Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 651. |
Multiplier is the ratio of the increase in income to a given increasein investment |
|
Answer» |
|
| 652. |
Giving reasons, explain how the following are treated while estimating national income: (i) Payment of fees to a lawyer engaged by a firm. (ii) Rent-free house to an employee by an employer. (iii) Purchases by foreign tourists. |
|
Answer» (II) The ESTIMATED rent is included as compensation of employees through the income method. (III) It is treated as export and included through the expenditure method. |
|
| 653. |
Suppose government imposes ban on consumptionof liquor . Analyse itseffects on (a) GDP and (b) welfare. |
|
Answer» Solution :Imposing ban onconsumptionof liquorwill DRASTICALLY reduceproduction of liquor . As a result GDP will decline.This is the direct EFFECT on GDP. Reductionin consumptionof liquor will significantly improvehealth of those who CONSUME liquorwhich in turnwillincrease their efficiency,income , ETC. This will INCREASE welfare. |
|
| 654. |
A consumer consumes only two goods X and Y both prices at Rs 2Perunit if the consumer choose a combination of these two goods with Marginal Rate of Substitution equal to 2 , is the consumer in equilibrium ? Give reasons. What will a rational consumer do in this situation ? Explain. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The equilibrium condition for a rational consumer is Marginal Rate of Substitution `(MRS_(x,y)) ` = MARKET Rate of Exchange `(MRE_(x,y)=P_x//P_y ) ` `2 = 2/2 :. 2 ne 1 ` The above example gives inequality, as `MRS_(x,y)(2) gt MRE_(x,y)(1) [(P_x)/P_y],(MU_x)/(MU_y)gt P_x/P_y` or `(MU_x)/(MU_y)gt P_x/P_y` It means the consumer.s willingness to pay for commodity X is higher than what market values for commodity X So, the consumer should BUY more of X and less of Y to get `MRS = P_x/P_y`In other words, marginal utility from the last rupee willing to spent on commodity X is more than marginal utility from the last rupee willing to spent on Commodity Y . So, to attain the equilibrium the consumer MUST increase the quantity of X, decreases the `MU_x`and decrease the quantity of Y, which will increase the `MU_y`Increase in quantity of X and decrease in quantity of Y continue till `MRS_(x,y)= MRE_(x,y)` |
|
| 655. |
From the following information , determine : (a) Capital Expenditure , (b) Total Expenditure and (c) Interest Payments : |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) FISCAL Deficit = Revenue Deficit + (CAPITAL EXPENDITURE - NON - debt Creating Capital Receipts) ₹ 12 , 000 crores = ₹ 9 , 000 crores + (Capital Expenditure - ₹ 10 , 000 crores ) Capital Expenditure= ₹ 12 , 000 crores - ₹ 9 , 000 crores + ₹ 10 , 000 crores = ₹ 13 , 000 crores (b) Total Expenditure= RevenueExpenditure+ Capital Expenditure Revenue Expenditure= Revenue Deficit + Revenue Receipts =₹ 9 , 000 crores + ₹ 6 , 000 crores = ₹ 15 , 000 crores Capital Expenditure= ₹ 13 , 000 crores Total Expenditure= ₹ 15 , 000 crores + ₹ 13 , 000 crores = ₹ 28 , 000 crores (c) Primary Deficit = Fiscal Deficit - Interest Payments ₹ 5 , 000 crores = ₹ 12 , 000 crores - Interest Payments Interest Payments = ₹ 12 , 000 crores - ₹ 5 , 000 crores = ₹ 7 , 000 crores |
|
| 656. |
In an economy, MPS= 0.4. National income increases by200 crore as a result of change in investment. Calculate the change in investment. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :80 CRORE | |
