Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 39301. |
Water rises upto a height of 12 cm into a capillary tube when placed vertically. Ifit is now tilted through 45^(@) from the vertical, length of the water in the capillary tube is |
|
Answer» 12 CM |
|
| 39302. |
The density of mercury is 13.6 gm/c.c at 0°C, and it is 13.15 gm/c.c at 130^(@)C. Calculate the coefficient of absolute expansion of mercury. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`26.32 XX 10 ^(-5) // ^(@)C` | |
| 39303. |
Find the expression of KE of the rigid body in rotational motion. |
Answer» Solution : Let us consider a rigid body rotating with angualar velocity `OMEGA` about an axis as shown in the figure. Every particle of the bdoy will have the same ANGULAR velocity `omega` and different TANGENTIAL velocities v BASED on its positions from the axis of rotation. Let us choose a particle of mass `m_(i)` situatedat distance `r_(i)` from the axis of rotation. It has a tangential velocity`v_(i)` given by the relation, `v_(i)=r_(i) omega`. The kinetic energy `KE_(i)` of the particle is `KE_(i)=1/2 m_(i)v_(i)^(2)` Since `v_(i)=r_(i)omega` `KE_(i)=1/2m_(i)(r_(i)omega)^(2)=1/2m_(i)(r_(i)^(2))omega^(2)` For the kinetic energy of the whole body, which is made up of large number of such particles, the equation is written with simmation as `KE=1/2(sum m_(i)r_(i)^(2))omega^(2)` where the term `sum m_(i)r_(i)^(2)` is the MOMENT of inertia I of the whole body. `I=sum m_(i)r_(i)^(2)` In rotational motion kinetic energy is `KE=1/2 I omega^(2)` |
|
| 39304. |
An object of mass 3 kg is at rest. Now a force of vecF=6t^(2)hati+4thatj is applied on the object, then the velocity of object at t=3 second is |
|
Answer» `18hati+3hatj` `F=ma"":.a=(BARF)/(m)=(1)/(3)(6t^(2)hati+4thatj)=2T^(2)hati+(4)/(3)thatj` `a=(dV)/(dt)"":.v=int_(0)^(t)adt=int_(0)^(3)2t^(2)hatjdt+int_(0)^(3)(4)/(5)thatjdt=18hati+6hatj` |
|
| 39305. |
A body of mass 1 kg begins to move under the action of a dependent force vec(F)=(2t hat(i)+3t^(2)hat(j))N where hat(i) and hat(j) are unit vectors along x and y axis. What power will be developed by the force at the time t ? |
|
Answer» `(2t^(2)+3T^(3))W` |
|
| 39306. |
The cross-sectional area of water pipe entering the basement is 4 x 10^(-4) m^(2). The pressure at this point is 3 x 10^(5) Nm^(-2) and the speed of water is 2 ms^(-1). This pipe tapers to a cross-sectional area of 2 x 10^(-4)m^(2) when it reaches the second floor 8 m above. Calculate the speed and pressure at the 2nd floor |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Since `A_(1)nu_(1)=A_(2)nu_(2)` `nu_(2)=(2xx4xx10^(-4))/(2XX10^(-4))` = 4m/s Using BERNOULLI’s Theorem `P_(2)=P_(1)+(1)/(2)RHO(upsilon_(1)^(2)-upsilon_(2)^(2))+rhog(h_(1)-h_(2))` `:. nu_(2)gtnu_(1)` `h_(2)gth_(1)` `=3xx10^(5)+(1)/(2)(1000)[(2)^(2)-(4)^(2)]-1000xx9.8xx8` `=2.16xx10^(5)N//m^(2)` |
|
| 39307. |
Which type of elastic modulus is there in liquid and gas ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :VOLUME - ELASTIC MODULUS (BULK modulus) | |
| 39308. |
