Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 551. |
If the firms are earning abno profits how will the 'number of firms in industry' change? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The NUMBER of FIRMS in the INDUSTRY will INCREASE. | |
| 552. |
Explain only two causes of decrease in supply of a commodity. |
|
Answer» Solution :A decrease in supply means that producers now supply LESS at a GIVEN price level. The conditions are (a) Rise in the prices of remuneration of factors of the production. (b) Rise in the prices of other GOODS. (c ) When the TECHNOLOGY BECOMES outdated. (d) Change in the objective of producer (decrease supply at the same price) (e ) Taxation policy of government rises. 
|
|
| 553. |
Mention and explain the two types of investment expenditures |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Induced INVESTMENT: It is directly influenced by the income level. It is done the marginal EFFCIENCY of investment is more than the rate of investment (B). Autonomous Investment: It is not affected by changes in the level of income. It is not guided by the profit MOTIVE. It is mainly done by the govt. |
|
| 554. |
Explain the role of (a) government spending and (b) taxation in influencingexcess demand. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(a) Government can influence excessdemand by reducinggovernment EXPENDITURE. This will reduce aggregate demand. Aggregate supply remaining unchange, excess demand will bereduced. (B) Government can influence excess demand increasingtaxation.Increasingdirect tax will reduce disposableincome. Increasingindirecttax will MAKE goods and services costlier, thusreducingtheir demand. The overall effect will reduce excess demand. |
|
| 555. |
What is the difference between balance of trade account and current account? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 556. |
Law of demand states that price and demand are positively related to each other. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 557. |
BOP is measured as: |
|
Answer» difference between invisible items of exports and IMPORTS |
|
| 558. |
Money supply includes _______ |
|
Answer» all DEPOSITS in bank |
|
| 559. |
The demand curve of a monopoly firm will be ……………….. . |
|
Answer» UPWARD sloping |
|
| 560. |
Why must aggregate demand be equal to aggregate supply at the equilibrium level of income andoutput? Explain with the help of a diagram. |
Answer» Solution :ACCORDING to KEYNES , the equilibrium is reached only when aggregate demand (AD) equals aggregate supply (AS) because at this level , there is no tendency for income andoutput to change.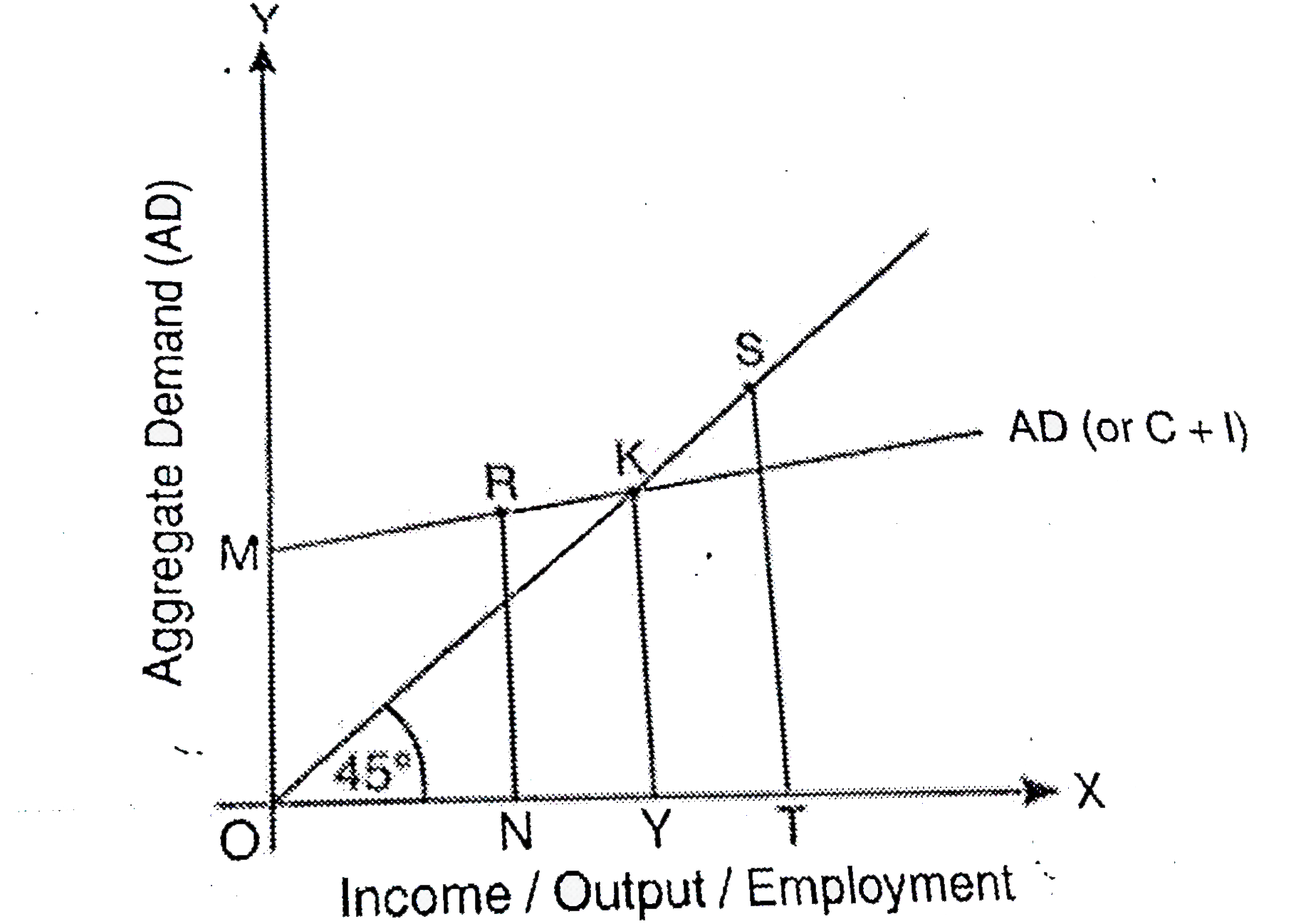 In thediagram equilibrium is at K where AD intersects `45^(@)` line. At this point , AD= AS When AD is more than AS (say, at point R) , then the planned inventory would fall below the desired level. To bring back the inventory at the desired level, the producers expand the output. More output means more income. Rise in output means rise in AS and rise in income means rise in AD. Both continue to rise till they reach K, where AD=AS. When AD is less than AS (say, at point S) then planned inventory rises above the desired level. To lear the unwanted increase in inventory, firms PLAN to reduce the output till AD BECOMES equal to AS. So equilibrium takes place only at point K, when AD=AS. |
|
| 561. |
