Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 38351. |
A person of mass 72 kg sitting on ice pushes a block of mass of 30kg on ice horizontally with a speed of 12ms^(1) . The coefficient of friction between the man and ice and between block and ice in 0.02. If g =10ms^-2, the distances between man and the block, when they come to rest is |
| Answer» ANSWER :D | |
| 38352. |
A student measures the thickness of a human hair using a microscope of magnification 100. He makes 20 observations and find that the average thickness (as viewed in the microscope) is 3.5 mm. What is the estimate of the thickness of hair? |
|
Answer» `0.5 CM` |
|
| 38353. |
The kinetic energy of a particle, executing SHM, is 16 J when it is at its mean position. If the amplitude of oscillations is 25 cm, and the mass of the particle is 5.12 kg, the time period of its oscillation is…………. |
|
Answer» `pi//5s` `T=(2pi)/(omega)=piAsqrt((2m)/(E))=pixx0.25xxsqrt((2xx5.12)/(16))=(pi)/(4)xxsqrt(0.64)=(pi)/(5)s` |
|
| 38354. |
A simple pendulum of length (10)/(3) meter with a bob of mass 3 m is hanging freely from a rigid support. A bullet of mass .m. is fired with a velocity 50ms^(-1) from the ground at an angle .theta. with the horizontal. When the bullet is at its highest point of its trajectory, it collides head on with the bob of the pendulum and gets embeded in the bob. After collision, if the pendulum moves through a maximum angleof 120^(@), then the value of .theta. is (g = 10ms^(-2)) |
|
Answer» `COS^(-1) (0.8)` |
|
| 38355. |
Describe the relationship between stress applied to a body and strain deveoped in it using graphical method? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Portion OA:In this region, stress is very small such that stress is proportional to strain, which means Hooke's law is valid. The point A is called limit of proportionality because above this point Hooke's law is not valid. The slope of the line OA gives the YOUNG's modulus of the wire. (ii) Portion AB:This region is reached if the stress is increased by a very small amount. In this region, stress is not proportional to the strain. But once the stretching FORCE is removed, the wire will regain its original length. This behaviour ENDS at point B and hence, the point B is known as yield point. The elastic behaviour of the material in stress-strain curve is OAB. (iii) Portion BC:If the wire is stretched beyond the point B, stress is increases and the wire will not regain its original length after the removal of stretching force. (iv) Portion CD:With further increase in stress (beyond the point C), the strain increases rapidly and reaches the point D. Beyond D, the strain increases even when the load is removed and BREAKS (ruptures) at the point E. Hence, the maximum stress (here D) beyond which the wire breaks is called breaking stress or tensile strength. The corresponding point D is known as fracture point. The region BDDE represents the PLASTIC behaviour of the material of the wire. |
|
| 38356. |
The numebr of significant figures in 2.64xx10^(4)kg is |
|
Answer» 2 |
|
| 38357. |
From an elevated point P a stone is projected verticallyupward. When it reaches a distance y below the point of projection its velocityis double the velocity when it was at a height y above p. The greatest height reached by it above P is |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 38359. |
