Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 1851. |
Write the name of the central bank of our country |
| Answer» | |
| 1852. |
What is the impact of excess demand? |
| Answer» Solution :EXCESS demand leads to inflation (i.e. CONTINOUS rise in prices) without any increase in output and empolyment as the ECONOMY is already operating at FULL employment level. | |
| 1853. |
If MPC=1, the value of multiplier is : (choose the correct alternative) |
| Answer» Solution :The VALUE of MULTIPLIER is `(1)/(1-MPC)`. Here, MPC. | |
| 1854. |
Identify the following as Microeconomic study or Macreconomic study Consumption expenditure by a family household. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1855. |
Creditcreationbycommercialbanksis determinedby: (Choosethe correctalternative) |
|
Answer» CASH RESERVE ratio (CRR) |
|
| 1856. |
Which one of the following is a stock variable ? |
|
Answer» income |
|
| 1857. |
When the entire output is sold in an accounting year, then vlaue of output is equal to : |
|
Answer» SALES + Change in stock |
|
| 1858. |
Factor income paid to non-residents withink the domestic territory of a country leads to : |
|
Answer» Increase in DOMESTIC Income |
|
| 1859. |
Explain three benefits of organic farming in India. |
|
Answer» Solution :(1) Cheaper inputs : Organic farming useslocally made cheaper inputs rather than costlier inputs likeHYV seeds, chemicalfertilizers and pesticides. (2) Organic food hasmore nutritionalvalue as compared to chemical inputs based forming. (3) Organic farming requiresmore labour. It is a good source of employment in rural AREAS. (4) There is largeexport demand organicfood worldwide. It can be a good source of EXPORT earnings. (5) It is eco-friendly . It is a clear cut advantage in pollution riddenIndia. |
|
| 1860. |
Explainthe distinctionbetween 'open unemployment' and'disguised unemployment'. |
|
Answer» Solution :Open unemploymentrefers to those unemployedwho are ABLE to work and willing to work but out of employmentdue to non-availability of EMPLOYMENT . Disguised unemployment REFERSTO those who are VISIBLY employedbut are not required in thatemployment in thesense that their removal will not affect total output. |
|
| 1861. |
When price of a good is Rs. 7 per unit, a consumer buys 12 units. When price falls to Rs. 6 per unit he spends Rs. 72 on the good. Calculate price elasticity of demand by using the percentage method. Comment on the likely shape of demand curve based on this measure of elasticity. |
|
Answer» Solution :`{:("Initial Price (P) = 7","Initial Expenditure = 84","Initial Quantity (Q) = 12"),("New Price "(P_(1))=6,"New Expenditure = 72","New Quantity "(Q_(1))=("Exp.")/("Price")=(72)/(6)=12),(DELTA P=(-)1,,Delta Q=0):}` `PED=(Delta Q)/(Delta P)xx(P)/(Q)=(0)/((-)1)xx(7)/(12)=0` ED is perfectly INELASTIC as quantity demanded does not change at all in response to change in price. Thus, its demand curve will be VERTICAL / parallel to y-axis. |
|
| 1862. |
Domestic product includes contribution of only resident producers within the domestic territory of the country. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1863. |
Find IDPAPS, private income, personal income and personal disposable income from the following data given below : |
|
Answer» Solution :`IDPAPS=NDP_(FC)-` Income from PROPERTY and ENTREPRENEURSHIP of government ADMINISTRATIVE departments - SAVINGS of non-departments of government `=45,000-1,200-800` `= rs 43,000` crore Private Income = IDPAPS + NFIA + Current transders from government + Current transfers from abroad + Interest on NATIONAL debt. `=43,000+200+600+400+1,300= Rs 45,500` crore Personal Income = Private income - Comporate tax - Corporate savings `=45,500-750-250= Rs 44,500` crore Personal Disposable = Personal income - direct tax - Misc. receipts `44,500-4,000-1,000= Rs 39,500` crore |
|
| 1864. |
Make a diagram representing full employment equilibrium. |
Answer» SOLUTION :
|
|
| 1865. |
