Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 501. |
At zero level of income, consuption is |
|
Answer» zero |
|
| 502. |
What are the conditions of consumer's equilibrium under the indifference curve approach ? What changes will take place if the conditions are not fulfilled to reach equilibrium ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) To define consumer equilibrium, we use Interference Curve map and the budget line . Two conditions for consumer Equilibrium (a) Necessary Condition Marginal RATE of Substitution = Market Rate of Exchange `[(P_x)/(P_y)]` Or , `MRS_(x,y)=P_x//P_y` MRS ( Market Rate of Exchange ) MRE Or `MRS_(x,y) =MRE[(P_x)/P_y]` `"*" ` If `MRS_(x,y) gt MRE [(P_x)/(P_y)]` , At point T in figure It means the consumer.s willingness to pay for commodity X is higher than what makes values for commodity X. So, the consumer should buy more of X and less of Y to get MRS `=P_x/P_y` 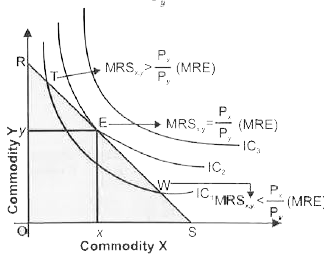 `"*"` If `MRS_(x,y) lt MRE [(P_x)/(P_y)]`, At point W in figure, It means the consumer willingness to pay for commodity X is lesser than what market value for commodity X ,So, consumer should buy less of X and more Y to get MRS = `p_x/p_y` (b) Sufficient Condition `MRS_(x,y)` Diminishing (Convex) at a point of equilibrium i.e., when `MRS_(xy)=MRE[P_x/P_y]` (ii) The consumer will reach equilibrium when the budget line is tangential to the higher possible Indifference Curve, i.e. ., where necessary and sufficient condition satisfy . In the above diagram , the consumer will reach equilibrium at point E where budget line RS is tangential to the higher possible `IC_2` (iii) The consumer cannot move to Indifference Curve , i.e. ., `IC _3`as this is beyond this money income. (iv) Even on `IC_2` all the other points except E are beyond his means . (v) HENCE , at point E, the consumer is in equilibrium where his satisfaction maximizes, given his income and prices of goods X and Y . In equilibrium at E , the slope of Budget line = the slope of Indifference Curve. Therefore `MRS_(xy)`is equal to the ratio of the price bof two goods `[(P_x)/(P_y)]` . |
|
| 503. |
What is the basic characteristic of money? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :GENERAL ACCEPTABILITY. | |
| 504. |
Price-taking firms, i.e., firms that operate in a perfectly competitive market are said to be "small" relative to the market. Which one of the following options best describes this smallness? |
|
Answer» The individual FIRM must have FEWER than 10 employees. |
|
| 505. |
Flexible exhange rate system is also known as: |
|
Answer» Managed floating SYSTEM |
|
| 506. |
Name the economic transactions, which are undertaken to make equilibrium in balance of payment. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 507. |
Explain the implications of large number of sellers in a perfectly competitive market. |
|
Answer» Solution :Large number of SELLERS - (i) The WORDS .large number. simply states that the number of sellers is large enough to render a single SELLER.s share in total market supply of the product insignificant. (ii) Insignificant share means that if only one individual firm reduces or raises its own supply, the prevailing market price remains unaffected. (iii) The prevailing market price is the one which was set through the intersection of market demand and market supply forces, for which all the sellers and all the buyers together are responsible. (iv) One single