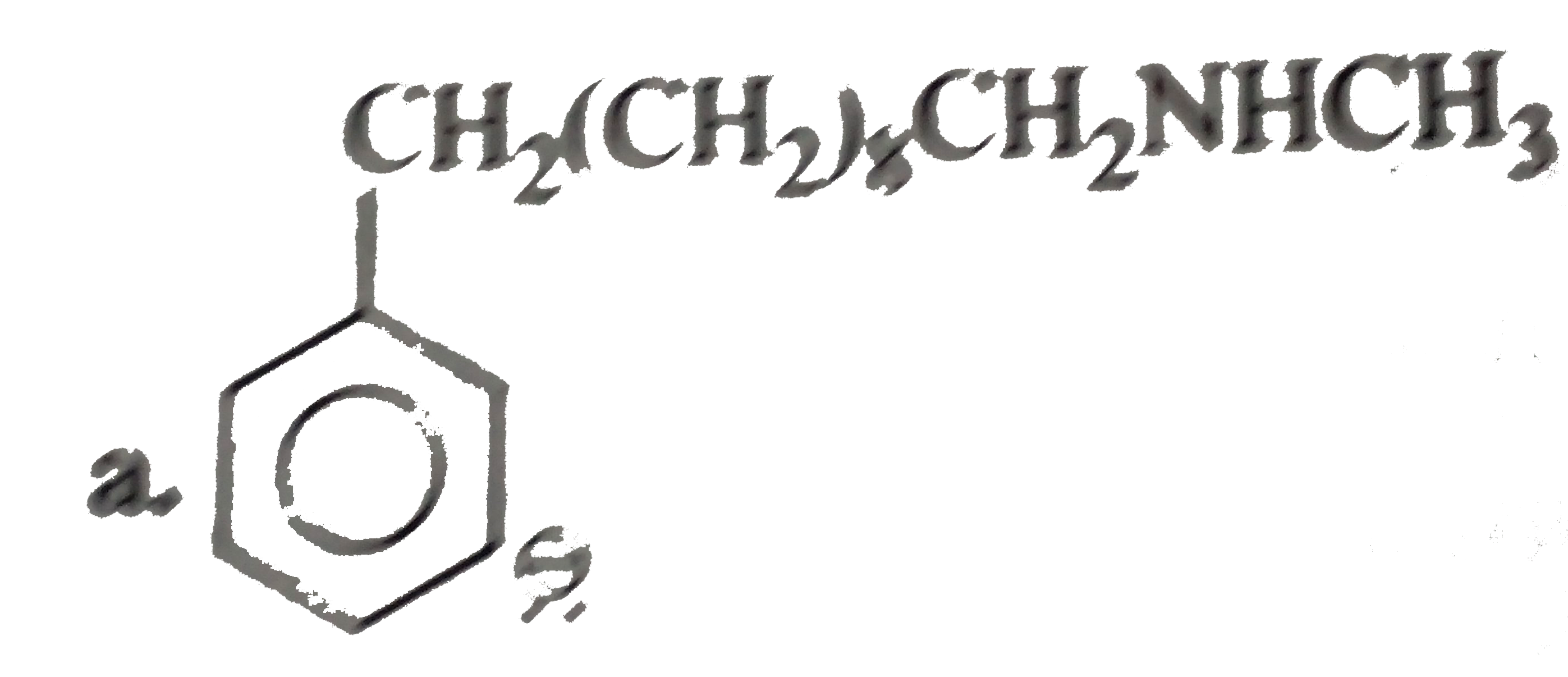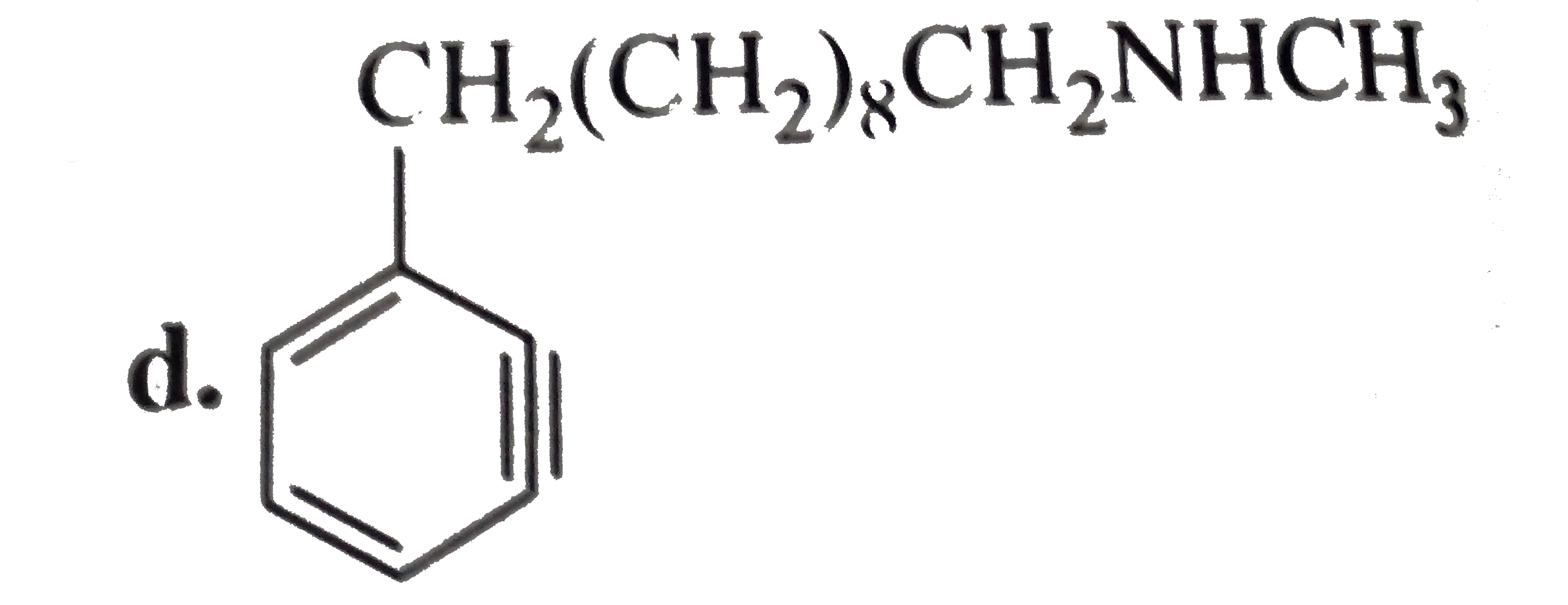Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 91301. |
A beaker contains a solution of substance 'A'. Precipitations of substance 'A' takes place when small amount of 'A' is added to the solution. The solution is ……. |
|
Answer» Saturated |
|
| 91302. |
A Beckmann rearrangement is effected b |
|
Answer» Sulphuric ACID 
|
|
| 91303. |
A Beckmann thermometer is used to measure |
|
Answer» low temperatures |
|
| 91304. |
A beaker contains a solution of substance'A' precipitation of substance 'A' takes place when small amount of 'A' is added to the solution. The solution is……… |
|
Answer» saturated |
|
| 91305. |
A beaker containing 2.0 moles of octane and another beaker containing 3.0 moles of nonane are enclosed in chamber-1. Another 2.0 moles of octane is mixed with 3.0 moles of nonane in a beaker, which is then enclosed in chamber-II. At equilibrium, the vapour in chamber-I is |
|
Answer» GREATER than the VAPOUR pressure in chamber-II |
|
| 91306. |
