Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 44651. |
Distinguish between the phenomena of nuclear fission and fusion. |
Answer» SOLUTION :
|
|
| 44652. |
Radioactiv edecay will occur as follows overset(220)86Rnrarroverset(216)84PO + overset(4)2He Half life =55s overset(216)84Porarroverset(212)82Pb + overset(4)2He Half life =0.66s overset(812)82Pbrarroverset(212)82BL + gamma^(@)(4)e Half life =10.6 h If a certain mass of radon (Rn=220) is allowed to decay in a certain container,then after 5 minutes the element with the greater mass will be |
|
Answer» radon `therefore Mass of Rn-220(left)=(1)/(2)^(5.5) M_(0)=(M_(0)/(45)` `therefore The mass converted in to Po-216 is `(44//45)` `M_(0)` Number of hlf lives of Po-216 in 5 minutes `=(5min)/(0.66)=(300)/(0.66)=455` `therefore Mass of Po-216left=((1)/(2))^(455)xx(44)/(45)M_(0)rarr0` This means that Po-216 formed will soon decay to lead HENCE lead will havemaximum mass NEARLY `(44)/(45)M_(0)` |
|
| 44653. |
What are sub atomic particles? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) The three main subatomic particles that form an atom are protons, neutrons and electrons. (II) Subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than the atom, proton and neutron are made up of QUARKS which is interact through gluons. (III) Subatomic particle having two types of particles, they are ELEMENTARY particle and COMPOSITE particle. |
|
| 44654. |
A capacitor of capacitance C_1 is charged to a potential V_1 , while another capacitor of capacitance C_2 is charged to a potential difference V_2 . The capacitors are now disconnected from their respective charging batteries and connected in parallel to each other Explain the reason for the difference of energy in parallel combination in comparison to the total energy before they are connected . |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FINAL energy `U_f` of the combinationis less than the total energy `U_i` of the combination before they are connected . It is on ACCOUNT of loss of electric charge due to amount of work DONE for transfer of charge between the capacitors on connecting them TOGETHER in parallel . | |
| 44655. |
(a) In Fig. 24-17 a, 12 electrons ( of charge -e ) are equally spaced and fixed around a circle of radius R. Relative to V = 0 at infinity, what are the electric potential and electric field at the center C of the circle due to these electrons? (b) The electrons are moved along the circle until they are nonuniformly spaced over a 120° arc (Fig. 24-17b). At C, find the electric potential and describe the electric field. |
|
Answer» Solution :(1) The electric POTENTIAL V at C is the algebraic sum of the electric potentials contributed by all the electrons. Because electric potential is a scalar, the orientations of the electrons do not matter. (2) The electric field at C is a vector quantity and thus the ORIENTATION of the electrons is important. Calculations: Because the electrons all have the same negative charge `-e` and are all the same distance R from C, Eq. 24-29 gives us `V=-12 (1)/(4 pi epsilon_(0)) (e )/( R).""` (Answer) (24-30) Because of the symmetry of the arrangement in Fig. 24-17 a, the electric field vector at C due to any given electron is canceled by the field vector due to the electron that is diametrically opposite it. Thus, at C, `overset(to) (E ) =0`. (Answer) 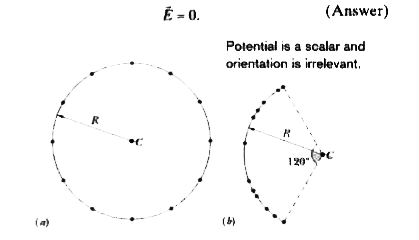 (B) Reasoning: The potential is STILL given by Eq. 24-30, because the distance between C and each electron is unchanged and orientation is irrelevant. The electric field is no longer zero, however, because the arrangement is no longer symmetric. A net field is now directed toward the charge distribution. |
|
| 44656. |
When a current changes from +2A to -2A in 0.05s, an emf of 8V induced in a coil. The coefficient of self induction of coil is |
|
Answer» 0.4H |
|
| 44657. |
If the area of each plate is S and the successive separations are d, 2d and 3d then the equivalent capacitance across A and B is: |
|
Answer» `(epsilon_aA)/(6D)` |
|
| 44658. |