seller has no option but to sell what it produces at this market determined price. This position of an individual firm in the total market is REFERRED to as price taker. This is a unique feature of a perfectly COMPETITIVE market. . Large number of buyers - (i) The words .large number. simply states that the number of buyers is large enough, that an individual buyer.s share in total market demand is insignificant, the buyers cannot influence the market price on his own by changing his demand. (ii) This makes a single buyer also a price taker. To sum up, the feature "large number" indicates ineffectiveness of a single seller or a single buyer in influencing the prevailing market price on its own, rendering him simply a price taker. |
|
| 508. |
When the quantity of a variable input is increased from 4 to 6 units, the total output increases from 85 units to 105 units. The marginal product of the variable input is 20 units. |
| Answer» Solution :False: Marginal product is addition to the TOTAL OUTPUT due to the increase in ONE UNIT variable input. Here, total output increases by 20 units due to two units increase in variable input. Hence, marginal product is 20/2 = 10 units. | |
| 509. |
A consumer demands 40 kg of a commodity when its price is Rs. 1 per kg. If the price increases by Rs. 0.10, what would be the quantity demanded ? PED =-1. |
|
Answer» Solution :`{:("ELASTICITY of demand "=-1),("Original Quantity (Q) = 40Original PRICE (P) = 1"),("New Quantity "(Q_(1))=? "New Price "(P_(1))=1.1),("CHANGE in Quantity " (Delta Q)=? "Change in Price " (Delta P)=0.1):}` `PED =(Delta Q)/(Delta P)xx(P)/(Q) "or" -1=(Delta Q)/(0.1)xx(1)/(40)` `Delta Q=-4` As, price is increasing, then quantity demanded must decrease by 4. So, New Quantity = Initial quantity `+ Delta Q=40+(-4)=36` |
|
| 510. |
Define deflationary gap. Or Give the meaning of deflationary gap. |
| Answer» Solution :Deflationary gap REFERS to the gap by which actual AGGREGATE DEMAND falls short of the aggregate demand REQUIRED to establish FULL employment equilibrium. | |
| 511. |
What is meant by 'official reserve transactions'? Discuss their importance in Balance of Payments. |
| Answer» Solution :The transaction carried by Monetary Authority of a country which causes change in official reserves is called official reserve transaction. It includes purchase or sale of currency in EXCHANGE market for foreign CURRENCIES or other assets. The reserves are drawn by selling foreign currencies in exchange market during deficit and foreign currencies are PURCHASED during surplus. When the official reserves increase or decrease it is called OVERALL BALANCE of payment surplus or deficit respectively.The importance of official reserve transactions in balance of payment is –a) Purchase of own currency buy a country is a credit item in the balance of payments and vice a versa.b) It helps to adjust the deficit or surplus in balance of payments. | |
| 512. |
Banks create credit : |
|
Answer» Out of NOTHING |
|
| 513. |
Under what condition, a producer would like to supply more at a given level or price ? |
|
Answer» Solution :An increase in SUPPLY MEANS that producers now supply more at a given price level. (a) FALL in the prices of other goods. (b) Fall in the prices of remuneration of factors of production (c ) IMPROVEMENT in Technology. (d) Change in objective or PRODUCER (increase the supply at the same rate ). (e) Taxation policy of governement falls. 
