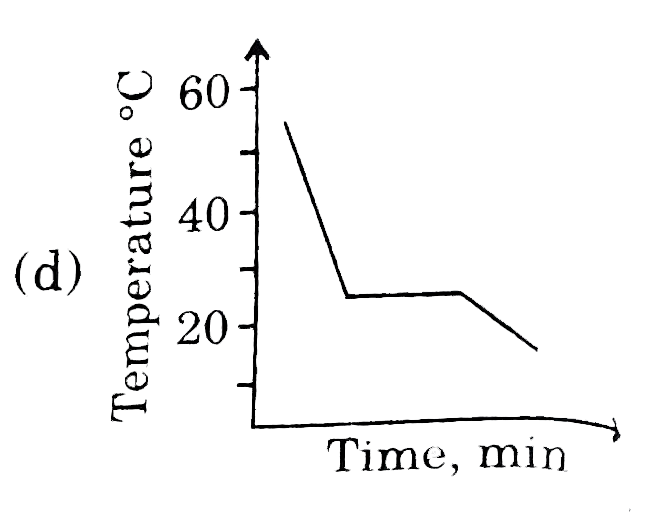Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 1701. |
Titanium is purified by …….. |
|
Answer» MOND process |
|
| 1702. |
When electric current is passed through acidified water, 1 12 mL of hydrogen gas at STP collected at the cathode in 965 seconds. The current passed in amperes is |
|
Answer» `1.0` (Since 22400 mL at STP =M.wt) Amount deposiled `=(Eq. wt xxi XXT)/(96500)` `therefore (2xx 112)/(22400) =(1xx965xxi)/(96500)` `i=1` AMP |
|
| 1703. |
Which of the following on hydrolysis forms acetic acid? |
|
Answer» `CH_(3)CN` |
|
| 1704. |
Which set contains only covalently bonded molecules ? |
|
Answer» `BCl_(3),SiCl_(4),PCl_(3)` |
|
| 1705. |
Under which conditions, do we use magnetic separation for concentration of ore? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :When either the METAL or the impurities are magnetic in PROPERTIES. | |
| 1706. |
Which of the following is the correct relation of the first law of thermodynamics? |
|
Answer» `DELTA = Q - W` |
|
| 1709. |
Which is correct about electron sea model ? |
|
Answer» It was PROPOSED by Lorentz |
|
| 1710. |
Which of the following is aromatic- |
|
Answer»

|
|
| 1711. |
Which of the following properties increases on going down from F to I in Group VII-A of the periodic table |
|
Answer» Electronegativity |
|
| 1712. |
Which is used as a painkiller ? |
|
Answer» ANTIBIOTIC |
|
| 1713. |
What is the number of donar atoms in dimethylglyoximato ligand? |
|
Answer» 1 |
|
| 1714. |
The relative basicity of amino follows the order as ……………… . |
|
Answer» `"Alkyl amines"gt"Aralkyl amines"gt "Ammonia"gt"N - aralkylamine"gt"Arylamine"` |
|
| 1715. |
When limestone is heated, CO_(2) is given off. The metallurgical operation is __________ |
|
Answer» SMELTING |
|
| 1716. |
Which of the following have identical bond order? |
|
Answer» `CN^(-)` `(SIGMA1S^(2))(sigma(1s^(2))(sigma2s^(2))(sigma*2s^(2))(sigma2p_(z)^(2))(pi2p_(x)^(2))(pi2p_(y)^(2))` and so their bond is same i.e. 3 The NUMBER of electrons in `CN^(+)` is 12 and in `O_(2)^(-)` is 17. |
|
| 1717. |
Two containers A and B have the some volume. Container A contains 5 mole of O_(2) gas. Containter B contains 3 moles of He and 2 moles of N_(2). Both the containers are separately kept in vacuum at the same temperature. Both the containers have very small orifices of the same area through which the gases leak out. Compare the rate of effusion of O2 with that of He gas mixture. |
|
