Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 44451. |
The length of a wire is cut to half what will be the effect on the increase in it's length under a given load ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :INCREASE in LENGTH will be REDUCED to HALF | |
| 44452. |
In the last question half of the inner sphere is removed along with its charge (i.e., the remaining half has charge(q)/(2) ). Find the force between the bigger and smaller hemispheres in the two cases shown in figure (a) and figure (b). |
|
Answer» |
|
| 44453. |
कीपक किसका भाग है - |
|
Answer» यूरिटर (मूत्रवाहिनी) |
|
| 44454. |
Electric potential is a………… quantity. |
|
Answer» SCALAR QUANTITY |
|
| 44455. |
Two stones are thrown from the top of a tower, one straight down with an initial speed and the second straight up with the same speed. When the two stones hit the ground, they will have speeds in the ratio : |
|
Answer» `2:3` |
|
| 44456. |
The poet describes our planet earth as: |
|
Answer» BEAUTIFUL BLUE Planet |
|
| 44457. |
A long solenoid 'S' has 'n' turns per meter, with diameter 'a'. At the centre of this coil we place a smaller coil of 'N' turns and diameter 'b' (where b lt a). If the current in the solenoid increases linearly, with time, what is the induced emf appearing in the smaller coil. Plot graph showing nature of variation in emf, if current varies as a function of mt^2+C. |
|
Answer» Solution :Magnetic field produced by long solenoid, `B=mu_0 NI` Magnetic FLUX linked with smaller solenoid, `phi=NAB` `=N(pib^2)(mu_0nI)` `phi=mu_0Npib^2nI` Induced EMF in smaller solenoid , `epsilon=-(dphi)/(dt)=-d/(dt)(mu_0N n pi b^2I)` `=-mu_0N n pib^2 (dI)/(dt)` `=-mu_0Nnpib^2 d/(dt)(mt^2+C)` `=-mu_0N n pib^2 m(2t)` `=-(2mu_0 N n pib^2m)t` `|epsilon|=(2mu_0Nnpib^2m)t` which is likely y=mx graph of induced emf `|epsilon|to t` is 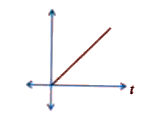
|
|
| 44458. |
I^(131)is an isotope of iodine that p decays to an isotope of xenon with a half-life of 8 days. A small amount of a serum labelled with I^131 is injected into the blood of a person. The activity of the amount of I^131 injected was2.4 xx 10^5 becquerel (Bq). It is known th a t the injected serum will get distributed uniformly in the blood stream in less th an h alf an hour. After 11.5 hours, 2.5 ml of blood is drawn from person’s body, and gives an activity of 115 Bq. The total volume of blood in the person’s body, in litres, is approximately (you m ay usee^(x) ~~ 1+x for |x| lt lt 1 and in 2 ~~ 0.7). |
|
Answer» Solution :The `BETA`-decay reaction is as follows:`I^(131) to Xe^(131) + beta` Given that the initial activity of the`I^(131)` , `A_(0)=2.4 xx 10^(4)` Bq Let the decay constant for `I^131` be A and the volume of the blood in the person’s body be V. The activity of the 2.5 ml of blood at time t, A = 115 Bq Thus, activity of 1 ml of blood, `115/2.5 =46` Bq thus, the activity of volume V of the blood, `A = 46 Bq` `A =A_(0)e^(-lambdat)` `46 V = 2.4 xx 10^(5)e^(-lambdat)` `lambda =(ln2)/T =(ln 2)/(8 "days") =(ln 2)/(8 xx 24)hr^(-1)` `46 V = 2.4 xx 10^(5) xx e^(-(0.7 xx 11.5)/(8 xx 24))` `46 V = 2.4 xx 10^(5) xx 0.9583` `V=(2.4 xx 10^(5) xx 0.9583)/46` =5 litres. |
|
| 44459. |
A sphere, disc and a ring each having same mass M and radius R roll down without slipping from an inclined plane. Which of three will reach foot of inclined plane first: |