Money is a liquid store of wealth. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 562. |
Which of thefollowingis nota QuantitativeMethodof Credit by : (Choose the correct alternative) |
|
Answer» OPEN marketoperation |
|
| 563. |
Measurement of national income at constant prices constitute its : |
|
Answer» Nominal value |
|
| 564. |
Balance of payments 'deficit' is the excess of: |
|
Answer» Current account PAYMENTS over current account receipts |
|
| 565. |
Unforeseen obsolescence of fixed capital assets during production is |
|
Answer» CONSUMPTION of FIXED capital |
|
| 566. |
Purely financial transactions, not included in national income : |
|
Answer» SALE of SHARES and bonds |
|
| 567. |
Classify the following as intermediate goods or final goods : Fees paid to the lawyer by a producer. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :INTERMEDIATE GOODS | |
| 568. |
Assuming that total investment is Rs. 4 crore, identify the equilibrium level of income from the data in question number 1. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 569. |
Identify the factor which generally keeps the price elasticity of demand for a good low : |
|
Answer» Variety of uses for that GOOD. |
|
| 570. |
Economic transactions in BOP are |
|
Answer» VISIBLE items |
|
| 571. |
What are two appraoches for determining the equilibrium level of income? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :According to the Keynesian Theory, equilibrium condition is generally stated in terms of aggregate demand (AD) and aggregate supply (AS). An ECONOMY is in equilibrium when aggregate demand for GOODS and services is equal to aggregate supply during a period of time.So, equilibrium is ACHIEVED when:AD = AS … (1)We know, AD is the sum total of Consumption (C) and Investment (I):AD = C + I … (2)Also, AS is the sum total of consumption (C) and saving (S):AS = C + S … (3)Substituting (2) and (3) in (1), we get:C + S = C + IOr, S = IIt means, according to Keynes, there are Two Approaches for determining the equilibrium level of income and employment in the economy: (i) AD-AS Approach(ii) S-I Approach | |
| 572. |
What happens to AC when MC is equal to AC? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :AC is CONSTANT and at its MINIMUM POINT. | |
| 573. |
Under which market form a firm is a price-taker? |
| Answer» SOLUTION : PERFECT COMPETITION. | |
| 574. |
Profits received from investments abroad is recorded in capital account. |
| Answer» Solution :False. It is recorded in CURRENT ACCOUNT as it NEITHER affects FOREIGN exchange ASSETS nor foreign exchange liabilities. | |
| 575. |
Classify the following as factor income or transfer income Dearness alloweance added to basic salary of an employee. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FACTOR INCOME | |
| 576. |
Reservebankof indiahasreducedCRR from4.25%to 4 %willthishelpincontrollinginflatoninindia ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :THISSTEP is notlikelytochecj inflationbecausea vutin CRRissupposedtorelease moreliquidityin theeconomywhich INTURN icreaselendingcapacityof CAPACITYOF commericalbanks . Hencethisstepproveinflatinginstead ofcheckingpricerise . | |
| 577. |
Interest income is a part of : |
|
Answer» Non- tax REVENUE |
|
| 578. |
Suppose there are two consumers in the market for a good and their demand functions are as follows : ** d_(1)(p)=20-p for any price less than or equal to 15, and d_(1)(p) =0 at ant price greater than 15. ** d_(2)(p) = 30-2p for any price less than or equal to 15 and d_(1)(p)=0 at any price greater than 15. Find out the market demand function. |