|
|
| 514. |
The measure of price elasticity of demand of a normal good carries minus sign while price elasticity of supply carries plus sign. Explain why? |
| Answer» Solution :The measure of PRICE elasticity of demand carries a minus sign because it SHOWS an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded i.e., other things remaining constant, as the price of a good rises or falls, the quantity demanded of the good falls (or rises). On the other hand, price elasticity of SUPPLY carries plus sign as there exists a positive relationship between the supply of a commodity and its price. To put in other WORDS, when the price of a good rises (or falls), then the quantity SUPPLIED will increases (or decrease), other things remaining unchanged. | |
| 515. |
Flexible exchange rate depends upon demand and supply of foreign exchange in the international money market. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :TRUE because flexible exchange rate is determined by forces of demand and supply of foreign exchange in the INTERNATIONAL money market. | |
| 516. |
How will an increase in the income of buyers of an inferior goods', affect its equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity? Explain with the help of a diagram. |
|
Answer» Solution :As we know inferior goods are those whose QUANTITY demanded varies inversely with the change in income. As given in the examination problemn if income of a consumer increases and good consumed is inferior good, equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity both fall. It can be shown with the help of the following figure. In the given figure price of inferior goods is MEASURED on vertical axis and quantity demanded and supplied is measured on horizontal axis. Initially, the equilibrium price is OP and equilibrium quantity is OQ. But as given in the examination problem when income of a consumer increases, the demand of inferior goods also falls SHIFTING the demand curve to the left from DD to ` D_(1)D_(1)` With new demand curve `D_(1)D_(1)` there 1S excess supply at initial price OP because at price OP demand is PB and supply is PA, so, there is excess supply of AB at price OP. DUE to this excess supply, competition among the producer the price fall. Due to fall in price, there is downward movement along the demand curve (Expansion in demand) from B to C and similarly, there is downward movement along. the supply curve (Contraction in supply) from A to C. So, finally, the equilibrium price falls from OP to `OP_(1)`, and equilibrium quantity also falls from OQ to `OQ_(1)`. Conclusion Due to increase in income of BUYER for inferior goods, (i) Equilibrium price falls from OP too OP. (ii) Equilibrium quantity also falls from OQ to `OQ_(1)`. ` (##FM_M_ECO_XII_P1_C12_E02_045_S01.png" width="80%"> |
|
| 517. |
Explain the relationship between the marginal products and the total product of an input. OR Explain the law of variable proportion with the help of total product and marginal product curves. OR Explain the likely behaviour of Total Product and Marginal Product when for increasing production only one input is increased while all other inputs are kept constant. OR State the different phases of changes in Total Product and Marginal Product in the Law of Variable Proportions. Also show the same in a single diagram. |
|
Answer» Solution :According to the Law of Variable Proportion when only one INPUT is increased while all other inputs are kept constant, Marginal Product and Total Product BEHAVE in the FOLLOWING manner: (z) When Marginal product rises (till Point `P_1`), Total product increases at an increasing rate (convex shape) (till point P). (ii) When Marginal product falls and remains positive (Till point `B_1` ), total product increases at a diminishing rate (CONCAVE shape) (till point A). (III) When Marginal Product is zero (at point `B_1` ), Total Product is at its maximum and constant (At point B). (iv) When Marginal product becomes negative (after point `B_1` ), total product falls (after point B). 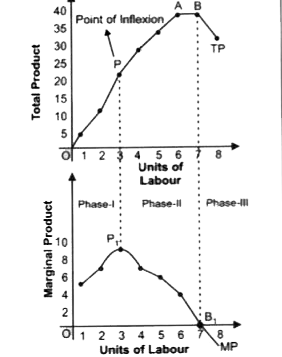
|
|
| 518. |
What are the conditions for short run shutdown point? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :PRICE = MINIMUM of SAVC (short run AVERAGE VARIABLE cost) Or TR = TVC |
|
| 519. |
All of the following items are determinants of demand except: |
|
Answer» 1.tastes and PREFERENCES. |
|
| 520. |
What can be the maximum value of MPS ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Maximium value of MPS is 1 which can be achieved when all of the ADDITIONAL INCOME is saved. | |