The resultant of two forces at right angles is 13N. The minimum resultant of the two forces is 7 N. The forces are |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 38360. |
Find the velocity with which a body can beprojected vertically upwards so that it can reach a height equal to the radius of the earth. The radius of the earth =6400 km, g=980 cm*s^(-2). |
|
Answer» Solution :Initial distance of the body from the centre of the earth=radius of the earth =R. Final distance of the body from centre of the earth =R+R=2R Let MASS of the earth =M , mass of the body =m, VELOCITY of projection from the earth.s surface =v, Hence , its kineitc energy on the earth.s surface `=1/2 mv^2` At a height R above the earth.s surface , the body stops momentarily and then falls. Hence, at that height R, KINETIC energy =0. Potential energy on the earth.s surface `=-(GMm)/(R)` `therefore` Again, potential energy at height R =`-(GMm)/(2R)` and its total energy at that height =0 `-(GMm)/(2R)=-(GMm)/(2R)` From the law of conservation of energy `1/2 mv^2-(GMm)/R=-(GMm)/(2R)` or, `1/2 mv^2=(GMm)/R -(GMm)/(2R)=(GMm)/(2R)` `=(GM)/(R^2)*(mR)/2=g*(mR)/2=1/2 mgR` `therefore v^2=gR` or `v=sqrt(gR)=sqrt(980xx64xx10^7)=79.2xx10^4 cm*s^(-1)` `=7.92xx10^5 cm*^(-1)=7.92 km*s^(-1)`. ALTERNATIVE METHOD: Let the radius of the earth be R, the potential energy of the bodyon the earth.s surface be 0 , and the acceleration due to gravity at a height h above the earth.s surface be `g^.`. Hence, the potential energy at height h is `mg^.h`. For a further increase dh height , let increase in potential energy be DW. `therefore dW=mg^.dh=mg""(R^2)/((R+h)^2)dh [because g^.=(R^2)/((R+h)^2)*g]` Hence , the total increase in the potential energy for an increase in height R from the surface of the earth, `int_0^WdW=int_0^Rmg""(R^2)/((R+h)^2)dh` `or,W=mgR^2[-1/(R+h)]_0^R =mgR^2(-1/(R+R)+1/R)` `=(mgR^2)/(2R)=1/2mgR` Let the kinetic energy of the body on the earth.s surface =`1/2 mv^2`. As per the question, the kinetic energy at a height R from the earth.s surface is 0. Hence,from the law ofconservation of energy, `1/2mv^2=1/2mgR or, v^2=gR` `or, v=sqrt(gR)=7.92xx10^5cm *s^(-1)=7.92 km*s^(-1)`. |
|
| 38361. |
A physical quantity 'P' is given by P= in_(0)L (Delta V)/(Delta t), where in_(0) is electric permittivity, L is length, Delta V is potential difference and Delta t is time interval. The dimensional formula of P is same as that of |
|
Answer» resistance |
|
| 38362. |
A small block of mass m is kept on a rough inclined surface of inclination theta fixed in an elevator. The elevator goes up with a uniform velocity V and the block does not slide on the wedge. The work done by the force of friction on the block in a time t will be |
|
Answer» ZERO |
|
| 38363. |
You lift a suitcase from the floor and keep it on a table. The work done by you on the suitcase does not depend on(a) the path taken by the suitcase(b) the time taken by you in doing so(c ) the weight of the suitcase(d) your weigt |
|
Answer» a, b & d are CORRECT |
|
| 38364. |
At 27^0 C,The KE of an ideal gas is E.if temperature is increased to 327^0 C,K.E is |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 38365. |