A beaker containing 20 g sugar in 100 g water and another containing 10 g sugar in 100 g water are placed under a bell - jar and allowed to stand until equilibrium is reached. How much water will be transferred from one beaker to the other ? |
|
Answer» Solution :At equilibrium, both solutions will have the same VAPOUR pressure which will be so when they have the same molar CONCENTRATION. Thus, some water from dilute solution will be transferred to concentrated solution. Suppose w g of water is transferred from beakder 1 containing 10 g sugar/100 g of water to the beaker 2 containing 20 g sugar/100 g of water. Taking the density of both the solutions to be nearly same `(="d g mL"^(-1))` Molar concentration of sugar in beaker 1 `=(10)/(342)XX(1)/(((100-w))/(d))xx1000=(10)/(342)xx(1000d)/(1000-w)"mol L"^(-1)` Molar concentration of sugar in beaker 2 `=(20)/(342)xx(1000d)/(1000+w)"mol L"^(-1)` `therefore""(10)/(342)xx(1000d)/(100-w)=(20)/(342)xx(1000d)/(1000+w)` `"or"(10)/(100-w)=(20)/(100+w)"or"(1)/(100-w)=(2)/(100+w)"or"100+w=200-2w` `"or"3w=100"or"2=33.3g` |
|
| 91307. |
A beaker containing 0.01 mole of C_12H_22O_11in 100 g of H_2Oand a beaker containing 0.02 mole of C_12H_22O_11 in 100 g of H_2Oare placed in a chamber and allowed to equilibrate. What is the concentration (mole fraction) of C_11H_22O_11in the resulting solutions? |