|
Answer» Ring `a=(gsintheta)/(1+1//MR^(2))` For sphere `I=(2)/(5)MR^(2)` `therefore a_("shere")=(5)/(7)gsintheta=0.7gsintheta` For disc `I=(1)/(2)MR^(2)` `therefore a_("disc")=(2)/(3)gsintheta=0.66gsintheta` For ring `I=MR^(2)` `therefore a_("ring")=(1)/(2)gsintheta=0.5gsintheta` Since acceleration is maximum for sphere therefore sphere will reach the ground FIRST. |
|
| 44461. |
The de Broglie wavelength is ___ of charge of particle. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :INDEPENDENT | |
| 44462. |
At points P and Q, two identical charges each q are placed. When we move from P to Q (oa - the line joining them), electrostatic potential |
|
Answer» goes on decreasing  Above figure shows the situation as per the statement. Consider a point A on the line segment `bar(PQ)` , at distance x from point P. Total electric potential at point A is, `V= V1 +V_(2)` `= (kq)/(x) +(kq)/(r-x)` `:. V= kq((1)/(x)+(1)/(r-x))` `:. (dV)/(dx)=kq[(-(1)/(x^(2)))-(1)/((r-x)^(2))(-1)]` `:. (dV)/(dx)=kq [(1)/((r-x)^(2))-(1)/(x^(2))]` Now taking `(dV)/(dx) =0` we get `0 =kq[(1)/((r-x)^(2))-(1)/(x^(2))]` `:. (1)/(r-x)^(2)=(1)/(x^(2))` `:. x^(2)=(r-x)^(2)` `:. x^(2)=r^(2)-2xr+x^(2)` `:. 2xr = r^(2)` `:. x =(r)/(2)` `implies "At" x = (r)/(2) V ` = max . OR V = min. Now `(d^(2)V)/(dx^(2))=(d)/(dx)((dV)/(dx))` `:. (d^(2)V)/(dx^(2))= (d)/(dx) [kq{(1)/((r-x)^(2))-(1)/(x^(2))}]` `=kq[-(2)/((r-x)^(3))(0-1)-(-(2)/(x^(3)))]` `:. (d^(2)V)/(dx^(2))=2kq[(1)/((r-x)^(3))+(1)/(x^(3))]` Now placing x = `(r)/(2)`in above equation `((d^(2)V)/(dx^(2)))_("at" x=(r)/(2))=2kq[(8)/(r^(3))+(8)/(r^(3))]` `= (32kq)/(r^(3))` `GT0` `implies "At" x = (r)/(2)` value of V is minimum. THUS, as we move from P to C, potential goes on decreasing initially, then potential becomes minimum at mid point C and then potential goes on increasing. |
|
| 44463. |
Focal length of thin lens of refractive index 1.5is 15 cm. When placed on liquid of refractive index 4/3, then its focal length will be ...... cm. |
|
Answer» 80.31 `=4xx15=60` cm |
|
| 44464. |
(a) In a metre bridgethe balance point is found to be at 39.5 cm from the end A,when the resistor Y is of 12.5 Omega . Determine the resistance of X. Why are the connectionsbetween resistors in a Wheatstone or metre bridge made of thick copper strips ?(b) Determine the balance point of the bridge above if X and Y are interchanged. (c ) What happens if the galvanometer and cell are interchanged at the balance point of the bridge? Would the galvanometer show any current ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Here Y= 12.5 `Omega`, length AD=`l_1` = 39.5 cm `because X/Y = (l_1)/((100 - l_1))` Hence `X = Y (l_1)/((100 -l_1)) = 12.5 XX (39.5)/(60.5) = 8.2 Omega` Connections are made of thick copper strips so that their resistance may be extremely small and negligible, because these RESISTANCES are not accounted for in the formula of metre bridge. (b) Let on interchanging X and Y, the new balance point is obtained at `l_2` , then `Y/X = (l_2)/((100 - l_2)) "or" (12.5)/(8.2) = (l_2)/((100 - l_2)) rArr l_2 = 60.5 cm` (c) At the balance point of the bridge if the galvanometer and cell are interchanged, it MAKES noeffect on balance CONDITION and the galvanometer will not show any deflection. |
|
| 44465. |