|
Answer» Solution :It can be seen from the given demand FUNCTIONS that Consumer1 do not want to emand the goofs for any price greater than or EQUAL Rs 20 and consumer 2 do not want to demand the goods for any price greater than Rs 15. Hence, the market demand function will be, `d_("market")[P] = d_(1)[P] + d_(2)[P]` `d_("demand")[P] = 20 -P + 30 -2P` `d_("market")[P] = 50 - 3P`, for any price `lt 50 //3` and `d_("market")[P] = 0.` any for any Price `GT = 50//3`. |
|
| 579. |
Explain any two methods of credit control used by central bank. |
|
Answer» Solution :BANK Rate : Bank rate is the rate which is fixed by the Central Bank. Credit is controlled by the central bank by making variations in the bank rate. This is the rate of interest which is charged from commercial bank for giving them loans. When the value of credit is to be increased, the bank rate reduces and vice-versa. Open market operations : In the open market operations, some activities going on such as buying and selling the government SECURITIES in open market. When the central bank is purchasing securities from the market it MEANS it wants to increase the volume of credit. Banks STARTS selling securities for increasing their CASH reserves i.e., their liquid assets increase. On the other hand, when central bank starts selling securities in the market it means it wants to control the volume credit, which are bought by the commercial banks. In the result their cash reserves are reduced and this effects their power of creating credit. |
|
| 580. |
Which of the following is not true about AD in a two-sector economy ? |
|
Answer» AD = Consumption+ SAVING |
|
| 581. |
Explain consumer's equilibrium with the help of Indifference Curve Analysis |
Answer» Solution :Consumer's equilibrium refers to the OPTIMUM combination of the two goods which a consumer can afford (given his income and price of two commodities) and this combination gives him maximum satisfaction that he possibly can get.  According to indifference curve analysis, consumer's equilibrium is established at a point where budget LINE is tangent to the highest ATTAINABLE indiference curve. At this point the slope of indifference curve i.e., `MRS ((Delta y)/(Delta x))` is equal to the slope of Budget line, i.e, `("Price of x")/("Price of y")` `:.` At point of consumer equilibrium (E), `MRS = (P_(x))/(P_(y)) or (Delta y)/(Delta x) = (P_(x))/(P_(y))` Conditions for consumer's equilibrium are: (i) Budget line should be tangent to the indifference curve, i.e., `MRS_(xy) = (P_(x))/(P_(y))` i.e., Slope of Indifference curve, `I_(e) =` Slope of Budget line. (iii) MRS is diminishing or Indifference curve is convex to the point of ORIGIN. |
|
| 582. |
From the following data about the Government Budget , determine : (a) Non - debt Creating Capital Receipts , (b) Fiscal Deficit and (c) Primary Deficit : |
|
