Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 751. |
Explain national income determination through the two alternative approaches. Use diagram. |
Answer» Solution :According to the Keynesian Theory, equilibrium condition is generally stated in terms of aggregate demand (AD) and aggregate supply (AS). An economy is in equilibrium when aggregate demand for goods and services is equal to aggregate supply during a period of time.So, equilibrium is achieved when:AD = AS … (1)We have SEEN how equilibrium level of national income is determined by the interaction of aggregate demand and aggregate supply.. But there is an alternative method for the explanation of the determination of national income. This alternative method EXPLAINS the determination of national income DIRECTLY by intended saving and investment So, equilibrium is achieved when :S = I ...... (2)The national incomedetermination can be better understood with the help of followng DIAGRAM: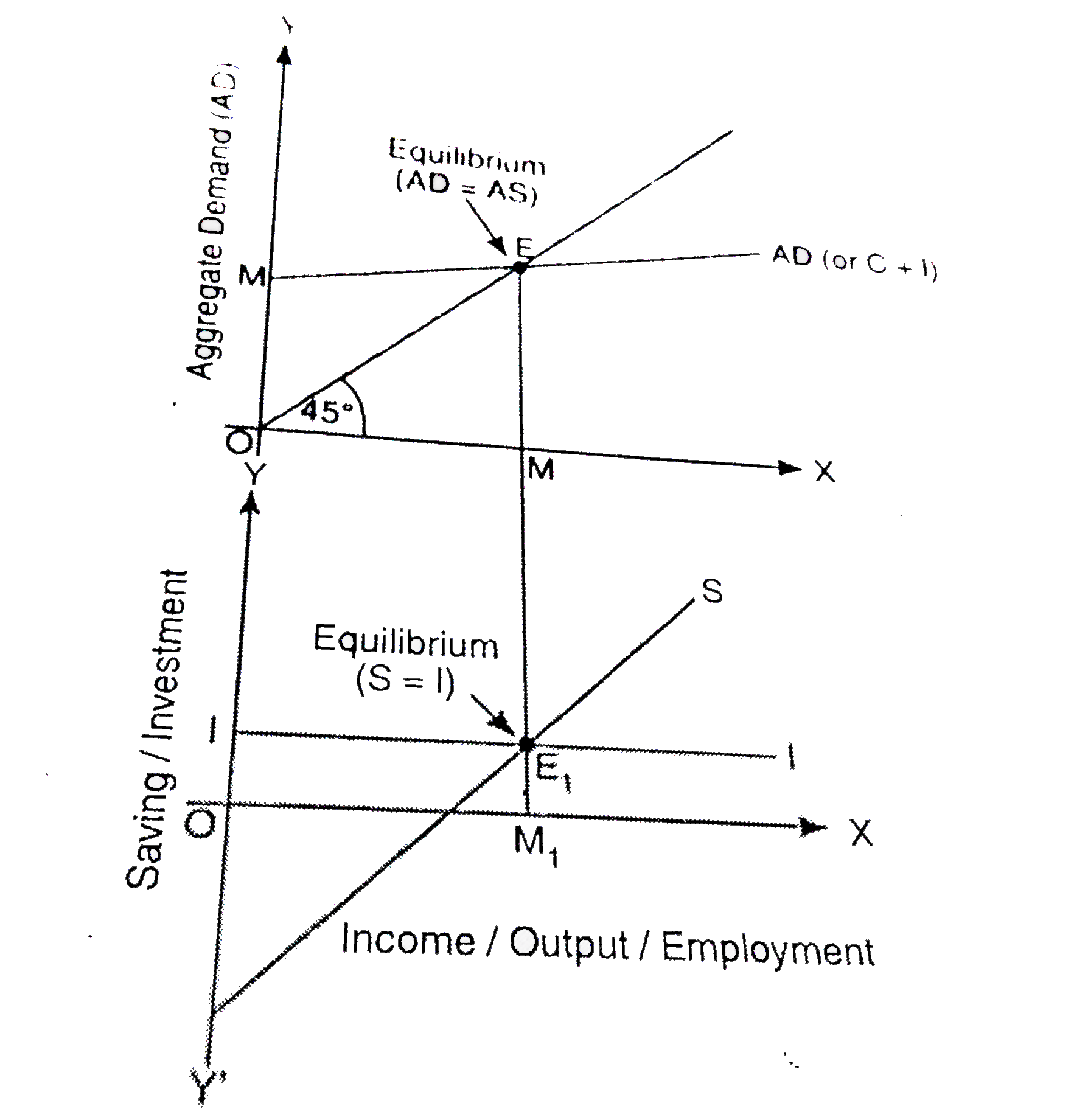 |
|
| 752. |
Illustrate with the help of a hypothetical numerical example the process fo credit creation |
| Answer» | |
| 753. |
Explain the 'unit of account' function of money .How has it solved the related problem created by barter |
| Answer» | |
| 754. |
Explain how is it possible for marginal product to fall while average product is rising? |
| Answer» Solution :AVERAGE PRODUCT can RISE even if marginal product is falling as LONG as the marginal product is higher than the average product. | |
| 755. |
Define market rate of exchange. |
Answer» SOLUTION :The rate at which market requires to sacrifice one commodity to gain an additional unit of another commodity is called market rate of exchange. 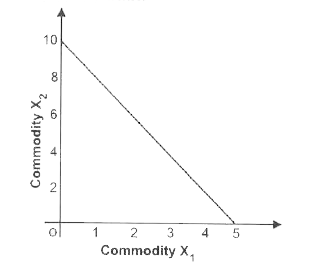 `MRE_(x_1,x_2)=("Change in Quantity of Good Sacrificed"(DeltaX_2))/("Change in Quantity of Good Gained"(DeltaX_1))` or, `MRE_(x_1,x_2)=("Gained"[P_1])/("Price of Good Sacrificed" [P_2])` This can be EXPLAINED with the HELP of the following diagram Let consumer.sMoney Income is 10 and Priceof commodity 1 is 2 and price of commodity 2 is 1. i.e., M = 10 , `P_1= 2 and P_2=1` . MRE is constant throughout because `P_1 and P_2`on the basis of which it is calculated are constant throughout. |
|
| 756. |
Explain the following (i) Why are imports deducted while calculating domestic product through the expenditure method ? (ii) Why is 'indirect tax' deducted while estimating national income by expenditure method ? (iii) Why are free facilities given the employees included in national income ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) IMPORTS are deducted because PFCE, GFCE and GDCF components of expenditure method contain expenditure on imports which are not produced in the domestic TERRITORY (ii) National income is NNP at factor cost. To arrive at factor cost indirect tax is deducted because this component of market price does not go to production units for distribution as factor payments (iii) FREE facilities to employees are addedbecause the ESTIMATED value of these facilities is compensation of employees and is in lieu of the services performed to production units |
|
| 757. |
In an economy , the equilibrium level of income is Rs.12,000 crore. The ratio of marginal propensity to consume and marginal propensity to save is 3:1. Calculate the additional investment needed to reach a new equilibruim level of income of Rs. 20,000 crore. |
