Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 38301. |
A block of mass m requires a horizontal force F0 to move it on a horizontal metal plate with constant velocity. The metal plate is folded to make it a right angled horizontal trough. Find the horizontal force F that is needed to move the block with constant velocity along this trough. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 38302. |
Amotorof powerP_0 isusedtodeliverwateratacertain ratethroughagivenhorizontalpipe.Toincreasethe rateof flowof waterthroughthesamepipentimes,the power of the moter is increased to P_1 to P_0 is |
|
Answer» n : 1 |
|
| 38303. |
The piston cylinder arrangement shon contains a diatomic gas at temperature 300 K The crooss sectinal area of the cylinder is 1 m^(2). Initially the height of the piston above th base of the cyclinder is 1 m. The temperature is now raised to 400 K at constatn pressure. Find tge bew jgeauggt if tge oustib avive tge vase if tge cylinder.If the psiton is now brouyght back to its original height without any heat losss, find the new equilibrium temperaturef of the gas. You can leave the answer in fraction. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 38304. |
Assertion : Deep inside a liquid density is more than the density on surface. Reason : Density of liquid increases with increase in depth. |
|
Answer» If both Assertion and REASON are correct and Reason is the correct EXPLANATION of Assertion. |
|
| 38305. |
Show that a=(v^2)/r and hence obtain an expression for centripetal force. |
|
Answer» Solution :Let `vecr` and `vecr`, be the position vectors and `vecv` velocities of the OBJECT when it is it point P and P. By definition, velocity at a point is ALONG the tangent at that point in the direction of the motion. Since the path is CIRCULAR, `vecv` is perpendicular to `vecr` and `vecv` is perpendicular to `vecr` Therefore, `/_\vecv` is perpendicular to `/_\vecr`. Average acceleration `(/_\vecv)/(/_\t)` is perpendicular to `/_\vecr` The magnitude of `veca` is, by definition, given by `|veca|=lim_(/_\t to0)(/_\vecv)/(/_\t)` The TRIANGLE formed by the position vectors is similarly to the triangle formed by the velocity vectors. 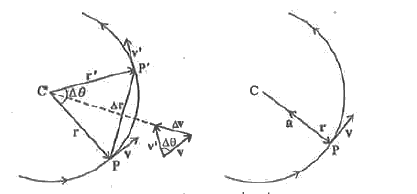 i.e, `(|/_\vecv|)/v=(|/_\vecr|)/r "or"|/_\vecv|=v(|/_\vecr|)r` Therefore, `|veca|=lim_(|/_\vecv)/(/_\t)=lim_(/_\t to0)(v|/_\vecr|)/(r/_\t)=(vecv)/(r)lim_(/_\t to0)(|/_\vecr|)/(/_\t)` If `/_\t` is very small, `/_\theta` will also small. The arc PP' is approximately equal to `|/_\vecr|` i.e., `lim_(/_\t to0)(|/_\vecr|)/(/_\t)=v` Thus, centripetal acceleration `|veca|=v/fv=(v^2)/(r)` and `veca=v/r(dvecr)/(dt)` The centripetal acceleration is always DIRECTED towards the centre. The centripetal force=ma. |
|
| 38306. |
What are the characteristics of geostationary satellite and polar satellite ? Why polar satellite are called weather satellite -Explain. |
|
