Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 801. |
What is meant by real flow or physical flow ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Real flow or physical flow refers to the flow of factor services fromhouseholds to FIRMS and the corresponding flow of goods and services from firms to HOUSEHOLDS. | |
| 802. |
________refers to a system in which foreign exchange rate is determined by market forces and central bank influences the exchange rate through intervention |
|
Answer» Fiexible EXCHANGE line PARALLEL to X-axis |
|
| 803. |
What is the relationship between a perfectly competitive firm's marginal cost curve and its short-run supply curve? |
|
Answer» Solution :The marginal cost curve of a perfectly COMPETITIVE FIRM is the firm.s shortrun SUPPLY curve at the point where price is equal to or GREATER than average variable cost. To determine its quantity supplied the firm equates the price of its product with its marginal cost. VALUE : Analytic |
|
| 804. |
Money supply does not include money held by government and banking system |
| Answer» SOLUTION :TUE. As money held by them do not come into ACTUAL circulation in the COUNTRY | |
| 805. |
What are the affects of disequilibrium (deficit) in BOP? |
|
Answer» Solution :The EFFECTS are: i) It reduces economic DEVELOPMENT of a COUNTRY. ii) It hampers economic development of a country. iii) It reduces foreign EXCHANGE RESERVES of a country. |
|
| 806. |
other things remaining the same, when in a country the market price of foreign currency falls, national income is likely" |
|
Answer» to RISE |
|
| 807. |
The maximum limitto accept payment in coins |
|
Answer» 500 |
|
| 808. |
An economy is in equilibrium MPC, National income=1000, Autonomous consumption expenditure=200, Investment expenditure=100. |
|
Answer» Solution :`Y=C+I` `Y=bar(C )+bY+I` 1000=200+B(1000)+100 b(1000)=700 `b=(700)/(1000)=0.7` |
|
| 809. |
Which one of the following is not an assumption of the theory of demand based analysis of indifference curve ? |
|
Answer» GIVEN scale of preferences as betweendifferent combinations of TWO goods. |
|
| 810. |
Explain the meaning of under-employed equilibrium. Explain two measures by which full employment equilibrium can be reached. |
|
Answer» Solution :A situation where the equilibrium level of income is established before the full employment level, is called under-employment equilibrium. At this level, aggregate demand is less than aggregate supply. So, for attaining the level of full employment, we have to INCREASE the level of aggregate demand. There are two methods which can be used to increase the level of aggregate demand. These are as follows : (i) Open market OPERATIONS as an instrument to correct defict demand : Open Market Operations refer to the buying and selling of securities either to the general public or to the COMMERCIAL banks in an open market. To curtail defict demand, the CENTRAL bank purchases securities in the open market. With purchase of securities, the central bank pumps in additional money into the economy. With the additional money the level of Aggregate Demand in the economy increases. Thus, the deficit demand is corrected. (ii) Bank rate as an instrument to correct deficit demand : Bank rate refers to the rate at which the central bank provides loans to the commercial banks. To curtail deficit demand, the central bank lowers the bank rate. This implies that cost of borrowing for the commercial banks from the central bank reduces. The commercial banks in turn reduce the lending rate (the rate at which they provide loans) for their customers. This reduction in the lending rate raises the borrowings capacity of the public, thereby, encourages the demand for loans and credit. Consequently, the level of Aggregate Demand in the economy increase and deficit demand is corrected. |
|
| 811. |