In an experiment the values of refractive index of glass were found to be 1.54, 1.53, 1.44, 1.54, 1.56, 1.45. The relative error and percentage error are |
|
Answer» 0.04, 4% |
|
| 38366. |
In which direction of themotion of the particle does centripetal force act ? |
|
Answer» parallel |
|
| 38367. |
A rubber ball filled with water, having a small hole os used as the bob of a simple pendulum. The perod of such a pendulum |
|
Answer» Is a constant |
|
| 38368. |
The percentage error in the measurement of mass and speed are 2% and 3% respectively. Maximum estimate of percentage error of K.E |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 38369. |
The Sun's angular diameter is 30''. The distance of Earth from Sun is 1.496xx10^(11) m, then find the diameter of the Sun. (1''= 4.85xx10^(-6) rad) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 38370. |
Two discs one of density 7.2 g/cm^(3) and the other of density 8.9 g/cm^(3) are of same mass and thickness. Their moments of inertia are in the ratio |
|
Answer» `8.9 : 7.2` As masses of two DISCS are equal , hence `(PI r_(1)^(2) t) rho_(1) = (pi r_(2)^(2) t) rho_(2)` or `(r_(1)^(2))/(r_(2)^(2)) = (rho_(2))/(rho_(1)) therefore (I_(1))/(I_(2)) = (rho_(2))/(rho_(1)) = (8.9)/(7.2)` |
|
| 38371. |
(a) When a molecule (or an elastic ball) hits a ( massive) wall, it rebounds with the same speed. When a ball hits a massive bat held firmly, the same thing happens. However, when the bat is moving towards the ball, the ball rebounds with a different speed. Does the ball move faster or slower?(b) When gas in a cylinder is compressed by pushing in a piston, its temperature rises. Guess at an explanation of this in terms of kinetic theory using (a) above. (c) What happens when a compressed gas pushes a piston out and expands. What would you observe ? (d) Sachin Tendulkar used a heavy cricket bat while playing. Did it help him in anyway ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Let the SPEED of the BALL be u relative to the wicket behind the bat. If the bat is moving TOWARDS the ball with a speed V relative to the wicket, then the relative speed of the ball to bat is V+ u towards the bat. When the ball rebounds (after hitting the massive bat) its speed, relative to bat, is V+ u moving away from the bat. So relative to the wicket the speed of the rebounding ball is V + (V + u) = 2V + u, moving away from the wicket. So the ball speeds up after the collision with the bat. The rebound speed will be LESS than u if the bat is not massive. For a MOLECULE this would imply an increase in temperature. You should be able to answer (b) (c) and (d) based on the answer to (a). (Hint: Note the correspondence, `"piston" to "bat", "cylinder"to "wicket", "molecule" to "ball"`.) |
|
| 38372. |
A black body of mass 34.38 gm and surface area 19.2cm^(2) is at an initial temperature of 400K. It is allowed to cool inside an evacuated enclosure kept at constant temperature 300K. The rate of cooling is 0.04^(@)C per second. The specific heat of the body in Jkg^(-1)K^(-1) is approximately |
|
Answer» 2800 |
|
| 38373. |
The amplitude of a simple harmonic oscillator is doubled. Which of the following is also doubled? |
|
Answer» Its frequency |
|
| 38374. |