Explain how geocentric theory is required by helliocentric theory using the idea of retrograde motion of planets. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) To explain this retrograde MOTION, Ptolemy introduced the concept of "epicycle" in his GEOCENTRIC model. According to this theory, while the PLANET orbited the Earth, it also underwent ANOTHER circular motion termed as "epicycle". (ii) A combination of epicycle and circular motion around the Earth gave rise to retrograde motion of the planets with respect to Earth. (iii) But Ptolemy's model became more and more complex as every planet was found to undergo retrograde motion. (iv) In the 15th century, the Polish astronmer Copernics proposed. (v) The helicentric model to explain this problem in a simpler manner. According to this model, the Sun is at the center of the solar system and all planets orbited the Sun. (VI) The retrograde motion of planets with respect to Earth is because of the relative motion of the planet with respect to Earth. |
|
| 39309. |
In the above probllem, the normal force between the ball and the shell in position B is (m=mass of ball) |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 39310. |
Two particles A and B of equal mass M are moving with the same speed u as shown in the figure. They collide completely inelastically and move as a single particle C. The angle 9 that the path of C makes with the X-axis is given by : |
|
Answer» `TAN theta =(SQRT(3) + sqrt(2))/(1-sqrt(2))` |
|
| 39311. |
Compare the components for the following vector equations (a) Thatj-mghatj=mahatj (b) vecT+vecF=vecA+vecB © vecT-vecF=vecA-vecB (d) Thatj+mghatj=mahatj |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Components of the VECTORS `T-mg=ma` (b) `barT_(x)+barF_(x)+barB_(x)` (or) `barT_(y)+barF_(y)=barA_(y)+barB_(y)` © `barT_(x)-barF_(x)+barB_(x)` (or) `barT_(y)-barF_(y)=barA_(y)+barB_(y)` (d) `T+mg=ma` |
|
| 39312. |
(n - 1) equal point masses each of mass m are placed at the vertices of a regular n-polygon. The vacant vertex has a position vector vecaw.r.t the centre of polygon. The position vector of centre of mass is |
|
Answer» `VECA/n` |
|
| 39313. |
Force of friction and tension in a string are |
|
Answer» Gravitational FORCES |
|
| 39314. |
In a system of units, the units of mass, length and time are 1 quintal, 1 km and 1h, respectively. In this system 1 N force will be equal to |
|
Answer» 1 new UNIT `THEREFORE" "1"N"=((1)/(100))((1)/(1000))(3600)^(2)=129.6" units"`. |
|
| 39315. |
The displacement of a particle moving along x-axis with respect to time t is x = at + bt^(2) - ct^(3)The dimensions of care |
|
Answer» `[T^(-3)]` Each term on RHS MUST have dimensions of x. `:. [ct^(3)]= [x]` or `[c]= ([x])/([t^(3)])= ([L])/([T^(3)])= [LT^(-3)]` |
|
| 39316. |
When a train of plane wave traverses a medium, individual particles execute periodic motion given by the equation y 4sin(pi)/(2)(2t x/8) Where the length are expressed in centimetres and time in seconds. Calculate the amplitute, wavelength, (a) the phase different for two positions of the same particle which are occupied at time interval 0.4 s apart and (b) the phase difference at any given instant of two particle 12 cm apart. |
|
Answer» Solution :The equation of a wave MOTION is given by `y=A SIN(2pi)/(lambda)(vt+x)`(i) Here, `y 4 sin(pi)/(2)(2t x/8)` This equation canbe written as `y 4sin(2pi)/(32)(16t x)` (ii) comparing `Eq`. (i)with `Eq`. (ii), we get Amplitude `A=4 CM,`wavelength `(lambda)=32 cm`, wave velocity `v=16 cm//s` here frequency is given as `f=(v)/(lambda)=(16)/(32)=(1)/(2)=0.5 HZ` (a). phase of a particle at INSTANT `t_(1)` is given by `phi_(1) (pi)/(2)(2t_(1) x/8)` The phase at instant `t_(2)` is given by `phi_(2) (pi)/(2)(2t_(1) x/8)` The phase difference is given as `phi_(1)-phi_(2)=(pi)/(2)[(2t_(1)+x/8)-(2t_(2)+x/8)]` `pi(t_(1)-t_(2)) pi(0.4)` `(As t_(1)-t_(2)=0.4)` `=180xx0.4=72^@``(pi rad=180^@)` (b). phase different at an instant between two particle with path different `(Delta)` is `phi=(2pi)/(lambda)xxDelta``(2pi)/(32)xx12``(As Delta=12 cm` `(3pi)(4)` |