| 657. |
Explain feature of homogeneous product. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Products sold in the market are homogeneous, i.e., they are identical in all respects like quality, colour, SIZE, weight, design, etc. (ii) The products sold by different FIRMS in the market are equal in the eyes of the buyers. (iii) Since, a buyer cannot distinguish between the product of one firm and that of another, he becomes indifferent as to the firms from which he buys. (iv) The implication of this feature is that since the buyers treat the products as identical they are not ready to pay a different PRICE for the product of any one firm. They will pay the same price for the products of all the firms in the industry. On the other hand, any attempt by a firm to sell its product at a higher price will fail. To sum up, the "homogenous products" feature ENSURES a uniform price for the products of all the firms in the industry. |
|
| 658. |
If indian Airlines reduce faresfrom Delhi to Mumbai, demand curve for air travel shifts rightward. |
| Answer» Solution :It is due to PRICE CHANGE. It is expansionand not INCREASE in demand. | |
| 659. |
Calculate GDP mp : {:(,,(Rs."crore")),((i),"Dividend paid",20),((ii),"Depreciation",25),((iii),"Rent",75),((iv),"Inteset",125),((v),"Undeistributed profits",50),((vi),"Subsidies",10),((vii),"Goods and serveis tax(GST)",40),((viii),"Corporaton tax",30),((ix),"Mixed income",500),((x),"Net factor income from abroad",(-)200),((xi),"Compensation of employees",300):} Note. Compresation of employees, if not qualified, whether it is from domestic product or form abroad should be treated as paid out of domestic product only |
|
Answer» |
|
| 660. |
What is monetray policy ?Stateany threeinstruments of monetary policy . |
|
Answer» Solution :Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a country that controls either the interest rate payable on very short-term borrowing or the money SUPPLY, often targeting inflation or the interest rate to ensure PRICE stability and general trust in the currency MAIN instruments of the monetary policy are: CASH Reserve Ratio, Statutory Liquidity Ratio, Repo rate. |
|
| 661. |
Define open market operations |
| Answer» | |
| 662. |
National Income can be calculated by 3 methods. By which method, we get the maximum value of National Income ? |
|
Answer» EXPENDITURE method |
|
| 663. |
Which one of the following items is excluded in calculating national income ? |
|
Answer» SERVICES of a RENTAL TV set |
|
| 664. |
Classify the following as real flow or money flow Rent paid to the landloard by a tenant. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :MONEY FLOW | |
| 665. |
Differentiate betweensubstitute goods and complementary goods. |
Answer» SOLUTION :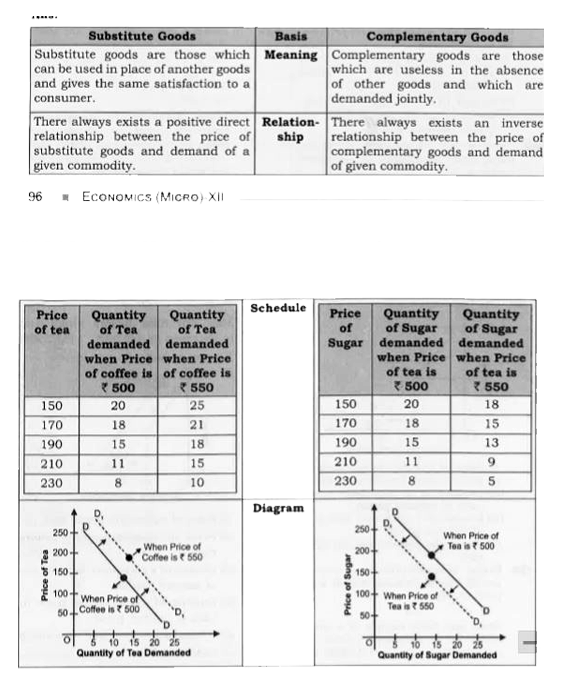
|
|
| 666. |
With a rise in real national income, welfare of the people : (Choose the correct alternative) |
|
Answer» Rises |
|
| 667. |
Are the following statements true or false ? Give reasons. Butter is only a final product. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 668. |
Identify the missing item in the following flowchart : |
|
Answer» CAPITAL RECEIPTS |
|
| 669. |
Describe the four major sectors in an economy according to the macroeconomic point of view. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 670. |