|
Answer» Solution :WATER vapour will be transferred from the more DILUTE solution to the more CONCENTRATED solution until both SOLUTIONS have the same concentration. 0.00269 |
|
| 91308. |
A bcc lattice is made up of two elements X and Y. Atoms of X occupy two corners and atoms of Y occupy the remaining lattice points.Derive the composition of the compound |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`XY_(7)` | |
| 91309. |
A bcc element (atomic mass 65) has cell edge of 420 pm. Calculate its density in g cm^(-3) . |
|
Answer» Solution :Atomic mass of element = 65 Edge length , a = 420 pm = `420 xx 10^(-10) cm` Number of ATOMS per unit CELL = 2 (for bcc structure) DENSITY of unit cell , (d) `=(ZXX M)/(N_A xx a^3 xx 10^(-30)) g cm^(-3)` `= (2 xx 65 g "mol"^(-1))/( 6.02 xx 10^(23) "mol"^(-1) xx (420)^3 xx 10^(-30)) cm^3` ` = 2.914 g cm^(-3)` |
|
| 91310. |
A basic volatile nitrogen compound give a foul smelling gas when treated with chaloroform and alcoholic potash. A0.295 gm sample of the substance dissolved in aqueous HCl and treated withNaNO_2 solution at0^@C libreated a colourless , odorless gas whose volume corresponded to112 ml atSTP. After the evoltion fo the gas was complte , the aqueous solution was distilled to give an orgfanic liquid which did not coniain nitrogen and wihic on watemiing with alkali and iodine gave a uellow preciptitate , Idntify the orginal substance assuming that it contains one (N) atom per molecule . |
Answer» Solution :A basic , volatile nitrogen compound is primary amine . 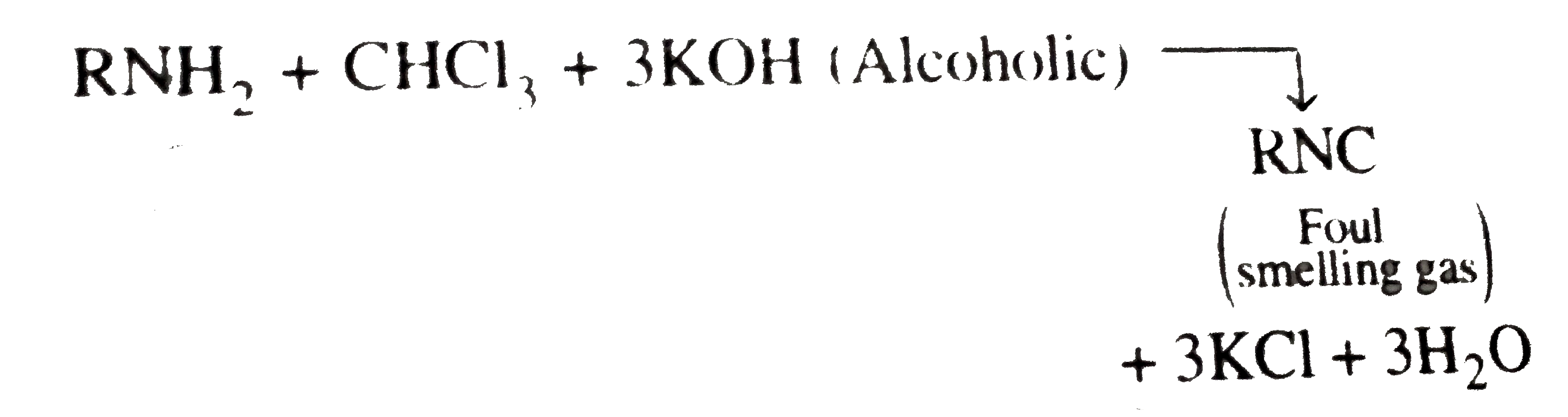 `NaNO_2 HCl overset(0^@C) (rarr) NaCl + HNO_2` ` UNDERSET ("It contains one (N) atom")(RNH_2+NHO_2) overset (0^@C)(rarr) R-underset (("Coloruless gas")) (OH +N_2 + N_2O)` At `STP 112 ml` of colorless gas is evolved with ` 0. 295 gm` sample of substance after treatment with aqueous `HCl` and ` NaNO_2` at ` 0^2C`. So ,a t ` STP 22400 ml` coloruless fas will be evolved with ` (0. 295 xx 2224000)/( 112) = 59 gm` of sample of such substance after above treatment . Hence , the MOLECULAR weith of ` RNH_2 ` is 59. `:.` Weightor ` R+ 14 +2 = 59` Weith of ` R= 43` So (R ), is ` C_3 H_7 - ( :. "Weigth of"C_3 H_7 -= 43)`. Thus , the GIVE substance is i. 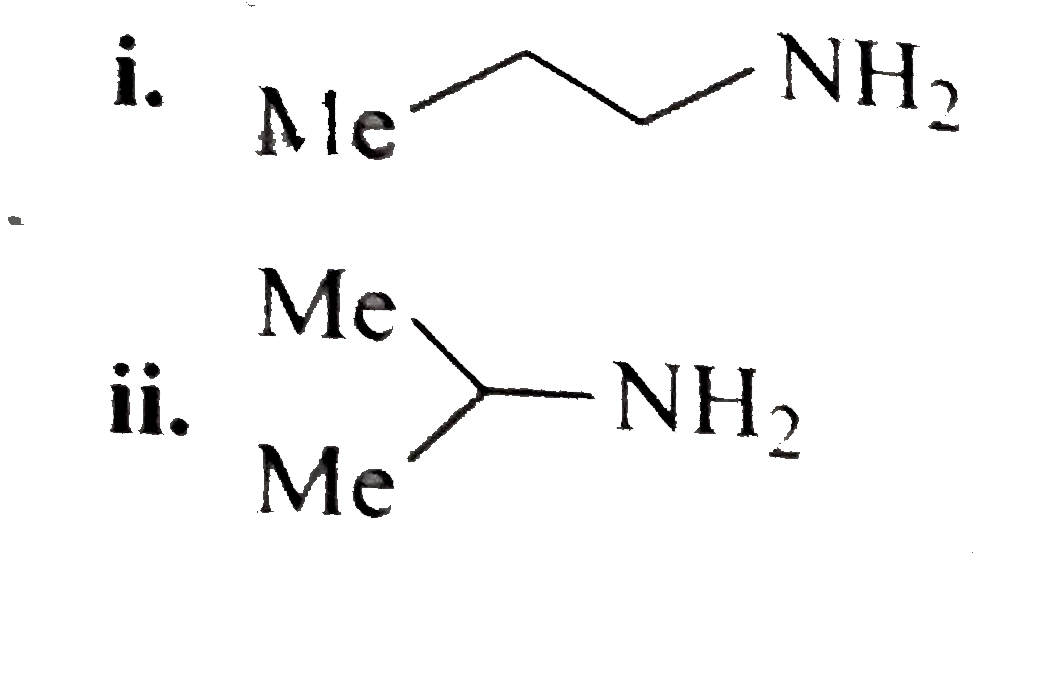 ii.  . .  . .