|
Answer» Multiplier (K) `= (1)/(MPS)=(1)/(0.25)=4` We ALSO know: k `=("Change in Income"(DeltaY))/("Change in Investment"(Deltal))` Given: Change in Income `(DeltaY) =20,000 = Rs. 8,000` crores i.e., `=(8,000)/("Change in Investment"(Deltal))` Hence, Change inInvestment `(Deltal) = Rs. 2,000` crores |
|
| 758. |
Indian investors lend abroad. Answer the following questions:In which sub-account and on which side of the Balance of Payments Account such lending is recorded? Give reasons.(b)Explain the impact of this lending on market exchange rate. |
|
Answer» (b) Lending abroad increases demand for foreign exchange. Supply of foreign exchange remains unchanged, exchange rate may rise. |
|
| 759. |
Explain 'banker to tne government function of the central bank |
| Answer» Solution :Central bank functions as a banker to the government—both central and state governments. It carries out all banking business of the government. Government keeps their cash BALANCES in the current account with the central bank. Similarly, central bank accepts receipts and makes payment on behalf of the governments.Also, central bank carries out exchange, remittance and other banking operations on behalf of the government. Central bank gives LOANS and advances to governments for temporary periods, as and when necessary and it also manages the public DEBT of the COUNTRY. Remember, the central government can borrow any amount of money from RBI by selling its rupees SECURITIES to the latter. | |
| 760. |
Foreign exchange transactions dependent on other foreign exchange transactions are called: |
|
Answer» CURRENT ACCOUNT TRANSACTIONS |
|
| 761. |
What is meant by LRR ? State its components. |
| Answer» Solution :LRR is the percentage ( ratio ) of deposits which banks are legally required to keep in the form of cash with (i) themselves and with (II) CENTRAL BANK. It has two components. The percentage of cash the banks keep with themselves is CALLED SLR and whatthey keep with Central Bank is called CRR. | |
| 762. |
Balance of Payments is a______concept. |
|
Answer» Stock |
|
| 763. |
When the price of a good falls from 10rs per unit to 8rs per unit, its supply falls by 25 units from 125 units. Calculate elasticity of supply (ES) by percentage method. |
|
Answer» <P> Solution : Percentage change in price= `(DeltaP)/(P)xx100=(2)/(10)xx100=20%` Percentage change in supply `= (DeltaQ)/(Q)xx100=(25)/(125)xx100=20%` `ES=1` (Supply is unit ELASTIC) ES is always positive due to DIRECT relationship between price and quantity supplied. |
|
| 765. |
The government budget of a hypothetical economy presents the following information . Which of the following value represents . Budgetary Deficit . (all fig . In ₹crores ) A . Revenue Expenditure =25 , 000 B . Capital Receipts = 30 , 000 C . Capital Expenditure= 35 , 000 D. Revenue Receipts = 20 , 000 E. Interest Payments = 10 ,000 F. Borrowing = 20, 000 |
|
Answer» ₹ 12, 000 Budgetary Deficit = Revenue Expenditure + CAPITAL Expenditure - (Revenue RECEIPTS + Capital Receipts) = 25, 000 + 35 , 000 - (20 ,000 + 30 , 000) =₹10 , 000 crores . |
|
| 766. |
Which of the following is not a subject matter of microeconomics? |
|
Answer» 1.Consumer's behavior |
|
| 767. |
