Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 42751. |
Assertion: A p-n junction with reverse biase can be used as a photo-diode to measure light intensity. Reason: In reverse bias condition the current is small but it is more sensitive to change in incident light intensity. |
|
Answer» If both the assertion and reason are true and reason is a true explantion of the assertion. 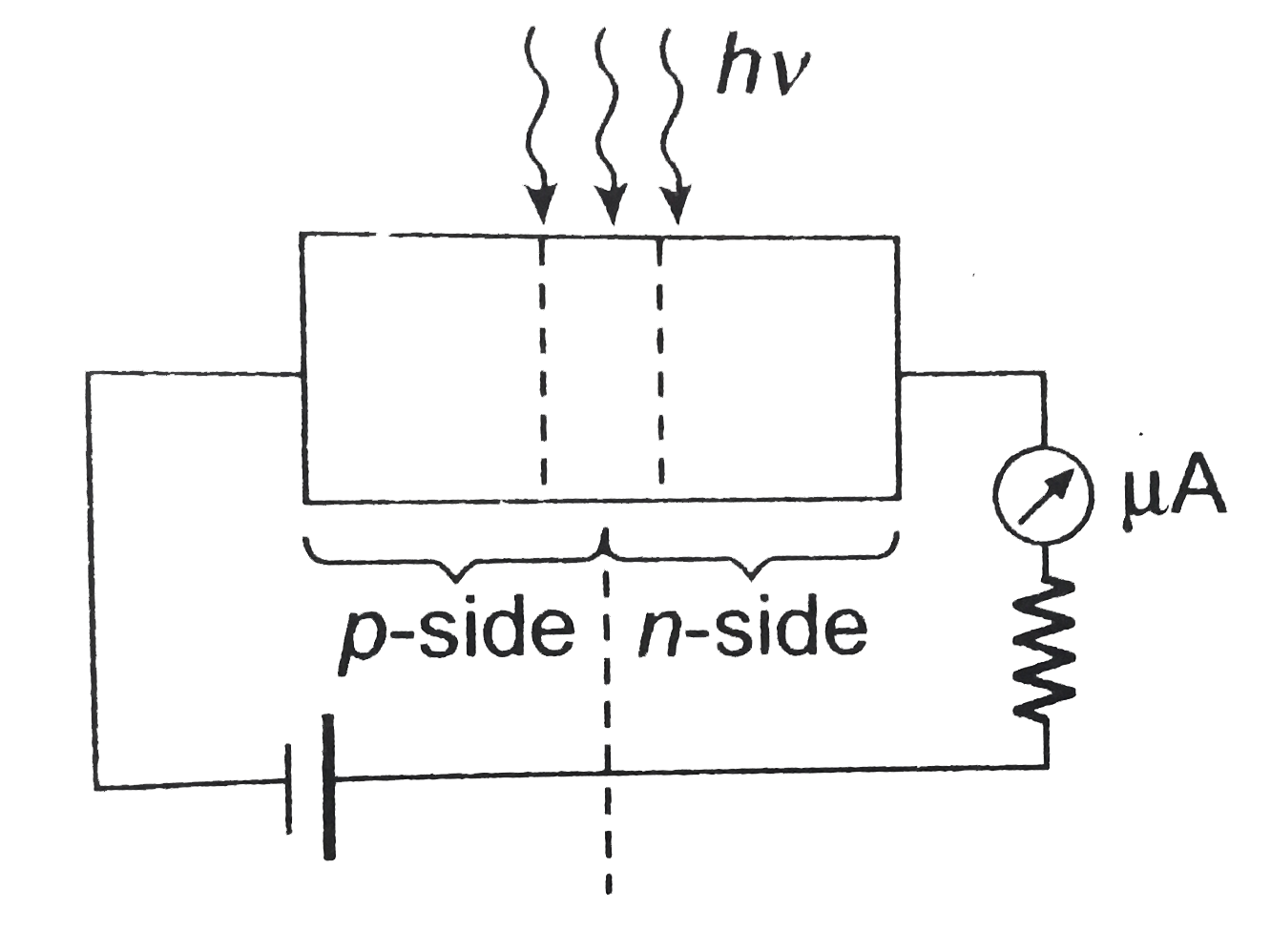 When such a `p-n` diode is illuminated with light photons having ENERGY `hvgtE_(g)` and intensities `I_(1).I_(2),I_(3)` ETC., the electron and hole pairs generated in the depletion layer (or near the junction) will be across the junction. There would be a change in the reverse SATURATION current as shown in figure. Hence, a measurement of the change in the reverse saturationcurrent as shown in figure current on illumination can give the values of the light INTENSITY. 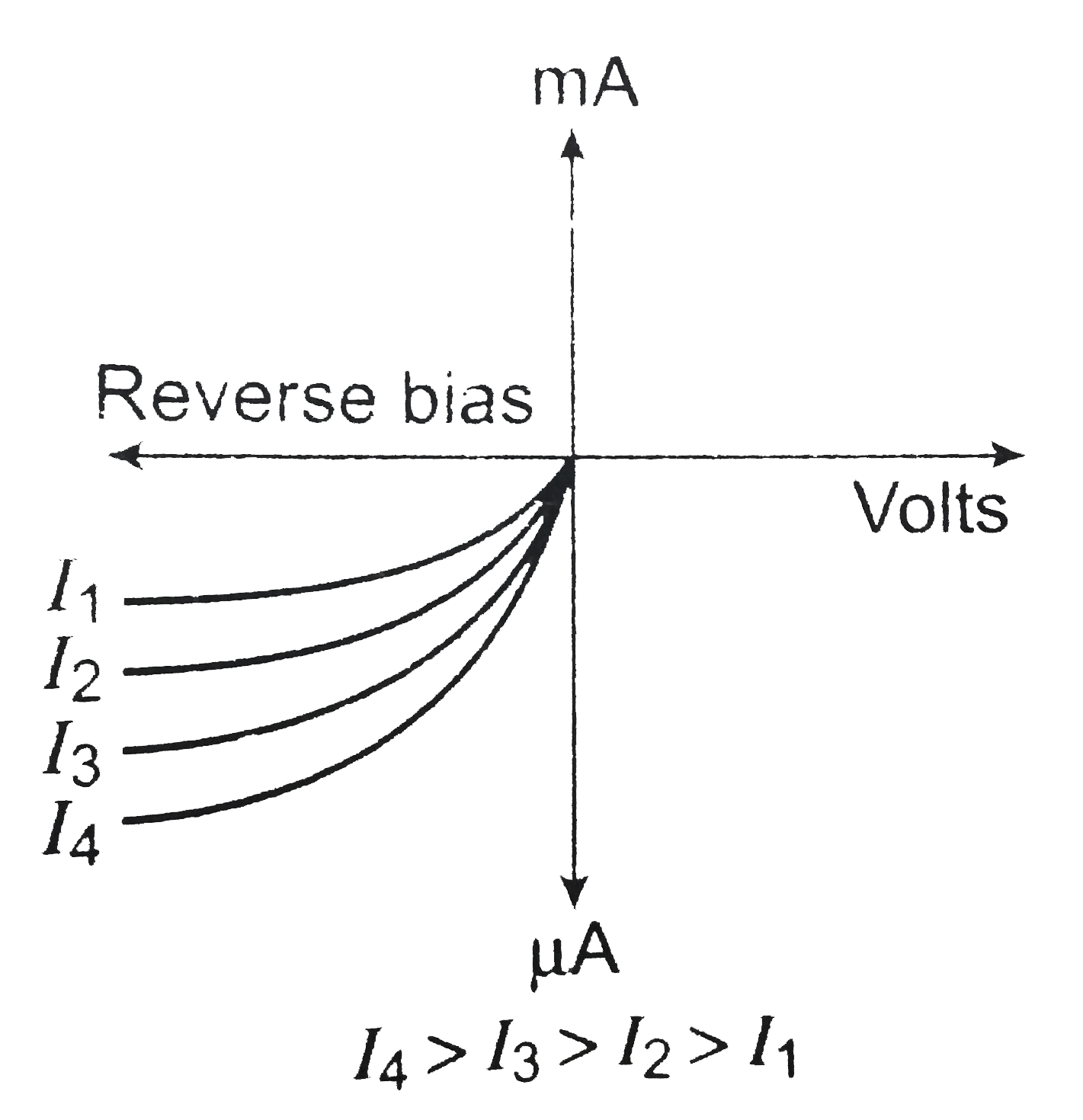 Hence, option (a) is true. |
|
| 42752. |
Which one of the following statements concerning the proper length of a meter stick is true? |
|
Answer» The proper LENGTH is ALWAYS one meter. |
|
| 42753. |
Define the term resolving power of a telescope. How does it get affected on (i) increasing the aperture of the objective lens, (ii) Increasing the focal length of the objective lens ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :For the term RESOLVING power. resolving power of a telescope `=(A)/(1.22lamda)`, where A is the APERTURE of telescope OBJECTIVE and `LAMDA` the wavelength of light. (i) On increasing the aperture of the objective lens the resolving power is increased in the same ratio. (ii) Focal length of objective lens has no effect on resolving power of telescope. |
|
| 42754. |
The Positively charged nucleolus of the atom has a radius of about 10^-13 cm. It was proved by: |
|
Answer» JOHN Dalton |
|
| 42755. |
Derive the relation f = R//2 in the case of a concave mirror. |
Answer» Solution :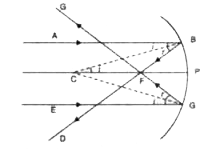 To Show that `f = R //2` for a Concave Mirror . Let a ray of light AB be incident, parallel to the principal AXIS, on a concave mirror. After refraction, the ray AB passes along BD,through the focus F. BC is NORMAL to the concave mirror at B. `/_ABC = /_ CBD `.....(1) ( According to the law of reflection ` /_i= /_ r )` We know that AB and PC are parallel to each other. `:. /_ ABC = /_ BCP ` ( alternate ANGLES )....... (2) From equations (1)and (2) , we get `/_ CBD = /- BCP ` Hence triangleBCF is isosceles `:. BF = CF`....(3) If the aperture of the mirror is small than B will be very close to P. `:.` BF = PF....(4) From equation ( 3) and( 4)we CONCLUDE that `CF = PF = ( 1)/(2) PC ` But by definition PF = f ( focal length )and PC = R ( radius of curvature ) i.e., `f = ( R )/( 2)` |
|
