and develops when light entering a raindrop undergoes two internal reflections. The angle of view for red toviolet in a secondary rainbow is, `52^@` to `54^@.` |
|
| 44550. |
The average binding energy per nucleon for the nuclei lying in the middle of periodic table, mass number 'A' ranging from 40 to 120, is nearly .............. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :8.5MeV PER NUCLEON | |