Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 42851. |
A circuit containing a 80 mH inductor and a 60 muF capacitor in series is connected to a 230 V, 50 Hz supply. The resistance of the circuit is negligible. (a) Obtain the current amplitude and rms values. (b) Obtain the rms values of potential drops across each element. (c) What is the average power transferred to the inductor? (d) What is the average power transferred to the capacitor? (e) What is the total average power absorbed by the circuit? [‘Average’ implies ‘averaged over one cycle’.] |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) For `V=V_(0)sin omega t` `I=(V_(0))/(|omegaL-(1)/(omegaC)|) sin (omega t +(pi)/(2)), " if "R=0` where - sign appears if `omegaL GT 1//omegaC`, and + sign appears if `omegaL lt 1//omegaC.` `I_(0)=11.6A, I_("rms")=8.24A` (b) `V_("Lrms")=207V, V_("Crms")=437V` (C) Whatever be the current I in L, actual VOLTAGE leads current by `pi//2`. THEREFORE, average power consumed by L is zero. (d) For C, voltage lags by `pi//2`. Again, average power consumed by C is zero. (e) Total average power absorbed is zero. |
|
| 42852. |
Two concentric circular coils X and Y of radii 16 cm and 10 cm, respectively, lie in the same vertical plane containing the north to south direction. Coil X has 20 turns and carries a current of 16 A, coil Y has 25 turns and carries a current of 18 A. The sense of the current in X is anticlockwise, and clockwise in Y, for an observer looking at the coils facing west. Give the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field due to the coils at their centre. |
| Answer» Solution :`5PI xx 10^(-4) T = 1.6 xx 10^(-3) ` T TOWARDS WEST . | |
| 42853. |
In series LCR circuit, the voltages across R, L and C shown in figure. The voltage of applied source is |
|
Answer» 110 volt or V = 50 V |
|
| 42854. |
A tank contains ethyl alcohol of refraction index 1.35. The depth of alcohol is 308 cm. A plane mirror is placed horizontally at a depth of 154 cm in it. An object is placed 254 mm above the mirror. Calculate the apparent depth of the image formed by the mirror. |
|
Answer» Solution :DEPTHOF the MIRROR = 1.54 m, OBJECT distance from the mirror = 0.254 m The image of the object is formed at a distance of 0.254 m behind the mirror. So the real depth of the image = 1.54 + 0.254 = 1.794 m `THEREFORE` Apparent depth of the image ` = ("real depth")/(MU) = (1.794)/(1.35) = 1.33m` |
|
| 42855. |
A kW signal is transmitted using a communication channel which provides attenuation at the rate of -2dB per km. If the communication channel has a total length of Skm, the power of the signal received is (gain in dB = 10log (P_(0)//P_(1) 0 |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 42856. |
The following table gives the lengths of four aluminium rods of uniform cross-section their diameters and potential difference maintained across the opposite ends of the rods. All the four rods are maintained at the same temperature. Now answer the following questions :(a) Which rod has maximum resistance ? (b) Which rod carries the maximum current ? (c) In which rod is the drift speed of electrons maximum ? (d) In which rod does the dissipation of electric energy take place at a maximum rate ? Give reason for each of your answer. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) ` becauseR = (rho L)/(A) = (4 rho L)/(pi D^2) rArr R PROP (L)/(D^2)` ` therefore R_1 : R_2 : R_3 : R_4 = (L)/(9D^2) : (2L)/(D^2) : (3L)/(4D^2) : (3L)/(D^2) = 1/9 : 2 : 3/4 : 3` It shows that `R_4` is maximum (B) Current `I= V/R` ` therefore I_1 : I_2 : I_3 : I_4 = (V)/(R_1) : (3V)/(R_2) : (2V)/(R_3) : (V)/(R_4) = (V.9 D^2)/(L) : (3V.D^2)/(2L) : (2V.4D^2)/(3L) : (V.D^2)/(3L)` ` = (9VD^2)/(L) : (3VD^2)/(2L) : (8VD^2)/(3L) : (VD^2)/(3L) = 9 : 3/2 : 8/3 : 1/3` It shows that `I_1` is maximum ( c) Drift speed `v_d prop 1/A "or" v_d prop V/L` ` therefore (v_d)_1 : (v_d)_2 : (v_d)_3 : (v_d)_4 = V/L : (3V)/(2L) : (2V)/(3L) : (V)/(3L) = 1 : 3/2 : 2/3 : 1/3` It shows that `(v_d)_2` is maximum (d) Rate of electrical energy dissipated `P = (V^2)/(R ) = (pi V^2 D^2)/(4 rho L) = P prop (V^2 D^2)/(L)` ` therefore P_1 : P_2 :P_3 :P_4 = (V^2 (3D)^2)/(L) : ((3V)^2 .D^2)/(2L) : ((2V)^2.(2D)^2)/(3L) : (V^2 D^2)/(3L) = 9 : 9/2 : 16/3 : 1/3 ` It shows that `P_1` is maximum. |
|
| 42857. |
Suppose that water drops are released from a point at the edge of a roof with a constant time interval Delta tis very short ie the number of drops falling through the air at any given instant is very large then the CM of the drops is very nearly at a height ( above the ground ) of k xx h. Find the value of 'k'. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 42858. |
