Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 42351. |
A capacitor having a capacitance of 100muFis charged to a potential difference of 24 V. The charging battery is disconnected and the capacitor is connected to another battery of emf 12 V with the positive plate of the capacitor joined with the positive terminal of the battery. Find the decrease in electrostatic field energy . |
|
Answer» 11.6 mJ |
|
| 42352. |
A capacitor having a capacitance of 100muFis charged to a potential difference of 24 V. The charging battery is disconnected and the capacitor is connected to another battery of emf 12 V with the positive plate of the capacitor joined with the positive terminal of the battery.Find the magnitude of work done on the battery |
|
Answer» 12.4 mJ |
|
| 42353. |
A capacitor having a capacitance of 100muFis charged to a potential difference of 24 V. The charging battery is disconnected and the capacitor is connected to another battery of emf 12 V with the positive plate of the capacitor joined with the positive terminal of the battery.Find the charge flown through the 12 V battery . |
|
Answer» `1200 MUC` |
|
| 42354. |
A source of sound stationary with respect to medium emits sound of frequency f and wavelength lambda.The speed of sound with respect to medium is C.speed of medium is V_m.The observer O_1 receives waves of frequency f_1 and wavelength lambda_1.The observer O_2 receives waves of frequency f_2 and wavelength lambda_2.Match the column given below if V_s is speed of source with respect to ground. |
|
Answer» `{:(,p,Q,R,s),((A),3,4,1,2):}` |
|
| 42355. |
A capacitor having a capacitance of 100muFis charged to a potential difference of 24 V. The charging battery is disconnected and the capacitor is connected to another battery of emf 12 V with the positive plate of the capacitor joined with the positive terminal of the battery. Find the charges on the capacitor before and after the reconnection. |
|
Answer» `1400 muC, 1200 muC` |
|
| 42356. |
What is temperature coefficient of resistivity? What are its units? |
| Answer» Solution :The ratio of the CHANGE in RESISTIVITY per `1^@`C rise in temperature to the resistivity at `0^@`C is CALLED the temperature coefficient of resistivity. Its units are `(C^@)^(-1)` or `K^(-1)` | |
| 42357. |
A circular coil of radius 8 cm and 20 turns rotates about its vertical diameter with an angular speed of 50 s^(-1) in a uniform horizontal magnetic field of magnitude 3 xx 10^(-2)T. Find the maximum and average value of the emf induced in the coil. |
|
Answer» Solution :Here r = 8 cm = 0.08 m, or area of COIL `A = pir^(2) = pi xx (0.08)^(2) = 64pi xx 10^(-4)m^(2), N = 20, omega = 50s^(-1) = 50 x 2pi rad s^(-1) = 100pi rad s^(-1) and B = 3 xx 10^(-2) T` `therefore` INDUCED emf `varepsilon = N B A omegasin omegat` `therefore` Maximum VALUE of induced emf `varepsilon_(max) = NBAomega = 20 xx 3 xx 10^(-2) xx 64pi xx 10^(-4) xx 100pi = 3.79 V` and average value of sinusoidal induced emf for the complete cycle = 0. |
|
| 42358. |
Laser light is considered to be coherent because it consist of |
|
Answer» MANY wavelengths |
|
| 42359. |
How does an unpolarised light get polarised when passed through a polaroid ? Two polaroids are set in crossed position. A third polaroid is placed between the two making an angle theta with the pass axis of the first polaroid. Write the expression for the intensity of light transmitted from the second polaroid. in what orientations will the transmitted intensity be (i) minimum and (ii) maximum ? |