Does a fall in incomehave the same effect on demand for the givencommodity? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :No, fall in INCOME does not have the same effect on DEMAND for the given commodity. (i)If the given commodity is a normal good, the fall in income will REDUCE the demand for the normal goods. (ii) If the given commodity is an inferior good, the fall in income will raise the demand for the inferior goods. (iii)If the given commodity is a necessity, the fall in income will not CHANGE the demand for the necessity of goods. |
|
| 768. |
What is the meaning of open market operations? |
| Answer» Solution :Open market operations refer to slae and PURCHASE of securities (GOVERNMENT securities) in the open market by the central BANK open market refers to COMMERICAL banks and PUBLIC | |
| 769. |
Give the meaning ot marginal propensity to save. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The marginal propensity to save (MPS) is the FRACTION of an INCREASE in income that is not spent on an increase in consumption. That is, the marginal propensity to save is the proportion of each additional dollar of household income that is USED for saving. It is the slope of the LINE plotting saving against income. | |
| 770. |
Averagepropensityto saveis alwaysgreater thanZero . Defend or refute . |
| Answer» SOLUTION :the givenstatementis refuted APS . Can benegative AL lowlevel of income whenconsumption EXPENDITURE is greaterthan income . | |
| 771. |
Calculate personal income and personal disposable income. |
|
Answer» Solution :1. Personal Income = Private income - Corporate tax - Corporate savings `=15,000-1,000-2,000` `= Rs 12,000` lakh 2. Personal disposable Income = Personal income - Direct tax - Misc. receipts `=12,000-2,500-1,500` `= Rs 8,000` lakh Here, ITEM no. 1 is not required as private income is GIVEN DIRECTLY. Item no. 4 is included in private income, hence not required. NOTE : More numerical questions on above formulae will be discussed after the differences. |
|
| 772. |
Reporateof interestis paidbycommericalbankandreversereopois paidby RBI. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 773. |
Why can the value of MPC be not greater than one ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Because we can CONSUME as MUCH as our INCOME has INCREASED. | |
| 774. |
A vertical supply curve parallel to Y-axis implies that the elasticity of supply is : |
|
Answer» ZERO |
|
| 775. |
State the law of supply. |
| Answer» Solution :It STATES that price of the commodity and QUANTITY supplied are POSITIVELY RELATED to each other when other factors remain constant (ceteris paribus) | |
| 776. |
Why does the difference between Average Total Cost and Average Variable Cost decrease with an increase in the level of output? Can these two be equal at some level of output? Explain. |
Answer» Solution :As, we know the difference between Average Total Cost and Average Variable Cost is average fixed cost `(AFC = ATC - AVC)` and AFC always decreases with the increase in output. It can be explained with the help of the following diagram and schedule.  It can be seen from the above diagram that there is a huge GAP between AC and AVC with the starting of production.  The gap between them decreases with the increase in production. It is so because the gap between AC and AVC is AFC and AFC always decreases with the increase in production. The point to be remembered is that AVC can NEVER touch AC curve because AFC cannot be Zero. 