Answer» Solution :Geostationary satellite are PLACED on the equatorial PLANE at a height of nearly 36000 km from the earth.s surface. Since the motion of such a satellite is same as that of the DIURNAL motion of the earth, the satellite seems to be stationary with respect to the earth.s surface. On the other hand, polar satellite are placed at a height of 800 km, from the surface of the earth, aligned with the polar plane. To revolve around the earth once, a polar satellite takes about 2 hours. Polar satellite are placed comparatively nearer to the earth.s surface and travel over a vast area while revolving . THUS they are suitable for observing the WEATHER and hence, are called .weather satellite.. |
|
| 38307. |
Is the work done bynon conservative force is always negative ? Discuss . |
| Answer» Solution :No. If the body does not move EVEN if a force acting on the body ,then work is zero due to frictional force and REASON for MOTION is FRICTION and work done due to the friction force is positive . | |
| 38308. |
A satellite is launched into circular orbit of radius R around the earth while a second satellite is launched into an orbit of Radius 1.02 R. The percentage change in the time periods of the two satellite is |
|
Answer» 0.7 |
|
| 38309. |
A uniform disc is rotating at a constantt speed in a vertical plane about a fixed horizontal axis passing through the centre of the disc. A piece of the disc from its rim detaches itself from the disc at the instant when it is at horizontal level with the centre of the disc and moving upward. Then about the fixed axis, the angular speed of the |
|
Answer» REMAINING DISC remains unchanged |
|
| 38310. |
A block of mass m hangs on a vertical spring. Initially the spring is unstreched, it is now allowed to fall from rest. Find (a) the distance the block falls if the block is released slowely, (b) the maximum distance the block falls before it beigns to move up. |
|
Answer» Solution :When the block FALLS slowely, it comes to rest at a distance `y_(0)`, which is referred to as the equlibrium POSITION. From, condition of equilibrium, `sumF_(y)=ky_(0)-MG=0 ory_(0)=(mg)/(k)`  (b) When the block is released suddenly, it oscilates about the equilibrium position. Initially the speed of the block INCREASES then reaches maximum value and then DECREASES to zero at the lowest position. In this situation the block oscillates about the equilibrium position. The block is released from rest, there fore its total mechanical energy initially. `E_(i)=U_(g)+U_(s)+K=0+0+0` Final total mechanical energy, `E_(f)=-mgy_(m)+(1)/(2)ky^(2)+0` From conservation of energy, `E_(i) = E_(f)` `0=-mgy_(m)+(1)/(2)ky^(2)ory_(m)=(2mg)/(k)=2y_(0)` |
|
| 38311. |
Hailstones falling vertically with a speed of 10 m s^-1, hit the wind screen (wind screen makes an angle 30^@ with the horizontal) of a moving car and rebound elastically. Find the velocity of the car if the driver finds the hailstones rebound vertically after striking. . |
|
Answer» Let the velocity of hailstone w.r.t. car be `vec v_(h,c)` Then `vec v_h = vec v_(h,c) + vec v_c` `(vec v_h)_x = (vec v_(h,c) + vec v_c)_x` `vec v_h = vec v_(h,c) + vec v_c` `(vec v_h)_x = (vec v_(h,c) + vec v_c)_x` But `(vec v_h)_x = 0`, since hailstones fall vertically down. `rArr (vec v_h)_x = -(v cos 30^@) rArr |vec v_c|_x = |vec v_(h,c)|_x` Now, `(vec v_h)_y = (vec v_(h,c) + vec v_c)_y` Since `(v_h)_y = -10 ms^-1 , (v_c)_y = 0 rArr -10 = -V sin 30^@ + 0` `V sin 30^@ = 10 rArr V = 20 ms^-1` `(vec v_c)_x = V cos 30^@ = 20 xx (SQRT(3))/(2) = 10 sqrt(3) ms^-1` `vec v_c = 10 sqrt(3) ms^-1`.  , ,  . .