|
Answer» Solution :A polaroid consists of long chain molecules aligned in a particular direction. If an unpolarised light wave is incident on such a polaroid then the polaroid absorbs the electric vectors of propagating light wave along the direction of the aligned molecules. THUS, in emergent light we have electric vector oscillating only along a direction perpendicular to the molecules (this direction is known as the pass axis of the polaroid). as a result the light wave gets linearly POLARISED. Let intensity of unpolarised light incident on the first polaroid be `I_(0)` then intensity of plane polarised light being transmitted by 1st polaroid will be `I_(1)=I_(0)//2`. When TWO polaroids are set in crossed positions and a third polaroid is placed between the two making an angle `theta` with the pass axis of the first polaroid, it makes an angle `90^(@)-theta)` with the pass axis of the second polaroid. therefore, in accordance with Malus law, the intensity of light transmitted from the second polaroid will be `I_(2)=I_(1)cos^(2)thetacos^(2)(90-theta)=Icos^(2)thetasin^(2)theta=(I)/(4)sin^(2)(2theta)=(I_(0))/(8)sin^(2)(2theta)` (i) The transmitted intensity will have a minimum value of zero when `sin2theta=0` i.e, `2theta=0` or `PI` that is `theta=0 or (pi)/(2)`. it MEANS when the third polaroid is held parallel to either first or the second polaroid, no light will be transmitted through the second polaroid. (ii) The transmitted intensity will have a maximum value of `(I_(0))/(8)` when `sintheta=pm1 or 2 theta=pm90^(@) or theta=45^(@)`. |
|
| 42360. |
A very long wire carrying a current 4sqrt2 A is bent at a right angles. The magnitude of magnetic field (|B|) at a point P lying on a line perpendicular to the bent wire at a distance, d=20 cm from the point of the bending will be (Let mu_(0)=4pixx10^(-7)H//m) |
|
Answer» `1muT` distance, d=20 cm =0.2m and current, `I=4sqrt2A` `:.` MAGNETIC field at a POINT P due to current carrying wire 1, 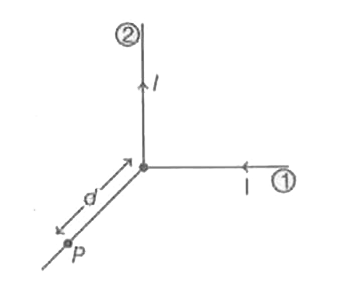 `B_(1)=(mu_(0))/(pi).(I)/(d)=10^(-7)xx(4sqrt2)/(0.2)` `=2sqrt2xx10^(-6)T` Magnetic field at point P due to current carrying wire 2, `B_(2)=(mu_(0))/(4pi).(I)/(d)=10^(-7)xx(4sqrt2)/(0.2)=2sqrt2xx10^(-6)T` since, `B_(1)andB_(2)` both are in perpendicular direction to each other HENCE the resultant magnetic field at point P, `B=sqrt(B_(1)^(2)+B_(2)^(2))` `=sqrt((2sqrt2xx10^(-6))+(2sqrt2xx10^(-6))^(2))` `=2sqrt2xx10^(-6)sqrt(1+1)` `=4xx10^(-6)T=4muT` Hence, the magnitude of the magnetic field is `4muT.` |
|
| 42361. |
The mean distance from Saturn to the sun is 9 times greater than the mean distance from Earth to the sun. how long is a saturn year? |
|
Answer» 18 Earth years |
|
| 42362. |
A body is released from rest from the top of an inclined plane of length 'L' and angle of inclination 'theta'. The top of plane of length (1)/(n)L(n gt 1) is smooth and the remaining part is rough. If the body comes to rest on reaching the bottom of the plane then find the value of coefficient of friction of rough plane. |
Answer» Solution :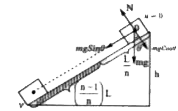 For smooth part : `V^(2)=2a_(1)(L)/(n)` For rough part : `0-V^(2)=2a_(2)((n-1)/(n))L` `2a_(1)(L)/(n)=-2a_(2)((n-1)/(n))L` `g SIN THETA=-g(sin theta-mu cos theta)(n-1)` `g sin theta[1+n-1]=mu g cos theta(n-1)` `mu = TAN theta[(n)/(n-1)]`. |
|
| 42363. |