Two ships, A and B, leave port at the same time. Ship A travels northwest at 24 knots, and ship B travels at 28 knots in a direction 40^(@) west of south (1 knot = 1 nautical mile per hour, see Appendix D). What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction of the velocity of ship A relative to B? ( c) After what time will the ships be 160 nautical miles apart? (d) What will be the bearing of B (the direction of B's position) relative to A at that time? |
| Answer» Solution :(a) 38.4 knotes, (B) `1.5^(@)` EAST of north, ( C) 4.2 h, (d) 1.5 WEST of DUE south | |
| 44659. |
Potential difference across the terminals of a cell is always less than its emf. |
| Answer» Solution : False - POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE across the terminals of a cell is greater than its emf when the cell is being CHARGED or some electrical DEVICE supplies current to the cell. | |
| 44660. |
In a diffraction pattern due to a single slit of width 'a' the first minimum is observed at an angle 30 when light of wavelength 5000 Å is incident on the slit. The first secodary maximum is observed at an angle of : |
|
Answer» `SIN^(-1)(2/3)` `sin 30^@ = lambda/a = 1/2 ""…(i)` The condition for the second minima ` sin THETA= (3 lambda)/(2a) = 3/2(1/2) implies theta = sin^(-1) 3/4`. |
|
| 44661. |
In an experiment with potentiometer to measure the internal resistance of a cell, when the cell is shunted by 5 Omega, the null point is obtained at 2m. when cell is shunted by 2012 the null point is obtained at 3m.The internal resistance of cell is |
|
Answer» `2 OMEGA ` |
|
| 44662. |
Two charged conducting spheres of radii a and b are connected to each other by a wire. What is the ratio of electric fields at the surfaces of the two spheres? Use the result obtained to explain why charge density on the sharp and pointed ends of a conductor is higher than on its flatter portions. |
|
Answer» Solution :With arbitrary q and Q FRO A and B respectively. `E_(A)/E_(B)=((1)/(4pi epsi_(0)) q/a^(2))/((1)/(4pi epsi_(0)) Q/b^(2))=q/Q . b^(2)/a^(2)` For equilaterial CONDITION, `V_(A)=V_(B)` `q/(4pi epsi_(0) a)=(Q)/(4pi epsi_(0)b) therefore q/Q=q/b ""E_(A)/E_(B)=a/b. b^(2)/a^(2)=b/a` `E=sigma/(epsi_(0))`. For pointed ends `sigma=q/A`. As `A to 0` E becomes EXTREMELY large. Flat MEANS `A to oo` hence. 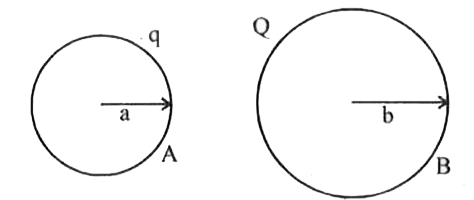
|
|
| 44663. |
If the radius of the first orbit of the hydrogen atom is 0.53 Å , then the de-Broglie wavelength of the electron in the ground state of hydrogen atom will be |
|
Answer» `0.53 Å` |
|
| 44664. |
Which of the following combinations of three different physical quantities P, Q, R can never be a meaningful quantity ? |
|
Answer» `PQ-R` |
|
| 44666. |
Explain the need for a feedback circuit in a transistor oscillator. |
| Answer» Solution :The CIRCUIT used to feedback a portion of the output to the input is called the feedback network If the portion of the output FED to the input is in phase with the input then the magnitude of the input SIGNAL INCREASES. It is necessary for sustained oscillations | |
| 44667. |
State which one of the following is correct |
|
Answer» Farad = COULOMB`XX"volt` |
|
| 44668. |
The current which comes into play in a region where the electric flux is changing with time is called_______. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :DISPLACEMENT CURRENT | |
| 44669. |
The wavelength of the first spectral line in the Balmer series of hydrogen atom is 6561 Å. The wavelength of the second spectral line in the Balmer series of singly- ionized helium atom is : |
|
Answer» 1215 Å `1/lambda=4R (1/4-1/(16))=(3R XX 4)/(16)` `lambda=1215Å` |
|
| 44670. |
Show that if at some part of a field the lines of force have the from of concentric circles whose centres are at point O (as given in Fig. 3.39), the field intensity at each point in this part of the field should be inversely proportional to the distance from the point O. . |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :For CLOSED path, net WORK is zero. `W_(AB) + W_(BC) + W_(CD) + W_(DA) = 0` `E_1 r_1 theta + 0 - E_2 r_2 theta + 0 = 0` or `E_1 r_1 = E_2 r_2` or `E prop (1)/( r)`.  . .