| 42756. |
The hydrogen atom in the ground state excited by means of light of lambda=975 Å. How many different lines are possible in resultant spectrum ? |
|
Answer» 4 |
|
| 42757. |
ABC is an equilateral triangular frame of mass m and side r. It is at rest under the action of horizontal magnetic field B (as shown) and the gravitational field. |
|
Answer» The frame remains at rest if the CURRENT in the frame is `(2mg)/(rB)` `A'B'=2A'O=(2)/(tan 60^(@)) ((rsqrt(3))/(4))=(r )/(2)` For equilibrium `mg-I((r)/(2))B` `I=(2mg)/(rB)` If loop is displaced by x, F= Restoring force `-I[((2)/(tan 60^(@)))(rsqrt(3)/(4)+x)]B+mg` `=-(IrB)/(2) + mg - (2IB)/(sqrt(3))x` `=-(2IB)/(sqrt(3))*x` `F prop (-x) x`, motion is SHM. `a=-(2IB)/(msqrt(3))*x` `T=2pi[(msqrt(3))/(2IB)]^(1//2) = pi[(rsqrt(3))/(g)]^(1//2)`. |
|
| 42758. |
A power supply with an e.m.f epsi and internal resustancer is connected to a variable resistance R. Find the dependence of the total power generated by the supply and of the power delivered to the external circuit on the load resistance. |
|
Answer» <P> |
|
| 42759. |
What is the frequency of electromagnetic waves produced by oscillating charge of frequency v ? |
| Answer» Solution :FREQUENCY of ELECTROMAGNETIC wave = Frequency of oscillating CHARGE = V. | |
| 42760. |
The capacity of a parallel plate air condenser is 2muF If the distance between the plates is 4cm and the area of each plate is 0.01m^2, the value of permittivity of air and units are respectively - |
|
Answer» `8 xx 10^(-12)" FARAD METRE"^(-1)` |
|
| 42761. |
Which of the following has the greatest viscosity ? |
|
Answer» Hydrogen |
|
| 42762. |
In the adjacent figure a cylindricalvessel of mass M and cross - sectional area A is placed inverted on a fixed smooth piston of same cross - sectionalarea fixed to the ground . The spacebetween the cylinder and priston is completely filled withliquidof densityrho. There is a small office of cross - sectionalareaa( a lt lt A) at the top top portionof this vessel . ( intially length of the liquidcolumn in the vessel is H ) |
|
Answer» `a/A SQRT((MG)/(2rhpoA))` |
|
| 42763. |
the correct form of Strokes law is (symbols have their usual meanings) |
|
Answer» `vecF=-6pietaavecv` |
|
| 42764. |
In the adjacent figure a cylindricalvessel of mass M and cross - sectional area A is placed inverted on a fixed smooth piston of same cross - sectionalarea fixed to the ground . The spacebetween the cylinder and priston is completely filled withliquidof densityrho. There is a small office of cross - sectionalareaa( a lt lt A) at the top top portionof this vessel . ( intially length of the liquidcolumn in the vessel is H ) Speedof the liquidwith which it comes out of the vessel is |
|
Answer» `SQRT(2gH)` |
|
| 42765. |