| 521. |
What are the two types of circular flows ? |
| Answer» Solution :The TWO TYPES of CIRCULAR flows are : (i) REAL flow , (ii) MONEY flow. | |
| 522. |
When AD exceeds AS, the inventories tend to : |
|
Answer» Rise |
|
| 523. |
What is meant by medium of exchange ? |
| Answer» Solution :It means that the money ACTS as an INTERMEDIARY for the sale and PURCHASE of goods in the MARKET to avoid problem of double coincidence of wants | |
| 524. |
What is government budget ? |
| Answer» Solution :A GOVERNMENT budget is an annual STATEMENT of estimated receipts and expenditure over a FISCAL year which runs from APRIL 1 to March 31 next year. | |
| 525. |
Anexcessof aggregatedemandoveraggregatesupplyalwaysimpliesa situationof inflatonarygap . Yourcomments? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :the ABOVESTATEMENT is trueconditioniftrueon theconditionifaggregatedemand is in excessofaggregatesupply atleveloffullemploymentin casesaggregatesupplyoroutputis notcorrespondingtofullemploymentorresouresin theeconomy, it willnotcauseinflationarygapRememberinflationarygapis a MEASURE ofamountof excessdemand overaggregatesupplyat fullemployment LEVEL . | |
| 526. |
How does the budget line change if the price of good 2 decrease by a rupee but the price of good 1 and the consumer's income remain unchanged ? |
Answer» SOLUTION :If PRICE of GOOD 2 (shown on y- axis) decreases , consumer can buy more pieces/quantity of good 2. The BUDGET line AB will pivot at B and rotate upwards to `A_1 B_1` 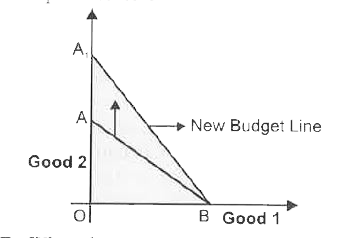
|
|
| 527. |
Causes of excess demand is |
|
Answer» INCREASE in MONEY supply |
|
| 528. |
Define tax and non-tax revenue. Give an example each. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :TAX revenue refers to all proceeds of taxes and other duties levied by the Central government. Non-tax revenue refers to all revenue receipts which arise from the SOURCES other than taxes. EXAMPLE of tax revenue is income tax and of non-tax revenue is DIVIDEND received. | |
| 529. |
Why does demand for foregin exchange arise of speculative activities ? |
| Answer» Solution :Demand for foreignexchange arises when people want to speculate on the volue of foreign currecny. Speculators demand foreign currency in the present period with the AIM of selling it in future at higher prices. For example, MANISH purchaases `1,000 US $ at Rs. 70 per DOLLAR with the EXPECTATION of selling the dollars at higher prices | |
| 530. |
What is the price elasticity of demand for the following demand curves :(i) Straight line demand curve parallel to X - axis.(ii) Straight line demand curve parallel to Y - axis.(iii) Mid - point of a straight line demand curve. |
|
Answer» Solution :The PRICE elasticity of DEMAND in the FOLLOWING cases will be : (i) Perfectly Elastic Demand (II)Perfectly INELASTIC Demand (iii)Unitary elastic Demand |
|
| 531. |
How are following treated in the estimation of domestic factor income ? Old age pension given by the governmet. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :No, it is not INCLUDED in the DOMESTIC factor INCOME as it is a transfer income (and not a factor income). | |
| 532. |
Explainthe "varyingreserverequirements " method of creditconrtalby thecentral bank. |
| Answer» Solution :When it is sought to restrict credit, the Central Bank may raise the reserve ratio. In 1960, for instance, the Reserve Bank of India REQUIRED the scheduled banks to maintain with it additional reserve equivalent to 25% of the increase in their bank deposits (later raised to 50%).The Reserve Bank has also the power to vary the CASH reserve ratio (CRR) which the banks have to maintain with it from the minimum requirement of 3% up-to 15% of the aggregate liabilities (7% since June 1982) raised in stages to 8.5% effective from August 27, 1983.Variations of reserve requirements affect the LIQUIDITY position of the banks and hence their ability to LEND. The raising of reserve requirements is an anti-inflationary measure inasmuch as it reduces the excess reserves of member-banks for potential credit expansion. The lowering of the reserve ratios has the opposite effect. | |
| 533. |
Explain the concept of money supply and its components |
| Answer» Solution :MONEY supply refers to the STOCK of money in the country on a particular day. It has TWO components : Currency with public outside the BANKS and demand deposits with banks. Demand deposits are deposits which can be withdrawn by WRITING cheque. Both these are directly usa ble for carrying out transactions at will | |