Answer» Solution :Revenue Deficit = Revenue Expenditure - Revenue Receipts ₹ 8 , 000 crores = ₹ 15 , 000 crores- Revenue Receipts Revenue Receipts= ₹ 15 , 000 crores -₹ 8 , 000crores =₹ 7 , 000 crores Interest Payments = `30%` of Revenue Deficit=₹ 8 , 000 crores `XX (30)/(100)`=₹ 2, 400 crores (a) Non-DEBT Creating Capital Receipts= Total Receipts Excluding Borrowing- Revenue Receipts ₹20 , 000 crores - ₹7 , 000 crores = ₹ 13 , 000 crores (b) FISCAL Deficit =Total Expenditure - Total Receipts Excluding Borrowings = (Revenue Expenditure + Capital Expenditure ) -₹ 20 , 000crores = ( ₹ 15 , 000 crores +₹ 22 , 000 crores ) -₹ 20 , 000 crores =₹ 17 , 000 crores OR Fiscal Deficit = Revenue Deficit + ( Capital Expenditure - Non- debt Creating Capital Receipts ) =₹ 8 , 000 crores + ( ₹ 22, 000 crores -₹ 13 , 000 crores ) =₹ 17 , 000 crores (c) Primary Deficit= Fiscal Deficit - Interest Payments = ₹ 17 , 000 crores - ₹ 2,400 crores = ₹ 14 , 600 crores |
|
| 583. |
How can increase in foreighn direct investment affect the price of foreign exchange? |
| Answer» Solution :Foreigndirect INVESTMENT raises the supply of foreign EXCHANGE leading to downward INFLUENCE on the price of foreign exchange | |
| 584. |
State any three causes of a leftward shift of a demand curve of a commodity. |
Answer» Solution :The condition are :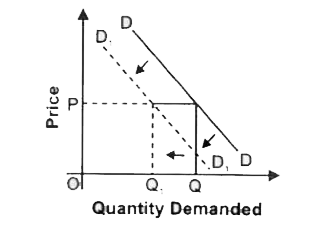 (i) Price of SUBSTITUTE goods falls. (II) Price of complementary goods rises. (iii) INCOME of a consumer falls in CASE of normal goods. (iv) Income of a consumerr rises in case of inferior goods. (v) When a preference becomes unfavourable. |
|
| 585. |
Government spends on child immunization progamme. Analyse its impact on Gross Domestic Product and welfare of the people. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :As government spends on child immunization programme it leads to increase in society's welfare. It is in the sense that if complete immunization is provided to CHILDREN of a national, then it prevents them from the deadly diseases and there will be drastic REDUCTIONS in the number of a child falling ill. This then checks absenteeism and drop out ratios from school. Complete vaccination also helps to reduce premature deaths. All these factors contribute to superior human capital, which ensures the better utilization of physical RESOURCES. With a higher probability of getting employed, there WOULD be greater participation in the production and output will be produced. Hence, it will raise the GDP and welfare of the country in long run. | |
| 586. |
What is the supply curve of a firm in the Long run ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) In the long period, supply is more elastic as all the FACTORS can be CHANGED and supply can be easily adjusted as per changes in price. (ii) The supply curve during long period is elastic, i.e., percentage CHANGE in QUANTITY supplied is GREATER than percentage change in price as shown below : 
|
|
| 587. |
Briefly discuss the following functions of central bank : (i) Currency authority ,(ii) Banker to the government,(iii) Banker's bank and supervisor. |
| Answer» | |
| 588. |
What is GNP deflator ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :It is a STATISTICAL tool used to measure the average level of PRICES of all GOODS and services that make up GNP. GNP DEFLATOR `=("Nominal GNP")/("Real GNP")xx100` |
|
| 589. |
Whatwill be the effect of increasein the'Repo Rate' on themoneysupply ? |
|
Answer» Money SUPPLY will increase |
|
| 590. |
canMPSor MPSeverbe nagative? Givereasoninsupprtofyouranswer . |