|
|
| 777. |
Goods produced for self-consumption will be included in national income. |
| Answer» Solution :True. Such goods CONTRIBUTE to the current OUTPUT and their imputed value will be included in national INCOME. | |
| 778. |
What determines the rate of foreign exchange? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The rate of FOREIGN exchange is deterined by forces of DEMAND and supply of foreign exchange. | |
| 779. |
When do you say there is excess demand for a commodity in the market ? |
| Answer» Solution :When MARKET price is below the EQUILIBRIUM price, then at that given price, DEMAND is greater than supply that leads to EXCESS demand. | |
| 780. |
Consumers often suffer because of their ignorance about the market situations and pay higher price than the equilibrium price. How can this be avoided? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Consumers should be vigilant and aware about the MARKET situation, i.e., they should know the prevailing market prices. In this way they WIL not suffer because of being IGNORANT Value: Awareness about Marketsituation | |
| 781. |
State the structure ofcooperativesinagricultural marking in India. |
|
Answer» Solution :VILLAGE level : Primary MARKETING Societies DISTRICT level : Central MarketingSocieties State level : CooperativeMarketingFederations NATIONAL : National CooperativeFederations |
|
| 782. |
Increase in margin requirements helps to control the situation of deficient demand. |
| Answer» Solution :False. MARGIN requirements needs to be reduced to enhance the CREDIT creatingpower of commercial banks and to CORRECT the DEFICIENT demand. | |
| 783. |
In a situation of fall in the sale of ice cream, the ice cream producer would like to reduce the production. What factors of production fixed or variable will be reduced by him? Explain with reasons. |
|
Answer» Solution :When SALE of ice cream decreases, profit of producer will fall by which he will TRY to CONTROL his cost of production but in short run he cannot CHANGE the cost of fixed factors therefore he will reduce the cost of variable factors. Value: ANALYTIC |
|
| 784. |
Fiscal deficit equals ______: |
|
Answer» INDIRECT PAYMENT |
|
| 785. |
The area of cultivable land is more or less fixed in a country. Under such conditions suggest two ways to increase the productivity of land. |
|
Answer» Solution :The productivity of LAND can be INCREASED by Using BETTER inputs and techniques of PRODUCTION and By shifting the USE of land from a low-value use of a high-value use. Value : Efficient Utilisation of resources |
|
| 786. |
Elaborate 'stabilization function' ofgovernment budget. |
| Answer» Solution :Economic stability means ABSENCE of large scale fluctuationsin price level which cause uncertaintyand HARDSHIPS to people. In inflationarysituation,GOVERNMENT can discouragespending by increasingtaxes and reducingits own expenditure. Indeflationaryconditions, governmentcan encouragespendingby lowering TAXES and increasingits own expenditure on publicworks. | |
| 787. |
Can Average revenue be zero. |
| Answer» Solution :False : AVERAGE revenue will be ZERO if a good is sold free of any charge. But these are not treated as economic goods. All economic goods command a price. HENCE, AR cannot be zero. | |
| 788. |
What are the 2 kinds of propensities to save ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(i) Average PROPENSITY to save (APS), (II) MARGINAL propensity to save (MPS). | |
| 789. |
Mention one main difference between a central bank and a commercial bank. |
| Answer» Solution : The CENTRAL bank has SOLE MONOPOLY in note issue, whereas, this power is not ENJOYED by a COMMERCIAL bank. | |