An Infinite current carrying wire having current I_0 is placed coaxially inside a hollow conducting infinite cylinder of radius R and having current I flowing along the length of the cylinder in the same direction as I_0what is the increment in magnetic pressure due to placing of the wire? |
|
Answer» `(mu_0l_0l)/(2pi^2R^2)` |
|
| 42766. |
Assertion: Two electrically neutral metal spheres in contact are moved closer to a charged object and then separated away from each other using insulating handles in the presence of e charged object, Both the neutral objects acquire equal and opposite charges. Reason: When two metallic objects in contact are brought closer to a charged object then electrons are transferred from one object to the other due to induction phenomenon. If we separate the objects in presence of a charged object then electrons are unable to flow back to the original object. |
|
Answer» If both ASSERTION and REASON are CORRECT and reason is a correct EXPLANATION of the assertion . |
|
| 42767. |
There are two parallel long straight wires of radii r and separation between their axes is kept d. Current loop is formed by joining the wires at ends. Current I flows in both parallel wires in opposite directions. Neglect the end effects and also neglect flux inside the wires. Calculate self-inductance per unit length of this system of wires. |
Answer» Solution : Consider an area segment of length l and width dx at a distance x from one of the wires as shown in FIGURE. Distance of this area segment from the other wire will be d -x because SEPARATION between wires is d. All DISTANCES are from the axes of wires. To calculate magnetic flux LINKED with this area segment we need magnetic field INTENSITY. Magnetic field intensity at the site of area segment can be written as follows: `B=(mu_(0) i)/(2pix)+(mu_(0) i)/(2pi(d-x))` Magnetic fields due to both the wires are added because the two are in same direction. Area of this segment is ldx, and we can multiply this with magnetic field intensity to get magnetic flux linked with this area segment. `dphi=Bldx=[(mu_(0) i)/(2pix)+(mu_(0) i)/(2pi(d-x))](ldx)` `implies dphi=(mu_(0) il)/(2pi)[(1)/(x)+(1)/((d-x))]dx` We can integrate the aboverelation to get total flux in between the two parallel wires. `implies phi=(mu_(0) il)/(2pi)int_(r)^(d-r)[(1)/(x)+(1)/((d-x))]dx` `implies phi=(mu_(0) il)/(2pi)["In x - In(d-x)"]_(r)^(d-r)` `implies phi=(mu_(0) il)/(2pi)[{"In (d-r) - In(d - d + r)"}-{"In r - In(d-r)"}]` `phi=(mu_(0) il)/(2pi)[{"In (d-r) - Inr"}-{"In r - In(d-r)"}]` `implies phi=(mu_(0) il)/(2pi)["In (d-r) - Inr - Inr + In(d-r)"]` `phi=(mu_(0) il)/(2pi)["2In(d-r) - 2Inr"]` `implies phi=(mu_(0) il)/(2pi)"In"((d-r)/(r))` We know that `phi=Li` Hence self-inductance for length l of this system can be written as follows: `implies Li=(mu_(0) il)/(pi)"In"((d-r)/(r))` `implies L=(mu_(0) l)/(pi)"In"((d-r)/(r))` `:.` Self-inductance per unit length can be written as `implies (L)/(l)=(mu_(0))/(pi)"In"((d-r)/(r))` |