|
| 39317. |
A hot water cools from 92^(@)C to 84^(@)C in 3 minutes when the room temperature is 27^(@)C. How long will it take for it to cool from 65^(@)C to 60^(@)C? |
|
Answer» Solution :The HOT water cools `8^(@)C` in 3 minutes. The average temperature of `92^(@)C` and `84^(@)C` is `88^(@)C`. This average temperature is `61^(@)C` above room temperature. By using equation, `(dT)/(T-T_(s))=-(a)/(MS)dt or (dT)/(dt)=-(a)/(ms)(T-T_(s))` `(8^(@)C)/("3 min")=-(a)/(ms)(61^(@)C)"...(1)"` Similarly the average temperature of `65^(@)C and 60^(@)C`. The average temperature is `35.5^(@)C` above the room temperature. Then we can write `(5^(@)C)/(dt)=-(a)/(ms)(35.5^(@)C)"....(2)"` By dividing both the equation, we get `((8^(@)C)/("3 min"))/((5^(@)C)/(dt))=-((a)/(ms)(61^(@)C))/(-(a)/(ms)(35.5^(@)C))` `(8xxdt)/(3xx5)=(61)/(35.5)` `dt=(61xx15)/(35.5xx8)=(915)/(284)="3.22 min"` |
|
| 39318. |
If the velocity of light c, Planks constant, h and the gravitational constant G are taken as fundamental quantities, then express mass, length and time in terms of dimensions of these quantities. |
|
Answer» Solution :Here, `c=[LT^-1],h=[ML^2T^-1],` `G=[M^-1L^3T^-2]` `becauseE=hv,h=E/v,G=((Fd^2)/(m_1m_2))` Let `m=c^xh^yG^zto(1)` `implies[M^1L^0T^0]=(LT^-1)^x(ML^2T^-1)^y(M^-1L^3T^-2)^Z` `implies[M^1L^0T^0]=M^(y-z)L^(x+2y+2z)T^(-x-y-2z)` Applying the principle of homegenity of DIMENSIONS, we get `y-z=1to(2),x+2y+3z=0to(3),` `-x-y-2z=0to(4)` Adding EQ.(2), eq.(3) and eq.(4). `2y=1impliesy=1/2` `therefore` From eq.(2) `z=y-1=1/2-1=(-1)/2` From eq.(4) `x=-y-2z=(-1)/2+1=1/2` Substituting the values of x,y & z in eq.(1) , we get `m=c^(1//2)h^(1//2)G^(-1//2)impliesm=sqrt((CH)/G)` Proceeding as above we can show that `L=sqrt((hG)/c^3)andT=sqrt((hG)/c^5)` |
|
| 39319. |
A man is standing on top of a building 100 m high. He throws two balls vertically, one at t = 0 and other after a time interval (less than 2s). The later ball is thrown at a velocity of half the first. The vertical gap between first and second ball is 15 m at t = 2. The gap is found to remain constant. The velocities with which the balls were thrown are (Take g = 10 m s^(-1)) |
|
Answer» `20 m s^(-1) , 10 m s^(-1)` taking the vertical upwards motion of the first stone up to highest point Here, u = `u_1`, v = 0 (At highest point velocity is zero) a = -g, S = `h_1` As `v^(2) - u^(2) = 2aS``THEREFORE (0)^(2) - u_(1)^(2) = 2(-g)h_1`or`h_1 = u_(1)^(2)/(2g)`...(i) For second stone, Taking the vertical upwards motion of the second stone up to highest point here, u = `U_2, v = 0, a = -g, S = h_2` As `v^(2) - u^(2)` = 2as `therefore(0)^(2) - (u_2)^(2) = 2(-g)h_2`or`h_2 = u_(1)^(2)/(2g)`.............(ii) As per question `H_1 - h_2 = 15 m , u_2 = u_1/2` SUBTRACT (ii) from (i), we get, `h_1 - h_2 = u_(1)^(2) /(2g)-(u_(2)^(2)/(2g))` On substituting the GIVEN information, we get `15 = u_(1)^(2)/(2g)-u_(1)^(2)/(2g)=(3u_(1)^(2))/(8g)` or `u_(1)^(2)=(15 xx 8g)/(3)=(15 xx 8 xx 10)/(3)= 400` or`u_1 = 20 m s^(-1)` and`u_2 = U_1/2 = 10 m s^(-1)` 
|
|
| 39320. |
Pitch of sound depends on ……….. . |
|
Answer» FREQUENCY |
|
| 39321. |
Temperature of a body theta is slightly more than the temperature of the surroundings theta_(0). Its rate of cooling ( R ) versus temperature of body (theta) is plotted, its shape would be : |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 39322. |
