Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 451. |
What are capital receipts Or Define the capital receipts of a government . |
|
Answer» Solution :Capital receipts REFER to those receipts of the GOVERNMENT which (i) create a liability for the government e.g. , loans (II) cause reduction in its assetse.g., DISINVESTMENT . |
|
| 452. |
Which oftheseis nota functionof central bank ? |
|
Answer» Accepting deposit of general public |
|
| 453. |
Foreign exchange market constitutes |
|
Answer» CENTRAL bank |
|
| 454. |
What are the objectives of a budget ? Write any two : |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) To reallocate resources. (b) To eradicate mass poverty and uneployment. (c) To REDUCE inequalities of income and wealth. (d) To reduce regional imbalances. (E) To manage PUBLIC enterprises. (f) To prevent business fluctuations and MAINTAIN PRICE stabillity, etc. |
|
| 455. |
Direct tax is called direct because it is collected directly from : |
|
Answer» The producers on goods produced |
|
| 456. |
Balance of payment is a _____ concept |
|
Answer» FLOW |
|
| 457. |
What is revenue of a firm ? Give meaning of average revenue and marginal revenue. What happens to average revenue when marginal revenue is : (i) Greater than average revenue , (ii) equal to average revenue , (iii) less than average revenue ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Revenue of a firm REFERS to RECEIPTS from the sale of OUTPUT in a given PERIOD. Average Revenue : The per unit revenue RECEIVED from the sale of givn amount of output is known as Average Revenue. Marginal revenue : Marginal revenue is the additional revenue when an additional unit of output is sold. (i) Average Revenue rises (ii) Average Revenue is constant and maximum (iii) Average revenue falls |
|
| 458. |
How does AFC behave as output is increased? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The SHAPE of AFC is downward sloping RECTANGULAR hyperbola. AFC falls as output increases because ` AFC =(TFC)/("Output")` and TFC remains constant. So, as output increases, TFC remains constant, but AFC falls. | |
| 459. |
APC can be difined as the fractionof change in income that is consumed. |
| Answer» Solution :FALSE. : It is DEFINED as the FRACTION of specific level of TOTAL income that is CONSUMED. | |
| 460. |
What are final products ? |
| Answer» Solution :FINAL goods REFER to those goods which are used either for final CONSUMPTION or for INVESTMENT. These are included in the national INCOME. | |
| 461. |
Why is the demand curve under monopoly less elastic as compared to the demand curve under monopolistic competition? |
| Answer» Solution :Demand curve under monopoly is less elastic as compared to the demand curve under MONOPOLISTIC competition due to absence of CLOSE SUBSTITUTES in monopoly. | |
| 462. |
How does the imposition of a unit tax affect the supply curve of a firm? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) A unit tax is a tax that the government imposes per unit sale of output. (ii) For example, suppose that the unit tax imposed by the government is 3RS. Then, if the FIRM PRODUCES and sells 20units of the goods, the total tax that the firm must pay to the government is `20xx3=60` (iii) So, if the unit tax increases, the firm.s cost of production increases which will SHIFT the SUPPLY leftward. 