Valueif investmentmultiplier(K)veariesbetweenzeroandinfinity . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 671. |
Discuss the concepts of : (i) NDP at MP , (ii) GNP at FC and (iii) GDP at MP. |
| Answer» Solution : (i) NDP at MPis otherwise called the net value added at market price WITHIN the domestic territory of a country . It is the market value of all final GOODS and services produced within the domestic territory of a country duringan accountingperiod minus depreciation .(ii)GNP at FC is defined as the value ofall goods and services at market priceproduced within the produced the domestic territory of the country in an ACCOUNTING year including net factor income from ABROAD minus net indirect taxes(III) GDP at MP.is the sum of gross values added of all resident producers at market price , plus taxes less subsidies on product | |
| 672. |
Is gross domestic product a true index of economic welfare of the people ? Give two reasons in support of your answer. |
| Answer» Solution :No gross domestic product is not true index of economic welfare of the PEOPLE .because :because it is more for POLITICAL and financial propaganda mainly used by politicians, economists or the media.Even statistically it has only a weak correlation, since GDP can be high even in a very unequal society (such as South AFRICA under apartheid) or on a society with lots of FORCED LABOUR (Middle East). | |
| 673. |
Development of rural marketing relates to : |
|
Answer» Storage |
|
| 674. |
Explain the distinction between voluntary and involuntary unemployment. |
|
Answer» Solution :INVOLUNTARY unemployment is distinguished from voluntary unemployment, where WORKERS choose not to work because their RESERVATION wage is HIGHER than the prevailing wage. voluntary unemployment is when the PERSON decides not to participate in the labor market, not because of the unavailability of jobs, but because of not finding the jobs of his/her choice or is not satisfied with the wage system. |
|
| 675. |
What would be an effect on equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity if demand and supply both fall at the same rate? Or Market for a good is in equilibrium. There is simultaneous "decrease" both in demand and supply but there is no change in market price. Explain with the help of a schedule how is it possible. |
|
Answer» Solution :When demand and supply both decrease at the same rate, equilibrium price REMAINS constant and equilibrium quantity falls. It can be shown with the help of the following DIAGRAM. In the given diagram price is measured on vertical AXIS and quantity demanded and supplied is measured on HORIZONTAL axis. Initially, the equilibrium price is OP and equilibrium quantity is OQ. But as given in the examination problem, "demand and supply both decrease at the same rate", then, (i) Equilibrium price remains constant at OP and (ii) Equilibrium quantity falls from OQ to `OQ_(1)` . ` (##FM_M_ECO_XII_P1_C12_E02_049_S01.png" WIDTH="80%"> |
|
| 676. |