A person looking through a telescope focuses lens at a point on the edge of the bottom of an empty cylindrical vessel. Next he fills the entire vessel with a liquid oif refractive index mu, without disturbing the telescope. Now, he observes the mid point of the vessel. Determine the radius to depth ratio of the vessel |
|
Answer» `1/2sqrt((1-MU^(2))/(mu^(2)+1))` |
|
| 44466. |
The VC shown in the diagram has zero error in it (as you can see) it is given that 9msd=10 vsd. (i). What is the magnitude of the zero error? (1 msd=1 mm) (ii). The observed reading of the length of a rod measured by this VC comes out to be 5.4 mm. if the vernier had been error free then reading of main scale would be _____and the coincidingdivision of vernier scale would be____ |
|
Answer» (II) 6,1 |
|
| 44468. |
Monochromatic light frequency 5.0xx10^(14) Hz is produced by a laser.The power emitted is 66 W. How many photons per second,on an average ,are emitted by the source? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`2XX10^(20)` Photon/second | |
| 44469. |
A condenser of capacity 1 mu F and a resistance 0.5 mega-ohm are connected in series with a DC supply of 2 V. The time constant of circuit is |
|
Answer» 2 s |
|
| 44470. |
If alpha particle colloides head on with a nucleus What is the value of impact parameter? |
|
Answer» Zero |
|
| 44471. |
Find the temperature in kelvin scale at which the fundamental frequency of an organ pipe isindependent of small variation in temperature in terms of the coefficient of linear expansion (a) of the material of the tube. |
|
Answer» `T_(0) = 5/(2ALPHA)` |
|
| 44472. |
Identical pieces of Geand Cu aretakenand cooled then |
|
Answer» RESISTIVITY of both increase |
|
| 44473. |
(A) : A magnetic field is produced either by a steady current or by a time varying electric field (R) : According to Ampere’s law ointbarB.bardl = mu_(0)i_(0)+mu_(0)epsilon_(0)(doint_(E ))/(dt) |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are TRUE and 'R' is the correct EXPLANATION of 'A'. |
|
| 44474. |
If an A.C. current of frequency 50 Hz is flowing through a conducting wire, then how many time does the current becomes zero in one second ? |
|
Answer» 25 times |
|
| 44475. |
To find tho magnetic field induction in the gap between the pole pieces of an electromagnet coil of 3.2 cm area made of 50 turns of thin wire connected to a ballistic galvanometer of 100 ohm resistance with a constant of 2 xx 10^(-5)"C/div" is inserted into it. When the coil is withdrawn from the field, the galvanometer pointer moves 20 divisions. What is the field induction? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 44476. |
A space station is covered by an envelope which is a blackened shell. The temperature of the envelope is T = 500 K that is constant due to the operation of applicances of the station. Determine the temperature of the shell if the station is enveloped by a thin spherical black screen of nearly the same radius as the radius of the shell. Assume that there are no radiations on this space station. |
|