|
|
| 463. |
Name any one step that government can take through the budget to check inflation that is causing hardships to the people |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Government can reduce its own EXPENDITURE to bring down DEMAND for goods and SERVICES. | |
| 464. |
Distinguish between : (a) Final good and intermediate good , (b) Consumption good and capital good. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :a) The differences are given in the table belowFinal goods:1.Used for final consumption.2.Ready for USE by final users.3.Ready for use by final users4.They are FINISHED goods.5.Value is calculated for GDP.Intermediate goods:1.Not used for final consumption.2.Not ready for use by final users.3.Used as RAW material for production of final goods.4.They are unfinished goods.5.Not calculated, as the value of final goods included the value of intermediate goods.6.e.g. flour, milk and sugar are intermediate goods used in making biscuits. b) Consumer goods are defined as the goods that are used for final consumption, i.e. the goods are not used for further processing. On the other hand, capital goods are those goods that are used for future production by the MANUFACTURERS, rather than by the consumers for final use. |
|
| 465. |
if these is excessdemandin theeconomy , it willgenerteremploymentopportuites in theeconomy.Comment. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :the givenstatementis incorrect.Excess demandis a situationwhenthereis nopossibilityof GREATER EMPLOYMENT opportunities as economy , is alreadyat full employment LEVEL. | |
| 466. |
Whether the following items will be included in National Income ? Give reasons for your answer. (i) Payment of electricity bill by a factory. (ii) Dividend on shares. (iii) Increase in stock of consumer goods with households. (iv) Bus fare paid by a passenger. (v) Gains from sale of shares. (vi) Rent earned by Reliance from its building in USA. (vii) Gifts from Abroad. (viii) Retained earnings of resident companies from abroad. (ix) Expenses of foreign visitors in India. (x) Gifts to a trust from Japan. (xi) Purchase of books by a student. (xii) Bonus to employees. (xiii) Interest paid by an individual on loan taken. (xiv) Expenditure on repair of fixed capital asset. (xv) Free medical facilities by the employer. (xvi) financial help to floodvitims. (xvii) Payment of telephone bill. (xviii) Employers contribution to Provident Fund. (xix) Rent received by an Indian from Building rented to Chinese Embassy. (x x) Free meals to employees. (x xi) Free meals to beggars. (x xii) Wages received by an Indian working in Britis Embassy. (x xiii) Medical facilities to government employees. (x xiv) Purchase of vegetables by a restaurant. (x xv) Government Expenditure on streel light. (x xvi) Purchase of a second hand machine from a domestic firm. (x xvii) Interest received on loans taken by government. (x xviii) Leave travel allowance paid to employees by a company. (x xix) Direct purchases made by resident households. (x x x) Interest received on debentures by debenture-holders. (x x xi) Montly allowance received by a college student from home. (x x xii) Expenditure incurred by a firm on sponsoring a Reality show. (x x xiii) Expenditure incurred by normal residents on foreign travel. (x x xiv) Prize won in a lottery. (x x xv) Expenditure by government in providing free education. (x x xvi) Money received by people from their family members who are permanently settied abroad. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) No, it is a part of intermediate consumption expenditure. (ii) Yes, as it is a part of PROFITS. (iii) No, as it is assumed that such goods are consumed, the moment they are purchased. (iv) Yes, it is a part of private final consumption expenditure. (v) No, as it is a capital gain. (vi) Yes, it is a tactor income from abroad. (vii) No, it is a transfer income. (viii) Yes, it is a factor income from abroad. (ix) Yes, it is a part of Net Exports. (x) No, it is a current transfer from rest of the WORLD. (xi) Yes, it is a part of private final consumption expenditure. (xii) Yes, it is a part of COE. (XIII) No, as it is a non-factor payment since the loan is not USED for production but for consumption. (xiv) No, it is a part of intermediate consumption expenditure. (xv) Yes, it is a part of COE. (xvi) No, it is a transfer payment (xvii) Yes, it is a part of private final consumption expenditure. (xviii) Yes, it is a part of COE. (xix) Yes, it is a factor income from abroad. (x x) Yes, it is a part of