A radioactive nuclide can decay simultaneously by two different processes which have decay constants, lamda_(1) and lamda_2 .The effective decay constant of the nuclide is lamda |
|
Answer» `LAMDA = lamda_(1) + lamda_(2)` |
|
| 42859. |
Careful measurement of the electric fieldat the surface of a black box indicates that the net outward fluxthrough the surface of the(a)what ist the net charge inside the box (b)if the net outward flux through the surface of the box wre zero could you conclude that there wereno charges inside the box why or why not |
| Answer» Solution :zero the numberof lines entering the CUBE is the same as the numberof lines LEAVING thecube | |
| 42860. |
In a Young.sdouble slit experiment set - up sourceS of wavelength5000 A^(0)illuminates twoslits s_(1) and S_(2)Which act as two coherentsources . The source S oscillates about is shownposition accodingto the equation y =0.5 sin pit . wherey is millimeteres and t in second.Find secondof centralmaxima as a function oftime with respectto .O. |
|
Answer» `y = ( cos 2 PI t) MM` |
|
| 42861. |
A Leclanche cell of emf 1.46 V balances against 292 cm of a potentio meter wire. If the current through the wire is 400 mA, the resistance per unit length of the potentiometer wire is |
|
Answer» `2 Omega//m` |
|
| 42862. |
What types of energy losses are associated with a transformer?How can we overcome these? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :REFER SECTION 7.14 | |
| 42863. |
A device 'X' is connected to an a.c. source. The variation of voltage, current and power in one complete cycle is shown in Fig. (a) Which curve shows power consumption over a full cycle? (b) What is the average power consuption over a cycle ? (c) Identify the device 'X'. |
|
Answer» Solution :A study of given curves in Fig. reveals that (a) power CONSUMPTION over a FULL cycle is represented by CURVE A. (b) Average power consumption over a full cycle = Zero , as is clear form curve A. (c ) The device X may be an inductor (L) or a capacitor (C )or their COMBINATION (LC) |
|
| 42864. |
Oersted's experimentdeals with the detection of____effect of electric current. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :MAGNETIC | |
| 42865. |
A series combination of a 2KOmega resistor and a 1KOmega resistor, is connected across a battery of emf 6V and negligible internal resistance. The potential drop, across the 2KOmega resistor is measured by (i) a 30kOmega voltmeter (ii) a 1kOmega voltmeter and (iii) both these voltmeter connected across it. If the voltmeter readings is the three cases are V_1, V_2 and V_3 respectively, arrange these reading in descending order. How will the three reading compare with one another if the potential drop were measured across the series combination of the 2kOmega and the 1kOmega resistor i.e., across the point A and B? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 42866. |
Which of following statements are correct ?(1) Wavelength of microwaves is greater than that of UV rays.(2) Wavelength of infrared radiation is less than that of UV rays.(3) Wavelength of microwaves is less than that of infrared waves.(4)Gamma rays have shortest wavelength in electromagnetic spectrum. |
|
Answer» (1) and (2) |
|
| 42867. |
Find the thickness of a nickel layer deposited on an article with surface area of 1200cm^(2) in the course of a 6-hour electrolysis at a current of 10.5 A. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 42868. |
A compound microscope consists of an objective lens of focal length 2.0 cm and an eyepiece of focal length 6.25 cm separated by a distance of 15cm. How far from the objective should an object be placed in order to obtain the final image at (a) the least distance of distinct vision (25cm), and (b) at infinity? What is the magnifying power of the microscope in each case? |
|
Answer» Solution :`v_(E)=-25cm and f_(e)=6.25cm" GIVE "u_(e)=-5cm, v_(o)=(15-5)cm=10cm`. `f_(o)=u_(o)=-2.5cm,"MAGNIFYING power = 20"` (b) `u_(o)=-2.59cm.` Magnifying power `=13.5`. |
|
| 42869. |
What happens when an uncharged conductor is placed near to a conductor? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 42870. |
In a step-up transformer, if the voltage in the secondary is increased, then the current in the primary |
|
Answer» increases |
|
| 42871. |
A ray light travels from a denser to a rarer medium. Then the ray |
|