Answer» Solution :Since both the containers are in the same conditions of P, V and T, `r_(O_(2))/(r_("mix"))=sqrt((M_("mix"))/(M_(O_(2)))` As the mixture contains three moles of He and 2 moles of `N_(2)`, the effective molecular weight of the mixture would be. `(3)/(5)xx4+(2)/(5)xx28=13.6` `therefore (r_(O_(2)))/(r_("mix"))=sqrt((13.6)/(32))=0.652` Though this solution looks OK, there is one big flaw in it. The error is that we have assumed that `He and N_(2)` from vessel B would effuse out with the same rate. This assumption was made in because we have taken the composition of the gas mixture coming out of the vessel to be same as that of the mixture that was inside the vessel. It should be duly noted that the two mixtures (inside and the are that effused out) have different compositions. Therefore first we must find the composition of the gas mixture coming out of the vessel B. `(r_(N_(2)))/(r_("He"))=(2)/(3) sqrt((4)/(28))=(2)/(3) sqrt((1)/(7))=0.252` This means that initially the ratio of moles of `N_(2)` to the moles of He coming out of the vessel are in the MOLAR ratio of 0.252 and not `(2)/(3)` Let moles of the He coming out to be x `therefore` Moles of `N_(2)` coming out is 0.252 x `therefore (n_(N_(2)))/(n_("total"))=(0.252 x)/(1.252x)=0.2` `(n_("He"))/(n_("total"))=0.8 rArr M_("mix") =0.2xx28+0.8xx4=8.8` `therefore (r_(O_(2)))/(r_("mix"))=sqrt((8.8)/(32))=0.52` |
|
| 1718. |
Which of the following methods are used determine rate of the reaction containing more than one type of reactants? (P)Intergrated rate equation method. (Q)Half life method. (R )Ostwald.s isolation method. |
|
Answer» Only R |
|
| 1719. |
Value of CFSE, in tetrahedral complex having 3d^4 configuration of metal lon, surrounded by weak field ligands. will be |
|
Answer» `-2/5 triangle_(t)` |
|
| 1720. |
What happen when borax treated with ammonium chloride? |
|
Answer» Solution :When borax treated with ammonium chloride, it forms BORON nitride. `underset(("Borax"))(Na_(2)B_(4)O_(7))+2NH_(4)Cl to 2NaCl+underset(("Boronnitride"))(2BN)+B_(2)O_(3)+2H_(2)O` |
|
| 1721. |
Which of the following is not suitable for use in a desiccator to dry substances |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 1722. |
When a transition metal ion (usually) is involved in octahedral complex formation, the five degenerate d-orbitals split into two set of degenerate orbitals (3+2). Three degenerate orbitals of lower energy (d_(xy),d_(yz),d_(zx)) and a set of degenerate orbitals of higher energy (d_(x^(2)-y^(2)" and "d_(z^(2)). The orbitals with lower energy are called t_(2g) orbitals and those with higher energy are called e_(g) orbitals. In octahedral complexes, positive metal ion may be considered to be present at the centre and negative ligands at the corner of a regular octahedron. As lobes of d_(x^(2)-y^(2)" and "d_(z^(2) lie along the axis, i.e., along the ligands, the repulsions are more and so, high is the energy. The