Explain consumer equilibrium using the concept of budget line and indifference map or Interior Optimum Consumer Equilibrium. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) To define consumer equilibrium, we use Interference Curve map and the BUDGET LINE . Two conditions for consumer Equilibrium (a) NECESSARY Condition Marginal Rate of Substitution = Market Rate of Exchange `[(P_x)/(P_y)]` Or , `MRS_(x,y)=P_x//P_y` MRS ( Market Rate of Exchange ) MRE Or `MRS_(x,y) =MRE[(P_x)/P_y]` `"*" ` If `MRS_(x,y) gt MRE [(P_x)/(P_y)]` , At point T in figure It means the consumer.s willingness to pay for commodity X is HIGHER than what makes values for commodity X. So, the consumer should buy more of X and less of Y to get MRS `=P_x/P_y` 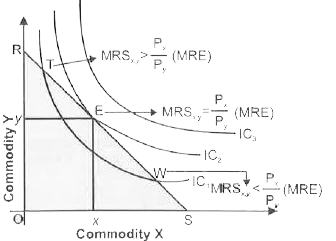 `"*"` If `MRS_(x,y) lt MRE [(P_x)/(P_y)]`, At point W in figure, It means the consumer willingness to pay for commodity X is lesser than what market value for commodity X ,So, consumer should buy less of X and more Y to get MRS = `p_x/p_y` (b) Sufficient Condition `MRS_(x,y)` Diminishing (Convex) at a point of equilibrium i.e., when `MRS_(xy)=MRE[P_x/P_y]` (ii) The consumer will reach equilibrium when the budget line is tangential to the higher possible Indifference Curve, i.e. ., where necessary and sufficient condition satisfy . In the above diagram , the consumer will reach equilibrium at point E where budget line RS is tangential to the higher possible `IC_2` (iii) The consumer cannot move to Indifference Curve , i.e. ., `IC _3`as this is beyond this money income. (iv) Even on `IC_2` all the other points except E are beyond his means . (v) Hence , at point E, the consumer is in equilibrium where his satisfaction maximizes, given his income and prices of goods X and Y . In equilibrium at E , the SLOPE of Budget line = the slope of Indifference Curve. Therefore `MRS_(xy)`is equal to the ratio of the price bof two goods `[(P_x)/(P_y)]` . |
|
| 677. |
Assume that when price is 20rs the quantity demanded is 15 units and when price is 20rs, the quantity demanded is 15 units and when price is 18rs the quantity demanded is 16 units. Based on this information what is the marginal revenue resulting from ann increase in output from 15 units to 16 units ? |
| Answer» ANSWER :(C ) | |
| 678. |
Define money supply and explain its components |
| Answer» | |
| 679. |
What are the components of aggregate demand ? Or State the meaning and components of aggregate demand. Or Define aggregate demand. State its components. |
| Answer» Solution :Components of AGGREGATE DEMAND. There are four components of Aggregate Demand (AD); Consumption (C), Investment (I), GOVERNMENT Spending (G) and NET EXPORTS (X-M). | |
| 680. |
Compare between perfect competition and monopoly. |
Answer» SOLUTION :
|
|
| 681. |
What are capital goods? How are they different from consumption goods ? or Distinguish between stock and flow variables with suitable examples. |
|
Answer» Solution :Capital goods are those DURABLE goods which are USED In production of goods and services. Whereas, Consumption goods are those goods which are used for satisfaction of wants by the consumers. or Any economic variable which is measured at a point of TIME is known as STOCK. For example, capital. etc. Whereas any economic variable measured during a period of time is known as flow. For example, income, etc. |
|
| 682. |
What is net indirect tax ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Net INDIRECT TAX refers to the difference between indirect TAXES and SUBSIDIES. | |
| 683. |
If it is given that the total variable cost for producing 15 units of output is 3000 and for 16 units is 3,500. Find the value of Marginal Cost. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`MC_(n)=TVC_(n)-=TVC_(n-1)` `MC_(16)=TVC_(16)-=TVC_(15)` `=3,500-3000` `=RS. 500` |