You are riding in an automobile of mass 3000 kg. Assuming that you are examining the oscillation characteristics of its suspension system. The suspension sags 15 cm when the entire automobile is placed on it. Also, the amplitude of oscillation decreases by 50% during one complete oscillation. Estimate the values of (a) the spring constant k and (b) the damping constant b for the spring and shock absorber system of one wheel, assuming that each wheel supports 750 kg. |
| Answer» Solution :`(a)5xx10^(4)Nm^(-1),(B)1344.6kgs^(-1)` | |
| 38375. |
A person trying to lose weight (dieter) lifts a 10 kg mass, one thousand times, to a height of 0.5m each time. Assume that the potential energy lost each time she lowers the mass is dissipated. Fat supplies 3.8xx10^(7) J of energy per kilogram which is converted to mechanical energy with a 20% efficiency rate. How much fat will the dieter use up? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`= 6.45 XX 10^(-3)KG` | |
| 38376. |
The number of particles crossing a unit area perpendicular to X-axis in unit time is given by n= -D (n_2 - n_1)/(x_2 - x_1). Where, n_1 and n_2 are number of particles per unit volume for the value of x meant to x_2 and x_1 .Find the dimensions of the diffusion constant D. |
|
Answer» `M^(@) L T^(3)` |
|
| 38377. |
A person trying to lose weight (dieter) lifts a 10 kg mass, one thousand times, to a height of 0.5m each time. Assume that the potential energy lost each time she lowers the mass is dissipated. How much work does she against the gravitational force? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`= 49, 000J` | |
| 38378. |
An equilateral prism of mass m rests on a rough horizontal surface with coefficient of friction mu. A horizontal force F is applied on the prism as shown in the figure. If the coefficient of friction is sufficiently high so that the prism does not slide before toppling, then the minimum force required to topple the prism is - |
|
Answer» `(mg)/(SQRT(3))` 
|
|
| 38379. |
Two clocks are being tested against a standard clock located in a national laboratory . At 12:00:00 noon by the standard clock, the regarding of the two clocks are : If you are doing an experiment that requires precision time interval measurements, which of the two clocks will you prefer ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The range of variation over the seven DAYS of observations is 162 s for clock 1, and 31s for clock 2. The average reading of clock 1 is much closer to the standard time than the average reading of clock 2. The important point is that a clock.s zero error is not as significant for precision WORK as its variation, because a .zero-error. can always be EASILY corrected . Hence clock 2 is to be preferred to clock 1. | |
| 38380. |
A swimmer wants to cross a 200 m wide river which is flowing at a speed of 2m/s. The velocity of the swimmer with respect to the river is 1m/s. How far from the point directly opposite to the starting point does the swimmer reach the opposite bank ? |
|
Answer» 20 m |
|
| 38381. |
The transverse displacement of a string (clamped at its both ends) is given by y(x, t) = 0.06 sin ((2 x)/(3) x) cos (120 pi t) where x and y are in m and t in s. The length of the string is 1.5 m and its mass is 3.0 xx 10^(-2) kg. Answer the following : (a) Does the function represent a travelling wave or a stationary wave? (b) Interpret the wave as a superposition of two waves travelling in opposite directions. What is the wavelength, frequency , and speed of each wave ? (c ) Determine the tension in the string. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Stationary wave (B) `l=3, n=60Hz, and v= 180 MS^(-1)` for each wave (c ) 648N |