Estimatethe value of Aggregate Demand in an economy if : {:("(a) Autonomous investment (I) ",,"= Rs. 100 crore."),("(b) Marginal Propensityto Save",,"= Rs. 0.2"),("(c) Level of Income (Y)",,"= Rs. 4,000 crores."),("(d) Autonomous Consumption Expenditure (c) ",,"= Rs. 50 crore"):} |
|
Answer» Solution :`{:("AD = C + I"),("= "BAR(C)"+MPC (Y)+I"):} ` `{:("= 50 + ( - 0.2) ( 4,000) + 100"),("= 50 + 3,200 + 100"):}` `{:(),(" = Rs. 3,350 crore"),():}` |
|
| 1866. |
Gifts and remittances to abraod are recorded in the |
|
Answer» CREDIT SIDE of CAPITAL account |
|
| 1867. |
Autonomusincreasein investmentproduces autonomousincreasein income . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1868. |
How does central bank control credit creation by commercial banks through open market operations ? Explain |
| Answer» Solution :Open market operations means the sale and purchase of all kinds of bills and securities by the ''central BANKS in the open market''. In narrow terms, this method, signifies sale and pruchase of government securities by central bank in the open market. In short, according to this method central bank CONTROLS the volume of CREDIT by increasing or decreasing the quantity of money in the economy through sale and purchase of securities in the money market. The functioning of this method is like this: When central bank of the country wants to increase the volume of credit, it starts purchasing securities from the market. These securities are generally bougth at a higher price than the market price. As such, banks start selling them, as a result of which their cash reserves increase, i.e., their liquid assets increase. As a result of this, banks now can create more credit. On the contrary, when central bank wants to control the volume of credit, it starts selling securities in the market which are bought by the COMMERCIAL banks. With the result, their cash reserves are reduced and this adversely AFFECTS their power of creating credit. In short, ''for expanding the volume of credit central bank purchases securities and for reducing the volume of credit, it sells securities in the open market. In this way, according to this method, the volume of credit is controlled and regulated by controlling and regulating the cash reserves and credit creating power of commercial banks. | |
| 1869. |
Which of the following options is a property of an indifference curve ? |
|
Answer» It is convex to the origin. |
|
| 1870. |
Explain the feature 'interdependence of firms' in an oligopoly market. |
| Answer» Solution :There exists a very HIGH degree of mutual interdependence between the firms in an oligopoly market. The price and the quantity decisions of a particular FIRM are dependent on the price and the quantity decisions of the rival (other) firms. HENCE, a firm must take into CONSIDERATION the probable rival REACTIONS, while formulating its own price and output decisions. | |
| 1871. |
Average propensity to consume can be greater than one. |
| Answer» Solution :True. : Average PROPENSITY to CONSUME can be GREATER than one when CONSUMPTION is greater than income. | |
| 1872. |
Japanese Embassy in India is a part of domestic territory of : |
|
Answer» India |
|
| 1873. |
Foreign exchange is a stock of |
|
Answer» FOREIGN currencies |
|
| 1874. |
When does NFIA become positive or negative ? |
| Answer» Solution :NFIA is POSITIVE when the INCOME earned by the NORMAL residents of the COUNTRY from abroad is more than the income earned by foreigers in India and vice versa. | |
| 1875. |
State the components of (i) current Account and (ii) capital Account. |
| Answer» Solution :(i) COMPONENTS of current account are (a) Export and import of goods, (b) Export and import of services, (c) UNILATERAL transfers and (d) Investment income (interest and dividend). These do not cause CHANGE in assets and liabilities. (ii) Components or various forms of capital account are (a) foreign investment, (b) Foreign loans and commercial BORROWINGS, (c) BANKING capital (includes assets and liabilities) and (d) Change in foreign exchange reserve. | |