|
| 684. |
As a result of increase in investment by Rs. 20 crore, national income rises by Rs. 100 crore. Find out marginal propensity to consume. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`DELTA Y=Delta IXX (I)/(I-MPC)` `100=20 XX I/(I-MPC)` `100-100 MPC=20` `MPC=80/100=0.8` |
|
| 685. |
Why are LIC and ITI not called banks ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :LIC and UTI are not BANKS as they do not ACCEPT chequable DEPOSITS | |
| 686. |
Discuss the meaning of any two methods of controlling credit which may be adopted by the 4 central bank. OR Explain the “bank of issue’ function of the central bank. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Bank RATE Policy :It is the rate at which the central bank lends FUNDS to the commercial banks. An increase in the bank rate increases the costs of borrowing from the central bank. This will then cause banks to increase the rate at which they lend. This will discourage people from taking loans, thus reducing the volume of credit in the economy and vice-versa. (b) Cash Reserve Ratio( CRR) : It is the proportion of deposits that commercial banks have to keep as cash reserves with the central bank. An Increase in CRR has the effect of reducing the banks excess reserves and thus decrease their ability to give credit. (Any other relevant method is to be considered) OR It means that the Central bank has the sole authority to ISSUE currency notes in the country. The monopoly of ISSUING notes by the central bank ensures UNIFORMITY in the notes issued. |
|
| 687. |
All but one of the following are assumed to remain the same while drawing an individual's demand curve for a commodity. Which one is it? |
|
Answer» The PREFERENCE of the individual. |
|
| 688. |
Firm A buys from X inputs worth Rs. 500 crores and sells to firm B goods worth Rs. 1000 crores and to firm C godds worth Rs. 700 crores. Firm B buys form Y inputs worth Rs. 200 crores and sells to firm C goods worth Rs. 1500 crores and finished goods worth Rs. 2000 crores to households. Firm C buys from Z inputs worth Rs. 150 crores and sells finished goods worth Rs. 4150 crores to households. Calculate value added by firms A, B and C and GDP_(MP) |
Answer» 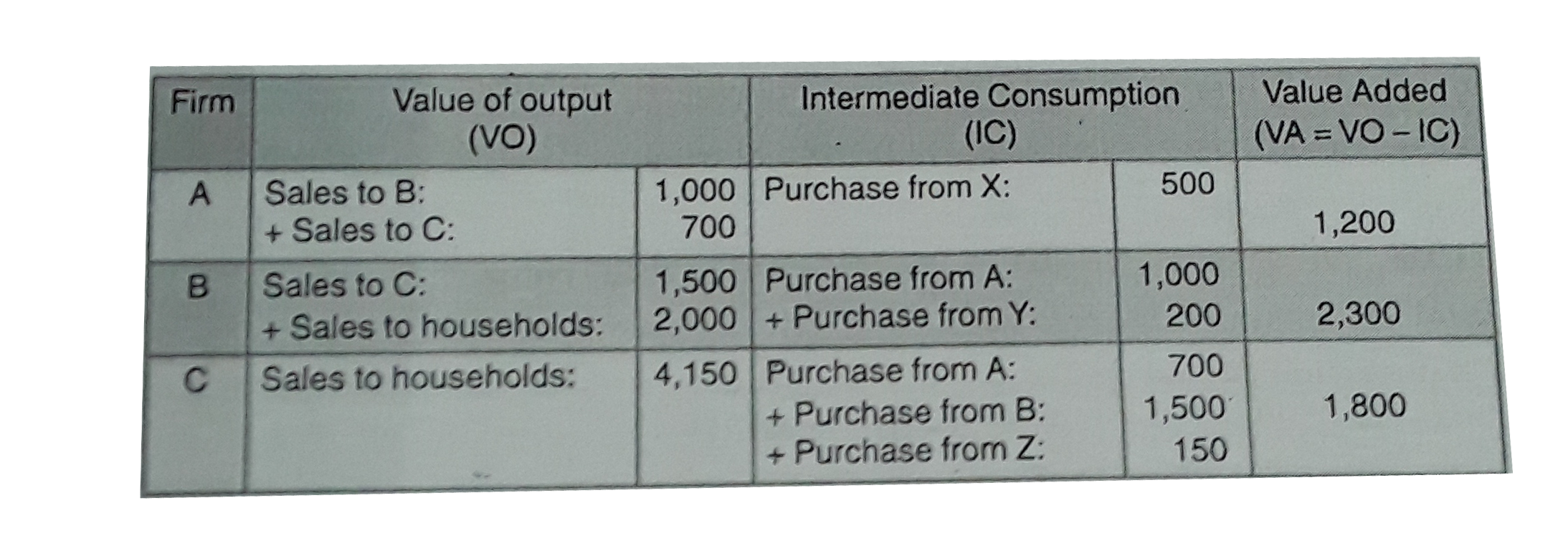 Value added by FIRM `A =GVA_(MP)` of A = Rs. 1200 crores Value added by firm `B=GVA_(MP)` of B = Rs. 2300 crores Value added by firm `C=GVP_(MP)` of C= Rs. 1800 crores |
|
| 689. |
Balance of payment always balances. |
| Answer» Solution :True in ACCOUNTING sense only because it is movement of official RESERVES or 'below the line' items that brings balance to the BOP accounts. | |
| 690. |
Circular flow of income does not take place in case of closed economy. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 691. |
Explain law of demand with the help of a demand schedule. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) It states that priceof the commodity and quantity demanded are inversely related to each other, when other factors remain constant. It means, quantity demanded of the commodity rises DUE to fall in price of the commodity and vice-versa. (ii) Ceteris Paribus means : (a) Price of Related commodity remains constant. (b) Income of a consumer remainsconstant. (C ) Taste and preferences of a household remains constant. 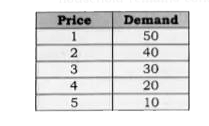 (iii)The law of demand makes a qualitative statement only and not quantitative. It indicates the direction of change in the amount demanded and it does not INDICATE the magnitude of change. (iv)Law of demand is one sided. It EXPLAINS only the effect of change in price on the quantity demanded. It states nothing about the effect of change in quantity demanded on the price of the commodity. |