|
| 38382. |
A thin circular ring of mass 'm' and radius R is rotating about its axis with a constant angular velocity omega. Tho objects each of mass M are attached gently to he opposite ends of a diameter of the ring. The new angular velocity of ring is |
|
Answer» `(OMEGAM)/(M+m)` |
|
| 38383. |
Two wooden blocks of masses1kg and 2kg are separated by a certain distance A bullet of mass 50g fired from a gun pierces through the block of mass1 kg and then stopped in the second block After the impact of the bullet both blocks start moving with the same speedCalculate the percentage loss in the initial velocity of the bullet when it is inbetween the two blocks . |
|
Answer» Solution :Here, ` M_(1) = 1 kgM_(2) = 2 kg ` ` m = 50 g = (50)/(1000) kg = (1)/(2) kg ` Let `upsilon` = initial velocity of the bullet `upsilon_(1)` = velocity of the bullet after PIERCING through the first block `V` = velocity of eachblock when hit by the bullet As the bullet penetrates first block as per the PRINCIPLE of conservation of linear momentum ` m upsilon = M_(1) V + m upsilon_(1) ` Again applying the same principlewhen the bullet is EMBEDDED in second block : ` m upsilon_(1) = (M_(2) + m) V ` ` upsilon_(1) = ((M _(2) + m ))/(m) = ((2 + 0.05))/(0.05) V = 41 V ` From (i) ` 0.05 upsilon = 1 V + 0.05 upsilon_(1) = V + 0.05 xx 41 V = 3.05 NV ` ` upsilon = (3.05 V)/(0.05) = 61 V ` `%` age loss in initial velocity of bullet `= ((upsilon - upsilon_(1) xx 100))/(upsilon) = ((61 V - 41V))/(61V) = (20)/(61) xx 100 = 32.8 % ` 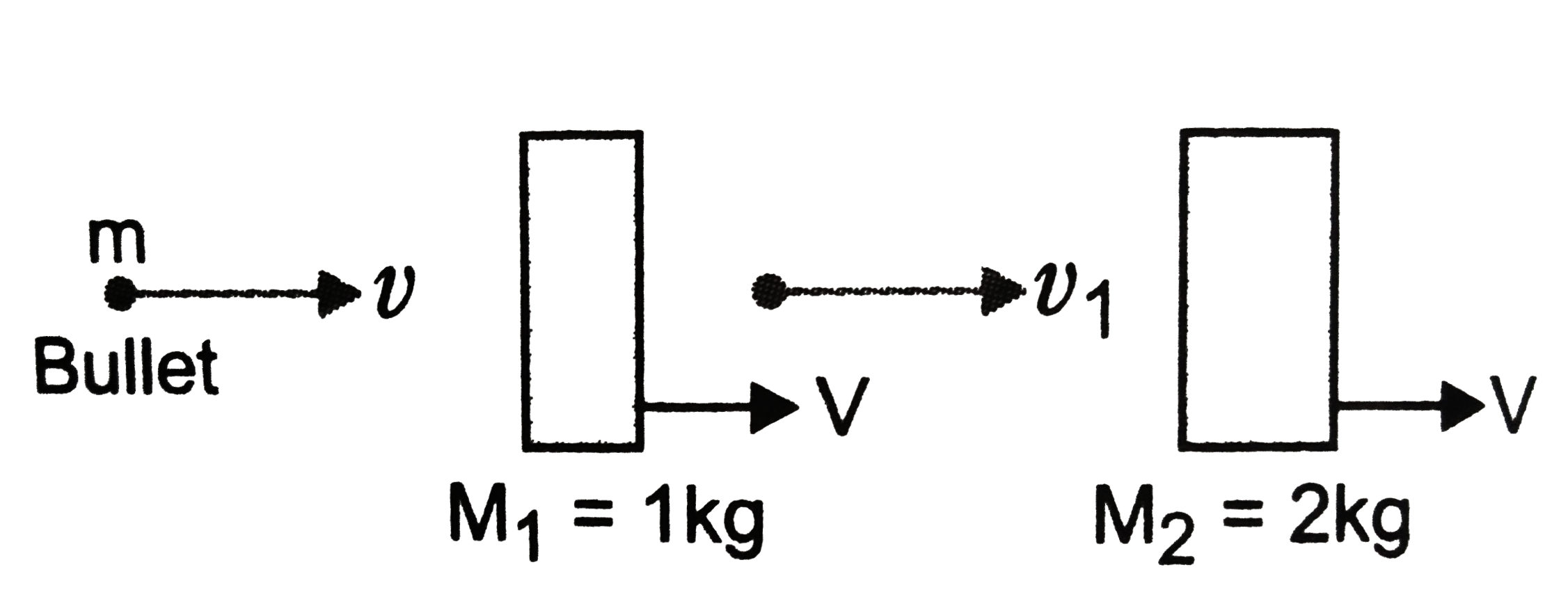 . .
|
|
| 38384. |
The damping force on an oscillator is directly proportional to the velocity. The units of the constant of proportionality are |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 38385. |
A particle is projected from point O on the ground with velocity u=5sqrt(5)m//s at angle alpha=tan^(-1)(0.5). It strikes at a point C on a fixed smooth plane AB having inclination of 37^(@) with horizontal as shwon in fig. If the partcle does not rebound, calculate. a. coordinastes of point C in reference tcoordinate system as shwon in the figure. b. maximum height from the ground to which the particle rises. (g=10m//s^(2)) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 38386. |
As the distance of a planet from the sun increases, then the tie period of revolution of the planet |
|
Answer» increases |
|
| 38387. |
A body of mass 1 kg is thrown upwards with a velocity 20 ms^(-1) .It momentarily come to rest after attaining a height of 18 m . How much energy is lost due to air friction (g = 10 m//s^(-2)) |
|
Answer» 30 J ` :. " Energy lost "= K - V ` ` = 1/2 mv^(2) -mgh` ` = 1/2 xx 1xx 400 -1 xx 10 xx 18` ` = 200 - 180 = 20 J ` |
|
| 38388. |
Three rods of samematerialand of samelengthhavingsamecross section areahavebeen joinedas shown . Theleft and rightends are keptat 0^(@)C and 90^(@)C respectively. Find thetemperatureat thejunctionof the three rods . |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`60^(@)C` | |
| 38389. |