The magnetic field existing in a region is given by B=B_(0)(1-x/y)hatk, where B_(0) and l ae constant x is the x coordinate of a point and hatk is the unit vector along Z axis.A square loop of edge and carrying a current is placed with his edges parallel to the x,y axes.Find the magnitude of the net magnetic force experienced by the loop. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 42364. |
The displacement of a particle executing S.H.M. is given x=5 sin 2 pit . What is it.s frequency? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`omega=2pi` `2pin=2pi` `n=1Hz` |
|
| 42365. |
The magnetic force depends on v which depends on the inertial frame of reference. Does then the magnetic force differ from inertial frame to frame ? Is it reasonable that the net acceleration has a different value in different frames of reference ? |
| Answer» Solution :YES, magnetic FORCE is depend on frame of REFERENCE. | |
| 42366. |
When the electron jumps from a level n = 4 to n = 1 level , the momentum of the recoiled hydrogen atom will be : |
|
Answer» Zero |
|
| 42367. |
A free neutron has half life of 14 minutes. Its decay constant is |
|
Answer» `8.25xx10^(-2) S^(-1)` |
|
| 42368. |
A charged oil drop of mass 9.75 xx 10^(-15) kg and charge 30 xx 10^(-16) C is suspended in a uniform electric field existing between two parallel plates. The field between the plates is (take g = 10 ms^(-2)) |
|
Answer» `3.25 V m^(-1)` |
|
| 42369. |
In an n-p-n transistor amplifier, the collector current is 9 mA. If90%of the electrons from he emitter reach the collector, then |
|
Answer» the base current is 10 mA |
|
| 42370. |
Photon is a quanta of light Briefly explain the effect of intensity and energy of the incident radiation on the photoelectric effect |
| Answer» Solution :As the intensitiy increases number of photoelectrons increases and as the energy of the INCIDENT photons increases. KE ALSO INCREASE. | |
| 42371. |
Calculate the energy released by fission from 2 gm of ._92U^235 in KWH. Given that the energy released per fission is 200 Mev. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :No. of atoms in 1 gm of `._92U^235 ="Avagadro NUMBER"/"mass number" =(6.023xx10^23)/235` Energy RELEASED per fission = 200 Mev `= 200xx10^6xx1.6xx10^(-19)` J Total energy released per gm, `E=(6.023xx10^23)/235xx200xx10^6xx1.6xx10^(-19)` J `=(6.023xx200xx1.6)/(235xx36xx10^5)xx10^10` KWH=`0.2278xx10^5` KWH Total energy released from 2 gm of `._92U^235` is `0.4556xx10^5` KWH |
|
| 42372. |
Calculate the kinetic energies of protons whose momenta are 0.10,1.0. and 10GeV//c, where c is the velocity of light. |
|
Answer» Solution :The formula is `T=sqrt(C^(2)p^(2)+m_(0)^(2)c^(4))-m_(0)c^(2)` THUS `T= 5.3MeV fo R p= 0.01(GeV)/(c )= 5.3xx10^(-3)GeV` `T= 0.433GeV fo r p=1.0(GeV)/(c )` `T=9.106GeV for p=10(GeV)/(c )` Here we have used `m_(0)c^(2)= 0.938GeV` |
|
| 42373. |
Protons accelerated by a potential difference of 6.8 MV bombard a stationary lithium target. The collision of a proton with a nucleus of Li^(7) isotope results in the birth of two alpha-particles which separate symmetrically with respect to the direction of the proton beam. Find the kinetic energy and the separation angle of the alpha-particles. |
|
Answer» `2K_(alpha)=(M_(H)+M_(Li)-2M_(alpha))xx931.5+K_(H)=24.2MeV` SInce the kinetic energy of the alpha-particle TURNS out to be MUCH lower than its rest energy, the alpha-particles PRODUCED in the reaction are nonrelativistic. The separation angle is found from the law of conservation of momentum `p_(H)=2p_(alpha)"cos"theta/2` But for a nonrelativistic particle `p=sqrt(2mK)`, so `"cos"theta/2=1/2sqrt((m_(H)K_(H))/(m_(alphaK_(alpha))))` 
|