|
|
| 44671. |
What is meant by term 'modulation' ? Draw a block diagram of a simple modulator for obtaining an AM signal. |
|
Answer» Solution :MODULATION : It is the PHENOMENON of super imposing the LOW frequency message signal on a high frequency wave (carrier wave) `y(t) = B x (t) + C x^(2) (t)` where B and C are constants This signal is passed through a band pass filter which rejects dc. The output of the band pass filter is therefore, an AM wave. Refer BLOCK Diagram : Q.12 O.D., 2008 Srt0I |
|
| 44672. |
The uncertainty in the position of an electron along an x axis is given as 50 pm, which is about equal to the radius of a hydrogen atom. What is the least uncertainty in any simultaneous measurement of the momentum component P_(x) of this electron? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`2.1xx10^(-24)kg.m//s` | |
| 44673. |
A box of mass m slides down a frictionless inclined plane of length L and vertical height h. what is the change in its gravitational potential energy? |
|
Answer» `-mgL` |
|
| 44674. |
Which of the following equation doesn't represent energy of charged capacitor ? |
|
Answer» `(Q^(2))/(2C)` |
|
| 44675. |
If the work done in blowing a bubble of radius R is W, then the work done in blowing a bubble of radius 2R from that solution is : |
| Answer» ANSWER :C | |
| 44676. |
The optical path of a monochromatic light is the same if it goes through 2.00cm of glass or x cm of ruby. If the refractive index of glass is 1.510 and that of ruby is 1.760 find the value of x. |
|
Answer» 1.716 CM |
|
| 44677. |
यदि n(A)=21,n(B)=8,n(AnnB)=4 तो n(B-A) का मान ज्ञात कीजिए। |
|
Answer» 12 |
|
| 44679. |
Magnetic field due to a ring having n turns at a distance x on its axis is proportional to (if r = radius of ring) ______ . |
|
Answer» `r/((x^(2)+r^(2)))` I = current n = number of turns The MAGNETIC field at x distance from the centre of ring `B=mu_(0)/(4pi)(nIr^(2))/((x^(2)+r^(2))^(3/2))rArrBprop(nr^(2))/((x^(2)+r^(2))^(3/2))` |
|
| 44680. |
A tuning fork has frequency 512 Hz. What can you say about its frequency when (i) its prongs are filed (ii) some wax is applied to its prongs ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Its FREQUENCY will be more than 512 HZ. (ii) Its frequency wil be LESS than 512 Hz. | |
| 44681. |
What is Bohr's correspondence principle? |
|