A spring having with a spring constant 1200 N m^(-1) is mounted on a horizontal table as shown in Fig. 14.24. A mass of 3 kg is attached to the free end of the spring. The mass is then pulled sideways to a distance of 2.0 cm and released. Determine (i) the frequency of oscillations, (ii) maximum acceleration of the mass, and (iii) the maximum speed of the mass. |
| Answer» Solution :FREQUENCY `3.2 s^(-1)`, MAXIMUM ACCELERATION of the MASS 8.0 m `s^(-2)`, maximum speed of the mass 0.4 m `s^(-1)`. | |
| 38390. |
A rocket with initial mass 8000 kg is fired vertically. Its exhaust gases have a relative velocity of 2500 m/s and are ejected at a rate of 40kg/s. (a) What is the initial acceleration of therocket? (b) What is its acceleration after 20 s have elapsed. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 38391. |
If young.s modulus y, surface tension s and time t are the fundamental quantities then the dimensional formula of density is |
|
Answer» `s^(2) s^(3) t^(-2)` |
|
| 38392. |
Two persons greet each other by shaking hands. What kind of force do they exert on each other? |
|
Answer» Gravitational |
|
| 38393. |
Two solids A and B float in water. It is observed that A floats with half of its volume immersed and B floats with 2//3 of its volume immersed. The ratio of their densities is |
|
Answer» `4:3` |
|
| 38394. |
The value of (17.5)^(2) is |
|
Answer» 306 |
|
| 38395. |
The refractive indices of glycerine and diamond with respect to air are 1.4 and 2.4 respectively. Calculate the speed of light in glycerine and diamond. From these results, calculate the refractive index of diamond with respect to glycerine. |
|
Answer» `2.143 TIMES 10^8 m//s,1.250 times 10^8 m//s,1.714` |
|
| 38396. |
While detemining the value coefficient of a gas, the initial volume is taken as its volume at |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 38397. |
If L=2.02m+-0.01m,L_(2)=1.02m+-0.01m,"determine"L_(1)+2L_(2). |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`L_(1)+2L_(2)=L_(1)+L_(2)+L_(2)` `(2.02m+-0.1m)+(1.02m+-0.01m)+(1.02m+-0.01m=4.06m+-0.03m` |
|
| 38398. |
A particle of mass 'm' is attached to three identical springs A, B and C each of force constant 'k' as shown in figure. If the particle of mass 'm' is pushed sightly against the spring 'A' and released. Find the period of oscillation |
|
Answer» Solution :When the particle of mass .m. at .0. is pushed by .y. in the direction of A, spring .A. will be compressed by .y. while B and C will be stretched by `y.= y cos45^(@)` , so the total restoring FORCE on the mass .m. ALONG .A0. is `RF=F_(A)+F_(B) cos 45 + F_(C)Cos 45 = ky + 2(ky^(1)) cos 45= ky+2k(ycos45)cos45` `F= -k^(1)y "with"k^(1)=2k implies T= 2pisqrt((m)/(k^(1)))= 2pisqrt((m)/(2k))` |
|
| 38399. |
Assertion: A child in a garden swing periodically presses his feet against the ground to maintain the oscillations. Reason: All free oscillations eventually die out because of the ever present damping force. |
|
Answer» If both assertion and reson are TRUE and reason is the correct EXPLANATION of assertion |
|
| 38400. |
Assuming the sun to be a spherical body of radius R at a temperature of TK, evaluate the total radiant power, incident on earth, at a distance 'r' from the sun (where r_0 is the radius of the earth and sigma is stefan's constant) |
|
Answer» `(R^(2) sigma T^(4))/( r^(2) )` |
|