|
|
| 38312. |
Give the quantities for which the following are the dimensions: M^(0)L^(0)T^(0) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 38313. |
A lift is freely falling from 8^(th) floor and is just about to stop at 4^(th) floor. Taking ground floor as origin and positive direction upwards for displacement, velocity, acceleration. Which one of the following is correct? |
|
Answer» `XLT0, vlt0, AGT0` |
|
| 38314. |
A man walks on a straight road from his home to a market 2.5km away with a speed of 5km//h . Finding the market closed , heinstantley turns and walks back home with a speed of 7.5km//h. The average speed of the man over the interval of time 0 to 40 nim , is equal to |
|
Answer» |
|
| 38315. |
A wheel in uniform motion about an axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to its plane is considered to be in mechanical (translation plus rotational) eqilibrium because no net external force ot torque is required to sustain its motion. However, the particles that constitute the wheel do experience a centripletal acceleration directed towards the centre. How do you reconcile this fact with the wheel being in equilibrium ? How would you set a half-wheel into uniform motion about an axis passing through the centre of mass of the wheel and perpendicular to its plane ? Will you require external forces to sustain the motion ? |
|
Answer» Solution :A WHEEL is a rigid body. The centripetal ACCELERATIONS of the particle of the wheel arise due to the internal elastic forces which cancel out in PARIES. In a half wheel, the distribution of mass about its centre of mass (through which axis of rotation PASSES) is not symmertical. Therefore, the direction of angular MOMENTUM of the wheel does not coincide with the direction of its angular velocity. Hence, an external torque is required to maintain the motion of the half wheel. |
|
| 38316. |
Two identical springs each of force constant k are connected in series Calculate the frequency of the system |
|
Answer» Solution :For series COMBINATION, the EFFECTIVE force COSTANT, `k_(s)=(kxxk)/(k+k)= (k)/(2)` `:.` Frequency, `v_(s)=(1)/(2pi) sqrt((k_(s))/(m))=(1)/(2pi) sqrt((k//2)/(m))` `=(1)/(2pi) sqrt((k)/(2m)) ""...(1)` |
|
| 38317. |
Figure shows the P- V diagram of an ideal gas undergoing a change of state from A to B. Four different parts I, II, III and IV as shown in the figure may lead to the same change of state. |
|
Answer» Change in internal energy is same in IV and III cases, but not in I and II. `dU_(A to B) = n C_V DeltaT` `=nC_V(T_B-T_A)` DEPENDS on only the temperature of A and B. HENCE, internal energy is same for all four paths. It depends on the temperature of A and B. Moreover, the work done from state A to state B.`W_(A to B)` = AREA under the graph `P to V` It is maximum for path I. |
|
| 38318. |
The angular frequency of a fan increases from 30 rpm to 60 rpm in pi s. A dust particle is present at a distance of 20 cm from axis of rotation. The tangential acceleration of the particle in pi s is |
|
Answer» `0.8 MS^(-2)` |
|
| 38319. |
A horizontal disc rotates freely about a vertical axis through its centre. A ring having the same mass and radius as the disc is now gently placed on the disc After same time, the two rotate with a common angular velocity |
|
Answer» some friction exists between the DISC and the rind |
|
| 38320. |
A projectile is thrown at an angle of 30^@with a velocity of 10m/s. the change in velocity during the time interval in which it reaches the highest point is |
|
Answer» 10m/s |
|
| 38321. |
The two ends of a metal rod are maintained at temperatures 100^(@)C and 110^(@)C. The rate of heat flow in the rod is found to be 4.0" Js"^(-1). If the ends are maintained at temperatures 200^(@)C and 210^(@)C, the rate of heat flow will be : |
|
Answer» `16.8" Js"^(-1)` (i) `H_(1)kA((110-100)/(L))` `H_(1)=10(kA)/(L)` (ii) `H_(2)=kA((210-20)/(L))=10(kA)/(L)` `:.H_(1)=H_(2)` `:." Js"^(-1)=H_(2)` |
|
| 38322. |
Is whole of the kinetic energy lost in any perfectly inelastic collision? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :No, only that MUCH AMOUNT of kinetic ENERGY is lost as is necessary for the CONSERVATION of momentum. | |