|
| 42374. |
Figure shows the output from a pressure monitor mounted at a point along thepath taken by a sound wave of a single frequency traveling at 343 m/s through air with a uniform density of 1.21 kg//m^3. The vertical axis scale is set by Delta p = 5.0 mPa. Ifthe displacement function of the wave is s(.x, t) = s_mcos(kx - omega t) , what are (a) s_m(b) k, and (c) omega ? The air is then cooled so that its density is 1.35 kg/m and the speed of a sound wave through it is 320 m/s. The sound source again emits the sound wave at the same frequency and same pressure amplitude. What now are (d)s_m, (c ) k, and (f) omega ? |
| Answer» Solution :`(a) 343 m//s , (B) 9.2rad//m (c ) 3142 rad//s ~~ 3.1 xx 10^3 rad//s , (d) 7.4 NM, (e ) 9.8 rad//m , (f) 3142 rad//s ~~ 3.1 xx 10^3 rad//s` | |
| 42375. |
What are the conditions when capacitor is in the parallel network? |
|
Answer» (I) (II) (J) |
|
| 42376. |
To excite the hydrogen atom from its ground state to second excited state…. eV energy is required. |
|
Answer» 3.4 |
|
| 42377. |
A wave travelling in air falls on a glass plate. It is partly refracted and partly refracted. What is the phase difference between the refracted and refracted waves ? |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 42378. |
(a) Compute the rms speed of a nitrogen molecule at 80.0^@ C. The molar mass of nitrogen molecules (N.) is given in Table 20-1. At what temperatures will the rms speed be (b) half that value and (c) twice that value? |
| Answer» Solution :`561 m//s, (B )~~ -185^@C, (c )( 1.14 xx 10^3 ) ^@ C` | |
| 42379. |
The force between two magnetic poles separated by a distance 'd' in air is F. At what distance between them the force becomes doubled. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION : According coulomb.s LAW we can write, `F = (mu_0)/(4pi) (m_1 m_2)/(d^(2))` i.e., ` F prop (1)/(d^(2)) implies (F_1)/(F_2) = (d_2^(2))/(d_1^(2))` `implies d_2^(2) = (F_1)/(F_2)d_1^(2) = (F)/(2F)d^(2)= (d^(2))/(2) or d_2 = (d)/(sqrt(2))` |
|
| 42380. |
A lift is ascending by acceleration g//3. What will be the time period of a simple pendulum suspended from its ceiling if its time period in stationary lift is T? |
|
Answer» `(T)/(2)` `T_(e)=2pisqrt((lxx3)/(4g))=(sqrt3)/(2)xx2pisqrt((l)/(g))=((sqrt3)/(2)).T` (b) is the CHOICE |
|
| 42381. |
A point source of monochromatic light emitting a lumninous flux Phi is positioned at the cnetre of a spherical layer of substance. The inside radius of the layer is a, the outside one is b. The coefficient of linear absorption of the substance is equal to x, the reflection coefficient of the surfcaes is equal to rho. Neglecting the secondary reflections, find the intensity of light taht passes through that layer. |
|
Answer» Solution :We have to derive the law of decrease of intensity in an absorbing medium taking in to account the natural geometrical fall-off (inverse sequare law) as well as absorption. Consider a thin sperical sheel of thickness `dx` and internal radius `X`. Let `I(x)` and `I(x+dx)` be the intersities at the inner and OUTER surfcaes of this shell. Then `4pix^(2)I(x)E^(-chi dx) = 4pi(x+dx)^(2) I(x+dx)` Except for the factor `e^(-chi dx)` this is the usual equation. we rewrite this as `x^(2)I(x) = I(x+dx) (x+dx)^(2) (1+chi dx)` `=(1+(dI)/(dx)dx) (x^(2)+2xdx)(1+chi dx)` or `x^(2)(dI)/(dx) + chi x^(2) I + 2XI = 0` Hence `(d)/(dx)(x^(2)I) + chi (x^(2)I) = 0` so `x^(2) I = Ce^(-chi x)` where `C` is a constant of intergration. In our case we apply this equation for `ale xle b` For `c le a` the usual inverse square law gives `I(a) = (Phi)/(4pia^(2))` Hence `C = (Phi)/(4pi) e^(chia)` and `I(b) = (Phi)/(4pib^(2)) e^(-chi(b -a))` This does not take into account reflection. When we do that we get `I(b) = (Phi)/(4pib^(2)) (1-rho)^(2) e^(-chi(b-a))` |