| 1876. |
If the supply curve is a vertical straight line, change in demand will not affect equilibrium price. |
| Answer» Solution :False: A vertical straight line supply CURVE IMPLIES that the quantity supplied cannot be CHANGED. If the demand increases, equilibrium PRICE will increase proportionately. | |
| 1877. |
whyis consumptionexpenditure ofinvoluntarolyunemployed not zeroat zerolevelof income ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Evenanunemployed workerwithno ( ZERO) incomehasto SPEND a minmumamountonconsumptiontokeephisbody andsoul togetheri.e.,to survivethisis calledautonomous consumptionsincehe isunemployedhavingno SOURCE. Of INCOME, heuseshispastsavingorassetsorborrows . | |
| 1879. |
Giving reasons, state whether the following statements are true or false: (i) A monopolist can sell any quantity he likes at a price. (ii) when equilibrium price of a good is less than its market price, there will be competition among the sellers |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) The statement is false. The price is fixed at a POINT where marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue. If a monopolist fixes a price less or more than the price fixed at EQUILIBRIUM point, the QUANTITY will be more or less than the equilibrium quantity but not the quantity that a monopolist would like to sell. (II) The statement is true. In this situation, market price is higher than the equilibrium price. As a result or which supply will be more than demand. As such there will be competition among the sellers. In other words, sellers would like to sell their entire quantity to meet the demand which (supply) is much more than the demand. |
|
| 1880. |
What would be an affect on supply curve of the following : (a) Decrease in tax on product. (b) Subsidy on production of goods. (c ) Rise in own price of a piece of goods |
Answer» Solution :(a) Decrease in tax on product. DUE to decreases tax on product the cost of PRODUCTION of a firm decreases and supply of a GIVEN commodity increases and thereby shifts the supply curve rightward as shown in the given figure :  (B) Subsidy on production of goods : If a government gives subsidy to a firm for production of goods, the cost of production of firm decreases for producing this goods, that will increase the supply and thereby shifting in the supply curve to the right as shown in the given figure:  (c ) Rise in own price of goods : Dueto rise in own price of good, the quantity SUPPLIED for a given commodity also rises because there is positive relationship between own price of good and quantity supplied of a given commodity. So, due to rise in price of commodity, there will be upward movement along the supply curve as given below : 
|
|
| 1881. |
The Indian Government launched Incredible india or Atulya Bharat Campaign to promote tourism in India . Howwill it effect the price of foreign exchange ? |
| Answer» Solution :The launch of INCREDIBLE India campaign will lead ot increases in SUPPLY of the foreign EXCHANGE in India (due to increases in foreigntourists). It will RESULT is decreases in price of the foreign exchange. | |
| 1882. |
What are the main forms of market? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) Perfect competition (ii) Imperfect competition. (a) MONOPOLY (b) MONOPOLISTIC competition (c ) Oliopolgy. |
|
| 1883. |
What is the behaviour of TP, when (i) MP rises (ii) MP falls, but remains positive (iii) MP is zero (iv) MP becomes negative? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The behaviour of TP in different cases will be: (i) TP increases at increasing rate. (ii) TP increases at diminishing rate. (iii) TP is at its maximum and CONSTANT. (IV) TP DECREASES. |
|
| 1884. |
Explain the roic of reverse repo rate in controlling money supply. |