| 38323. |
A ball is projected vertically upwards with a velocity v . It comes back to ground in time t. which v-t graph shows the motion correctly ? |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 38324. |
State Newton's law of cooling verify with an experiment. |
|
Answer» <P> Solution :(i) It states that the rate of cooling of a body is directly proportional to the temperature differ between the body and the surroundings.(ii) Consider a spherical calorimeter of mass m whose outer surface is blackened. It is filled with HOT water of mass m, the calorimeter with thermometer is suspended from a stand. (iii) The calorimeter & the hot water radiate heat energy to the surrounding. Using a stop clock, the temperature is noted for every 30 second interval of time see the temperature falls by about `20^(@)C`. The readings are tabulated. If the temperature falls from `T_(1)` to `T_(2)` in t sec, the quantity of heat energy lost by radiation `Q=(ms+m_(1)s_(1))(T_(1)-T_(2))`, where 'S' is the specific heat capacity of the MATERIAL of the calorimeter & `S_(1)` - specific heat capacity of water. Rate of cooling = `("Heat energy lost")/("time "t_(n))` `therefore (Q)/(E)=((ms+m_(1)s_(1))(T_(1)-T_(2)))/(t)` Room temperature - `T_(0)` (v) Average excess temperature of the colorimeter over that of the surroundings = `(T_(1)+T_(2))/(2)-T_(0)` (vi) Acceleration to Newton's law of cooling `(Q)/(t)prop((T_(1)+T_(2))/(2)-T_(0))` (vii) Assume the pressure of the gas remains constant during an infinitesimally small outward displacement dy then work done `dW-F.dx=P.A.dx` `dW=P.dV` (viii) Total work done by the gas from volume `V_(1)` to `V_(2)` is `W=underset(V_(1))overset(V_(2))intP.dv` (ix) But `PV^(gamma)` = constant (k) `gamma=(C_(P))/(C_(V))` `therefore W=underset(V_(1))overset(V_(2))intkV^(gamma)dV=k[(V^(1-gamma))/(1-gamma)]_(v_(1))^(v_(2))" "[becauseP=(k)/(V^(gamma))]` `thereforeW=(k)/(1-gamma)[V_(2)^(1-gamma)-V_(1)^(1-gamma)]` `W=(1)/(1-gamma)[kV_(2)^(1-gamma)-kV_(1)^(1-gamma)]` `P_(2)V_(2)^(gamma)=P_(1)V_(2)^(gamma)=k` (x) Subtract the value of k `therefore W=(1)/(1-gamma)[P_(2)V_(2)^(gamma),V_(2)^(1-gamma)-P_(1)V_(1)^(gamma),V_(1)^(1-gamma)]` `W=(1)/(1-gamma)[P_(2)V_(2)-P_(1)V_(1)]` It `T_(2)` is the final temperature of the gas in adiable expansion, then `P_(1)V_(1)=RT_(1),P_(2)V_(2)=RT_(2)` `therefore W=(1)/(1-gamma)[RT_(2)-RT_(1)]` This is the equation for the work done during adiabating process. |
|
| 38325. |
If radius of earth becomes half, then find the weight. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`implies` Weight `W = MG =(GM_em)/R_e^2` Since the RADIUS becomes half, `W. = mg. = (GM_(e) m)/((R_e^2)/4)` `:. W. = 4 ((GM_em)/R_e^2)` `W. = 4W` |
|
| 38326. |
A body of mass 1.5 kg is allowed to slide down along a quadrant of a circle from the horizontal position. In reaching to the bottom, Its velocity is 8m/s. The work done in overcoming the friction is 12J. The radius of circle is (g = 10 ms^(-2)) |
|
Answer» 4 m |
|
| 38327. |
In Millikan's oil drop experiment what is the terminal speed of an unchanged drop of radius 20xx10^-5m and density 1.2xx10^3 kg. m^-3. Take the viscosity of air at the temperature of the experiment to be 1.8xx10^-5Pa. s. How much is the viscous force on the drop at that speed ? Neglect buoyancy of the drop due to air. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`5.8cm. S^-1, 3.9xx10^(-10)N` | |
| 38328. |
Two capacitors of capacities (3pm0.09)mu F and (6pm 0.09)muF are connected in parallel. Their equivalent capacity is |
|
Answer» `( 2 PM 0.13 ) MU F` |
|
| 38329. |
Explain surface energy and surface tension. |