Answer» doesn't bend at all |
|
| 42872. |
Find the ratio of de Broglie wavelength of molecules of hydrogen and helium which are at temperatures 27^(@)C and 127^(@)C respectively |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Since, `lamda=(H)/(mv)=(h)/(SQRT(3mkT))` `(lamda_(H))/(lamda_(He))=sqrt((m_(He)T_(He))/(m_(H)T_(H)))=sqrt((8)/(3))` |
|
| 42873. |
The probability of electrons to be found in the conduction band of an intrinsic semiconductor at a finite temperature |
|
Answer» increase EXPONENTIALLY with increasing band gap `n=n_oe^(-E_g//k_(B)T)` |
|
| 42874. |
यदि समुच्चय A में 5 अवयव हैं तथा समुच्चय B में 6 अवयव है तो A से B में एकैकी तथा आच्छादक प्रतिचित्रणों कि संख्या हैं : |
|
Answer» 720 |
|
| 42875. |
Cyclotron is suitable only for accelerating…………………….but not……………. . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 42876. |
Obtian the equation for lateral displacement of light passing through a glass slab. |
|
Answer» Solution :Consider a glass slab of thickness t and refractive index n is KEPT in AIR medium. The path of the light is ABCD and the refractions occur at two points B and C in the galss slab. The angles of incidence I and refraction r are measured with respect to the normal `N_(1) and N_(2)` at the twopoints B and C respectively. The lateral displacement L is the perpendicular distance CE drawnbetween the path of light and the undeviated path of light at point C. In the right agle triangle `Delta BCE`, `sin(i-r)=(L)/(BC),BC=(L)/(sin(i-r))` In the right angle triangle `Delta BCF`, `cos(r)=(t)/(BC),BC=(t)/(cos(r))` Equating equations (1) and (2) `(L)/(sin(i-r))=(t)/(cos(r))` After rearranging, `L=t(sin(i-rr)/(cos(r)))` Lateral displacement depends upon the thickness of the slab. Thickher the slab, greater will be the lateral displacement. Greater the angle of incident, larger will be the lateral displacement. 
|
|
| 42877. |
Consider the situation shown in the figure. The capacitor A has a charge q on it where as B is uncharged. The charge appearing on the capacitor B a long time after the switch S is closed is |
| Answer» ANSWER :B | |
| 42878. |
A body of mass m is raised through a distance equal to the radius of the earth from earth's surface. The change in P.E. will be: |
|
Answer» mgR `DeltaU=U_(2)-U_(1)=(GMm)/(R )[-(1)/(2)+1]=(GMm)/(2R)=(gR^(2)m)/(2R)` `=(1)/(2)mgR`. Thus CORRECT choiceis (a). |
|
| 42879. |
A reversible Carnot's engine is working between 260 K and 300K. It takes 500 cal of heat from sink. Heat rejected to the source at higher temp. for this refrigerator is: |
|
Answer» 400 CAL `Q_(2)=500 cal. Q_(1)=?` Here, for refrigerator also `(Q_(1))/(Q_(2))=(T_(1))/(T_(2))` ` Q_(1)=Q_(2)xx(T_(1))/(T_(2))=500 xx (300)/(260)` `Q_(1)=576 cdot 9 cal = 577 cal`. Hence, correct CHOICE is (d). |
|
| 42880. |
A rocket is launched vertically from the surface ofthe earth with an initial velocity v. How far above the surface of earth will it go? Neglect the air resistance. (where R is the radius of the earth ) |
|
Answer» `R((2gR)/v^2-1)^(-1//2)` TOTAL ENERGY = Kinetic energy + Potential energy `=1/2mv^2-(GmM)/R` At the highest POINT,v=0, Potential energy = `-(GmM)/((R+h))` where h is the MAXIMUM height. According to the law of conservation of MECHANICAL energy, we get `1/2mv^2-(GmM)/R=-(GmM)/(R+h),1/2v^2=(GMh)/((R)(R+h))` `1/2v^2=(gRh)/(R+h) "" (because g=(GM)/g^2)` `(R+h)/h=(2gR)/v^2, h=R((2gR)/v^2-1)^(-1)` |
|
| 42881. |
Consider the circuit shown in the figure. The switch has been in position 1 for a long time. Answer following questions: (a) find current through 2R. (b) find potential difference across the capacitor. (c) At t = 0 the switch is moved to position 2. What current flows through the capacitor immediately after the switch is placed to position 2? (d) Draw a graph of current Vs time for the current through the capacitor after the switch is moved to position 2. Indicate the time on the graph when the current becomes 37% of its value immediately after the switch is put to position 2. |
|
Answer» (B) `(2V)/(3)` (C) `(V)/(6R)` (d) `(##IJA_PHY_V02_C08_E01_045_A01##)` |
|
| 42882. |