|
|
| 91311. |
A, B,C and D are four elements with E_(oxd)^(0) as +2.82V, +2.71V, +1.67V, -2.87V respectively . The strongest reducing agent is |
|
Answer» A |
|
| 91312. |
A: Bauxite is purified by leaching process R: Aluminium oxide reacts with NaOH to form soluble sodium meta aluminate. |
|
Answer» If both Assertion & REASON are true and the reason is the correct EXPLANATION of the assertion, then mark (1). |
|
| 91313. |
A basic volatile compound gave a foul smelling gas when treated with CHCl_(3) and alc. KOH. A 0.295 g sample of the substance dissolved in aqueous HCl and treated with NaNO_(3) solution at 0^(@)C liberated a colourless, odourless gas whose volume corresponds to 112 ml at STP. After the evolution of gas was complete, the aqueous solution gave an organic liquid which did not contain nitrogen and on boiling with I_(2) in the presence of alkali gave a yellow precipitate. When the basic volatile compound is reacted with CHCI_(3) and KOH a new compound is formed. This new compound on reduction gives |
|
Answer» `CH_(3)-UNDERSET(NH_(2))underset(|)CH-CH_(3)` |
|
| 91314. |
A basic, volatile nitrogen compound gave a foul-smelling gas when treated withchloroform and alcoholic potash. A 0.295-g sample of the substance dissolved in aq. HC1 and treated with NaNO, solution at 0°C, liberated a colourless, colourless gas whose volume corresponded to 112 inL at STP. After the evolution of the gas was complete, the aqueous solution was distilled to give an organic liquid which did not contain nitrogen, and which on warming with an alkali and iodine, gave a yellow precipitate. Identify the original substance. Assume that it contains one N atom per molecule. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`(CH_3)_2 CHNH_2` (ISOPROPYLAMINE ) | |
| 91315. |
A basic volatile compound gave a foul smelling gas when treated with CHCl_(3) and alc. KOH. A 0.295 g sample of the substance dissolved in aqueous HCl and treated with NaNO_(3) solution at 0^(@)C liberated a colourless, odourless gas whose volume corresponds to 112 ml at STP. After the evolution of gas was complete, the aqueous solution gave an organic liquid which did not contain nitrogen and on boiling with I_(2) in the presence of alkali gave a yellow precipitate. The molecular weight of the basic volatile compound is |
|
Answer» 59 22400 …......... ? `IMPLIES` 59 |
|
| 91316. |
A basic volatile compound gave a foul smelling gas when treated with CHCl_(3) and alc. KOH. A 0.295 g sample of the substance dissolved in aqueous HCl and treated with NaNO_(3) solution at 0^(@)C liberated a colourless, odourless gas whose volume corresponds to 112 ml at STP. After the evolution of gas was complete, the aqueous solution gave an organic liquid which did not contain nitrogen and on boiling with I_(2) in the presence of alkali gave a yellow precipitate. The compound must contain |
|
Answer» `CH_(3)-NH_(2)` |
|
| 91317. |
A basic refractory material among the following is |
|
Answer» `Al_(2)O_(3)` |
|
| 91318. |
A : Basic hydrolysis of ester is bimolecular in nature. R : Acidic hydrolysis of ester is pseudo first order reaction. |
|
Answer» If both Assertion & REASON are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion, then mark (1). |
|
| 91319. |
A basic buffer can be prepared by mixing |
|
Answer» `CH_3COONa` and `CH_3COOH` |
|
| 91320. |