lobes of the remaining three d-orbitals lie between the Axis i.e., between the ligands. The repulsions between them are less, so lesser the energy. In the octahedral complexes, if metal ion has electrons more than 3, then for pairing them, the options are (i) Pairing may start with 4th electron in t_(2g) orbitals. (ii) Pairing may start normally with 6th electron when t_(2g)" and "e_(g) orbitals are singly filled. In which of the following configurations, hybridisation and magnetic moment of octahedral complexes are independent of nature of ligands. (P) d^(3) configuration of any metal cation (Q) d^(6) configuration of IIIrd transition series metal cation (R ) d^(8) configuration of Ist transition series metal cation (S) d^(7) configuration of any metal cation Select the correct code: |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 1723. |
When a transition metal ion (usually) is involved in octahedral complex formation, the five degenerate d-orbitals split into two set of degenerate orbitals (3+2). Three degenerate orbitals of lower energy (d_(xy),d_(yz),d_(zx)) and a set of degenerate orbitals of higher energy (d_(x^(2)-y^(2)" and "d_(z^(2)). The orbitals with lower energy are called t_(2g) orbitals and those with higher energy are called e_(g) orbitals. In octahedral complexes, positive metal ion may be considered to be present at the centre and negative ligands at the corner of a regular octahedron. As lobes of d_(x^(2)-y^(2)" and "d_(z^(2) lie along the axis, i.e., along the ligands, the repulsions are more and so, high is the energy. The lobes of the remaining three d-orbitals lie between the Axis i.e., between the ligands. The repulsions between them are less, so lesser the energy. In the octahedral complexes, if metal ion has electrons more than 3, then for pairing them, the options are (i) Pairing may start with 4th electron in t_(2g) orbitals. (ii) Pairing may start normally with 6th electron when t_(2g)" and "e_(g) orbitals are singly filled. Which of the following electronic arrangement is/are possible for inner orbital octahedral complex. (P) t_(2g)^(3)e_(g)^(2)""(Q) t_(2g)^(6)e_(g)^(1) (R ) t_(2g)^(3)e_(g)^(0)""(S) t_(2g)^(4)e_(g)^(2) Select the correct code : |
|
Answer» <P>P, S |
|
| 1724. |
When a transition metal ion (usually) is involved in octahedral complex formation, the five degenerate d-orbitals split into two set of degenerate orbitals (3+2). Three degenerate orbitals of lower energy (d_(xy),d_(yz),d_(zx)) and a set of degenerate orbitals of higher energy (d_(x^(2)-y^(2)" and "d_(z^(2)). The orbitals with lower energy are called t_(2g) orbitals and those with higher energy are called e_(g) orbitals. In octahedral