Answer» Solution :As is know, Bohr's atom model has been replaced by quantum machanical model. According to this model, electrons in an atom do not move AROUND the nucleus in definite orbits. However, the probability of finding the electron is high NEAR the Bohr orbit radius, and at the same time, the probability of finding the electron between these orbits is not zero. According to Bohr's correspondence principle, the predictions of quantum theory must corresponds to the predictions of classical theory in the regions of sizes where classical theory must corresponds to the predictions of classical theory in the regions of sizes where classical theory holds. for large size wherein classical theory holds good, quantum number n becomes large. We MAY thereofore rewrite Bohr's correspondence principle as: `underset(ntooo)(LIMIT)`[quantum physics]=(Clasical Physics) for example, quantum condition for EMISSION of radiation is `hv=E_i-E_f` And Maxwell's classical theory says that an electron revolving with orbital frequency f must radiate light waves of frequency f. Calculations show that for quantum number number n as large as 10000, the difference in v and f is less than 0.015%. Thus Bohr's correspondence principle is established. |
|
| 44682. |
An electric bulb illuminates a plane surface. The intensity of illumination on the surface at a point 2 m away from the bulb is 5 xx 10^(-4) phot ("lumen"//cm^(2)). The line joining the bulb to the point makes an angle of 60^(@)with the normal to the surface. The intensity of the bulb in candela is |
|
Answer» `40 SQRT(3)` |
|
| 44683. |
The wavelength of light in the visible region is about 390 nm for violet colour ,about 550 nm (average wavelength) for yellow-green colour and about 760 nm for red colour. (a)What are the energies of photons in (eV) at the (i) violet end, (ii)average wavelength,yellow-green colour,and (iii) red end of the visible spectrum ? (Take h=6.63xx110^(-34)) js and 1 eV=1.6xx10^(-19)J). (b)From which of the photosensitive material with work functions listed n Table 11.1 and using the results of (i),(ii) and (iii) of (a), can you build a photoelectric device that operates with visible light? |
|
Answer» Solution :Here `lambda_(v)=390 nm=39xx10^(-8)m` `lambda_(yg)=550 nm =55xx10^(-8)m` `lambda_(R)=760 nm=76xx10^(-8)m` `h=6.63xx10^(-34) Js` leV`=1.6xx10^(-19)J` `c=3xx10^(8)m//s` Energy of incident photon , `E=hv=(hc)/(LAMBDA)` (in joule) `therefore E=(hc)/(elambda)to(in eV)` (i)For violet COLOUR, `E_(V)=(hc)/(elambda_(V))=(6.63xx10^(-34)xx3xx10^(8))/(1.6x10^(-19)xx39xx10^(-8))` `therefore E_(V)0.31875xx10^(1)` `therefore E_(V)~~3.19 eV` (ii) for yellow red light `E_(yg)=(hc)/(elambda_(yg))=(6.63xx10^(-34)xx3xx10^(8))/(1.6xx10^(-19)xx5xx10^(-8))` `therefore E_(yg)=0.226xx10^(1)` `therefore E_(eg)~~2.26 eV` (iii) For red light, `E_(R)=(hc)/(elambda_(R))=(6.63xx10^(-34)xx3xx10^(8))/(1.6xx10^(-19)xx76xx10^(-8))` `therefore E_(R)=0.163569xx10^(1)` `therefore E_(R)~~1.64 eV` (b)  For photoelectric emission energy of incident light should be equal or more than work function of