| Answer» Solution :Reverse repo rate' is the rate of interest at which the COMMERCIAL BANKS park their surplus funds with the central bank. The central bank can control money supply by changing the reverse repo rate (RRR). RISE in RRR ENCOURAGES commercial banks to park more funds with the central bank This REDUCES funds available for lending to general public by the commercial banks. | |
| 1885. |
Out of the following , which aggregate represents 'National income ' ? |
|
Answer» `N NP_(MP)` |
|
| 1886. |
Distinguish between final goods and intermediate goods. Give an example of each. |
|
Answer» Solution :FINALS goods are those goods which are used by the consumers for final use. For example- A pen. Intermediate goods are those goods which are not ready for final consumption and are used as RAW materials for further production. These goods are not meant for SALE. For example - BODY of a pen. |
|
| 1887. |
Total Utility increases as long as marginal utility is positive (+). |
| Answer» Solution :TRUE : Because TU is the SUM of marginal utilities and MU is POSITIVE. | |
| 1888. |
Discuss briefly the meanings of: (i) Fixed Exchange Rate (ii) Flexible Exchange Rate (iii) Managed Floating Exchange Rate |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) Fixed Exchange Rate: is the exchange rate determined by the government for CONVERSION of domestic currency into foreign currency. (ii) FLEXIBLE Exchange Rate: is the rate of exchange which is determined by the market FORCES of demand and supply in the foreign exchange market. (III) Managed Floating Exchange Rate: Floating rate influenced by buying and selling foreign exchange by the central bank in the foreign exchange market. |
|
| 1889. |
Discuss briefly the meanings of (i) Fixed Exchange Rate (ii) Flexible Exchange Rate (iii) Managed Floating Exchange Rate |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Fixed Exchange Rate: is the exchange rate determined by the government for conversion of DOMESTIC currency into foreign currency. (II) Flexible Exchange Rate: is the rate of exchange which is determined by the market FORCES of demand and supply in the foreign exchange market. (III) Managed Floating Exchange Rate: Floating rate influenced by buying and selling foreign exchange by the central bank in the foreign exchange market. |
|
| 1890. |
How an initial increase in investment affects the level of final income of the economy? Show its working with a suitable numerical example. |
|
Answer» Solution :Initial increase in investmentincrease in investmentthe finalincomeof theeconomy. Investmentmultiplierexplainsthis effect, MONEY Multiplier(k) is the ratio of the increasein National Income `(DeltaY)`due ofa givenincreasein investments `(DelatI)` . `K = {DeltaY//DeltaI}` For eg. If an additional investment of 1,000 croresis madeby governmentfor a bullet train project ina country , thisextra investmentwill generate an extraincome of 1,000 crores ,as expenditure of one is incomefor another. ALSO, it is assumed that Marginal Propensityto CONSUME of the countryis 0.8 .Anadditionalinvestmentof 1000 crores `(DeltaI)`madeby governmentwill generate extraincomeof 1000 crores in first round. If MPCof thiscountry is 0.8, the nationalswhoarenationals who are receivingthisadditionalincome willspends 80% portion of thisadditionalincomei.e.,800 crores , whichin return, becomes additionalincome during thirdround . Similarin thirdround, 640 crores of income is generated . Consumptionexpenditure in everyround willbe 0.8 times of additionalincome receivedincome reviewedfromprevious round.  Thus, an initial investment of Rs. 1000 crores leads to a TOTAL increase of Rs. 5000 crores in the income. As a result, Multiple (K) `=(DeltaY)/(DeltaI)=(5000)/(1000)=5` |
|
| 1891. |
Differentiate between National Income at Current Prices and National Income at Constant Prices. While of the two presents a better view of the economic growth of economy and why ? |