(a) Based on the nature of intermolecular forces, classify the following solids: Sodium sulphate, Hydrogen. (b) What happens when CdCl_(2) is doppd with AgCl? ( c) Why do ferrimagnetic substances show better magnetism than antiferromagnetic substances? |
| Answer» Solution :(a) SODIUM SULPHATE: ionic SOLID, Hydrogen: molecular solid (non-polar). | |
| 91321. |
(a) Based on the nature of intermolecular forces, classify the following solids: Silicon carbide, Argon. (b) ZnO turns yellow on heating. Why? ( c) What is meant by groups 12-16 compounds? Give an example. |
| Answer» Solution :These are the compounds prepared by combination of group 12 and group 16 elements and behave like semiconductors, e.g., ZnS, CdS, CdSe, etc. The bonds in these compounds are not PERFECTLY covalent and the IONIC CHARACTER depends on the electronegativities of the two elements. | |
| 91322. |
(a) Based on the nature of intermolecular forces, classify the following solids: Benzene, Silver. (b) AgCl shows Frenkel defect while NaCl does not. Give reason. ( c) What type of semiconductor is formed when Ge is doped with Al? |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Benzene: MOLECULAR solid, Silver: metallic solid. AGCL shows Frenkel DEFECT, while NaCl does not, this is because size of `Ag^(+)` ion is smaller than `Na^(+)` ion. So, `Ag^(+)` ion can easily fit into interstitial site of crystal lattice while `Na^(+)` does not. ( c) p-type semiconductor is formed as Al is TRIVALENT (group-13 ELEMENT). |
|
| 91323. |
A base type indicator B differs in colour from its conjugate acid.(BH^(+)) .Acidic form is red in colour while basic form is blue in colour. Human eye can sense blue colour distincity when ratio of blue form concentration to red form cocnentration is (a)/(b). or more.However ,red colour can be sensed by human eye distinctly when ratio of red form concentration of blue form concentration is (c)/(d) or more. Determine the pH range of solution in which human eyes will be unable to observe distinct red or distinctly blue colour.Take ionisation of B as K_(eq). |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`:.pOH=pK_(eq)+log((["Acidic form"])/(["Baic form"]))=pK_(eq)+log((["Red"])/([BLUE]))` `(pOH)_(blue)=pK_(eq)+log((B)/(a))` and `p(OH)_(red)=pK_(eq)+pK_(eq)+log((C)/(d))` so RANGE `=pH_(blue)` to `pH_(red)=14-pK_(eq)-log((b)/(a))` to `14-pK_(eq)-log((c)/(d))` |
|
| 91324. |
A base is dissolved in water yields a solution with a hydroxide ion concentration of 0.05 mole "litre"^(-1). The solution is |
|
Answer» Basic `pOH = -LOG [OH^(-)] = -log[ 5xx 10^(-2)]` `pOH = 1.30, pH + pOH = 14`. `pH = 14 - pOH = 14 - 1.30 = 12.7`. |
|
| 91325. |
A base dissolved, in water yields a solution with a hydroxyl ion concentration of 0.5 mol "litre"^(-1). The solution is |
|
Answer» Basic `pOH = 2 log 5 = 1.3` `pH + pOH = 14 rArr pH = 14-1.3 = 12.7`. |
|
| 91326. |
A base can absract an alpha - H atom from |
|
Answer» `CH_(2) = CH_(2)` |
|
| 91327. |
A balloon weighing 50 kg is filled with 685.2 kg of helium at 1 atm pressure and 25^(@)C . What will be its pay load if it displaced 5108 kg of air ? |
|
Answer» 4372.8kg Pay LOAD = Mass of displaced air - Mass of balloon `= 5108-735.2= 4372.8 kg ` |
|
| 91328. |
A balloon weighing 50 kg has a radius of 10 m. What will be its payload if it isfilled with He at 1 atm and 25^@C. Density of air = 1.22 kg m^(-3). Also calculate its payload if H_2is filled in place of He. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :4893.8 KG, 4715.4 kg | |