metal. Here energy of violet light is `E_(V)=3.19 eV` Which is more than work function of NA ,K and `C_(s)` hence photoelectric device will work which depend on radiation of violet colour. Energy of yellow light `E_(yg)`=2.26 eV which is more than work function of `C_(S)` hence photoelectric device will work which depend on radiation of yello-green colour. Energy of red colour is `E_(R)`=1.64 eV which is less than work function of metals given in table.Hence photoelectric device which work on red colour will not work. |
|
| 44684. |
A uniform rope of length L, resting on a frictionless horizontal table is pulled at one end by a force F. What is the tension in the rope at a distance x form the end where the force is applied? |
|
Answer» F(L -X) |
|
| 44685. |
The conduction band and valence band in a good conductor |
|
Answer» Are WELL separated by a FORBIDDEN BAND |
|
| 44686. |
A hollow cone floats with its axis vertical upto one third of its height in a liquid in a liquid of relative density 0.8 and with its vertex submerged. When another liquid of relative density rho is filled in it upto one third of its height, the cone floats upto half its vertical height. The height of the cone is 0.10m and the radius of the circular base is 0.05m. Find the specific gravity rhois given. |
Answer»  `(r)/(x)=(R)/(H)implies r=(R)/(h)x` `r_(1)=(R)/(h)xx(h)/(3) implies r_(1)=(R)/(3)W=B` `mg=(1)/(3)pi((R )/(3))^(2)xx(h)/(3)xx(4)/(5) g` `m=(1)/(27)xx(1)/(3)piR^(2)HXX(4)/(5)"".....(1)` when liquid is fille in cone. `W=B` `(m+(1)/(3)pi((R)/(3))^(2)(h)/(3)rho]g` `=(1)/(3) pi ((R)/(2))^(2)(h)/(2)xx((4)/(5))g` `[m+(1)/(27)xx(1)/(3)piR^(2)hrho]=(1)/(10)xx(1)/(3)piR^(2)h"".....(2)` From (1) and (2) `(1)/(27) [rho+(4)/(5)]=10implies rho=1.9` 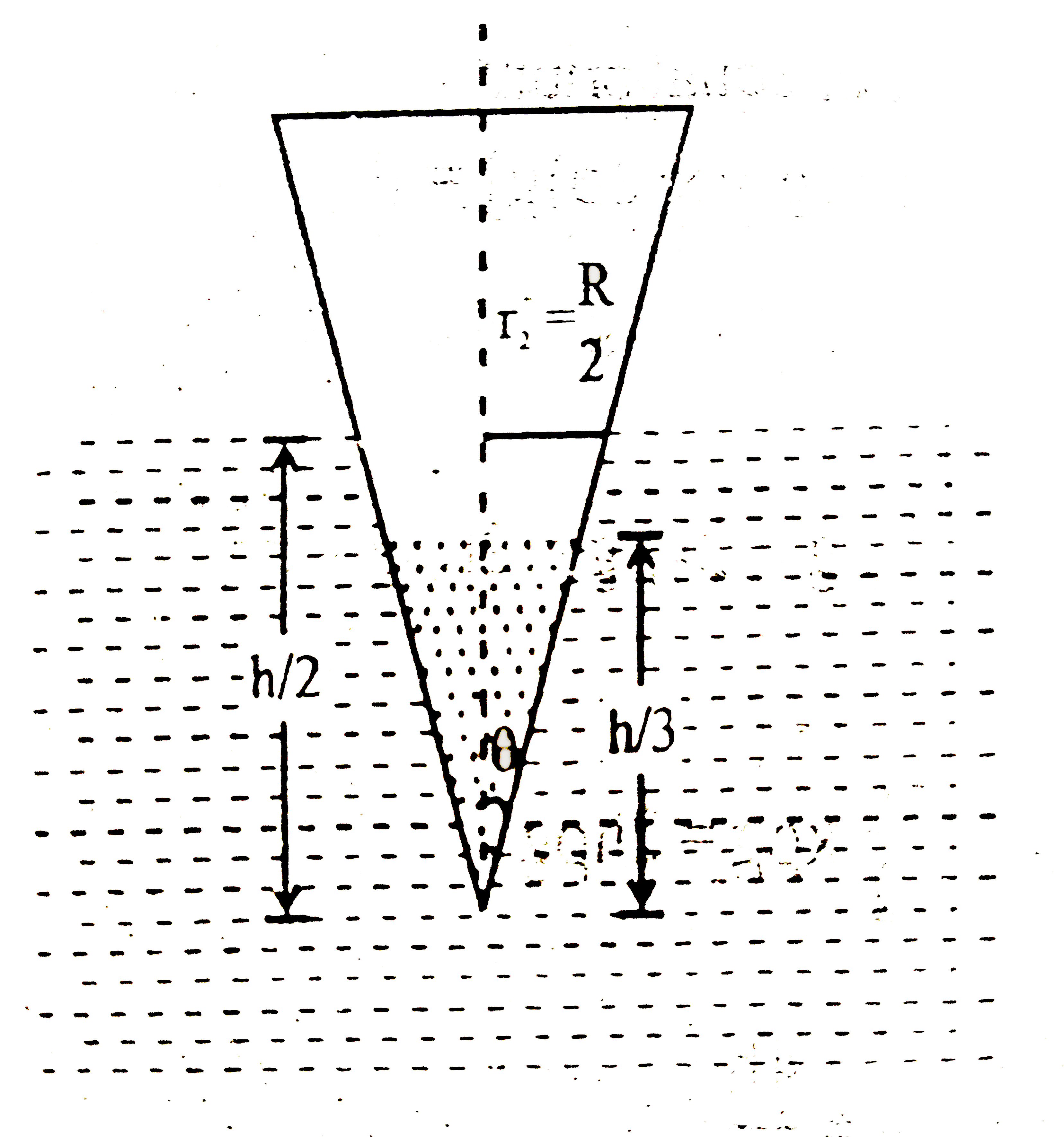
|
|
| 44687. |
There are two identical spheres A and B. Now charge Q is established on each sphere. There is a third identical neutral sphere C. Now sphere C is first brought in contact with A and separated then brought in contact with B and separated. After this what will be charge on C ? |
|
Answer» Q `Q/2` Electric charge when they are brought in CONTACT: `=(Q + Q/2)/(2)` `=(3Q)/4` |
|
| 44688. |
We transfer 1000 J as heat to a diatomic gas, allowing the gas to expand with the pressure held constant. The gas molecules each rotate around an internal axis but do not oscillate. How much of the 1000 J goes into the increase of the gas's internal energy? Of that amount, how much goes into Delta K_( "trans") (the kinetic energy of the translational motion of the molecules) and AK (the kinetic energy of their rotational motion)? |
|