|
| 42768. |
Find the potential difference between the points A and B for the network shown in Fig. 4.52. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 42769. |
Obtain the equation of electric potential energy of a system of two electric charges in external electric field. |
Answer» Solution :Two electric charges `q_(1)` and `q_(2)` are brought from INFINITY distance through distance `r_(1)` and `r_(2)` relative to origin in external electric field. The work done in bringing the charge `q_(1)`, from infinity through `r_(1)`, distance, `W_(1)=q_(1)V(vecr_(1))` and work done in bringing `q_(2)` through distance `r_(2)` . Here work is done not only against the external field `vecE` but also against the field due to `q_(1)` `W_(2) = q_(2)V(vecr_(2))` Work done on `q_(2)` against the field due to `q_(1)`. `W_(3)=(kq_(1)q_(2))/(r_(12))` where `r_(12)` is the distance between `q_(1)` and `q_(2)` The total potential energy of the system = the total work done in ASSEMBLING the configuration or potential energy `U=q_(1)V(vecr_(1))+q_(2)V(vecr_(2))+(kq_(1)q_(2))/(r_(12))` |
|
| 42770. |
(A): Common emitter mode of a transistor is widely used (R): Current gain, voltage gain, and power gain are maximum in C.E mode of a transistors. |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are TRUE and 'R' is the correct EXPLANATION of 'A' |
|
| 42771. |
The only force acting on a 2.0kg canister that is moving in an xy plane has a magnitude of 5.0 N. The canister initially has a velocity of 4.0 m/s in the positive x direction and some time later has a velocity of 6.0 m/s in the positive y direction . How much work is done on the canister by the 5.0 N force during this time? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 42772. |
("he")/(4 pi m ) has the same dimensions as (h= Planck'sconstant , e = charge, m = mass .) |
|
Answer» MAGNETIC MOMENT |
|
| 42773. |
An electromagneticwavetravellingin theX- directionhasfreqencyof2 xx 10^(14)Hzand electricfieldforthiswave? |
|
Answer» `VECB( x,t)= ( 3 xx 10^(-8)T ) SIN[ 2PI( 1.5 xx 10^(-6) x -2xx 10 ^4t)]` ` B_0= (E_0 )/(c ) ` thus ,`B_0=(27)/( 3xx 10^8 ) = 9 xx 10^(-8) T ` the angularfrequency is givenby `omega = 2pi f = 2 pi xx 2xx 10^(14)Hz ` Thedirectionof oscillationof the magneticfieldcan beeitheralongY - axisor z- axis thusthe possiblechoiceshouldbe ` vecB(x,t)= ( 9xx 10 ^(-8)T ) hatk sin ` ` [ 2 pi( 1.5 xx 10^(-6) x-2 xx 10^(14) t)]` HEncethe correctoptionis (b) |
|
| 42774. |
Calculate the impact parameter of a 5 MeV particle scattered by 90^(@) when it approaches a gold nucleus. |
|
Answer» `15.27 X 10^(-14)` m |
|
| 42775. |
