Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 1801. |
Distinguish between inflationary gap and deflationary gap. State two measures by which these can be corrected. |
Answer» Solution :Deflationary gap : It prevails when aggregate demand is less than aggregate supply at the FULL employment level of output. In other words, deflationary gap represents the situation of UNEMPLOYMENT attributable to the fact that at full employment level of output in the DIAGRAM RF is deflationary gap.  Inflationary gap - This is the situation where economy operates at a level which is greater than full employment. In other words, the gap between aggregate demand and aggregate supply is known as inflationary gap. In the diagram RN is inflationary gap. Volume of credit should be supervised and controlled for correcting the situation of deflationary and inflationary gap.  Two METHODS can be adopted for controlling these two gaps: (i) Open market operations: If the central bank of the country will buy the securities from commercial banks, this will increase the capacity of credit PAYING of these banks. This way teh deflationary situation can be corrected. If the central bank of the country sells the securities in the open market then the situation of inflationary gap will be controlled. Because of this the level of aggregate demand and their credit paying capacity will be reduced. (ii) Bank Rate: Bank rate should be reduced. This will decline the rate of interest. This is for controlling deflationary gap. In the case of inflationary gap bank should increase their rate, so that rate of interest will go up and the demand for credit will decline. This will affect aggregate demand. |
|
| 1802. |
Potato chips and popcorn are substitutes.A rise in the price of potato chips will ……….. The demand for popcorn and the demand of potato chips will ………….. |
|
Answer» 1.INCREASE, increase |
|
| 1803. |
The nominal GDP of a country for year 2 is Rs. 200 billion and price index is 200. Find real GDP. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`"Real GDP"=("Nominal GDP")/("PRICE index")xx100` `=(200)/(200)xx100="RS. 100 billion"` |
|
| 1805. |
Are the following statements true or false ? Give reasons. Indirect taxes cannot be avoided in any circumstances . |
| Answer» Solution :False . Indirect TAXES can be AVOIDED in certain circumstances , by not entering into those TRANSACTIONS , which CALL for such taxes. | |
| 1806. |
Describe the steps invloved in the estimation of national income by income method. State any two precautions that must be taken while estimating national income by this method. |
| Answer» Solution :Following are the main steps involved in estimating national income by income method:(i) Identify enterprises which employ factors of production (LAND, labour, CAPITAL and enterprise).(ii) Classify factor payments into various categories like rent, wages, interest, profitand mixed income (or classify factor payments into COMPENSATION of employees, mixed income and operating surplus).(iii) Estimate amount of factor payments made by each enterprise.(iv)Sum up all factor payments made within domestic territory to get Domestic Income (NDP at FC).(u) Estimate net factor income from abroad which is added to Domestic Income to derive National Income.For correct computation of national income by income method, following precautions need to be taken:(i) Only factor INCOMES which are earned by rendering productive services are included. All types of transfer income like old-age pension, unemployment allowance, etc. are excluded.(ii) Sale and purchase of second-hand goods are excluded since they are not part of production of current year but commission paid on sale of second-hand goods is included as it is reward for rendering productive services. Likewise, sale proceeds of shares and bonds are not included. | |
| 1807. |
Why is an Indifference curve generally convex to the origin. |
Answer» Solution :(i) As, weknow quantity of one commodity increases, its marginal rate of substitution falls because , of law of diminishing marginal UTILITY Marginal rate of substitution is a slope of Indifference curve and WHENEVER slope [MRS] decreases it makes the curve convex to the point of origin. 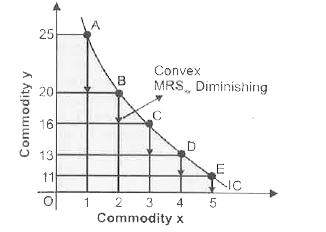 (ii) In the above diagram , units of y are measured on vertical axis and units of x on horizontal axis. When hte consumer moves from combination A (1x + 25y ) to B (2x + 20y) , he acquires one additional unit of x and forgoes (sacrifice) 5 units of y , if he wants to get the same level of satisfaction. The consumer has to reduce the consumption of y when the increases the consumption of x. The number of units of good y that the consumer is willibg to sacrifice for an additional unit of goodx, so as to maintainthe same level of satisfaction is technically called the marginal rate is substitution of x for y and is denoted by `MRS_(xy)`. (III) So, the `MRS_(xy)` when the consumer move from combination A to B is 5 : 1 , further as the consumer move from combination B to C, he acquires one more units of x, but the consumer forgoes a smaller number of y, i.E ., `MRS_(xy)` at this stage is 4 : 1 . It may be observed now that MRS diminishes as the consumer moves from combination A to B , B to C, C to D, D to E. The consumer forgoes less and less units of y as he acquires additional unit of x. |