COE. (x xi) No, it is a transfer payment. (x xii) Yes, it is a factor income from abroad. (x xiii) Yes, it is a part of Government final consumption expenditure. (x xiv) No, it is a part of intermediate consumption expenditure. (x xv) Yes, it is a part of Government final consumption expenditure. (x xvi) No, as it has already been included in the year of its original purchase. (x xvii) No, as such interest is treated as a transfer income because government generally borros money to meet its consumption expenditure and no productive activity is linked with such loan. (x xviii) Yes, as it is a part of COE. (x xix) Yes, it is a part of private final consumption expenditure. (x x x ) Yes, Interest received is a factor income debenture is a sort of loan taken by a production unit. (x x xi) No, it a transfer income. (x x xii) No, it is a part of intermediate consumption expenditure. (x x xiii) Yes, it is a part of private final consumption expenditure. (x x xiv) No, as it is a WINDFALL gain and there is no productive activity involved in it. (x x xv) Yes, it is a part of Government final consumption expenditure. (x x xvi) No, it is a transfer income. |
|
| 467. |
Give meaning of "Return to a Factor". |
| Answer» Solution :Return to a FACTOR STATES that change in the physical OUTPUT of a good when only the quantity of ONE input is INCREASED, while that of other input is kept constant. | |
| 468. |
If the total deposits createdby commercial banks is ₹ 1000 crores and legalreserve requirements is 40%, thenamountof intitaldepositswill be _. |
|
Answer» ₹ 2,000 CRORES |
|
| 469. |
The following table gives the marginal product schedule of labour. It is also given that total product of labour is zero at zero level of employment.Calculate the total and average product schedules of labour. |
Answer» SOLUTION :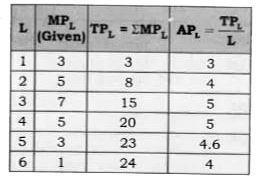
|
|
| 470. |
In a very short period market |
|
Answer» The SUPPLY is fixed |
|
| 471. |
If the total receipts are ₹ 3 , 000 crores and total expenditure is ₹ 4 , 200 crores , how much will be the budgetary deficit ? |
| Answer» Solution :Budgetary DEFICIT = Total Expenditure -Total RECEIPTS = 4, 200 - 3000 = ₹ 1, 200 CRORES . | |
| 472. |
Define fixed exchange rate. |
| Answer» Solution :Fixed exchange RATE is the rate which is fixed in terms of GOLD or any other currency by the government. It REMAINS fixed till it is CHANGED by the government or monetary AUTHORITY. | |
| 473. |
Discuss the meaning of consumption goods and capital goods. |
|
Answer» Solution :Capital goods are any tangible assets used by one business to produce goods or SERVICES as an input for other businesses to produce consumer goods. They are also known as INTERMEDIATE goods, durable goods, or economic capital. The most common capital goods are property, plant, and equipment (PPE), or fixed assets such as buildings, MACHINERY and equipment, tools, and vehicles. A consumer good is any good purchased for consumption and not used later for the production of another consumer good. Consumer goods are sometimes called final goods because they end up in the hands of the consumer or the end user. When economists and statisticians calculate gross domestic product (GDP), they do so BASED off consumer goods. |
|
| 474. |
When marginal costs are below average total costs, |
|
Answer» AVERAGE FIXED costs are rising |
|
| 475. |
How will you treat the following in the calculation of Gross Domestic Product of India ? Give reasons for your answer. (i) Profit earned by a branch of foreign bankin India. (ii) Salaries of Indian employees working in embassy of Japan in India. (iii) Salary of residents of Japan working in Indian embassy in Japan. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) yes, it will be INCLUDED in the GROSS Domestic Product of INDIA as profits are earned within the domestic territory of India. (ii) No, it will not be included in the Gross Domestic Product of Indiaas the embassy of Japan is not a part of the domestic territory of India. (iii) Yes, it will be included in the Gross Domestic Product of India as the INDIAN Embassy is a part of the domestic territory of India. |
|
| 476. |
Distinguish between average propensity to consume and marginal propensity to consume. Can the value of average propensity to consume be greater than 1? Give reasons for your answer. Or Distinguish between average propensity to consume and marginal propensity to consume. Which of these two can be greater than one and when ? |