The government budget of a hypothetical economy presents the following information, (all fig. in Rs cror) {:("A. Revenue Expenditure",=,"25,000"),("B. Capital Receipts",=,"30,000"),("C. Capital Expenditure",=,"35,000"),("D. Revenue Receipts",=,"20,000"),("E. Interest Payments",=,"10,000"),("F. Borrowings",=,"20,000"):} Which of the following value represents Fiscal Deficit. |
|
Answer» RS 12,000 |
|
| 812. |
Define national income . OR Define national product . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 813. |
If TU remains the same, MU may be negative or positive . |
|
Answer» Solution :False : TU DECREASES if MU is negative , and TU INCREASES if MU is positive. It is constant and maximum only if MU = 0 |
|
| 814. |
A consumer spends Rs.1,000 on a good priced at 10 per unit. When its price falls by 20 percent, the consumer spends Rs.800 on the good. Calculate the price elasticity of demand by the Percentage method. |
|
Answer» Solution :Given : INITIAL Total EXPENDITURE `(TE_(0))` = Rs.1000 Final Total Expenditure `(TE_(1))`=Rs.800 Initial Price `(P_(0))`=Rs.10 Percentage CHANGE in price =-20 Percentage change in price = `(P_(1)-P_(0))/(P_(0))xx100` `-20=(P_(1)-10)/(10)xx100` `-(200)/(100)=P_(1)-10` `P_(1)=8` `{:("Price (P)","Total Expenditure (TE)=Price (P)"xx "Quantity (Q)","Quantity (Q)"=(TE)/(P)),(P_(0)=Rs.10,TE_(0)=Rs.1000,Q_(0)=100),(P_(1)=Rs.8,TE_(1)=Rs.800,Q_(1)=100):}` Now, `E_(d)=(-) ("Percentage change in quantity demanded")/("Percentage change in price")` `E_(d)=(-)((Q_(1)-Q_(0))/(Q_(0))xx100)/(-20)` `E_(d)=(-)((100-200)/(100)xx100)/(-20)` `E_(d)=0` `therefore E_(d)=0` Thus, the price elasticity of demand is 0. |
|
| 815. |
What is excess demand ? Explain the role of Reverse Reop Rate in removing it. |
|
Answer» Solution :Excess Demand is the amount by which the aggregated demand exceeds aggregate SUPPLY at full employment level. It causes inflation. Reverse Rope Rate is the rate of interest paid by the central bank on deposits by commercial bank. Central Bank can reduce excess demand by raising the Reverse Repo Rate. When the rate is raised, it encourages the commercial banks to park their FUNDS with the central bank. This reduces lending capacity of the comercial banks. Lending by the commercial banks to public DECLINE LEADING to fall in aggregate demand. |
|
| 816. |
There is given the market price of a piece of goods , how does a consumer decides as to how many units of that piece of goods to buy . |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) When purchasing a unit of a COMMODITY a consumer compares its price with the expanted utility from the utility obtained is the benefit, and the pricepayable is the cost , the consumer compares benefit and the cost. He will by the unit of commodity only if the benefit is is greater than or at latest equal to the cost. (ii) Equilibrium conditions for single commodity consumer Equilibrium . (a) Necessary Condition Marginal utility of Money = price `""...(1)` Or `(" Marginal Utility of a Product in Util " [MU_x])/("Marginal Utility of One Rupe "[MU_R]) " = Price of X"....(2)` In particular, the condition (1) saya that themarginal utility of a product in terms of Money should be equal to its price. Sometimes this is loosely stated as Marginal Utility is equal to price, i.e. ., MU = price . `"*"`If MU `gt`price `implies` As a rational consumer he willContinue to purchase an additional unit on a commodity as long as MU = price . `implies` MU `gt`Price impulse benefit is greater than cost and when ever benefit is greater than cost the consumer keeps on consuming additional unit of a commodity till MU = price . `implies` It is so because according to the law of diminishing marginal utility MU falls moreis purchased . As MU falls it is bound to become equal to the price at some point of purchase. `"*"` If MU `lt`Price `implies` As a rational consumer he will have to REDUCE the consumption of a commodity as long as MU = price . `implies MU lt`price implies when benefit is less than cost , never benefit is less than cost the DRESSING the additional