| 534. |
Two drivers - Tom and Jerry - each drive upto a gas station. Before looking at the price, each places an order. Tom says, ''Id' fill 10 gallons of gas.'' Jerry says, ''Id' fill gas worth $ 10.'' What is each driver's price elasticity of demand ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Tom.s price ELASTICITY of demand is zero, because he wants the same QUANTITY REGARDLESS of the price. Jerry.s price elasticity of demand is one, because he spends the same AMOUNT on gas, no MATTER what the price, which means his percentage change in quantity is equal to the percentage change in price. Value : Analytic |
|
| 535. |
Why is repament of loan a capital expenditure ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Because it REDUCES GOVERNMENT's LIABILITY. | |
| 536. |
Under employment equilibrium is a situation where the aggregate demand is equal to aggreagate supply when the resources are not fully employed. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 537. |
High powered money includes only the cash reserves of commercial banks. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :False. In addition to CASH RESERVES of commercial banks, high powered MONEY also Includes currency HELD by public. | |
| 538. |
A person becoms a human resource when he/she: |
|
Answer» Is WILLING to work |
|
| 539. |
When does managed floating system become dirty floating? |
|
Answer» Solution :Under the system of MANAGED floating, floating of exchange rate is managed by the monetary AUTHORITY of the country by following some RULES and regulations (Guidelines for the management of floating exchange RATES). If the floating exchange rates are managed WITHOUT observing any rules and regulations, it becomes dirty floating. |
|
| 540. |
Real flow is also known as nominal flow. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 541. |
What does BOP account of a country record? |
| Answer» Solution :BOP ACCOUNT of a country records all TRANSACTIONS in GOODS, services and ASSETS between RESIDENTS of a country and ROW. | |
| 542. |
If MPC =0.5, find change in income, if investment increases by 400 crore. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :800 CRORE | |
| 543. |
A reduction in govermment spendingleads to fall in the income and purchasing power of the people. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :True, The level of output will not RISE as economy is already at full EMPLOYMENT level and there is no idle capacity in the economy. | |
| 544. |
Are the following statements true or false ? Give reasons. Rise in revenue deficit will always lead to higher fiscal deficit . |
| Answer» Solution :False.Fiscal deficit is also influenced by CAPITAL RECEIPTS and EXPENDITURE of the government in addition to REVENUE receipts and expenditure. | |
| 545. |
Discuss the concept of factor income and transfer income with the help of examples. |
|
Answer» Solution :Factor INCOME is a payment received in exchange of any good or service while as Transfer Income is received without RENDERING any service or good. Factor Income includes wages, rents, profit and INTEREST while as Transfer Income comprises gifts, subsidies, donations, pensions, SCHOLARSHIPS ETC. |
|
| 546. |
What is a competitive market? Briefly describe a type of market that is not perfectly competitive. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) A competitive market is a market in which there are many buyers and many sellers of an identical product so that each has a negligible IMPACT on the market price. (II) Another type of market is a monopoly in which there is only one seller. (iii) There are also other markets that fall between perfect COMPETITION and monopoly i.e. MONOPOLISTIC competition. Value: Analytic |
|
| 547. |
State the relationship between multiplier and MPC. |
| Answer» Solution :The HIGHER the marginal propensityto consume (MPC) , thegreateris the value of themultiplier . THUS, there EXISTS apositive RELATIONSHIP between MPC and investment multiplier (K).Multiplier (K) = 1/1-MPC | |
| 548. |
Which of the three countries has highest percentageof population above poverty line ? |
|
Answer» CHINA |
|
| 549. |
Money as medium of exchange solves the barter's problem of ' lack of double coincidence of want ' |
|
Answer» |
|
| 550. |
The short run, as economists use the phrase, is characterized by: |
|
Answer» 1.At least one FIXED factor of PRODUCTION and FIRMS NEITHER leaving nor ENTERING the industry. |
|