Answer» Solution :(1) The transfer of energy as heat to a gas under constant pressure is related to the resulting temperature increase `Delta T` via Eq. 21-25`(Q=nC_p Delta T )`. (2) Because the gas is diatomic with molecules undergoing rotation but not oscillation, the molar specific heat is, from Fig. 21-12 and Table 20-3, `C_p ` =(7/2)R. (3) The increase AE, in the internal energy is the same as would occur with a constant volume process resulting in the same AT. THUS, from Eq, 21-24, `Delta E_( i nt ) = nC_VDelta T`From Fig. 21-12 and Table 20-3, we see that `C_v = (5/2)`R. (4) For the same n and AT, AE is greater for a diatomic gas than for a monatomic gas because additional energy is required for rotation. Increase in `E_( i nt )`: Let.s first get the temperature change AT due to the transfer of energy as heat. From Eq. 21-25, SUBSTITUTING (7/2) R for `C_p`, we have ` Delta T= (Q )/( 1/2nR ) ` We next FIND `Delta E_(i nt )` from Eq. 21-24, substituting the molar specific heat `C_v ( = 5//2R)` for a constant volume process and using the same `Delta T`. Because we are dealing with a Diatomicgas,Let .s callthsichange`DeltaE_( i n t , d ia )` equation21-24gives us ` DeltaE_( i n t , i d a )= n C_V DeltaT= n 5/2R((Q )/( 7/2nR ))=(5)/(7 )Q` ` = 0.71428 Q = 714.3J` In words, about 71% of the energy transferred to the gas goes into the internal energy. The rest goes into the work required to increase the volume of the gas, as the gas pushes the walls of its container outward. Increase in K: If we were to increase the temperature of a monatomic gas (with the same value of n) by the amount given in Eq. 21-30, the internal energy would change by a smaller amount, call it `DeltaE_(" int , dia")`because rotational motion is not involved. To CALCULATE that smaller amount, we still use Eq. 21-24 but now we substitute the value of `C_V `, for a monatomic gas-namely,`C_v =3//2 .`so ` Detla E_( " int mon ")= n3/2R Delta T ` Substituting for `Detla `T from Eq. 21-30 leads us to ` DeltaE_( " int . mon")=n(3)/(2)R ((Q )/(n 7/2 R)) = 3/7Q ` `=0.42857Q= 428.6J.` Learn: For the monatomic gas, all this energy would go into the kinetic energy of the translational motion of the atoms. The important point here is that for a diatomic gas with the same values of n and `Delta `T, the same amount of energy goes into the kinetic energy of the translational motion of the molecules. The rest of `Delta E_(" int. dia ")`. (that is, the additional 285.7 ) goes into the rotational motion of the molecules. Thus, for the diatomic gas, ` DeltaK_("trans") = 428.6J andDelta K_(r o t)= 285.7J` |
|
| 44689. |
Which of the following quantities increae when wavelength in increased? Consider only the magnitudes |
|
Answer» the POWER of a CONVERGING lens |
|
| 44690. |