Explain how Newton derived his law of gravitation from Kepler's third law. |
|
Answer» Solution :Newton considered the orbits of the planets as circular. For circular orbit of radius r, the centripetal acceleration towards the centre is `a=-(v^2)/(r)""...(1)`  Here v is the velocity and r, the distance of the planet from the centre of the orbit. The velocity in TERMS of known quantities r and T, is `v=(2pir)/(T)""...(2)` Here T is the time period of REVOLUTION of the planet. Substituting the value of 'v' in equation (1) we get , `a=-(((2pir)/(T))^(2))/(r)` `=-(4PI^(2)r)/(T^2)""...(3)` Substituting the value of 'a' from (3) in Newton's second law, F = ma where 'm' is the mass of the planet. `F=-(4pi^(2)mr)/(T^2)""...(4)` From Kepler's third law, `(r^3)/(T^2)=k("constant")""...(5)` `(r)/(T^2)=(k)/(r^2)""...(6)` By equation (6) in the force expression, we can arrive at the law of gravitation. `F=-(4pi^(2)mk)/(r^2)""...(7)` Here negative sign implies that the force is ATTRACTIVE and it acts towards the centre.He equated the constant `4pi^(2)k` to GM which turned out to be the law of gravitation. `F=-(GMm)/(r^2)` |
|
| 39323. |
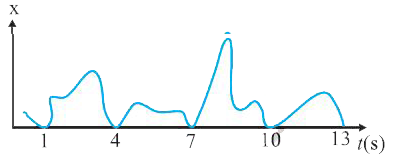
Fig. 14.23 depicts four x-t plots for linear motion of a particle. Which of the plots represent periodic motion? What is the period of motion (in case of periodic motion) ? |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 39324. |
A constant power is supplied to a rotating disc. The relationship between the angular velocity ( omega) of the disc and number of rotations (n) made by the disc is governed by |
|
Answer» `OMEGA PROP N^(1//3)` |
|
| 39325. |
Match list I with list II LIST - I(a) Centrifugal force(b) Centripetal force(c ) Tangential force (d) Angular velocityLIST - II(e ) Along the axis of rotation (f) Towards the centre of rotation(g) Away from the centre of rotation(h) Changes the angular velocity |
|
Answer» a-h, B-g, c-f, d-e |
|
| 39326. |
A 2kg stone is swung in a vertical circle by attaching it at the end of a string of length 2m. If the stringcan with stand a tension 140.6N, the maximum speed with which the stone can be rotated is |
|
Answer» `22ms^(-1)` |
|
| 39327. |
A particle is in linear simple harmonic motion between two points, A and B, 10 cm apart. Take the direction from A to B as the positive direction and give the signs of velocity, acceleration and force on the particle when it is at 6 cm away from B going towards A |
Answer» SOLUTION : VELOCITY is negative, ACCELERATION and force are POSITIVE |
|
| 39328. |
A particle is in linear simple harmonic motion between two points, A and B, 10 cm apart. Take the direction from A to B as the positive direction and give the signs of velocity, acceleration and force on the particle when it is at 3 cm away from A going towards B |
Answer» SOLUTION : VELOCITY, ACCELERATION and FORCE all are POSITIVE |
|
| 39329. |
A particle is in linear simple harmonic motion between two points, A and B, 10 cm apart. Take the direction from A to B as the positive direction and give the signs of velocity, acceleration and force on the particle when it is at 2 cm away from B going towards A, |
Answer» SOLUTION : VELOCITY, ACCELERATION and FORCE all are NEGATIVE |
|
| 39330. |
A particle is in linear simple harmonic motion between two points, A and B, 10 cm apart. Take the direction from A to B as the positive direction and give the signs of velocity, acceleration and force on the particle when it is at the mid point of AB going towards A, |