In the arrangement shown in figure pulleys and strings are ideal m_(1) gt m_(2). S is spring balance which is itself massless. The reading of balance will be |
|
Answer» `G(m_(1)-m_(2))` |
|
| 42776. |
A bomb is dropped from an aircraft travelling horizontally at 150ms^(-1)at a height of 490m. The horizontal distance travelled by the bomb before it hits the ground is |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 42777. |
A parallel bema of fast moving elecyrons in incident normally on a narrow slit. A screen is placed at a large distance from the slit.If the spped if the electrons is increased, which of the following statement is correct. |
|
Answer» Diffraction PATTERN is not observed on the screen in the CASE of electrons |
|
| 42778. |
In Young's double slit experiment, The locus of the point P lying in a plane with a constant path difference between two interfering waves is |
|
Answer» a hyperbola |
|
| 42779. |
Consider the quantities, pressure, power, energy, impulse, gravitational potential, electrical charge, temperature, area. Out of these, the only vector quantities are |
|
Answer» IMPULSE, pressure and AREA |
|
| 42780. |
Statement- 1 : When the cell is in the open circuit, there is no force on a test charge inside the electrolyte is in the cell Statement-2 :Three is no field inside the cell, when is it open circuit. |
|
Answer» Statement - 1: is true ,Statement - 2: is true ,Statement - 2: is CORRECT explanation of statement - 1, |
|
| 42781. |
A transverse sinusoidal wave of amplitude a, wavelength lamdaand frequency f is travelling on a stretched string. The maximum speed of any point on the string is v/10, where v is the speed of propagation of the wave. If a = 10^(-3) m and y = 10m/s, then lamda and f are given by |
|
Answer» `lamda = 2pi xx 10^(-2) m` |
|
| 42782. |
Assertion A pulsar is a source of radio waves that varies in intensity at regular intervals Reason A pulsar is a rotating neutron star |
|
Answer» Both Assertion and REASON are TRUE and Reason is the CORRECT explanation of Assertion |
|
| 42783. |
If a lens of focal length f is divided into two equal parts and both pieces are put in c o n - tact as shown in fig. The resultant focal length of combination are |
|
Answer» `0,F,OO` |
|
| 42784. |
(a). Consider circuit in figure. How much energy is absorbed by electrons from the initial state of no current (ignore thermal motion) to the state of drift velocity? (b). Electrons give up energy at the rate of RI^(2) per second to the thermal energy. what time scale would number associate with energy in problem (a)? n=number f electron/volume=10^(29)//m^(3). Length of circuit =10cm, cross-section=A=(1mm)^(2). |
|