| Answer» Solution :National Income at Current Price:It is the money value of final goods and services produced by normal residents of a country in a year, measured at the prices of the current year. For EXAMPLE, MEASUREMENT of India. National Income of 2013-2014 at the prices of 2013-2014.i. It is also KNOWN as Nominal National Income.ii. It does not show the TRUE picture of economic growth of a country as any increase in nominal national income may be due to rise in price level without any change in physical output.So, in order to eliminate the effect of price changes, national income is also estimated at a constant price.National Income at Constant Price:It is the money value of final goods and services produced by normal residents of a country in a year, measured at base year price. Base Year is a normal year which is free from price fluctuations. Presently 2004-2005 is taken as the base year in India. If we measure India National Income of 2013-2014 at the prices of 2004-2005, then it is termed as National Income at constant price.i. It is also known as Real National Income.ii. It shows the true picture of economic growth of a country as any increase in real national income is due to increase in output only.The National Statistical Commission (NSC), has suggested to revise the base year to 2011-12 from the current base year of 2004-05 for the CALCULATION of new Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of the country | |
| 1892. |
What are the measures to correct budget deficits ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Mainly there are TWO types of measures to correct budget deficits : By reducing (containing ) the deficit By financing the deficit I . Reducing or Containing the Deficit in Budget . The deficit in budget can be reduced or contained through : (i) Raising Government Receipts : Government should make plans to INCREASE its receipts Government shouldimpose new taxes and increase the rate of EXISTING taxes . Taxation should be progressive in nature . Increase in taxation should not hit the inducement to invest . Apart from taxes , non tax revenue should also be increased e.g. , licence fee , escheat, special assessment etc. (ii) Reduction in Government Expenditure : It can be done through better planning and administration . Government should take steps to reduce non-developmental expenditure . Government should invite private sector to develop the economy. II. By Financing the Deficits. If government is not ABLE to bridge the gap between its estimated expenditure and receipts then the deficit may be financed by the following ways : (i)Monetary Expansion . It is deficit financing which is done by printing currency notes to the extent of the deficit . It refers to borrowings by the government from RBI against required securities . It needs to be carefully done , otherwise it may lead to inflation , if more than required MONEY comes into circulation . (ii) Borrowing from the Public . To finance its deficit , the government borrows from the general public by issuing various securities . (iii) Disinvestment . It refers to financing the deficit by selling government assets to the private sectors . Here the government sells its existing shares in public sector to the private sector . |
|
| 1893. |
Sales by Firm A are Rs. 80 crores and sales by firm B are Rs. 300 crores. Value added by B and C are equal. Value of output of C and D are Rs. 280 crores each. Value added by D is Rs. 120 crores and GDP_(MP) is Rs. 520 crores. Assuming A's value of inputs are zero, calculate: (i) Value added by firm B and firm C, (ii) Value of Inputs of firm B, (iii) Value of Inputs of firm C. |
|
Answer» Let the value added by firm B=X It means: Value added by firm B = Value added by firm C=x Value of INPUTS of firm D = Value of output - Value Added =280-120=160 Value of inputs of firm B and firm C are taken C are taken as `VI_(B) " and " VI_(C )` respectively 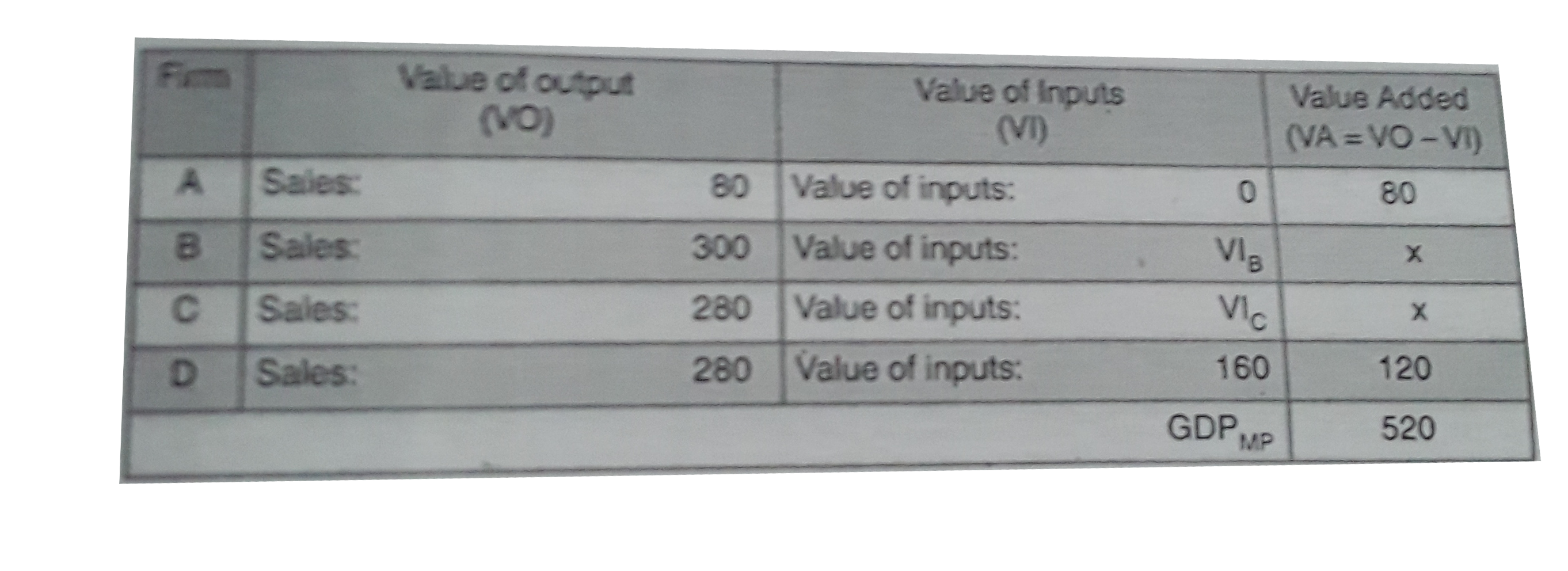 Value added by firm A =80 Value added by firm B =x Value added by firm C =x Value added by firm D =120 `GDP_(MP)""=520` It means: `80+x+x+120=520` 2x=520-200 or x=Rs. 160 crores Value of Inputs of firm B = Value of output - Value Added = 300-160= Rs. 140 crores Value of Inputs of firm C = Value of output - Value Added = 280-160= Rs. 120 crores |