If an electron in a hydrogen atom jumps from the 3rd orbit to the 2nd orbit, it emits a photon of wavelength lambda. When it jumps from the 4^(th) orbit to the 3^(rd) orbit, the corresponding wavelength of the photon will be |
|
Answer» `(20)/(7) lambda` `(1)/(lambda)=R((1)/(2^(2))-(1)/(3^(2)))...(1)` Wavelength of photon when electron makes transition from FORTH orbit to third orbit `(1)/(lambda.)=R((1)/(3^(2))-(1)/(4^(2)))...(2)` by taking ratio of (1) and (2) `(lambda.)/(lambda)=((1)/(4)-(1)/(9))/((1)/(9)-(1)/(16))=((5)/(36))/((7)/(144))=(20)/(7)` `:. lambda.=(20)/(7) lambda` |
|
| 44691. |
Using Bohr's formula for energy quantization determine the excitation energy. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :As `E= -13.6z^2eV/n^2`, `E_2 - E_1 = 48.4eV` | |
| 44692. |
A particle of mass m starts from rest and moves in a circular path of radius R with a uniform angular acceleration alpha The kinetic energy of the particle after n revolutions is |
|
Answer» `N ALPHA m R^(2)` |
|
| 44693. |
During a thunder storm the movement of water molecules within the clouds creates friction partially causing the bottom part of the clouds to become negatively charged. This implies that the bottom of the cloud and the ground act as a parallel plate cpacitor . If the electric field between the cloud and ground exeeds the dielectric breakdown of the air (3xx10^(6)Vm^(-1)) lightning will occur. (a) If the bottom part of the cloud is 1000 m above the ground determine the electric potential difference that exists between the cloud and ground. (b) In a typical lightning phenomenon around 25 C of electrons are transferred from cloud to ground . How much electrostatic potential energy is transferred to the ground? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(a) ELECTRIC field between the cloud and ground, V = Ed `V = 3xx10^(6)xx1000 = 3xx10^(9)V ` (a) Electrons transferred from cloud to ground , q = 25 C Electron static potential energy , `U = (1)/(2) CV^(2)"" [ C = (q)/(V) ] ` `= (1)/(2) qV = (1)/(2) xx25 xx3 xx10^(9)` `U = 37.5 xx10^(9)` J |
|
| 44694. |
A circular coil of radius 10cm and 25 turns is rotated about its vertical diameter with an angular speed of 40rads^(-1), in a uniform horizontal magnetic field of magnitude 5xx10^(-2)T. Calculate the maximum emf induced in the coil. Also find the maximum current in the coil if the resistance of the coil is 15Omega. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Emf induced in the coil =`EPSILON=nAB omegasin (omegat)=epsilon_0 sin omegat` Area = `pir^2` `epsilon=(25xx3.14xx10xx10^(-2)xx10xx10^(-2)xx5xx10^(-2)xx40)sin (40t)` `epsilon` = 1.57 sin 40 t `epsilon_0`=1.57 Volt `I=epsilon/R =(1.57(sin 40t)V)/15, I_(max)=epsilon_0/R= (1.57V)/(15Omega)` = 0.1047 A = 0.11 A Current `I_(INST)`=0.1047 sin 40t A `I_(max)`=0.11 A |