Answer» Solution :(a). By ohm's law, current I is given by `I=6V//6Omega=1A` But, `I "net"Av_(d)` or `v_(d)=(i)/("neA")` On substituting the values For, `n=`number of electron/volume `=10^(29)//m^(3)` Length of cirucit=10cm, cross-section `=A=(1mm)^(2)` `v_(d)=(1)/(10^(29)xx1.6xx10^(-19)xx10^(-6))` `=(1)/(1.6)xx10^(-4)m//s` THEREFORE, the energy absorbed int he form of KE is given by `KE=(1)/(2)m_(e)v_(d)^(2)xxnAI` `=(1)/(2)xx9.1xx10^(31)xx(1)/(2.56)xx10^(20)xx10^(8)xx10^(6)xx10^(1)` `=2xx10^(-17)J` (b). POWER loss is given by `P=I^2R=6xx1^(2)=6W=6J//s` Since, `P=(E)/(t)` Therefore, `E=Pxxt` or `t=(E)/(P)=(2xx10^(-17))/(6)=10^(-17)s` |
|
| 42785. |
Prove that the Lenz's law is a specific representation of the law of conservation of energy and state Lenz's law. |
|
Answer» Solution :In 1834, German PHYSICIST Heinrich Friedrich Lenz (1804-1865) deduced a rule, known as Lenz.s law which gives the polarity of the induced emf in a clear and concise fashion. The statement of the law is: "The polarity of induced emf is such that it tends to produce a current which opposes the change in magnetic flux that produced it." The negative sign shown in equation `epsilon=-(dPhi_B)/(dt)` represents this effect. 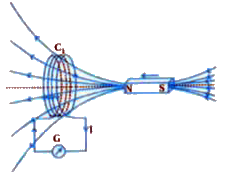 In figure, we see that the North-pole of a bar magnet is being pushed towards the closed coil. As the North-pole of the bar magnet moves towards the coil, the magnetic flux through the coil increases. Hence current is induced in the coil in such a direction that it opposes the increase in flux. This is possible only if the current in the coil is in a counter-clockwise direction with respect to an observer situated on the side of the magnet. Note that magnetic moment associated with this current has North polarity towards the North-pole of the approaching magnet. Similarly, if the North-pole of the magnet is being withdrawn from the coil, the magnetic flux through the coil will decrease. To counter this decrease in magnetic flux, the induced current in the coil flows in clockwise direction and its South-pole faces the receding North-pole of the bar magnet. This WOULD result in an attractive force which opposes the motion of the magnet and the corresponding decrease in flux. Suppose that the induced current is in the direction as shown in figure (b) which is opposite to the one depicted in figure. In that case, the South-pole due to the induced current will face the approaching North-pole of the magnet. The bar magnet will then be attracted towards the coil at an ever increasing acceleration. If this can happen, a gentle push on the magnet will initiate the process and its velocity and kinetic ENERGY will continuously increase without using any energy. This violates the law of conservation of energy and hence can not happen. 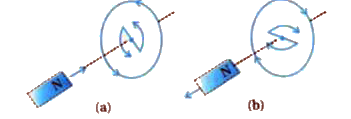 Now consider the correct case shown in figure. In this situation, the bar magnet EXPERIENCES a repulsive force due to the induced current. Therefore, a person has to do work in moving the magnet. The energy spent by the person is dissipated by Joule heating produced by the induced current, which is compatible with conservation of energy. |