|
| 1808. |
What do you mean by capital account? Briefly discuss its components. |
| Answer» Solution :The remaining half of the Balance of PAYMENT is Capital Account, which records the movement of capital in the ECONOMY due to capital receipts and expenditure. It recognises foreign investment in DOMESTIC assets and domestic investment in foreign assets. The DETAILS can be recorded by analysing the inflow and outflow of funds from the nation’s economy. The funds can be in the form of loans or investments.Under Capital Account, investments made by both public and private sectors are taken together. The capital flow may either be debt creating or non-debt creating. The following are the components of Capital Account:Foreign Direct Investment: Investment and control in a company based in a country by a foreign company.Portfolio Investment: Investment in stocks, bonds, DEBTS and other financial assets.Government loans to the Government of other countries of the world. | |
| 1809. |
State two measures by which a central bank can attempt to reduce the inflatinary gap. |
| Answer» Solution :(i) INCREASE in bank rate. (II) SALE of government securities. | |
| 1810. |
Explain the credit creation role of commercial banks with help of a numerical example. |
|
Answer» Solution :The process of money creation by the commercial banks starts as soon as people deposit money in their respective bank accounts. After receiving the deposits, as per the CENTRAL bank guidelines, the commercial banks maintain a protion of total deposite in form of cash RESERVES. The remaining portion left after maintaining cash reserves of the total deposits is then lend by the commercial bank to the general public in form of credit, loans and advances. Now assuming that all transactions in the economy are routed through the commercial banks, then the money borrowed by the BORROWERS again comes back to the banks in form of deposits. The commercial banks again keep a portion of the deposits as reserves and lend the rest. The deposit of money by the people in the banks and the subsequent lending of loans by the commercial banks is a recurring process. It is due to this continuous process that the commercial banks are able to create credit money a multiple times of the initial deposits. The process of creation of money is explained with the help of the following numerical example  Suppose, initially the public deposited Rs 10,000 with the banks. Assuming the Legal Reserve Ratio to be 20% the banks keep Rs 2,000 as minimum cash reserves and lend the balance amount of Rs 8,000 (Rs 10,000 - Rs 2,000) in form of loans and advances to the general public. Now, if all the transactions taking place in the economy are routed only through banks then, the money borrowed by the borrowers is again routed back to the banks in form of deposits. Hence, in the second ROUND there is an increment in the deposits with the banks by Rs 8,000 and the total deposits with the banks now rises to Rs 18,000 (that is Rs 10,000 + Rs 8,000). Now, out of the new deposits of Rs 8,000, the banks will keep 20% as reserves (that is, Rs 1,600) and lend the remaining amount (that is Rs 6,400). Again, this money will come back to the bank and in the third round, the total deposite rises to Rs 24,400 (i.e., Rs 18,000 Rs 6,400) The same process continues and with EACHROUND the total deposits with the banks increases. However, in every subsequent round the cash reserves diminishes. The process comes to an end when the total cash reserves (aggregate of cash reserves from the subsequent rounds) become equal to the initial deposits of Rs 10,000 that were initially held by the banks. As per the above schedule, with the initial deposits of Rs 10,000, the commercial banks have created money of rs 50,000 |
|
| 1811. |
Explain with the help of an example, the basis of classifying goods into final goods and intermediate goods. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The basis of CLASSIFICATION is the end-use of the product. Goods which are used by the producers in the process of production such as raw material or goods purchased for resale, are known as INTERMEDIATE goods, e.g. shirt purchased by a firm for resale. These goods are still within the production boundary. Goods which are OUTSIDE the boundary line of production and are ready for use by their final USERS are called final goods, e.g. shirt purchased by a consumer. | |
| 1812. |
Differentiate between devaluation and depreciation |
| Answer» Solution :Devaluation and DEPRECIATION Definition. A devaluation occurs when a country MAKES a conscious DECISION to lower its exchange rate in a fixed or semi-fixed exchange rate. A depreciation is when there is a FALL in the value of a currency in a FLOATING exchange rate. | |