Five charges, q each are placed at the corners of a regular pentagon of side 'a' as in figure: (a) (i) What will be the electric field at O, the centre of the pentagon ? (ii) What will be the electric field at O if the charge from one of the corners (say A) is removed ? (iii) What will be the electric field at O if the charge q at A is replaced by -q ? (b) How would your answer to (a) be affected if pentagon is replaced by n-sided regular polygon with charge q at each of its corners ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) (i)The POINT O, the centre of the pentago, is equidistant from all the charges at the end point of pentagon. THUS, due to symmetry the electric field due to all th charges are cancelled out. As a resul electric field at O is zero. (ii) When charge q is removed from A ne electric field at the centre due to remaining charges `E=(kq)/r^(2)` along OA. (iii) If charge q at A is REPLACED by - q then electric field due to this negative charge `vecE_(-q) =(kq)/r^(2)` along OA. (b) If pentagon is replaced by n-sided regulai polygon with charge q at each of its corners Here, again charges are symmetrical about the centre. The net electric field at O would continue to be zero, it doesn.t depend on the number of sides or the number oi charges. HENCE, the answer of (a) would not be affected. |
|
| 42883. |
Assertion: On going away from a point charge or a small electric dipole, electric field decreases at the same rate in both the cases Reason:Electric field is inversely proportional to square of distance from the charge or on electric dipole |
|
Answer» Both ASSERTION and Reason are TRUE and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion |
|
| 42884. |
Calculate the Lande's g factor for atoms (a) in S states, (b) in singlet states. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :From the Lande fromula `G=1(J(J+1)+S(S+1)-L(L+1))/(2J(J+1))` (a) For `S` states `L=0`. This implies `J=S`. Then, if `S=0` (For SINGLET states `g` is not defined if `L=0`) (b) For single states, `J=L` `g=1+(J(J+1)-L(L+1))/(2J(J+1))=1` |
|
| 42885. |
Name the different types of currents flowing thorugh p-n junction diode. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The CURRENT FLOWING due to the majority carriers and minority carriersThe trarisifent current The surface leakage current. | |
| 42886. |
In a chamber, a uniform magnetic field of 6.5 G (1 G = 10^(-4) T) is maintained. An electron is shot into field with a speed of 4.8 xx 10^(-6) ms^(-1) normal to the field. Explain, why the path of the electron is a circle. Determine the radius of the circular orbit. (e = 1.6 xx 10^(-19) C , m_e = 9.1 xx 10^(-31) kg). |
|
Answer» Solution :Here `B = 6.5 G = 6.5 xx 10^(-4) T, q = e = 1.6 xx 10^(-19) C, m_e = 9.1 xx 10^(-31) KG and v = 4.8 xx 10^(6) m s^(-1)` When an electron is shot into the magnetic field in a direction normal to the field, force acting on it `[F = B e v]` is acting is a direction perpendicular to both `v` and B and provides the necessary centripetal force to make the path of electron a circular path. RADIUS of the circular orbit, `r = (m_e v)/(e B) = (9.1 xx 10^(-31) xx 4.8 xx 10^(-6))/(1.6 xx 10^(-19) xx 6.5 xx 10^(-4)) = 4.2 xx 10^(-2) m " or " 4.2 cm`. |
|
| 42887. |
Consider the situation shown in figure. The two slits S_(1) and S_(2) placed symmetrically around the central line are illuminated by a monochromatic light of wavelength lambda. The separation between the slits is d. The light transmitted by the slits falls on a screen Sigma_(1) placed at a distance D from the slits. The slit S_(3) is at the central line and the slit S_(4) is at distance z from S_(3). Another screen Sigma_(2) is placed a further distance D away from Sigma_(1). Find the ratio of the maximum to minimum intensity observed on Sigma_(2) if z equal to (1) z = (lambda D)/(2d) (2) (lambda D)/(d) (3) (lambda D)/(4d) |
|
Answer» `2, 25 , OO` |
|
| 42888. |
Find the value of colour coded resistance shown is fig |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 42889. |
The forward bias of a diode is wrongly given above . a. Redraw the above circuit correctly . b. Draw the graph of current I with voltage V in forward bias . c. Classify the following circuit diagram into forward bias , reverse bias , unbias |
Answer» SOLUTION :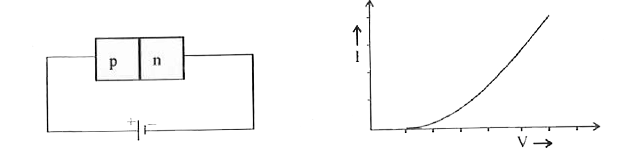 i.Reverse biasii. FORWARD BIAS iii. Reverse bias IV . Unbias |
|
| 42890. |
I Young.s double slit experiment if one of the slits is closed |
|
Answer» the CENTRAL FRINGE is dark |
|
| 42891. |
Torque experienced by electric dipole is ..................... . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 42892. |
What is erosion (अपरदन)? |
|
Answer» It is called weathering of rocks |
|
| 42893. |
Simplify the Boolean identifyAC+ABC=AC |
|
Answer» Solution :STEP1: Step 1: AC (1 + B) = AC.1 (OR law-2] Step 2: AC. 1 = AC [AND law - 2] Therefore, AC + ABC = AC Circuit Description Thus the GIVEN STATEMENT is proved. 