|
| 42786. |
The wavelength of the first line of Lyman series is lamdba for hydrogen atom. Find out the wavelength of first line of Pfund series. |
|
Answer» Solution :If `lambda` is the wavelength of first line in Lyman series then `(1)/(lambda)=R[(1)/(1^(2))-(1)/(2^(2))]=R[(1)/(1)-(1)/(4)]` `(1)/(lambda)=(3R)/(4) ....(1)` `RARR` is the wavelength of first line in Pfund series then, `(1)/(lambda.)=R[(1)/(5^(2))-(1)/(6^(2))]=R[(1)/(25)-(1)/(36)]` `(1)/(lambda.)= (11F)/(900)...(2)` `rArr` Taking ratio of equation(1) and (2) `(lambda.)/(lambda)=(3R)/(4)xx(900)/(11R)=(2700)/(44)` `lambda.=61.36 lambda` |
|
| 42787. |
Consider the quantities: pressure, power, energy, impulse, gravitational potential, electrical charge, temperature, area. Out of these, the only vector quantities are |
|
Answer» IMPULSE, PRESSURE and area |
|
| 42788. |
Thematerials suitablefor makingelectromagnets should have |
|
Answer» LOW retentivity and HIGH coercivity |
|
| 42789. |
The magnetic moment associated with a circular coil of 35 turns and radius 25 cm, if it carries a current of |
|
Answer» `72.2A m^(2)` Then magnetic moment associated with this CIRCULAR coil `M = NIA = NIpi r^(2)=35xx11xx3.14xx(25xx10^(-2))^(2)` `=75.56"A m"^(2)` |
|
| 42790. |
A block is pushed up a rough inclined plane of 45°. If the time of descent is twice the time of ascent, the coefficient of friction is |
|
Answer» 0.6 |
|
| 42791. |
The power of sound from the speaker of radio is 10 W. Now, the power of sound from the speaker of the radio is increased to 400 W by increasing the volume of the radio. The power increased in dB as compared to original power is nearly |
|
Answer» 8 |
|
| 42792. |
What is shunt ? Explain its function in circuit. |
|
Answer» Solution :1. Shunt : The small resistance connected parallel to galvanometer is called shunt (S). 2. Uses : (i) Due to shunt, galvanometer is protected against DAMAGE. (II) To convert ammeter from galvanometer. (iii) By USING proper value of shunt, range of ammeter can be increased. |
|
| 42793. |
What are the number of electrons and neutrons in ""_(92)^(236)U atom ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :No. of electrons 92 No.Of neutrons 236 -92 = 144. |
|
| 42794. |
The total energy of a body of mass 100 g performing SHM is 0.2 J. Find its maximum speed . |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Data :`m = 0.1 kg , E = 0.2 J` The total energy of the body, ` E = 1/2 momega^(2) A^(2) = 1/2 m (omegaA)^(2)` But `omegaA` = maximum speed `(v_("MAX"))` ` :. v_("max") = sqrt((2E)/m) = sqrt((2 xx 0.2)/(0.1))` = 2 m/s |