| Answer» SOLUTION :MPS or MPCevercan neverbe nagative(-)the reasonis thatMPsis theratiobetweenadditionalsaving`(Delta S)`and additional income`(Delta Y)` i.e.,MPS `=(Delta C)/(DeltaY) .` since `(Delta C)/(Delta Y)`repesentslope ofsavingfunctionwhichis alwayspostitiveand `(Delta C) /(DeltaY)`repesents slpeofconsumptionfunctionwhichisalwayspostitive and `(Delta C)/(Delta Y) `repesentsslopeof consumptionfunctionwhichisalwayspositivetherefore , NEITHER MPSnorMPcaneverbe NEGATIVE | |
| 591. |
The non- tax revenue in the following is : |
|
Answer» INCOME TAX |
|
| 592. |
" Demand and supply are like two blades of a pair of scissors". Comment. |
| Answer» Solution :The given statement is correct. Both the BLADES of a pair of scissors are EQUALLY important to cut a piece of CLOTH. Similarly, both demand and supply are NEEDED for determining price in the market. There is no use for demand for a product if there is no supply for the product and supply is not needed if there is no demand for the product. One of the two may play more active ROLE in price determination in the short run. But, both are needed to determine the price in the long run. | |
| 593. |
What would be an effect on equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity when demand and supply both shift leftward? Or There is simultaneously decrease in demand and supply of a commodity, when will it result in: (i) No change in equilibrium price (Case I) (ii) A fall in equilibrium price. (Case III). Or Market for a good is in equilibrium. There is simultaneous "decrease" in both demand and supply of the goods. Explain its effect on market price. |
|
Answer» Solution :there are following three cases: CASE I: When demand and supply both decrease at the same rate The given DIAGRAM price is measured on vertical axis and quantity demanded and supplied is measured on horizontal axis. Initially, the equilibrium price is OP and equilibrium quantity is OQ. But when "supply decreases and demand also decreases but at a same rate" then, (i) Equilibrium price REMAINS CONSTANT at OP, and (ii) Equilibrium quantity falls from OQ to`OQ_(1)` Case II: When demand decreases, supply also decrease but at a much faster rate In the given diagram price is measured on vertical axis and quantity demanded andsupplied is measured on horizontal axis. Initially, the equilibrium price is OP and equilibrium quantity is OQ. But when "demand decreases and supply also decreases but at a much faster rate" then, (i) Equilibrium price rises from OP to `OP_(1)`, and (ii) Equilibrium quantity falls from OQ to `OQ_(1)`. Case III: When supply decreases, demand also decreases but at a must faster rate In the given diagram price is measured on vertical axis and quantity demanded and supplied is measured on horizontal axis. Initially, the equilibrium price is OP and equilibrium quantity is 0Q. But when "supply decreases and demand also decreases but at a much faster rate" then, (i) Equilibrium price fails from OP to `OP_(1)` : and (ii) Equilibrium quantity also falls from OQ to `OQ_(1)` . ` (##FM_M_ECO_XII_P1_C12_E02_051_S01.png" width="80%"> ` (##FM_M_ECO_XII_P1_C12_E02_051_S02.png" width="80%"> ` (##FM_M_ECO_XII_P1_C12_E02_051_S03.png" width="80%"> |
|
| 594. |
Who are the producers of money ? |
| Answer» Solution :The producers of MONEY are (i) Government of the country and(II) the BANKING system of the country including the CENTRAL BANK and the commercial banks. | |
| 595. |
The total cost at 5 units of output is Rs. 30. The fixed cost is Rs. 5. The average variable cost at 5 units of output is: |
|
Answer» RS. 25 |
|
| 596. |