complexes, positive metal ion may be considered to be present at the centre and negative ligands at the corner of a regular octahedron. As lobes of d_(x^(2)-y^(2)" and "d_(z^(2) lie along the axis, i.e., along the ligands, the repulsions are more and so, high is the energy. The lobes of the remaining three d-orbitals lie between the Axis i.e., between the ligands. The repulsions between them are less, so lesser the energy. In the octahedral complexes, if metal ion has electrons more than 3, then for pairing them, the options are (i) Pairing may start with 4th electron in t_(2g) orbitals. (ii) Pairing may start normally with 6th electron when t_(2g)" and "e_(g) orbitals are singly filled. Select incorrect match for the following complexes. |
|
Answer» `[IrF_(6)]^(3-)(Delta gt P)` |
|
| 1725. |
The value of any colligative property of any electrolyte is determined experimentally, it is found to be higher than the theoretically calculated vallue using the usual expressions. This is because the electrolytes undergo dissociation in the solution. Similarly, in case of some substances association takes place, e.g., acetic acid in benzene and the experimental value of colligative value. The experimentally observed molar masses come out to be different than the theoretical values. These are called abnormal molar masses. In such cases, a correction factor, i, called van't Hoff factor is introduced which is a ratio of observed value of colligative property to calculated value when the solution behaves ideally. Knowing i, the degree of dissociation or association of the solute can be calculated. Which of the following aqueous solution will have the highest freezing point |
|
Answer» 0.1 M urea |
|
| 1726. |
The value of any colligative property of any electrolyte is determined experimentally, it is found to be higher than the theoretically calculated vallue using the usual expressions. This is because the electrolytes undergo dissociation in the solution. Similarly, in case of some substances association takes place, e.g., acetic acid in benzene and the experimental value of colligative value. The experimentally observed molar masses come out to be different than the theoretical values. These are called abnormal molar masses. In such cases, a correction factor, i, called van't Hoff factor is introduced which is a ratio of observed value of colligative property to calculated value when the solution behaves ideally. Knowing i, the degree of dissociation or association of the solute can be calculated. The van't Hoff factor for 0.1 M Ba(NO_(3))_(2) solution is 2.74. The degree of dissociation is |
|
Answer» `91.3%` Total `=1+2alpha` `therefore i=1+2alpha` or `alpha=(i-1)/(2)=(2.74-1)/(2)=0.87=87%` |