|
| 42795. |
Assume that there is no repulsive force between the electrons in an atom but the force between positive and negative charges is given by coulomb's law as usual. Under such circumstances, calculate the ground state energy of a He-atom. |
|
Answer» Solution :In a helium atom `(._2He^(4))`, there are two protons and two neutrons in the nucleus. Two electrons are revolving around the nucleus in the first orbit. We are GIVEN that there is no repulsive force between the electrons. for He nuclues, CHANGE, `Z = + 2e`.As two electrons of change `(-2e)` revolve around the nuclues, therefore the formula for energy in nth orbit WOULD be `E_(n) = - (me^(4)(Z^(2)))/(8 in_(0)^(2)n^(2)h^(2)) = - (4 me^(4))/(8 in_(0)^(2)n^(2)h^(2)) = 4E` The ground state will have two electrons, each of energy `E = - (me^(4))/(8 in_0^2 (1)^2h^2)=-13.6 eV` `:.` The total ground state energy of He atom =`4E=4(-13.6)eV=-54.4eV` |
|
| 42796. |
A conducting rod MN moves with a speed v parallel to a long straight wire which carries a constant current i, as shown in Fig. The length of the rod is normal to the wire. Find the emf induced in the total length of the rod. State which end will be at a lower potential. |
|
Answer» Solution :The magnetic field induction due to current i is different at different sections of the rod, because they are at different DISTANCES from the wire.Let us, first of all, subdivide the entire length of the conductor MN into elementary sections. Consider a section (shown shaded in the figure (b)) of thickness dx at a DISTANCE X from the wire. As all the three, V, B and (dX) are mutually normally to each other, so the emf induced in it is de = Bvdx. (from N to M by Fleming.s right hand rule)  For the rest of sections, the induced emf is in the same sense, (i.e, from N to M) `THEREFORE ` Total emf induced in the conductor is ` e = int de = int_b^(b+a) Bvdx` Substituting for `B = (mu_0 i)/(2pi x)`,the above equation gets changed to ` e =int_b^(b+a) (mu_0 iv dx)/(2pi x)` ` e = (mu_0iv)/(2pi)[ln x]_(b)^(b-a) " or" e = (mu_0 iv)/(2pi) ln (1+alb)` |
|
| 42797. |
The distance of closest approach of alphaparticle to the nucleus was taken as a measure of |
|
Answer» Atomic radius |
|
| 42798. |
On what factors does resolving power of a compound microscope. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Resolving POWER = `2musintheta\lambda` Thus, it DEPENDS on the wavelength of light used to illuminate the OBJECT, RI of glass, forming the objective and semi vertical angle of the cone. |
|
| 42799. |
Voltmeter reading in the given circuit is (voltmeter is ideal) |
|
Answer» 6 V |
|
| 42800. |
When a carpet is beaten by a stick, the dust particles drop down according to : |
|
Answer» NEWTON's 1ST 1aw of MOTION |
|