|
| 44695. |
In free space, two particles of mass m each are initially both at rest at a distance a from each other. They start moving towards each other due to their mutual gravitational attraction. The time after which the distance between them has reduced to (a)/(2) is: |
|
Answer» `((pi+2)/(4sqrt(2)))((a^(3))/(Gm))^(1//2)` Let the instantaneous velocity of each particle be v Let the time after which the distance between the particles has reduced to `(a)/(2)` be T Then, for the particle that was initially at `x=(a)/(2)`, `(Gm^(2))/((2R)^(2))=-m("DVD")/(dr)""implies""(Gm)/(r^(2))=-(4vdv)/(dr)` `implies""-4int_(0)^(v)dvd=Gmint_(a//2)^(r)(dr)/(r^(2))impliesv^(2)=(Gm)/(2)((1)/(r)-(2)/(a))impliesv=-[(Gm)/(2)((1)/(r)-(2)/(a))]^(1//2)` [v is negative because the velocity is towards the -X direction] `implies""(dr)/(dt)=-[(Gm)/(2)((1)/(r)-(2)/(a))]^(1//2)implies-int_(a//2)^(a//4)sqrt((r)/(a-2r))dr=sqrt((Gm)/(2A))int_(0)^(T)dt` `implies""int_(a//2)^(a//4)sqrt((r)/(a-2r))dr=-sqrt((Gm)/(2a))T""...(i)` Let us now evaluate the integral `I=int sqrt((r)/(a-2r))dr` Let `r=(a sin^(2)theta)/(2)""implies""dr=a sin theta cos theta d theta` Therefore, `I=(a)/(sqrt(2))int sin^(2)theta d theta=(a)/(2sqrt(2))int(1-cos2theta)d theta=(a)/(2sqrt(2))[theta-(1)/(2)sin 2theta]` Since `r=(a sin^(2)theta)/(2),theta=sin^(-1)sqrt((2r)/(a))` and `sin2theta=2sin theta cos ttheta=2(sqrt((2r)/(a)))(sqrt(1-(2r)/(a)))=(sqrt(8r(a-2r)))/(a)` So, `I=(a)/(2sqrt(2))(sin^(-1)sqrt((2r)/(a))-(sqrt(2r(a-2r)))/(a))=(a)/(2sqrt(2))sin^(-1)sqrt((2r)/(a))-(sqrt(r(a-2r)))/(2)` Therefore, from equation (i), sin `T=-sqrt((2a)/(Gm))((a)/(2sqrt(2))sin^(-1)sqrt((2r)/(a))-(sqrt(r(a-2r)))/(2))_(a//2)^(a//4)=-sqrt((2a)/(Gm))(-(a)/(2sqrt(2))((pi)/(4))-(1)/(2)((a)/(2sqrt(2))))` Hence, `""T=sqrt((a)/(Gm))((api)/(8)+(a)/(4))=((pi+2)/(8))sqrt((a^(3))/(Gm))` |
|
| 44696. |
In p-type semiconductor, |
|
Answer» major CURRENT carrier are electrons |
|
| 44697. |
The energy contained in a small volume through which an electromagnetic wave is passing oscillates with |
|
Answer» zero FREQUENCY |
|
| 44698. |
Compare dia, para and ferromagnetism. |
Answer» SOLUTION :
|
|
| 44699. |
What does q_1 +q_2 =0, signify in electrostatics? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :It SIGNIFIES that `|q_1|=|q_2|` but SIGNS of `q_1 andq_2 `are MUTUALLY OPPOSITE. | |
| 44700. |
A galvanometer of 25 ohm resistance can read a maximum current of 6mA. It can be used as a voltmeter to measure maximum potential difference of 6V by connecting a resistance to galvanometer. Identify the correct choice from the following |
|
Answer» `1025Omega` in SERIES |
|