unit of a commodity till MU = price. `implies` It is so because according to the law of diminishing marginal utility, MU rises as less units are consumed. As MU rises , it is bound to become equal to the price at some point of purchase . (b) Sufficient condition: Total gain falls as more is purchased after equilibrium . it means that consumer continues to purchase so long as total gain is increasing or at least constant. (iii) It can be explained with the help of the following schedule : 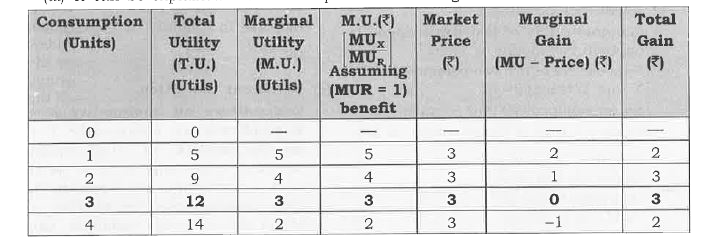 (a) SUPPOSE , the price of commodity X in the market is Rs3 per unit .It means he has to pay Rs3 per unit for all the units he buys.Suppose, the unility obtained from the first unit is 5 utils(=Rs 5)The consumer will buy this unit because the utility of this unit is greater than the price and this process continues till Marginal utility = price as shown in the above schedule at quantity 3 . (b) Consumer will not buy the fourth unit utility of this unit is 2 unit because utility of this unit is 2 utils (= Rs 2)which is less than the price . It is not worth buying the fourth unit. The consumer will restrict his purchase to only 3 units. |
|
| 817. |
Devaluation which means fall in value of domestic currency in terms of foreign currency takes place in ____ |
|
Answer» Flexible Exchange Rate REGIME |
|
| 818. |
What is meant by cash Reserve Ratio? |
| Answer» Solution :Cash reserve RATIO refers to the minimum percentage of TIME and demand deposits required to be kept by every COMMERICAL BANK with RBI | |
| 819. |
Classify the following as intermediate goods or final goods : Coal purchased by a factory. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :INTERMEDIATE GOODS | |
| 820. |
If there is decrease in supply, producer moves downward along the same supply curve ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FALSE : When there is decrease in supply, supply curve SHIFTS leftward PARALLEL to ORIGINAL supply curve. | |
| 821. |
Average variable cost can fall even when marginal cost is rising. |
| Answer» Solution :TRUE: It is so because MC is confined to single UNIT i.e., why it FALLS rapidly and rise rapidly. As AVERAGE cost is shared by all the units of the COMMODITY, i.e., why it falls gradually and rise gradually. | |
| 822. |
The average product of labour is maximized when marginal product of labour: |
|
Answer» 1.Equals the AVERAGE PRODUCT of labour. |
|
| 823. |
Quality of life is influenced by : |
|
Answer» Income |
|
| 824. |
Giving reason explain how should the following be treated in estimating gross domestic product at market price ? (i)Fees to a mechanic paid by a firm. (ii) Interest paid by an individual on a car loan taken from a bank. (iii) Expenditure on purchasing a car for use by a firm. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) It is not included because it is an intermediate cost of the FIRM. (ii) It is not included because the loan is TAKEN to meet CONSUMPTION expenditure and therefore interest paid on such a loan is not a FACTOR payment. (iii) It is included because it is an INVESTMENT expenditure, a final expenditure. |
|
| 825. |
Explain ''large number of buyers and sellers'' feature of a perfectly competitive market. |
|
Answer» Solution :There are very large number of buyers in perfect competition. No individual BUYER can influence the market price because of its large number. Every buyer buys only a fraction from the total sale of the product. Buyers like firms have to accept the price which is FIXED by the supply and DEMAND of the whole industry. Buyers can buy any quantity of product at this price. Similarly sellers are ALSO very large in number having very small share in the market. Sellers cannot influrence the market price and can sell any quantity on the prevailing price. That is why firms are called price-takers in perfectly competitive industry. |
|
| 827. |
Are concepts of 'demand for domestic goods' and 'domestic demand for goods' the same? |