| 1813. |
What are open market operations? How do these work as a method of credit contral ? or How does a central bank control the availability of credit by open market opertions? Explain |
| Answer» | |
| 1814. |
Choose the correct alternative in the following questions. MPS equals : |
|
Answer» `1-MPC` |
|
| 1815. |
Value of marginal propensity to consume can be greater than one. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FALSE. : It is not POSSIBLE as change in consumption cannot be more thanchange in income. | |
| 1816. |
Explain the role of repo rate in controlling inflation |
| Answer» | |
| 1817. |
Which of the following is not the reason for excess demand? |
|
Answer» Fall in the propensity to consume |
|
| 1818. |
What are the functions of a commerical bank? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(a) primary functions: (i) Accepting deposits (II) Advancing of loans (B) SECONDARY functions: (i) Overdraft facility ,(ii) Discounting bills of exchange ,(iii) Agency functions ,(iv) Indvestment of funds |
|
| 1819. |
Which one of the following alternatives illustratea decrease in unemployment using the PPF? |
|
Answer» A MOVEMENT down ALONG the PPF. |
|
| 1820. |
An increase ₹250 crores in investment in an economy resulted in total increase in income of ₹1000 crore. Calculate the following : (a) MPC (b) Change in savings (c ) Change in consumption expenditure (d) Value of multiplier. |
|
Answer» Solution :Multiplier(K)=`(DeltaY)/(DELTAI)=1000/250` or K=4 `K=1/(1-MPC)` `4=1/(1-MPC)` or 4-4MPC 4MPC=3 or `MPC=3/4=0.75` `MPC=(DELTAC)/(DeltaY)` or `0.75=(DeltaC)/1000` `DeltaC=₹750 ` CRORE `DeltaS=DeltaY-DeltaC=1000-750=₹250` crore |
|
| 1821. |
Which of the following pairs of goods is an example of substitutes ? |
|
Answer» 1.Tea and sugar. |
|
| 1822. |
One characteristic not typical of Oligopolistic industry is its: |
|
Answer» HORIZONTAL demand curve. |
|
| 1823. |
How should the following be treated in estimating national income of a country ? Give reasons. Addition to stocks during a year. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Yes, as CHANGE in stock is a part of gross DOMESTIC CAPITAL formation (investment EXPENDITURE). | |
| 1824. |
Who are considered as residents of a country? |
| Answer» Solution :These INCLUDE individuals, FIRMS, GOVERNMENT agencies and monetary authority (RBI) of a COUNTRY. | |
| 1825. |
Fiscal deficit equals : |
|
Answer» INTEREST PAYMENTS |
|
| 1826. |
There is an inverse relationship between the value of marginal propensity to save and investment multiplier. Or Size of investment multiplier is given by the inverse of marginal propensity to save |
| Answer» Solution :INVESTMENT multiplier (K) is inversely RELATED to marginal propensity to SAVE (MPS) as `k=(1)/(MPS)` | |
| 1827. |
What precaustions (any four) should be taken while estimating national income by expenditure method ? |
| Answer» Solution :Precaution: (i) Expenditure on intermediate goods should not be INCLUDED, only expenditure on final goods should be included. (ii) Estimated expenditure on production for SELF consumption should be included. (III) TRANSFER of payments should not be included.(IV) Expenditure on financial assets should not be included. | |
| 1828. |
When is operatiing surplus in a producing unit zero ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :A firm's net value added at FC is distributed as factor INCOME in the form of rent, wages, INTEREST and profit. Sum of rent, interest and profit (i.e., income from property and entrepreneurship) is called operating surplus. Clearly, operating sulphus is zero : (i) When loss to the firm is equal to sum of rent, interest and profit. In other words, income generated by the firm is just equal to COMPENSATION of EMPLOYEES (ii) In general government enterprises and non-profit institutions serving households which do not earn income from property and entrepreneurship. |
|
| 1829. |
Law on demand explains quanūtauve relationship between price and quantity demanded. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1830. |
When exchange rate in terms of domestic currency rises : |
|
Answer» EXPORTS BECOME cheaper |
|
| 1831. |
Given Cash Reserve Ratio 0.19 and Statutory Liquidity Ratio 0.06, how much will be the credit creation if there are new deposits of Rs 1,000 crore in commercial banks. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Legal reserve ratio `= "CRR" + SLR = 0.19 + 0.6 = 0.25` Credit creation = NEW deposit `1//"LRR" = 1000 xx 1//0.25 = RS 4,000` CRORE |
|
| 1832. |
Other things remaining unchanged, when in a country the price of foreign currency rises, national Income is _____ |
|
Answer» LIKELY to RISE |
|
| 1833. |
Identify the following items as visible or invisible: (a) Export of jute, (b) Export of software services. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1834. |
An economy is in equilibrium. From the following data, calculate MPS. (i) Income=10,000 (ii) Autonomous consumption =500 (iii) Consumption expenditure = 8,000 |
|