|
| 1894. |
Which of the following constitute the reason for difference between Market Prices and Factor Cost ? |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 1895. |
Even the price of petrol is very high but still its demand is very high. How can the demand of petrol be decreased? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) By car pooling (ii) by using public TRANSPORT SYSTEM (III) By using alternative and renewableresources of petrol such as solar ENERGY. value : Awarness for EFFICIENT use of resources |
|
| 1896. |
Distinguish (a) between current account and capital account, and (b) between autonomous transactions and accommodating transactions of balance of payments account. |
| Answer» Solution :a) Current Account: An account which records the export and import of merchandise and unilateral transfers done during the year by a nation are known as Current Account.Capital Account:An account which records the TRADING of foreign assets and liabilities during the year by a country is known as Capital Account.b)Autonomous transactions are the transactions between the residents of two countries which TAKE place due to the consideration of profit. Autonomous items are not conditioned by the BoP status of the country, i.e. these are independent. These transactions are not done to establish identity of BoP. These are also known as ‘above the line items’ and take place in both the accounts of BoP, i.e. current and capital account.Accommodating . transactions are those transactions which are not done due to the consideration of profit but to restore identity of BoP. These are undertaken to maintain balance in the BoP account. These transactions correct the disequilibrium in autonomous items of BoP account. Accommodating transactions are also known as ‘below the line items’ and include foreign exchange reserves and BORROWINGS to meet BoP DEFICIT.BoP deficit When the payments of a country on account of autonomous transactions EXCEED the receipts of the country on account of autonomous transactions, this difference is termed as BoP deficit.BoP Deficit = Receipts on Account of Autonomous Transactions < Payments on Account of Autonomous Transactions | |
| 1897. |
At what point equilibrium rate of foreign exchange is determined? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Equilibrium rate of EXCHANGE is determined at the POINT where DEMAND and supply of foreign exchange are EQUAL. | |
| 1898. |
Calculate (a) Depreciation , (b) Subsidies, (c) NDP at FC. |
|
Answer» = GNP at MP - NNP at MP = 1, 07 , 000 - 1, 00, 000 =₹ 7 , 000 crores (b) Subsidies = GNP at FC - GNP at MP + Indirect Tax = 95 , 000 - 1, 07 , 000 + 14, 000 =₹ 2 , 000 crores (c) NDP at FC = NDP at MP - (Indirect Tax - Subsidies ) = 1, 00, 422 - (14 , 000 - 2, 000) =₹ 88 , 422 crores |
|
| 1899. |
Expenditure Method focuses on measurement of National Income at : |
|
Answer» Phase of production of goods and services |
|
| 1900. |
Price elasticity of demand for a product is 'unity'. A household buys 25 units of this product at the price of Rs. 5 per unit. If the price of product rises by Rs. 1, how much quantity of the product will the household buy ? |
|
Answer» <P> Solution :`{:("Original Quantity (Q) = 25 unitsOriginal Price (P) = Rs. 5"),("NEW Quantity "(Q_(1))=? "RISE in Price "(Delta P)=-Rs. 1),("Change in Quantity "(Delta Q)=? "New Price "(P_(1))=Rs. 6),("Elasticity of Demand (ED) = 1"):}`Price Elasticity of demand `(ED)=(Delta Q)/(Delta P)xx(P)/(Q)` `1=(Delta Q)/(1)xx(5)/(25)i.e.,Delta Q=5` units. As price is increasing, the quantity demanded will DECREASE. It means that New quantity = Original quantity (Q) - Change in quantity `(Delta Q)=25-5` = 20 units New Quantity = 20 units |
|