| Answer» Solution :First, APC refers to the RATIO of absolute CONSUMPTION absolute INCOME at a particular point of time. On the other hand MPC represents the ratio of change in consumption to change in income; MPC is the RATE of change in APC.At initial levels, APC>1 , becauseC>Y. | |
| 477. |
State the main functions of money. Explain the significance of 'store of value' function of money. Explain briefly any two functions of money Explain the significance of medium of exchange function of money Explain the significanceor 'unit of value' function of money State the four functions of money .Describe any one. |
| Answer» | |
| 478. |
Who regulates noney supply? Choose the correct allternative: (a) Government of India . (b) Commerical bank (c ) Reserve Bank of India , (d) Planning commission |
| Answer» | |
| 479. |
How can a government budget help reduce inequalities through redistribution of income ? Explain. |
| Answer» Solution :Government can reduce such inequalities of income and wealth, through its budgetary policy. Government can INFLUENCE distribution of income through levying taxes on the rich and granting subsidies to the POOR. Government levies high rate of tax on rich people reducing their DISPOSABLE income and lowers the tax rate on lower income group. Again, government provides subsidies and amenities to people whose income level is LOW. PUBLIC expenditure can be useful in reducing inequalities. | |
| 480. |
Flexible Exchange Rate System is also known as : |
|
Answer» SUPPLY |
|
| 481. |
What is the effect of increase in national income (or aggregate demand) on foreign exchange rate? Explain. |
| Answer» Solution :When national income (or AGGREGATE demand) increases, spending on imported goods in likely to GO up. With increase in IMPORTS, demand for foreign exchange will ALSO go up. SUPPLY of foreign exchange remaining the same, the exchange rate is likely to rise causing depreciation of domestic currency. | |
| 482. |
Indian investors borrow from abroad. Answer the following: (a) In which sub-account and on which side of the Balance of Payments Account will this borrowing be recorded? Give reason, (b) Expain what is the impact of this borrowing on exchange rate. |
| Answer» Solution :a)BORROWINGS from abroad are RECORDED in the `CAPITAL Account` of the BOP because these give rise to foreign EXCHANGE liabilities.b) These are recorded on the credit side because these bring foreign exchange into the country. | |
| 483. |
The market demand for a good at Rs. 5 per unit is 50 units. Due to increase in price, the market demand falls to 30 units. Find out the new price if the price elasticity of demand is (-)2. |
|
Answer» Solution :`{:("ORIGINAL Quantity (Q) = 50 unitsOriginal Price (P) = RS. 5"),("New Quantity "(Q_(1))=30 " unitsNew Price "(P_(1))=?),("Change in Quantity "(Delta Q)=-20 " unitsChange in Price "(Delta P)=Delta P),("Elasticity of Demand (ED) = "(-)2):}` Price Elasticity of demand (ED) `=(Delta Q)/(Delta P)xx(P)/(Q)` `-2=(-20)/(Delta P)xx(5)/(50)=Delta P=Rs. 1` As the quantity demanded is decreasing, price will INCREASE. It means, New Price = Original Price (P) + Change in Price `(Delta P) = 5+1=Rs. 6` New Price = Rs. 6 |
|
| 484. |
State the distinction between explicit each. Explicit cost and implicit cost. Give an example of each. |
Answer» SOLUTION :
|
|
| 485. |
Suppose a firm is producing a level of output such that MRgtMC. What should the firm do to maximise the profit? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :MR = MC is the condition for maximum profit. In the GIVEN question `MRgtMC`, thus the firm has the CAPACITY to increase production so as to earn maximum profit. So the firm increases its production. VALUE: Analytic |
|
| 486. |
When price of a good rises from₹5 to₹6 per unit, its demand falls from 20 units to 10 units. Compare the expenditure on the good to determine whether demand is elasic or inelastic |
|
Answer» Solution :`{:("Price (Rs.)","Quantity (in units)","Total Expenditure in Rs."("Price"XX"Quantity")),("5","20","100"),("6","10","60"):}` Demand is HIGHLY ELASTIC `(ED gt 1)` as total expenditure has decreased from Rs. 100 to Rs. 60 with an increase in the price from Rs. 5 to Rs. 6. Demand is highly elastic `(ED gt 1)`. |
|
| 487. |
Discuss the situation when aggregate demand is more than aggregate supply at full employment income level. |
| Answer» Solution :When Aggregate Demand is greater than Aggregate Supply at FULL employment, such a situation is known as Excess Demand or inflationary GAP. It is called inflationary because this leads to a rise in general price LEVEL of the ECONOMY. | |
| 488. |