Answer» Solution :The total amount of heat Q emitted in space per UNIT time remains UNCHANGED since it is determined by the energyliberated during the operation of the applicances of the station. As given in the question, the appliances produces heat at constant rate. Since only the outer surface of the screen EMITS into space ( this radiation depends only on its temperature ), the temperature of the screen must be equal to the initial temperature T = 500K of the station. Also, it is important to remember that the screen emits the same amount of heat Q inward. This radiation the ENVELOPE of the station and is absorbed by it. Calculations `:` Therefore, the total amount of heat supplied to the station per unitis the sum of th heat Q liberated during the operation of the appliances and the amountof heat Q absorbed by the inner surface of the screen, that is, equal to 2Q. According to the heat balance condition, the same amount of heat must be emitted, `2Q = A sigma T_(x)^(4)` and hence `(Q)/( 2Q) = ( T^(4))/( T_(x)^(4))` where `T_(x)`is the required temperature of the envelope of the station. FINALLY, we obtain `T_(x) = root (4)(2T) -= 600K` The temperature of the envelope has increased because to gain in thermal equilibrium it must emit more energy than before as it is receiving more energy than before. |
|
| 44477. |
Two point charges +q_(1) and +q_(2) are located at two points with position vectors vecr_(1) and vecr_(2). Finda negativecharge q_(3) and the position vector vecr_(3) of the point at which it has to be placed for the force acting on each of the three charges to be equal to zero. |
Answer» Solution :For the equilibrium of `q_(3)`  `(1)/(4pi in_(0)) {(q_(2)q_(3)(bar r_(2)-barr_(3)))/(|barr_(2)-barr_(3)|^(3)) +(q_(1)q_(3)(barr_(1)-barr_(3)))/(|barr_(1)-barr_(3)|^(3))}=0` but `(barr_(2) -barr_(3))/(barr_(2)-barr_(3))=-(barr_(1)-barr_(3))/(|barr_(1)-barr_(3)|) or (q_(2))/(|barr_(2)-barr_(3)|^(2))=(q_(1))/(|barr_(1)-barr_(3)|^(2))` or `sqrt(q_(2)) (barr_(1) -barr_(3))=sqrt(q_(1)(barr_(3) -barr_(2))` `RARR barr_(3)=(sqrt(q_(2))barr_(1)+sqrt(q_(1))barr_(2))/(sqrt(q_(1))+sqrt(q_(2)))` For the equilibrium of `q_(1)` `(1)/(4pi in_(0)) {(q_(3)(barr_(1)-barr_(3)))/(|barr_(1)-barr_(3)|^(3)) +(q_(2)(barr_(2)-barr_(1)))/(|barr_(2)-barr_(1)|^(3))}=0` or `q_(3)=(q_(2)|barr_(1)-barr_(3)|^(2))/(|barr_(2)-barr_(1)|^(2))` SUBSTITUTING the value of `r_(3)`, we GET `q_(3)= (-q_(1), q_(2))/( (sqrt(q_(1)) +sqrt(q_(2)))^(2))` |
|
| 44478. |
A electron is located in unidimensional square potential well with infinitely high walls. The width of the well equal to l is such that energy level is very dense. Find the density of the energy levels dN//dE,i.e., their number per unit energy interval,as a function of E. Calculate dN//dE for E= 1.0 eV if l= 1.0cm. |
|
Answer» Solution :We have found that `E_(N)=(n^(2)pi^(2) ħ^(2))/(2ml^(2))` Let `N(E )=` number of states upto `E`. This number is `n`. The number of states upto `E+dE is N(E+dE)=N(E )+dN(E )=1` and `(dN(E ))/(dE)=(1)/(DELTAE)` Where `DeltaE=` difference in engines between the `n^(th)` & `(n+1)^(th)` LEVEL `=((n+1)^(2)-n^(2))/(2ml^(2))pi^(2) ħ^(2)=(2n+1)/(2ml^(2))pi^(2) ħ^(2)` `~=(pi^(2) ħ^(2))/(2ml)xxsqrt((2ml^(2))/(pi^(2) ħ^(2)))sqrt(E)xx2` `=(pi ħ)/(l)sqrt((2)/(m)sqrt(E ))` Thus `(dN(E ))/(dE)=(l)/(pi ħ)sqrt((m)/(2E))` For the given case this gives `(dN(E ))/(dE)= 0.816xx10^(7)` level PER `eV` |
|
| 44479. |
A body projected at 45^(@) with a velocity of 20 m/s has a range of 10m. The decrease in range due to air resistance is (g=10ms^(-1)) |
|
Answer» 0 |
|
| 44480. |