Answer» Solution :An extra energy is associated with surface of liquid , the creation of more surface keeping volume fixed requires additional energy. As SHOWN in figure (a) a U- shape frame is made from wire , the wire PQ slide without firction over the rides AP and BQ. This frame dipped and taken out of the soap solution , thin film APQB is formed from the frame. In figure (a) film is in equilibrium. In figure (b) it is shown that the film is STRETCHED at extra distance d. Since the area of the surface increases ,the system now more energy , means that some work has been done against an internal force. Let this internal force be F.The work done by the applied force is , `W=vecF*vecd=Fd` ...(1) From the CONSERVATION of energy , this is stored as additional energy in the film. If the surface energy of the film is S per unit area , the extra area is 2ld. (Because `DeltaA`=length `xx` breadth ld and film has two free surface,so 2ld is present. The liquid in between , so there are two surfaces and the extra energy is`=(2ld)S`. `thereforeW=(2ld)S=SDeltaA[because2ld`= increase in area] `thereforeS=(W)/(DeltaA)` `thereforeS=(fd)/(2ld)=(F)/(2l)` This quantity S is the magnitude of surface tension .It is EQUAL to the surface energy per unit area of the liquid interface and is also equal to the forceper unit lenght exerted by the FLUID on the movable bar. |
|
| 38330. |
The gravitational potential energy of a body at distance r from the centre of earth is U. Its weight at a distance 2r from the centre of earth is |
|
Answer» U/r |
|
| 38333. |
A child running a temperature of 101^(@)F is given an antipyrin (i.e. a medicine that lowers fever) which causes an increase in the rate of evaporation of sweet from his body. If the fever is brought down to 98^(@)F in 20 min., what is the average rate of extra evaporation caused, by the drug ? Assume the evaporation mechanism to be the only way by which heat is lost. The mass of the child is 30 kg. The specific heat of human body is approximately the same as that of water and latent heat of evaporation of water at that temperature is about 580cal.g^(-1). |
|
Answer» Solution :Here, fall in TEMP. = `DeltaT=101-98=3^(@)F=3xx5/(9)""^(@)C=5//3""^(@)C` Mass of child, m = 30 kg SP. heat of human body = sp. heat of water, `c=1000cal.kg^(-1)""^(@)C^(-1)` `therefore` Heat lost by the child, `DeltaQ=mcDeltaT=30xx1000xx5/3=50000"cals"` If m. be the mass of water evaporation in 20 min. then, `m.L=DeltaQorm.=(DeltaQ)/L=50000/580=86.2g` `therefore` AVERAGE rate of EXTRA evaporation = `86.2/20=4.31g"min"^(-1)` |
|
| 38334. |
In non-uniform circular motion , particle will have . . . . . And tangential acceleration |
|
Answer» centripetal |
|
| 38335. |
A particle moves on a circle of radius r with centripetal acceleration as function of time as a_e = k^2 rt^2where k is a positive constant. Find the resultant acceleration. |
|
Answer» `kt^2` |
|
| 38336. |
Law od gravitation is not applicable if (A) Velocity of moving objects are comparable to velocity of light (B) Gravitational field between objects whose masses are greater than the mass of sun. |
|
Answer» A is true, B is FALSE |
|
| 38337. |
The dimensional equation for magnetic flux is |
|
Answer» `ML^(2)T^(-2)I^(-1)` |
|
| 38338. |
The potential energy in joules of a particle of mass 1 kg moving in a plane is given by U = 3x + 4y, the position coordinates of the point being x and y, measured in metres. If the particle is initially at rest at (6, 4), then: |
|
Answer» its ACCELERATION is of magnitude `5 m//s^(2)` |
|
| 38339. |
A disc of mass 50 kg rotates freely about a fixed horizontal axis through its centre. A thin cotton pad fixed to its rim can absorb water. Water drips onto the pad at the rate of 25 grams per sec, falling along a line passing through the horizontal axis. The angular velocity of the disc will get reduced to one fourth of its initial value time ____x10^(3) s. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 38340. |
Statement I : For a floating body to be in stable equilibrium, its centre of buoyancy must be located above the centre of gravity. Statement II : The torque developed by the weight of the body and the upthrust will restore the body back to its normal position, after the body is disturbed. |
|
Answer» Statement I is true, statement II is true , statement II is a CORRECT EXPLANATION for statement I. |
|
| 38341. |