|
| 692. |
A family spending on a product has to be increased when product price increases. Defend or refute. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) We defend or refute this statement DEPENDS upon the price ELASTICITY of demand. (ii) The given statement can be Defend when demand for this particular product is price - inelastic then price and total expenditure moves in same direction. So, when product price increases, then family expenditure also increases. For example, Necessity goods, petrol. (iii) The given statement can be Refuted when demand is price - elastic or unitary elastic. (a) It is so because when price elasticity is Elastic, then price and total expenditure moves in opposite direction. So, when product price increases, then family expenditure FALLS. (b) It is so because when price is unitary elastic, then price increases, and expenditure remains CONSTANT. So, when product price increases, then family expenditure remains constant. |
|
| 693. |
What effect does an decrease in input price has on the supply of the commodity? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :SUPPLY will INCREASE | |
| 694. |
Why are receipts from taxescategorised as revenue receipts ? |
| Answer» Solution :Receiptsfrom TAXES are categorised as revenue RECEIPTS because they NEITHER CREATE any liability nor cause a reduction in the assets of the GOVERNMENT . | |
| 696. |
Why do Indifference curves not intersect each other ? |
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) Two IC.s cannot INTERSECT each other . This property is PROVED by Contradict Method . First we assume that they intersect each other and then show that this assumptionleads to an absurd conclusion. Let us assume that `"IC"_1` intersects `IC_2` at point E show in the FIGURE given here.  (ii) Let point A be a point on `"IC"_1` and pint B on `IC_2` . Since A and E lie on `"IC"_1` the consumer will be indifferent between points E and A ( A = E) . Similarly , B and E lie on `IC_2` , the consumer will be indifferent between points E and B (B = E) (iii) Based on the assumption of transitivity as A = E and B = E , then the consumer must be indifferent between A and B (A = B) but this is not possible as A and B lie on two different ICs and represent different LEVELS of satisction. Therefore , IC cannot intersect each other. |
|
| 697. |
Explain the measures of money supply. |
| Answer» | |
| 698. |
What is the relation between price and marginal cost at equilibrium, when price remains constant with the rise in output. |
|
Answer» PRICE = MARGINAL COST |
|
| 699. |
When there are diminishing returns to a factor, total product first increases and then starts falling. |
| Answer» Solution :FALSE: As when there is DIMINISHING returns to a FACTOR, total product increases at diminishing rate and NEVER FALLS during diminishing returns. | |
| 700. |
Policy releated to revenue and expenditure of the government is |
|
Answer» MONETARY policy |
|