The intensity at the maximum in a Young.s double slit experiment is I_0. Distance between two slits is d= 5lambda, where lambda is the wavelength of light used in the experiment. What will be the intensity in fornt of one of the slits on the screen placed at a distance D= 10d? |
|
Answer» `I_0` |
|
| 44481. |
What shall be the image in the plane mirror when the object is real ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :VIRTUAL and VICE VERSA | |
| 44482. |
No current flows between two charged bodies when connected, if they have the same |
|
Answer» capacity |
|
| 44483. |
Discuss about pile of plates. |
| Answer» Solution :The phenomemon of polarisation by reflection is used in the construction of PILE of plates. It consists of a number of GLASS plates placed one overthe other. The plates areincilined at an angle of `33.7^(@)(90^(@) - 56.3^(@))` to the axis of thetube. A beam of unpolarised light is allowed to FALL on the pile of plates along the axis of the TUBE. So the angle of incidence of light will be at `56.3^(@)` which is the polarising angle for glass. The vibrations perpendicular to the plane of incidence ae reflected at each SURFACE and thoseparallel to it are transmitted. The larger the number of surfaces, the greater is theintensityof the reflected plane polarised light. The pile of plates is used as a polarizer and alsoas an analyser. | |
| 44484. |
A short bar magnet of magnetic moment 5.25 xx 10^(-2) JT^(-1) is placed with its axis perpendicular to the earth's field direction. At what distance from the centre of the magnet, the resultant field is inclined at 45^@ with earth's field on (a) its normal bisector, and (b) its axis. Magnitude of the earth's field at the place is given to be 0.42 G. Ignore the length of the magnet in comparison to the distances involved. |
Answer» Solution : Here , `m =5.25 XX 10^(-2) J T^(-1) and B_E = 0.42 G = 4.2 xx 10^(-5) T` (a) As shown in fig. 5.01 (a) , let at a DISTANCE `r_1` along the normal bisector of the magnet the resultant field is inclined at `45^@` with the earth.s field `B_E` `thereforetan 45^@ =(B_(AQ))/(B_E) impliesB_E ` or ` (mu_0)/(4pi) * (m)/(r_1^3) = B_E` `impliesr_2 = [(mu_0)/(4pi) * (m)/(B_E)]^(1/3) =[(10^(-7)xx 5.25xx10^(-2))/(4.2xx10^(-5))]^(1/3)= 5 xx 10^(-2)m = 5 cm` (b) As shown in fig. 5.01 (b) , let at a distance `r_2` along the axis of the magnet , the resultant field is inclined at an angle `45^@` with the earth.s field `B_E` . Then, `B_("AXIAL") =(mu_0)/(4pi) * (2m)/(r_2^3) = B_E tan 45^@ = B_E` `impliesr_2 =[(mu_0)/(pi) * (2m)/(B_E)]^(1/3) =[(10^(-7)xx 2 xx 5.25xx10^(-2))/(4.2 xx 10^(-5))]^(1/3) = 6.3xx10^(-2) cm` |
|
| 44485. |
A pointcharge + mu c is a distance 5 cm directly above the centre of a square of side 10 cm aswhat is the magnitudeof the electricflux throughthe square |
Answer» Solution :Situation given in the statement is equivalent to following situation. 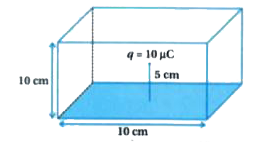 Here given point charge `q= 10 muC`can be considered to be at the centroid of a cube of side length 10 cm. This POSITION of charge is SYMMETRIC to all the six identical faces of a cube. Hence, total ELECTRIC FLUX `phi_(t)`emanating from charge q is shared equally by these six faces. Hence, electric flux passing through one face (bottom face given in the statement) will be, `PHI = 1/6 phi_(t)` `=1/6 (q/epsilon_(0))` `=(10 xx 10^(-6))/(6v xx 8.85 xx 10^(-12))` `therefore phi = 1.883 xx 10^(5) Nm^(2)//C` |