| Answer» Solution :Both the concepts are not the same. The REASON is that demand for domestic GOODS is a wider concept as it INCLUDES both the demand for goods at home and abroad. As compared to it 'domestic demand for goods' includes demand by only the domestic country, not by foreign COUNTRIES. | |
| 828. |
Which of the following is not the function of the Central Bank? (Choose the correct alternative) |
|
Answer» BANKING FACILITIES to government |
|
| 829. |
Sale of financial assets by central bank to finance deficit in BOP. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :ACCOMMODATING | |
| 830. |
What is excess demand? Explain the role of Reverse Repo Rate in removing it. |
| Answer» Solution :Excess demand refers to the situation when aggregate demand (AD) is more than the aggregate supply (AS) corresponding to FULL employment level of OUTPUT in the economy. It is the excess of anticipated expenditure over the value of full employment output. Excess demand gives rise to an inflationary gap. REVERSE Repo Rate-Reverse Repo Rate is the rate of interest at which Commercial Banks can park their SURPLUS funds with the Central Bank, for short period. If Reverse Repo Rate is increased, then it is followed by increase in market rate of interest. Accordingly, cost of CREDIT also increases. It will reduce flow of credit as desired. | |
| 831. |
A country'sresources are fully and efficiently employed. The problem of scarcity exists. What advice would be given to raise the efficiency level of the human resource to fight scarcity? |
|
Answer» Solution :Spread a education and training. VALUE: AWARENESS about efficientutilization of RESOURCES. |
|
| 832. |
What is the impact of deficient demand on production and employment? |
| Answer» Solution :PRODUCTION and employment will DECREASE due to SHORTAGE of AGGREGATE demand. | |
| 833. |
A country's GDP and National Income are increasing. Higher GDP is generally taken as greater welfare of people. However this generalisation may not always be correct. Why ? Give reasons. |
|
Answer» Solution :`**""`If rise in NATIONAL income is due to : PRODUCTION of more of war time goods such as explosives, guns, bombs etc or due to production of more of goods which are SOCIALLY undesirable such as opium, liquor etc, then INCREASED GDP may not be welfare oriented. `**""`If there is unequal distribution of income, economic welfare may not increase. |
|
| 834. |
Give one example of ''externality'' which reduces welfare of the people |
| Answer» Solution :AIR POLLUTION from motor vehicles is an example of a negative EXTERNALITY. The cost of the air pollution for the REST of the society is not compensated by the producers or by the users FO motor vehicles. | |
| 835. |
Suppose the technology for producing personal computers improves and, at the same time, individuals discover new uses for personal computers so that there is greater utilisation of personal computers. Which of the following statements/factors will happen to equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity? |
|
Answer» PRICE will INCREASE, quantity cannot be determined. |
|
| 836. |
How does the equilibrium price of a 'normal' commodity change when income of its buyers fall? Explain the chain of effects. |
|
Answer» Solution :As we know that normal goods are those whose QUANTITY DEMANDED varies positively with the change in income. As GIVEN in the examination problem if income of a consumer falls and goods consumed is normal goods, then both equilibrium PRICE and the equilibrium quantity fall. It can be shown with the help of the given figure. In the given figure price of normal goods is measured on vertical axis and quantity demanded and supplied is measured on horizontal axis. Initially, the equilibrium price is OP and equilibrium quantity is OQ. But as given in the examination problem when income of a consumer falls the demand of normal goods ALSO falls shifting the demand