Generation and distribution are the two phases in circular flow of income. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 489. |
What is the shape of a supply curve ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Supply curve is a POSITIVELY shaped upward SLOPING curve. | |
| 490. |
Gross domestic product at market price is equal to : |
|
Answer» compensation of employees + operating surplus + mixed income of self-employed. |
|
| 491. |
A poor household with no or very little income remains underfed. If the household's income rises, how will it affect household's demand for low - quality rice. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Household.s DEMAND for RICE will RISE. | |
| 492. |
If net national products is given at Market Prices , we "____" indirect taxes and "________"subsidies to get National income of the economy. |
|
Answer» ADD , SUBTRACT |
|
| 493. |
Because of product differentiation under monopolistic competition, price tends to be higher than what it ought to have been in real terms and hence consumers suffer. How? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) PRODUCT differentiation is created by artificial differences such as change in colour, fragrance, CERTAIN features etc. (ii) But as such all the products are close substitutes to each other. (iii) This feature of product differentiation results in the downward SLOPING demand curve because of which prices tend to be more and hence the CONSUMERS suffer. |
|
| 494. |
Explain foreign exchange reforms undertakenUnder New Economic Policy(1991). |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Government devalued INDIA's rupee. The idea was to make exports cheaper to ATTRACT more inflow of foreignexchange. Government shifted from FIXED exchangerateregimeto flexibleexchange rate regime i.e. market determined exchange rate. |
|
| 495. |
Explain the production method of estimating national income. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Product method is that which estimates the NATIONAL income by measuring the contribution of final OUTPUT and services by each producing enterprise in the domestic territory of a country during a given accounting PERIOD. | |
| 496. |
in the Government of aa country 'sbudget for theyear2013-14,thefinanceminister proposedtoraise the tax on crore per annum is theobjective onlyto earnrevenuefor theGovernment ?What possoblewelfare objectivecan youthinkof fromtheseproposals ? explain . |
|
Answer» Solution :Besides theobjectiveof RAISING more revenue, theproposalsalsoserve somewelfareobjectives * Firstly , raising taxon CIGARETTES will makecigarettescostlier anddiscourage smoking .less smoking *Secondly, raisingincometax on incometaxin incomes aboverupees onecrore WILLHELP in reducinginequalities in INCOME *thirdlythe extra revenueraisedfrom theseproposals , ifspent onhealthand educationof thepoorwill alsoraise welfare of THEPOOR. |
|
| 497. |
What precautions (any four) should be taken while estimating national income by production method ? "" OR State the various precautions of Product Method that should be kept in mind while estimating national income. |
| Answer» Solution :Precautions of Product METHOD: 1. Avoid double counting. 2. Production for SELF consumption should be included. 3. Sale of second hand GOODS is not to be included. 4. Production from ILLEGAL activities is not to be included. 5. Value of services rendered by housewives/family members is not to be included | |
| 498. |
Calculate national income : {:(,,(Rs."crore")),((i),"Net imports",15),((ii),"Net current transfers from abroad",10),((iii),"Goods and service tax(GST)",30),((iv),"Net change in stocks",5),((v),"Net domestic capital formation ",60),((vi),"Private final consumption expenditure",350),((vii),"Government expenditure on providing free services",75),((viii),"Depreciation",10),((ix),"Net factor income to abroad",(-)15),((x),"Subsidies",5):} |
|
Answer» |
|
| 499. |
Anaddtionin thevaluecan alsotakeplaceevenwhenthe comodity doesnot go thoughanytransformationComment. |
| Answer» Solution :The givenstatementis correctit happenswhena COMMODITYIS PURCHASED for resaleforexampleif a retailersells TVfor Rs. 12,000 after PURCHASING it FORRS. 11,000 thenthere is no transformation in TV YET valueadded is Rs. 1,000 | |
| 500. |
If the decrease in demand meets with an increase in supply, equilibrium price will fall. |
| Answer» Solution :True: As we know whether DEMAND decreases or SUPPLY INCREASES both lead to an decrease in equilibrium price. HENCE, equilibrium price will fall. | |