|
| 42382. |
Light of wavelength lambda = 500 nm falls on two narrow slits placed a distance d = 50 xx 10^(-4) cm apart, at an angle phi = 30^(@) relative to the slits shown in figure. In front of the lower slit, a slab of thickness 0.1 mmand refractive index 3/2 is placed. The interference pattern is observed on a screen at a distance D = 2m from the slits S_(1)O = S_(2)O = d//2 If the transparent slab is removed the fringe pattern shifts upward, the number of fringes shifted upward are |
|
Answer» 50 |
|
| 42383. |
A positron with kinetic energy T= 750 keV strikes a stationary free electron. As a result of annihilation, two gamma quanta with equal energies appear. Find the angle of divergence between them. |
|
Answer» Solution :By momentum conservation `sqrt(E^(2)-m_(e )^(2)C^(4))=2(E+m_(e )c^(2))/(2)"cos" (THETA)/(2)` or `"cos "(theta)/(2)= sqrt((E-m_(e )c^(2))/(E+m_(e )c^(2))) =sqrt((T)/(T+2M_(e )c^(2)))` Substitution GIVES `theta= 98.8^(@)` 
|
|
| 42384. |
A vertically thrown up body reaches 20m at a place on the earth. The height to which it goes on the moon if projected with same velocity is [g_"moon"=g_"earth"/6] |
|
Answer» 40m |
|
| 42385. |
Light of wavelength lambda = 500 nm falls on two narrow slits placed a distance d = 50 xx 10^(-4) cm apart, at an angle phi = 30^(@) relative to the slits shown in figure. In front of the lower slit, a slab of thickness 0.1 mmand refractive index 3/2 is placed. The interference pattern is observed on a screen at a distance D = 2m from the slits S_(1)O = S_(2)O = d//2 The interference minima closest to B is of order |
|
Answer» 50TH minima |
|
| 42386. |
Light of wavelength lambda = 500 nm falls on two narrow slits placed a distance d = 50 xx 10^(-4) cm apart, at an angle phi = 30^(@) relative to the slits shown in figure. In front of the lower slit, a slab of thickness 0.1 mmand refractive index 3/2 is placed. The interference pattern is observed on a screen at a distance D = 2m from the slits S_(1)O = S_(2)O = d//2 The position of central maxima is at an angular position 'theta' with line OB |
|
Answer» `30^(@)` above OB |
|
| 42387. |
A coil having resistance 15Omegaand inductance 10H is connected across a 90 Volt de supply. Determine the value of current after 2 sec. What is the energy stored in the magnetic field at that instant |
|
Answer» Solution :Given that `R = 15 Omega ,L = 10 H, E = 90` Volt Peak value of current `I_0= E/R= 90/15 A = 6A ` also `tau_L = L/R = 10/15 = 0.67 sec` Now `I =I_0 (1 - e^((-Rt)/(L)) )` , after 2 sec `I = 6 [1-e^(-2//0.67) ] = 6[1-0.05] = 5.7A` Energy stored in the magnetic field `U= 1/2 LI^2 = 1/2 XX 10 xx (5.7)^2 J = 162.45J` |
|
| 42388. |
We know that the gravitational field strength is zero insdie a spereical shell of matter. The electrical field strenght is zero not only insdie an isolated charged spherical conductor but inside an isolated cunductor of any shap . Is the gravitational field strength inside, say, a cubical shell of matter zer? if not, in what respect is the analogy not complete? |
| Answer» Solution :GRAVITATIONAL field strength inside a cubical shell of MATTER is not zero. Mass is CONSIDERED concentrated at the centre of a sphereical shell only and, not for other shapes, but there are free ELECTRONS in a conductor and they always arrange themselves so that net field inside it BECOMES zero at every point. | |