curve to the left from DD to `D_(1)D_(1)`. With new demand curve `D_(1)D_(1)` there is excess supply at initial price OP because at price OP demand is PB and supply is PA, so there is excess supply of AB at price OP. Due to this excess supply competition among the producer will fall the price. Due to fall in price there is downward movement along the demand curve (Expansion in demand) from B to C and similarly, there is downward movement along the supply curve (Contraction in supply) from A to C. So, finally, the equilibrium price falls from OP to `OP_(1)`, and equilibrium quantity also falls from OQ to `OQ_(1)`, Conclusion Due to decrease in income of a buyer for normal goods, (1) Equilibrium price falls from OP to `OP_(1)`. (2) Equilibrium quantity also falls from OQ to `OQ_(1)`. ` (##FM_M_ECO_XII_P1_C12_E02_044_S01.png" width="80%"> |
|
| 837. |
The value of multiplier is : (choose the correct alternative) |
|
Answer» `(1)/(MPC)` |
|
| 838. |
A firm is in equilibrium if marginal cost curve cuts average revenue curve from below. |
| Answer» Solution :FALSE: A FIRM is in EQUILIBRIUM if marginal COST curve CUTS marginal revenue curve from below | |
| 839. |
A producer received 10000rs when the price of a commodity was 100rs per unit. The receipts increased to 15000 when price increased by 20rs. Calculate the elasticity of supply ? |
Answer» Solution : PRICE Elasticity of Supply (ES)=`(DeltaQ)/(DELTAP)xx(P)/(Q)=(25)/(20)xx(100)/(100)=1.25` ES`=1.25` (Supply is highly elastic as `ES gt 1`) ES is always positive DUE to direct RELATIONSHIP between price and quantity supplied. |
|
| 840. |
Consider a market where there are just two consumer and suppose their demands for the good are given as follows: Calculate the market demand for the good. |
Answer» SOLUTION :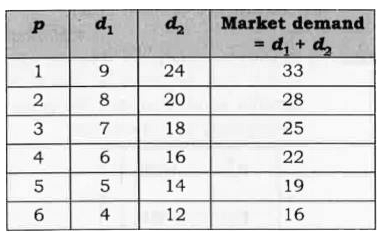
|
|
| 841. |
Primar deficit in a government budget is |
|
Answer» REVENUE EXPENDITURE- Revenue receipts |
|
| 842. |
What is average propensity to consume ? How is it calculated ? |
| Answer» Solution :AVERAGE propensity to CONSUME (APC) refers to the ratio of consumption EXPENDITURE (C ) to the corresponding LEVEL of income (Y), i.e. APC = `("Consumption(C)")/("Income(Y)")` | |
| 843. |
Law of Demand is a : |
|
Answer» 1.quantitative STATEMENT |
|
| 844. |
Who out of the following is not included in ''Residents'' in BOP transactions? |
|
Answer» Firms |
|
| 845. |
Tick the wrong option: |
|
Answer» APC can be more than 1 |
|
| 846. |
What is the marginal product of an input? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Marginal PRODUCT of an INPUT is an addition to the total product when an additional unit of a variable factor is employed. MP `=("CHANGE in output")/("Change in input")= (DELTA q)/( Delta L)` |
|
| 847. |
Define flexible exchange rate system OR What is floating rate ? |
| Answer» Solution : Felxible of Floating exchanges rate SYSTEM REFERS to a system in which the EXCHANGE rate of DIFFERENT currencies is DETERMINED by the forces of demand and supply in the foreign exchange market | |
| 848. |
Which of the following is a phase of circular flow of income ? |
|
Answer» Generation PHASE |
|
| 849. |
Currency is issued by the central bank, yet we say that commercial banks create money. Explain. How is this money creation by commercial banks likely to affect the national income? Explain |
|
Answer» Solution :Money SUPPLY has two components: Currency with public and demand deposits with commercial banks. Currency is ISSUED by the central bank while deposits are created by commercial banks by lending money to the people. In this WAY commercial banks also create money. Commercial banks lend money mainly to investors. The rise in investment in the ECONOMY leads to rise in national income through the multiplier EFFECT. |
|
| 850. |
What are flow variables ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FLOW VARIABLES REFER to those variables, which are measured pver a period of time. | |