If planned investment fails short of planned saving, then stock of goods tend to pile up Or Investment accumulate when planned saving. |
| Answer» Solution :Excess of PLANNED savings (say, 25,000 crore) over planned Investment (say, 20,000 crore) means that EXPENDITURE in the economy is LESS than what producers had expected or ITINDICATES that household are not consuming as much as the FIRMS expected them to. As a result, the stock of goods tends to pile up. | |
| 597. |
How is price elasticity of demand affected by: (i) Number of substitutes of available for the goods. (ii) Nature of the good |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Number of Substitutes Available for the Good: The demand for a good that has more number of substitutes available will be relatively more elastic and ed `gt 1`. This is because a slight increase in the price will push the consumers to shift their demand away from the good to its substitutes. On the other hand, with a slight fall in price the consumers would shift their demand from the substitutes towards the goods. Thus, the goods having a large number of close substitutes will have elastic demand. On the contrary, if a good has no close substitutes, then it will have an inelastic demand. (ii) Nature of the good: The price elasticity of demand depends on the nature of a good. The goods and serives can be broadly divided into three categories - Necessities, LUXURIES, JOINTLY-demanded goods. The three types of goods have different values of elasticity as discussed below. (a) NECESSITY goods: These goods are those goods which a consumer demands for sustaining his life. A consumer cannot reduce the consumption of these goods. The demand for such goods does not change much in response to the changes in their prices. Even when the price rises the consumer cannot reduce their demand. Hence, such goods have an inelastic demand `(ed gt 1)` (b) Luxury goods: Luxuries are the good which are not essential, rather, are consumed for leisure or COMFORT purposes. For example, air conditioner, branded garments, etc. The demand for such goods is highly responsive to changes in their prices. A rise in the price, reduces the demand for them and vice-versa. Thus, such goods have high price elasticity. (c) Jointly -demanded goods: Jointly-demanded goods are those goods that are demanded together. The joint consumption of such goods collectively satisties WANTS. For example, sugar and tea. A rise in the price of one good does not reduce its demand if the demand for its complement good has not reduced. For example, a rise in the price of sugar will not reduce its demand if the demand for tea has not decreased. Hence, such goods have an inelastic demand `(ed gt 1)` |
|
| 598. |
Explain why the demand curve facing a firm under monopolistic competition is negatively sloped? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) The demand CURVE of a firm under monopolistic competition is negatively SLOPED because of product differentiation. (II) The product of the sellers are differentiated but close substitutes of one another. (iii) Each SELLER has some degree of MONOPOLY power of .Making. the price. But since there are many close substitutes available, the result is downward sloping and elastic demand curve. |
|
| 599. |
Which of the following are covered under the domestic territory of India ? |
|
Answer» STATE Bank of India in London |
|
| 600. |
What are time deposits ? |
| Answer» | |