|
| 1727. |
The value of any colligative property of any electrolyte is determined experimentally, it is found to be higher than the theoretically calculated vallue using the usual expressions. This is because the electrolytes undergo dissociation in the solution. Similarly, in case of some substances association takes place, e.g., acetic acid in benzene and the experimental value of colligative value. The experimentally observed molar masses come out to be different than the theoretical values. These are called abnormal molar masses. In such cases, a correction factor, i, called van't Hoff factor is introduced which is a ratio of observed value of colligative property to calculated value when the solution behaves ideally. Knowing i, the degree of dissociation or association of the solute can be calculated. The boiling point of 0.1 molal K_(4)[Fe(CN)_(6)] solution will be (Given K_(b) for water = 0.52^(@)"C kg mol"^(-1)) |
|
Answer» `100.52^(@)C` `THEREFORE T_(b)=5xx0.1xx52=0.26` `therefore T_(b)=100+0.26=100.26^(@)C` |
|
| 1728. |
Vapour density of a substance is dependant of : |
|
Answer» Volume |
|
| 1729. |
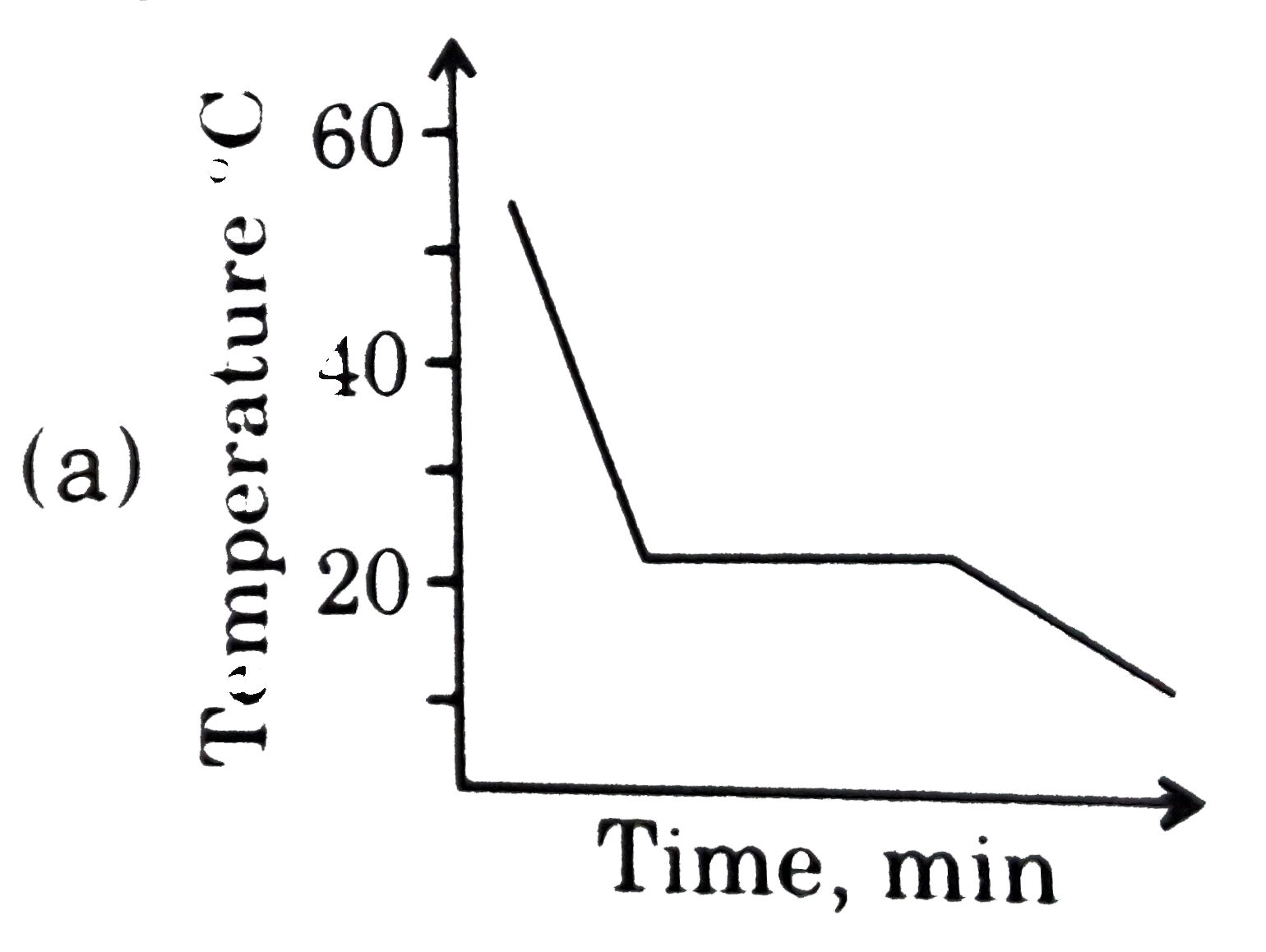
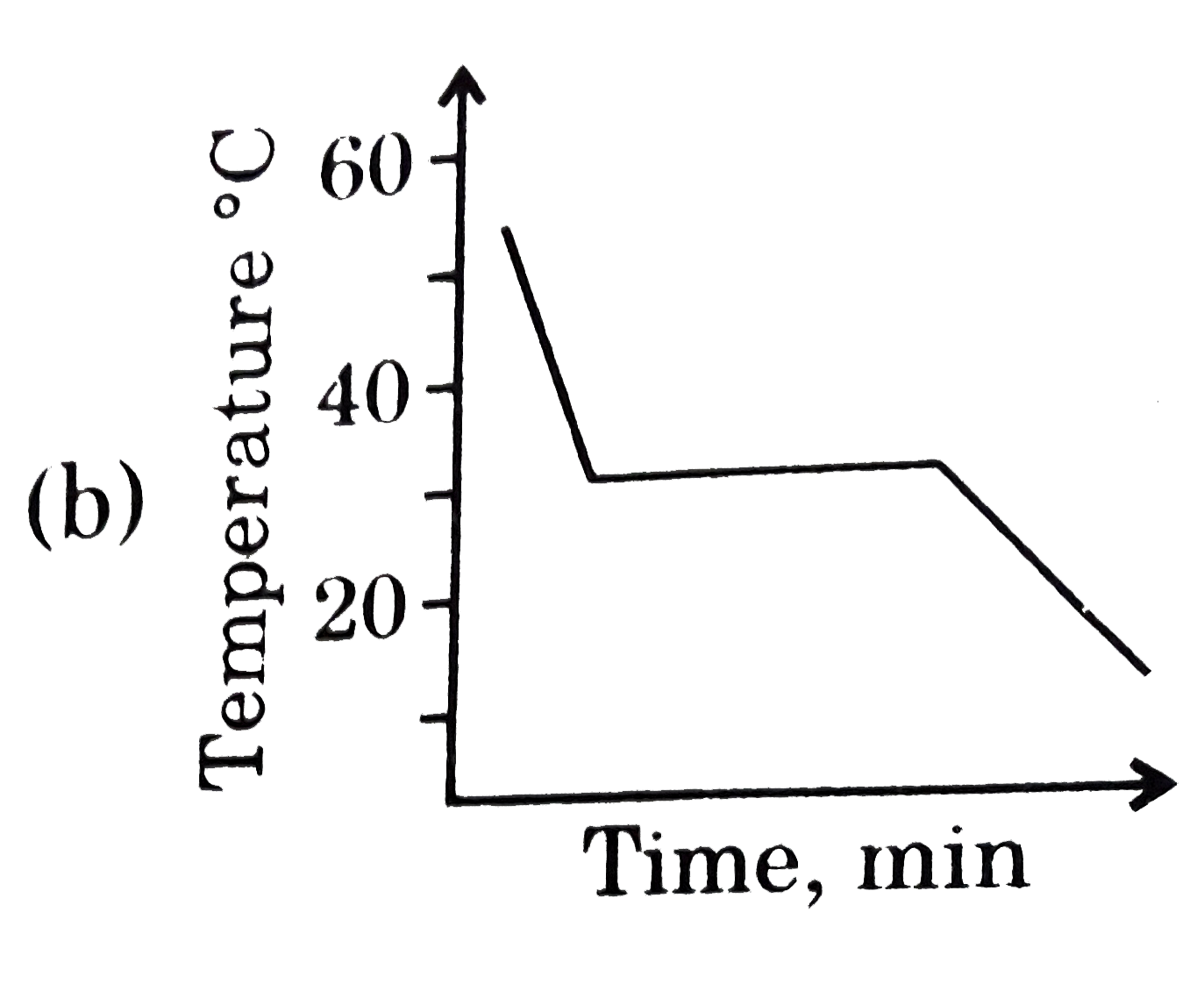
This diagram represents the behaviour of a pure solvent upon cooling. Which of the diagrams below best represents the cooling curve of a solution in that solvent upon cooling ? (Assume that all diagrams are drawn to the same scale.) |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 1730. |
The smog is essentially caused by the presence of : |
|
Answer» `O_3` and `N_2` |
|
| 1731. |
Which of the following chemicals are used to manufacture methyl isocyanate that caused Bhopal tragedy (i) Methyl amine (ii) Chloroform/KOH (iii) Phosphine (iv) Dimethylamine |
|
Answer» (i) and (III) |
|
| 1732. |
Which of the following is expected to have highest boiling point ? |
|
Answer» `(CH_3)_2CHCl` |
|
| 1733. |
The sealed containers of the same capacity and at the same temperature are filled with 44 g of H_(2) in one and 44 g of CO_(2) in the other. If the pressre of carbon dioxide in the second container is 1 atm. That of hydrogen in the first container would be. |
|
Answer» Solution :`(P_(1)V_(1))/(P_(2)V_(2))=(n_(1)RT_(1))/(n_(2)RT_(2))=(n_(1)T_(1))/(n_(2)T_(2))` As, `V_(1) =V_(2) & T_(1) =T_(2)` `(P_(1))/(P_(2))=(n_(1))/(n_(2))` `(P_(H_(2)))/(P_(co_(2)))=(n_(H_(2)))/(n_(co_(2)))` `(P_(H_(2)))/(1)=(44//2)/(44//44)=22` atm Hence, (C ) is the correct answer. |
|
| 1734. |
Which of the following statement is/are correct with the extraction of silver? |
|
Answer» Zinc is used to extract silver by solvent extraction from molten lead in Parke's process. |
|
| 1735. |