|
| 44486. |
The electric and magnetic field, associated with an e.m. wave, propagating along the +z axis, can be represented by |
|
Answer» `VECE=E_(0)hatj, vecB=B_(0)hatk` Hence `vecE=E_(0)hati, vecB=B_(0)hatj`. |
|
| 44487. |
Two fixed, identical conducting plates (alpha and beta), each of surface area S are charged to -Q and q, respectively, where Q gt q gt 0. A third identical plate (gamma), free to move is located on the other side of the plate with charge Q at a distance d (figure). The third plate is released and collides with the plate beta. Assume the collision is elastic and the time of collision is sufficient to redistribute charge amongst beta and gamma. (a) Find the electric field acting on the plate gamma before collision. (b) Find the charges on beta and gamma after the collision. (c) Find the velocity of the plate gamma after the collision and at a distance d from the plate beta. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(a). Find electric field at plate `gamma` before collision is equal to the sum of electric field at plate `gamma` due to plate `ALPHA and beta`. The electric field at plate `gamma` due to plate `alpha` is `E_(1)=(-Q)/(S(2epsi_(0)))` to the left. The electric field at plate `gamma` due to plate `beta` is `E_(2)=(q)/(S(2epsi_(0)))`, to the right HENCE, the ent electric field at plate `gamma` before collision, `E=E_(1)+E_(2)=(q-Q)/(S(2epsi_(0)))`, to the left if `Q gt q` (b) During collision, plates `beta and gamma` are together. Their potentials become same. Suppose charge on plate `beta ` is `q_(1)` and CAHRGE on plate `gamma` is `q_(2)`. At any point O, in between the two plates, the electric field must be zero. Electric field at O due to plate `alpha=(-Q)/(S(2epsi_(0)))`, to the left Electric field at O due to plate `beta=(q_(1))/(S(2epsi_(0)))`, to the right ltBrgt Electric field at O due to plate `gamma=(q_(2))/(S(2epsi_(0)))`, to the left As the electric field at O is zero, therefore ltBrgt `(Q+q_(2))/(S(2epsi_(0)))=(q_(1))/(S(2epsi_(0)))` `thereforeQ+q_(2)=q_(1)` `Q=q_1+q_2` . . .(i) As there is no loss of charge o collision, ltBrgt `Q+q=q_(1)+q_(2)` On solving eqs. (i) and (ii), we get `q_(1)=(Q+q//2)`=charge on plate `beta` `q_(2)=(q//2)`=charge on plate `gamma` (c) After collision, at adistance d from plate `beta`. Let the VELOCITY of plate `gamma` be v. After the collision, electric field at plate `gamma` is `E_(2)=(-Q)/(2epsi_(0)S)+((Q+q//2))/(2epsi_(0)S)=(q//2)/(2epsi_(0)S)` to the right just before collision, electric field at plate `gamma` is `E_(1)=(Q-q)/(2epsi_(0)S)` If `F_(1)` is force on plate `gamma` before collision, then `F_(1)=E_(1)Q=((Q-q)Q)/(2epsi_(0)S)` Total work done by the electric field is round trip movement of plate`gamma` `W=(F_(1)+F_(2))d` `=([(Q-q)Q+(q//2)^(2)]d)/(2epsi_(0)S)=((Q-q//2)^(2)d)/(2epsi_(0)S)` ltBrgt If m is mass of plate `gamma`, the KE gained by plate `gamma=(1)/(2)mv^(2)` According to work-energy principle, `(1)/(2)mv^(2)=W=((Q-q//2)^(2)d)/(2epsi_(0)S)` `gamma=(Q-q//2)((d)/(mepsi_(0)S))^(1//2)`. |
|
| 44488. |
The magnifying power of an astronomical telescope for normal adjustment is 10 and the length of the telescope is 110 cm. Find the magnifying power of the telescope when the image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision for normal eye |