Answer» SOLUTION : At the mid POINT of AB (at mean position .O.) velocity is MAXIMUM and negative as the particle MOVES towards A. acceleration and force are ZERO |
|
| 39331. |
A particle is in linear simple harmonic motion between two points, A and B, 10 cm apart. Take the direction from A to B as the positive direction and give the signs of velocity, acceleration and force on the particle when it is at the end B, |
Answer» SOLUTION : At the end .B. VELOCITY = 0, ACCELERATION and FORCE are negative |
|
| 39332. |
A particle is in linear simple harmonic motion between two points, A and B, 10 cm apart. Take the direction from A to B as the positive direction and give the signs of velocity, acceleration and force on the particle when it is at the end A, |
Answer» Solution : At the end .A. particle is at extreme position hence velocity is zero. As it is acted up on by RESTORING FORCE TOWARDS mean position .O. its ACCELERATION and force ACTING on it are positive |
|
| 39333. |
State the law of floatation. |
| Answer» Solution :The law of floatation STATES that a body will FLOAT in a liquid if the weight of the liquid displaced by the IMMERSED PART of the body EQUALS the weight of the body. | |
| 39334. |
. (A): Comets move around the sun in elliptical orbits. The gravitational force on the comet due to sun is not normal to the comet.s velocity but the work done by the gravitational force over every complete orbit of the comet is zero (R): Gravitational force is a non conservative force. |
|
Answer» Both .A. and .R. are TRUE and .R. is the correct explanation of .A. |
|
| 39335. |
Which of the following are positive and which are negative work done ? Work done by friction on a body sliding down an inclined plane. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :NEGATIVE | |
| 39336. |
In the Searle's method to determine the Young's modulus of a wire, a steel wire of length 156 cm and diameter 0.054 cm is taken as experimental wire. The average increase in length for 1 1/2 kg wt is found to be 0.050 cm. Then the Young's modulus of the wire. |
|
Answer» `3.002xx10^(11)N//m^(2)` |
|
| 39337. |
It is well known that a raindrop falls under the influence of the downward gravitational force and the opposing resistive force. The latter is known to be proportional to the speed of the drop but is otherwise undetermined.Consider a drop of mass 1.00 g falling from a hwight 1.00 km .It hits the groundwith a speed of 50.0 ms^(-1) (a) What is the work done gravitational force ? (b) What is the work done by the unknown resistive force ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(a) Wg = 20 J , (B) `Wr = - 17.55` |
|
| 39338. |
Define vibratory motion. Give example |
| Answer» Solution :If an object or particle executes a to-and-fro motion about a fixed point then it is said to bein vibratiory motion . This is sometimes also called OSCILLATION . EG: Vibration of a string on a GUITAR . | |
| 39339. |
(A): In the pressure equation P=(1)/(3)av_(rms)^(2),the term 'a' represents density of gas (R ):rms velocity of gas v_(rms)=sqrt((3RT)/(M)) |
|
Answer» Both (A) and ( R) are TRUE and (R ) is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of (A) |
|
| 39340. |
A scooter can produce a maximum acceleration of 5ms^(-2). Its brakes can produce a maximum retardation of 10ms^(-2). The minimum time in which it can cover a distance of 1.5 km is? |