Supposeapersonwantsto increasethe efficienyof thereversibleheatenginethatisoperatingbetween100^(@)C and 300^(@)C Hehadtwowaysto increasethe efficiency . ( a)Bydecreasing thecoldreservoirtemperaturefrom 100^(@)C to 50^(@)Candkeepingthe hotreservoirtemperatureof the hotreservoirfrom 300^(@)Cto 350^(@)Cbykeepingthecoldreservoirtemperatureconstnatwhichis thesuitablemethod ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Heat engine operates at initial temperature `=100^(@)C+273=373K` Final temperature `=300^(@)C+273=573 K` At MELTING point `=273K` `"Efficiency "eta=1-(T_(2))/(T_(1))=1-(272)/(573)=0.3491, eta=34.9%` (a) By DECREASING the cold RESERVOIR, efficiency `T_(1)=350^(@)C+273=623K, T_(2)=100^(@)C+273=373K` `eta=1-(T_(2))/(T_(1))=1-(323)/(573)=0.436` `eta=43.6%` (B) By increasing the temperature of hot reservoir, efficiency, `T_(1)=350^(@)C+273=623K, T_(2)=100^(@)C+273=373K` `eta=1-(T_(2))/(T_(1))=1-(373)/(623)=0.401` `eta=40.12%` Method (a) More efficiency than method (b). |
|
| 38342. |
A ballet dancer spins about a vertical axis at 120 rpm with arms outstretched. With her arms folded, the moment of inertia about the axis of rotation decreases by 40%. Calculate the new rate of rotation. |
|
Answer» Solution :`n_(1)=120 rpm , n_(2)= ?"" I_(1)omega_(1)=I_(2)omega_(2)` Let `I_(1)=100` UNITS, then `I_(2)=60` units `100xx120 = 60xx omega_(2) rArr omega_(2)=200` rpm. |
|
| 38343. |
The error in the measurement of radius of a drde is 0.6%. Find the percentage error in the calculation of the area of the circle. |
| Answer» SOLUTION : AREA `A=pir^2(DELTAA)/Axx100=2xx(DELTAR)/rxx100=2xx0.6=1.2%` | |
| 38344. |
Two rods of different materials having coefficients of thermal expansion alpha_(1) , alpha_(2) and Young's Moduli Y_(1), Y_(2) respectively are fixed between two rigid massive walls. The rods are heated such that they undergo the same increase in temperature. There is no bending of the rods. If alpha_(1) : alpha_(2) = 2 : 3, the thermal stresses developed in the two rods are equal provided Y_(1) : Y_(2) is equal to |
|
Answer» `2:3` Compression in the rod `Deltal_(1)= (-F)/(A) (l_(1))/(Y_(1))` or the length of the rod remains unchanged `alpha_(1)l_(1)DELTA theta= (-Fl_(1))/(AY_(1))` or `alpha_(1) Delta theta = (-F)/(AY_(1))--- (i)` Similarly for second rod `alpha_(2) Delta theta = (-F)/(AY_(2))--- (ii)` `(alpha_(1))/(alpha_(2))=(Y_(2))/(Y_(1))or(Y_(1))/(Y_(2))=(alpha_(2))/(alpha_(1))=(3)/(2)` |
|
| 38345. |
A block of mass 15 kg is placed on a long trolley . The coefficient of friction between the block andthe trolley is 0.18. The trolley accelerates from rest with 0.5ms^(-2) for 20s and then moves with uniform velocity. Discuss the motion of theblock as viewed by (a) a stationary observer on theground (b) as observer moving with the trolley. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 38346. |
The moment of inertia of a thin uniform rod of mass M and length L about an axis passing through its midpoint and perpendicular to its length is I_(0) . Its moment of inertia about an axis passing through one of its ends and perpendicular to its length is |
|
Answer» `I_(0) +ML^(2)//2` `I = I_(CM) + Md^2` where `I_(CM)` is the moment of inertia of the given rod about an axis passing through its centre of mass and perpendicular to its length and d is the distance between TWO parallel axes. Here `I_(CM) = I_(0) , d = (L)/(2) therefore I = I_(0) + M ((L)/(2))^(2) = I_(0) + (ML^(2))/(4)` |
|
| 38347. |
From a uniform disk of radius R, a circular hole of radius R/2 is cut out. The centre of the hole is at R/2 from the centre of the original disc. Locate the centre of gravity of the resulting flat body. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :at R/6 from the CENTER of original disc OPPOSITE to the center of CUT PORTION | |
| 38348. |
A satellite s is moving in an elliptical orbit ,paround the earth. The mass of the satellite is very small compared to the mass of the earth, Then, |
|
Answer» The acceleration of s is always directedtowards the centre of EARTH. |
|
| 38349. |
If the value of 'g' on the surface of the moon is g// 6, the time period of a pendulum on the surface of the moon w.r.t time period on the earth will be |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 38350. |
(A) : The soldiers marching on a suspended bridge are advised to go out of steps. (R): Frequency of marching steps may match with the natural frequency of oscillation of bridge. |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are true and R' is the correct EXPLANATION of 'A' |
|