|
Answer» |
|
| 44489. |
To shield an instrument from anexternal magnetic field it may be placed in a cabinet made up of : |
|
Answer» Wood |
|
| 44490. |
The dual nature of light is exhibited by |
|
Answer» A) diffraction and PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT |
|
| 44491. |
Dot or scalar product two vectors vecA=2hati-3hatj+hatk and vecB=2hatj+2hatk is |
|
Answer» 0 |
|
| 44492. |
Young.s double slit experiment is carried out by using green , red and blue light . One color at a time . Thr fringe widths recorded are beta_(G),beta_(R ) and beta_(B) respectively .Then |
|
Answer» `beta_(G) gt beta_(BETA) gt beta_(R)` |
|
| 44493. |
Deduce the relation f^(2) =ab , where 'a' and 'b' are the distance of an object and itsreal image from the principal focus and 'f' its focal length . |
|
Answer» Solution :GIVEN, u = F + a,v = f + b SUBSTITUTING the values in the mirror equation, we GET`(1)/(f) = (1)/(u) + (1)/(v) = (1)/(f + a) + (1)/(f + b) ` `(1)/(f) = ((f + b) + (f + a ))/((f + a) (f + b)) = ( f + b + f + a)/(f^(2) + bf + af + AB)` `f^(2) + bf + f^(2) + af = f^(2) + bf + af + ab"" therefore f^(2)= ab ` |
|
| 44494. |
Assertion : The magnetic filed at the ends of a very long current carrying solenoid is half of that at the center. Reason : If the solenoid is sufficiently long, the field within it is uniform. |
|
Answer» If both ASSERTION and REASON are TRUE and the reason is the CORRECTEXPLANATION of the assertion. |
|
| 44495. |
A proton and helium necleus are shot into a magnetic field at right angles to the field with same kinetic energy. Then the ratio of their radii is |
|
Answer» both acquire same energy |
|
| 44496. |
A particle moves with an intial velocity v_(0) and retardation alphav, where v is its velocity at any time t. |
|
Answer» The particle will cover a TOTAL distance `v_(0)//alpha` |
|
| 44497. |
Three resistance P,Q,R each of 2Omega and an unknown resistance S form the fourth arm of a Wheatstone's bridge circuit. When a resistance of 6Omega is connected in parallel to S, the bridge gets balanced what is the value of S ? |
|
Answer» `2OMEGA` |
|
| 44498. |
A uniform wood panel of mass 35.0 kg is hinged ver tically on a wall by two hinges, one 0.300 m from its top and the other 0.300 m from its bottom. The panel is 2.10 m tall and 0.910 m wide. A y axis extends upward through the hinges and an x axis extends outward along the panel's width. If each hinge supports half the panel's weight, what are the forces on the panel at (a) the top hinge and (b) the bottom hinge, both in unit-vec notation? |
| Answer» Solution :(a) `F_("TOP")= (-104N)HATI+(172N)HATJ`, (B) `F_("BOTTOM")= (+104N)hati+ (172N)hatj` | |
| 44499. |
The instananeous voltages at three terminals marked X,Y and Z are given by v V_(Y)=V_(0)sin(omegat+(2pi)/(3))andV_(Z)=V_(0)sin(omegat+(4pi)/(3)). An ideal volmeter is configured to read rms value of the potential difference between its terminal. It is connected between points X and Y and then between Y and Z. The reading(s) of the voltmeter will be |
|
Answer» `V_(XY)^(rm)=V_(0)sqrt((3)/(2))` |
|
| 44500. |
In the following circuit, the current flowing through 1 kOmega resistor is |
|
Answer» 0 mA |
|