| 790. |
Giving reason comment on the shape of Production Possibilities curve based on the following schedule. |
Answer» Solution :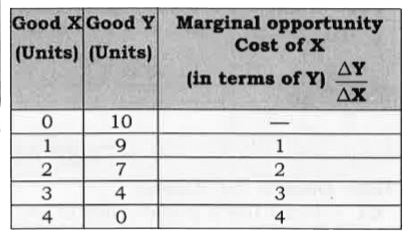 The PRODUCTION Possibility CURVE is DOWNWARD sloping concave because of increasingmarginal OPPORTUNITY COST. |
|
| 791. |
Giving reason comment on the shape of production Possibilities curve based on the following schedule. |
Answer» Solution :  The PRODUCTION Possibility CURVE is downward SLOPING CONCAVE because of increasing marginal opportunity cost. |
|
| 792. |
Giving reason comment on the shape of production Possibilities curve based on the following schedule. |
Answer» SOLUTION :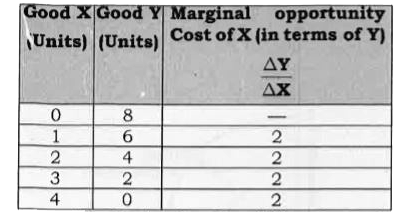 The production POSSIBILITY Curve is DOWNWARD sloping STRAIGHT LINE because of constant marginal opportunity cost. |
|
| 793. |
Which of the following items raises the supply of foreign exchange ? |
|
Answer» Import of GOODS from CHINA |
|
| 794. |
Giving reason comment on the shape of Production Possibilities curve based on the following schedule. |
Answer» SOLUTION :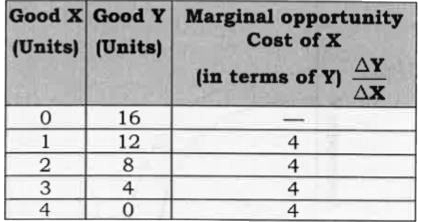 The production Possibility CURVE is downward SLOPING straight LINE because of constant marginal opportunity COST. |
|
| 795. |
A growing country is one with : |
|
Answer» Rising GNP at constant PRICES |
|
| 796. |
Calculate 'Net National Product at Market Price' and 'Personal Income'* * :(Rs.crores) (i) Transfer payments by government 7(ii) Government final consumption expenditure 50(iii) Net imports (-)10(iv) Net domestic fixed capital formation 60 (v) Private final consumption expenditure 300 (vi) Private income 280(vii) Net factor income to abroad (-)5(viii) Closing stock 8(ix) Opening stock 8(x) Depreciation 12(xi) Corporate tax 60(xii) Retained earnings of corporations 20 |
|
Answer» Solution :`N NP_(MP)` = PRIVATE final consumption expenditure + Government final consumption expenditure + (Net DOMESTIC fixed capital formation + depreciation) + CHANGE in stock - Net imports - depreciation - Net FACTOR income to abroad `N NP_(MP)=300+50+60+12+(8-8)-(-10)-12-(-5)` `N NP_(MP)`=Rs.425 CRORE |
|
| 797. |
What precautions (any four) should be taken while estimating national income by income method ? |
| Answer» Solution :Precautions: (i) Transfer of payments should not be includes as there is no value addition in the economy. (ii) CAPITAL gains from sale of old GOODS should not be INCLUDED. (iii) Commission etc of brokers on sale of old goods should be included as these are reward for rendering factor SERVICES. (IV) Transaction in financial assets should not be included. | |
| 798. |
Whichoftheseconditionsis neededfora financialinstitution to become a bank ? |
|
Answer» ACCEPTING deposit |
|
| 799. |
What is the nature of i) Relation between price and demand of foreign exchange ii) Relation between price and supply of foreign exchange? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :There is INVERSE relationship between rate for foreign EXCHANGE and demand for foreign exchange. There is positive relationship between rate of foreign exchange and SUPPLY of foreign exchange. |
|
| 800. |
Calcualate Opreating surplus : {:(,,(Rs."crore")),((i),"GNP at market price",1000),((ii),"Wages and salaries",400),((iii),"Consuption of fixd capital",400),((iv),"Net factor income to abroad",(-)10),((v),"GST",100),((vi),"Social security contributions by emlytyees",60),((vii),"Subsidies",20),((viii),"Mixed income of the self-emplyoed",200),((ix),"Inteset",40),((x),"Social security cobntribution by employers",100):} |
|
Answer» |
|