What type of devation is shown by a mixture of ethnol and acetone ? What type of azeotrope is formed on mixing the two ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`+ve` DEVIATION, MAXIMUM BOILING AZEOTROPE. | |
| 1736. |
The role of addition of Me_(3)SiCl during the hydrolysis followed by conduction of Me_(3)SiCl_(2) is. |
|
Answer» To catalyte the reaction. |
|
| 1737. |
Which one of the following does not give tetrathionate as the product, when treated with an aq solution of hypo? |
|
Answer» `C1_(2)` |
|
| 1738. |
What will be the emf for the given cell Pt|H_(2)(P_(1))|H_((aq))^(+)||H_(2)(P_(2))|Pt |
|
Answer» `(RT)/(F)ln(P_(1))/(P_(2))` Cathodic reaction: `2H^(+)toH_(2)(P_(2))` `E_("cathode")=-(RT)/(2F)ln (P_(2))/([H^(+)]^(2)),E_("anode")=-(RT)/(2F)ln([H^(+)]^(2))/(P_(1))` `E_("INF")=E_("anode")+E_("cathode")` ltBrgt `=-(RT)/(2F)ln((H^(+))^(2))/(P_(1))-(RT)/(2F)ln(P_(2))/((H^(+))^(2))` `=-(RT)/(2F)ln(P_(2))/(P_(1))=(RT)/(2F)ln(P_(1))/(P_(2))` |
|
| 1739. |
Whch of the following is an example of Freidel- Crafts reaction? |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 1740. |
The stability of ferric ion is due to: |
|
Answer» COMPLETELY FILLED d-orbitals |
|
| 1741. |
Which of the following amino acid has pH greater than 7 ? |
| Answer» Solution :Lysine | |
| 1742. |
Which of the following has dodechahedral geometry |
|
Answer» `[ReH_(9)]^(2-)` |
|
| 1743. |
Whichof the followingreactswithnot answerCarbylaminereaction ? |
|
Answer» `CH_(3)CH_(2)NH_(2)` |
|
| 1744. |
Which one is the first antibiotic produced by microorganism? |
|
Answer» PENICILLIN |
|
| 1745. |
What are copolymers ? Give one example of a copolymer. |
| Answer» Solution :Polymers whose repeating structural UNITS are derived from two or more TYPES of monomer units are CALLED copolymers. For example , nylons, polyester , MELMAC, Buna-N, etc. | |
| 1746. |
When two atoms of hydrogen combine to form a molecule of hydrogen gas, the energy of the molecule is: |
|
Answer» GREATER than that of SEPARATE atoms |
|
| 1747. |
Which of the two is functional isomer? Glucose and lactose or xylose and galactose. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The FUNCTIONAL ISOMER : GLUCOSE and LACTOSE. | |
| 1748. |
Which of the following statements regarding the manufacture of H_(2)SO_(4) by Contact process is not true? |
|
Answer» Sulphur is burnt in air to form `SO_(2)` |
|
| 1749. |
When 9.65 Coulomb of electricity is passed through a solution of silver nitrate (Atomic weigth of Ag = 107.85g), the amount of silver deposited is ………………….. . |
|
Answer» `10.8 mg` `= 1.08 xx 10^(-2)g = 10.8 mg`. |
|
| 1750. |
Which is not present in clear hard water ? |
|
Answer» `MG(HCO_3)_2` |
|