| 42389. |
Draw a graph, showing the effect of potential on photoelectric current. Hence define stopping potential. |
|
Answer» Solution :Effect of potential on photoelectric current. Light of fixed intensity `I_(1)`and FREQUENCY v be made to fall on photosensitive plate. The electrode C is made negative so that the current becomes zero. Let it be `V_(0)`(called stopping potential). Now the potential of C is increased in steps and a graph is plotted. The graph is as shown in the figure.  If the same experiment is repeated with radiation having intensity `I_(2) (I_(2) GT I_(1))` the SATURATION current will be higher but stopping potential is the same. It means that stopping potential is independent of intensity of incident radiations. The retarding potential, `V_(0)`for which the photoelectric current just becomes zero is called stopping potential or cut-off potential. If mass of electron is m, charge e and MAXIMUM velocity is `v_("max")` then : `1/2 mv_("max")^(2) = eV_(0)` And `v_("max") = sqrt((2eV_(0))/m)`. |
|
| 42390. |
Plot a graph showing variation of stopping potential (V_(0)) with the frequency (v) of the incident radiation for a given photosensitive material. Hence, state the significance of the threshold frequency in photoelectric emission. Using the principle of energy conservation, write the equation relating the energy of incident photon, threshold frequency and the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons. |
|
Answer» Solution :A graph showing variation of stopping potential `V_(0)` with the frequency v of the INCIDENT radiation for a GIVEN photosensitive material is SHOWN in figure. Threshold frequency is the minimum frequency of incident radiation for a given photosensitive surface for causing potoelectric EMISSION. if frequency of incident radiation is less than the threshold frequency, no photo electric emission takes place irrespective of the INTENSITY of incident radiation. let a photon of energy E=hv is incident on a photosensitive material of work function `phi_(0)=hv_(0)` with kinetic energy of photoelectron `K_(max)`. then in accordance with the law of conservation of energy : `E=phi_(0)+K_(max)` `implies hv=hv_(0)+K_(max) or h(v-v_(0))=K_(max)` |
|
| 42391. |
Assertion: Television signals are recieved throgh sky-wave propagation. Reason: The ionosphere reflects em wave of frequencies greater than a critical frequency. |
|
Answer» If both the ASSERTION and reason are true and reason is a true explantion of the assertion. |
|
| 42392. |
A wire kept in east west direction is allowed to fall freely, will an emf be induced in the wire? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :YES, because there will be a CHANGE of MAGNETIC FLUX. | |
| 42393. |
A cell of negligible internal resistance is connected to a potentiometer wire and potential gradient is found. Keeping the length as constant, if the radius of potentiometer wire is increased four times, the potential gradient will become (no series resistance in primary) |
| Answer» ANSWER :D | |
| 42394. |
Two insulated charged copper spheres A and B have their centres separated by a distance of 50 cm. What is the mutual force of electrostatic repulsion if the charge on each is 6.5 xx 10^(-2)C?The radii of A and B are negligible compared to the distance of separation. b. What is the force of repulsion if each sphere is charged double the above amount and the distance between them is halved? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(a) `1.5 xx10^(2)` N (B) 0.24 N |