|
|
| 42894. |
A capacitor with capacitance C whose interelectrode space is filled up with poorly conducting medium with active resistance R is connected to a source of alternating voltage V=V_(m) cos omegat. Find the time dependence of the steady - state current flowing in lead wires. The resistance of the wires is to be neglected. |
|
Answer» Solution :We use the complex voltage `V=V_(m) e^( i omegat). ` Then the voltage across the capacitor is `(I-I^('))(1)/( iomegaC)` and that across the resistance `RI^(') ` and both equal `V`. Thus `I^(')=(V_(m))/( R) e^(I omegat), I-I^(') =iomegaCV_(m)e^(iomegat)` Hence `I=(V_(m))/( R)(1+ iomegaRC) e^(iomegat)` The actual voltage is OBTAINED by taking the real part. Then `I=(V_(m))/(F) sqrt(1+ ( omegaRC)^(2))cos ( omegat+ varphi)` Where ` tan varphi= omega RC` Note `rarr A` condenser with poorly conducting material `(` dielectric of high resistance `)` be the plates is equivalen to an an ideal condenser with a high resistance JOINED in `p` between its plates. 
|
|
| 42895. |
The displacement of two interfering light waves are y_(1)=4 sin omega t" and "y_(2)= 3 cos (omega t). The amplitude of the resultant waves is (y_(1)" and "y_(2) are in CGS system) |
|
Answer» 5 cm |
|
| 42896. |
A conductor of resistance 3Omega is stretched uniformly till its length if doubled. The wire is now bent in the form of an equivalent triangle. The effective resistance between the ends of any side of the triangle in ohm is |
|
Answer» `(9)/(2)Omega` |
|
| 42897. |
A stationary shell explodes into two fragments, having masses in the ratio of 1:2. The heavier fragment attains a Kinetic energy of 100J. The Kinetic energy released in the explosion is |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 42898. |
A bead B of mass 'm' can travel without frictionn on a smooth horizontalwire "xx"^('). The bead is connected to a block of identical mass by an ideal string passing over an ideal pulley. The system, as shown, is in vertical plane. The system is allowed to fall. Find the speed of block A at the instant when string connected to the bead B makes an angle 37^(@) with vertical. |
|
Answer» `SQRT(AG)` `h=a/(COS60^(@))-a/(cos 37^(@))=(3a)/4` `mgh=1/2 mv_(A)^(2)+1/2 mv_(B)^(2)` Also, `v_(B)sin 37^(@)=v_(A)` `implies (3ag)/4=(v_(A)^(2))/2[1+(5/2)^(2)]` `=v_(A)=3/2 sqrt((3ag)/17)` |
|
| 42899. |
If alpha=60//61 for a transistor, the value ofbeta is |
|
Answer» 50 |
|
| 42900. |
Differentiate between polarised and un-polarised light. How are these represented ? |
Answer» Solution : In polarised light vibrations of electric vectors are taking place in a PARTICULAR plane only but in UNPOLARISED light vibrations of electric vector take place in all POSSIBLE directions PERPENDICULAR to the DIRECTION of propagation of light. Figure represent unpolarised light. Figure represent plane polarised light with plane of paper as the plane of vibration. Figure also represent plane polarised light but its plane of vibration is perpendicular to the plane of paper. |
|