Answer» Solution :`C=barC+bY` 8000=500+B(10,000) b(10,000)=7500 `b=(7500)/(10,000)=0.75` or MPC=0.75 We know that MPC + MPS =1 0.75+MPS=1 MPS=1-0.75 |
|
| 1835. |
What is primary value? |
| Answer» Solution :In a fixed EXCHANGE rate SYSTEM, the value of currency would be fixed in TERMS of other country or in terms of gold, this value is known as PARITY value. | |
| 1836. |
Explain the role the government can play through the budget in influencing allocation of resources. |
| Answer» Solution :The GOVERNMENT through its budgetary policy can reallocate the resources to different areas. In a mixed economy, the private producers aim towards profit maximisation, while, the government AIMS towards welfare maximisation. The private SECTOR always tend to divert resources towards areas of HIGH profit, while, ignoring areas of social welfare. In such a situation, the government through its budgetary policy reallocates resources to maintain a balance between the social objectives of welfare maximisation and economic objective of profit maximisation. For example- government levies taxes on socially harmful goods such as tobacco, etc., and provides subsidies for the socially desirable goods suh as FOOD grains, kerosene, etc. | |
| 1837. |
The sum of net value added at factor cost of all the producing units of an economy gives : |
|
Answer» GROSS domestic PRODUCT at market price |
|
| 1838. |
Giving reasons classify the following into direct tax and indirect tax: (i) Wealth tax, (ii) Entertainment tax and (iii) Income tax, (iv) Capital gain tax. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Wealth tax is a direct tax because its LIABILITY to pay tax and burden of tax falls on the same person. (ii) Entertainment tax (like the one included in cinema ticket) is an indirect tax because its burden can be SHIFTED. (III) Income tax is a direct tax because its liability to pay and its burden falls on the same person. (iv) CAPITAL GAIN tax is a direct tax because its impact and incidence lie on the same person. |
|
| 1839. |
Giving reasons classify the following into direct tax and indirect tax: (i) Wealth tax, (ii) Entertainment tax and (iii) Sales tax |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) WEALTH tax is a direct tax because its LIABILITY to pay tax and burden of tax falls on the same person. (ii) Entertainment tax (like the one included in CINEMA ticket) is an indirect tax because the liability to deposit tax LIES with the owners of cinema-house but the burden falls on the viewers. (III) Sales tax is an indirect tax because the liability lies with the seller but the burden falls on the buyers. |
|
| 1840. |
Which of the following fact is correct about MPC ? |
|
Answer» VALUE of MPC varies between O and 1 |
|
| 1841. |
What does Monopolistic Competition mean? |
| Answer» Solution :It refers to a MARKET SITUATION in which there are many firms which SELL CLOSELY related but differentiated PRODUCTS. | |
| 1842. |
Why money supply is termed as a stock concept? |
| Answer» Solution :Money Supply is a Stock Concept as it is CONCERNED with a particular POINT of TIME. | |
| 1843. |
Average product will increase onlywhen marginal product increases. OR Average product rises only where marginal product rises. |
| Answer» Solution :False: Average product MAY increase EVEN if MARGINAL product does not increase. Marginal product RISES and FALLS at a faster rate than the average product. Marginal product curve cuts the average product at its maximum point which implies that average product may be increasing even if marginal product is falling. | |
| 1844. |
What is the reaction of AP, when: (i) MP is more than AP. (ii) MP is less than AP. (iii) MP is equal to AP. |
|
Answer» Solution :The REACTION of AP in different cases will be: (i) AP will rise. (II) AP will fall but it will REMAIN POSITIVE. (iii) AP will be constant and at its maximum point. |
|
| 1845. |
value of investmentmultiplier(K)variesbetweenzeroandonfinfy trueor false ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Falsebeacausevalueof Kvariesbetween1andinfinity . | |
| 1846. |
Quantity measured at a point of time. |
|
Answer» depreciation |
|
| 1847. |
___ refers to actual saving in an economyduring a year. |
|
Answer» Ex-ante SAVING |
|
| 1848. |
The price elasticity of supply of a commodity is 2.5 . At a price of 5rs per unit, its quantity supplied is 300 units. Calculate its quantity supplied at a price of 4rs per unit. |
Answer» Solution : Price Elasticity of Supply (ES) `=(DeltaQ)/(DeltaP)xx(P)/(Q)` `=2.5=(DeltaQ)/(1)xx(5)/(300)`, i.e., `DeltaQ=150` As price decreases, then quantity SUPPLIED will ALSO decrease. It means, New Quantity =ORIGINAL Quantity (Q)-CHANGE in Quantity `(DeltaQ]` =`300-150=150` units New Quantity `=150` units |
|
| 1849. |
Value added means value of : |
|
Answer» Output at market prices |
|
| 1850. |
Gross Investment is also known as : (i) Gross Domestic Capital Formation, (ii) Gross Capital Formation, (iii) Groos Fixed Capital Formation, (iv) Gross Domestic Fixed Capital Formation. |
|
Answer» Both (i) and (ii) |
|