|
| 42395. |
What is phasor ? |
| Answer» Solution :A quantity which VARIES sinusoidally with TIME and represnted as the PROJECTION of a ROTATING vector is called PHASOR. | |
| 42396. |
-10 mu C, 40mu C and q are the charges on three identical spherical conductors P Q and R respectively. Now P and Q attract each other with a force F when they are separated by a distance d. Now P and Q are made in contact with each other and then separated. Again Q and R are touched and they are separated by a distance 'd'. The repulsive force between Q and R is 4F. Then the charge q is |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 42397. |
The current in the forward bias is known to be more (~mA) than the current in the reverse bias (~muA). What is the reason then to operate the photodiodes in reverse bias? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :For an n-type semiconductor, the majority carrier density `(n_(e ))` is larger than the minority hole density `(n_(h))` (mean`n_(e ) gt gt n_(h))`. On illumination,let the excess electrons and holes GENERATED be`Delta n_(e )` and `Delta n_(h)` RESPECTIVELY, so `n._(e )=n_(e )+Delta n_(e )` `n._(n)=n_(h)+Delta n_(h)` where `n._(e )` and `n._(h)` are the electron and hole concentration respectively due to intensity of light INCIDENT on p-n junction. And `n_(e ) and n_(h)` are carriers concentration when there is no illumination. But `Deltan_(e )=Delta n_(h) and n_(e ) gt gt n_(h)`, hence fractional change in majority carriers is `((Delta n_(e ))/(n_(e )))` and for minority carrier is `((Delta n_(h))/(n_(h)))` which is much less than majority carriers. The fractional change due to the photo effects on the minority carrier DOMINATED reverse bias current is more easily measurable than the fractional change in the forward bias current. Hence, photodiodes are preferably used in the reverse bias condition for measuring light intensity. |
|
| 42398. |
Two Charges -q each are separated by distance 2d. A third charge +q is kept mid point O. Findpotential energy of +q as a function of small distance x from O dueto q charges. Sketch P.E. v//s x and convince yourselfthat the charge at O is in an unstable equillibrium. |
|
Answer» Solution :In fig, two charges`-Q` each are shownat Aand B, where `AB = 2d`. A charge `+q` is kept at MID point O of `AB, OP = x` is small displacementof `+q` charge. Therefore, potential energy of `+q` charge at P due to the two charges `-q` each is `U = (1)/(4pi in_(0)) [-(q^(2))/(d + x) - (q_(2))/(d - x)] = (q^(2))/(4pi in_(0)) (2d)/(d^(2) - x^(2))`...(i) The potential energy (u) versus x GRAPH is as shown in Fig. Now `(dU)/(dx) = (-q^(2) (2d))/(4pi in_(0)) (2x)/(d^(2) - x^(2))`..(ii) At `x = 0`, From (i) `U_(0) = (-2q^(2))/(4pi in_(0) d)`, and from (ii), `(dU)/(dx) = 0` `:. x = 0` is an EQUILIBRIUM point Now `(d^(2) U)/(dx^(2)) = ((-2dq^(2))/(4pi in_(0))) [(2)/((d^(2) - x^(2))^(2) - (8x^(2))/(d^(2) - x^(2))^(3))]` `(d^(2) U)/(dx^(2)) = ((-2dq^(2))/(4pi in_(0))) (1)/((d^(2) - x^(2))^(3)) [2 (d^(2) - x^(2)) - 8x^(2)]` At `x = 0, (d^(2) U)/(dx^(2)) = ((-2dq^(2))/(4pi in_(0)))(1)/(d^(6)) (2d^(2)) = - (q^(2))/(pi in_(0) d^(3))` which is less thanzero. Hence, the equilibrium of chargeq at O is unstable.  
|
|
| 42399. |
When a p-n diode is reverse biased, then |
|
Answer» no current flows |
|
| 42400. |
Cos330^(@) sin600^(@) + cos120^(@) sin150^(@) = |
|
Answer» 44257 |
|