Answer» SOLUTION : If v is the maximum velocity attained, then during acceleration is between A, B `v^(2)-o^(2)=2xx5xxS_(1)impliesS_(1)=(v^(2))/(10)`, Also, during RETARDATION `o^(2)-v^(2)=2xx10xxS_(2)impliesS_(2)=(v^(2))/(20)` `S=S_(1)+S_(2)implies1500=(v^(2))/(10)+(v^(2))/(20)=(3v^(2))/(20)or` `v^(2)=(1500xx20)/(3)=10000 or v=100ms^(-1)` `v=alphat_(1)impliest_(1)=(100)/(5)=20SEC` `v=betat_(2)impliest_(2)=(100)/(10)=10sec` Total time `=20+10=30sec`. |
|
| 39341. |
A ball of mass 50 g falls from rest vertically downwards through a distance of 40 m and hits the ground. Find the kinetic energy and final velocity of the ball before it hits the ground (g = 9.8 ms^(-2)). |
|
Answer» Solution :MASS of ball, m = 50 gm `= 50 XX 10^(-3)` kg , Height of fall, h = 40 m , g = 9.8 `ms^(-2)` From law of conservation of energy, loss in P.E = gain in K.E. `RARR mgh = (1)/(2) MV^(2) and v = sqrt(2 gh)` K.E. = mgh `rArr` K.E. = `50 xx 10^(-3) xx 9.8 xx 40 = 19.6` J Final VELOCITY, `v = sqrt(2 xx 9.8 xx 40) = 28 ms^(-1)` |
|
| 39342. |
What is the Poisson's ratio of the substance whose volume remains unchanged under elastic strains? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39343. |
The graphical variation of the readings of an arbitrary scale X and Reaumer scale corresponding to the same temperatures. The temperature in Kelvin scale when the readings of the two scales coincide will be |
|
Answer» 323 |
|
| 39344. |
An automobile that is towing a trailer is accelerating on a level road. The force that the automobile exerts on the trailer is |
|
Answer» equal to the force the TRAILER EXERTS on the automobile |
|
| 39345. |
A body is projected with a velocity 50ms^(-1). Distance travelled in 6^(th) second is [g=10ms^(-2)] |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 39346. |
If reflecting and transmitting powers of a body are 0.2 and 0.3 units, then its Absorptive power will be |
|
Answer» 0.1 |
|
| 39347. |
A capilary tubes of radius R is dipped vertically in a liquid with surface tension T. If the rise of the liquid in the tube is h then the weight of the liquid column in the tube is |
| Answer» ANSWER :A | |
| 39348. |
The mass of moon is 1% of mass of earth. The ratio of gravitational pull of earth on moon and that of moon on earth will be |
|
Answer» `1:1` |
|
| 39349. |
The Marina trench is located in the Pacific Ocean, and at one place it is nearly eleven km beneath the surface of water. The water pressure at the bottom of the trench is about 1.1 xx 10 ^(8)Pa. A steel ball of initial volume 0.32 m^(3) is dropped into the ocean and falls to the bottom of the trench. What is the change in the volume of the ball when it reaches to the bottom ? |
|
Answer» Solution :`P =1.1 xx 10 ^(8) pa` `B =1.6 xx 10 ^(11) NM ^(-2)` BULK modulus `B = (P)/((Delta V)/(V))` (MAGNITUDE) `B = (PV)/(Delta V) ` `therefore Delta V =(PV)/(B) = (1.1 xx 10 ^(8) xx 0.3)/(1.6 xx 10 ^(11))=22 x 10 ^(-5)` `~~ 2.2 xx 10 ^(-4) m ^(3)` Notye : Answer of Text-book is not matching, if for steel B = 140 GPa, then the answer of Text-book will be `Delta V =2.51 xx 10 ^(-4) m ^(3).` |
|
| 39350. |
The density of water is more than the density of air . Even then clouds containing water droplets don’t fall and continue to float. Explain. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :At terminal velocity `v_T (alpha r^2)`, dur to SMALL size of droplets in the CLOUD, `v_T` is very small, so the cloud falls very SLOWLY towards earth and appears to float in the SKY. | |