| 91329. |
A balloon of 1 L volume is fill withO_(2) gas, kept in a spaceship at STP. Now this spaceship is send in space & ballons is released out of the spceship. Then ballon expands upto bursting then calculate work done by balloon. |
|
Answer» 0 |
|
| 91330. |
A balloon has a volumn of 10 L at a pressure of 1 atm. When the balloon is immersed to the bottom of a lake, its volumn reduces to 1.25 L. Assuming 1 atm. Pressure to be equivalent to 10 m column of water and no change in temperature, what is the depth of lake ? |
|
Answer» 70 m |
|
| 91331. |
A balloon filled with helium rises to a certain height at which it gets fully inflated to a volume of 1 xx 10^(5) litres. If at this altitude temperature and atmospheric pressure is 268 K and 2 xx 10^(-3) atm respectively, what weight of helium will be required to fully inflate the balloon ? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 91332. |
A balloon filled with ethane is pricked with a sharp point and quickly plunged into a tank of hydrogen at the same pressure . After some time, the balloon wil |
|
Answer» be enlarged |
|
| 91333. |
A balloon containing 1 mole air at 1 atm initially is filled further with air till pressure increases to 3 atm. The intialdiameter of the balloon is 1 m and the pressure at each state is proportion to diameter of the balloon. Calculate ( a) No.of moles of air added to change the pressure from 1 atm to 3 atm. ( b) balloon will burstif either pressure increases to 7 atm or volume increases to 36 pi m^(3).Calculate the number of moles of air that must be added after initial condition to burst the balloon. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 91334. |
A ballon of diameter 20 meter weights 100 Kg. Calculate its pay load, if it is filled with He at 1.0 atm and 27^(@)C. Density of air is 1.2 kgm^(-3) [R=0.082 dm^(3)" atm k"^(-1)" mol"^(-1)] |
|
Answer» Solution :Weight ballon `=100 KG =10xx10^(4)g` VOLUME of ballon `=(4)/(3) pi r^(3)` `(4)/(3)xx(22)/(7)xx((20)/(2)xx100)^(3)` `=4190xx10^(6) cm^(3)` `=4190xx10^(3)` LITRE Weight of gas (He) in balloon `=(PV)/(RT)` `=(1xx4190xx10^(3)xx4)/(0.082xx300)` `=68.13xx10^(4)g` `:.` Total weight of gas and balloon `=68.13xx10^(4)+10xx10^(4)=78.13x10^(4)g` Weight of air displaced `=(1.2x4190xx10^(4))/(10^(3))` `=502.x10^(4)g` `:.` Pay load =wt of air displaced -(wt)of baloon +wt of gas) `:.` Pay load `=502.xx110^(4)-78.13xx10^(4)` `=424.67xx10^(4)g` |
|
| 91335. |
A ballon weighing 50 kg is filled with 685.2 kg of helium at 1 atm pressure and 25^(@)C. What will be its pay load if it displaced 5108 kg of air ? |
|
Answer» 4372.8 KG `=50+685.2` `=735.2`kg PAY LOAD = Mass of displaced air - Mass of balloon `=5108-735.2=4372.8 G` Hence, (A) is the correct answer. |
|
| 91336. |
A balanced chemical equation is in accordance with |
|
Answer» Avogadro's law |
|
| 91337. |
A + B to CH_3 -OC (CH_3 ) overset( HI) to X+ Y Correct statement among the following is |
|
Answer» A and B are `CH_3O NA and (CH_3)_3 CBR` |
|
| 91338. |
A + B to CH_3 -OC (CH_3)_3 overset(HI)(to)X + YCorrect statement among the following is |
|
Answer» A and B are `CH_3ONa` and `(CH_3)_3 CBR` |
|
| 91339. |
A+B rarr CH_(3)-O-C(CH_(3))_(3) overset(HI)rarrX+Y Correct statement among the following is |
|
Answer» A and B are `CH_(3)Ona` and `(CH_(3))_(3)` CBr |
|
| 91340. |
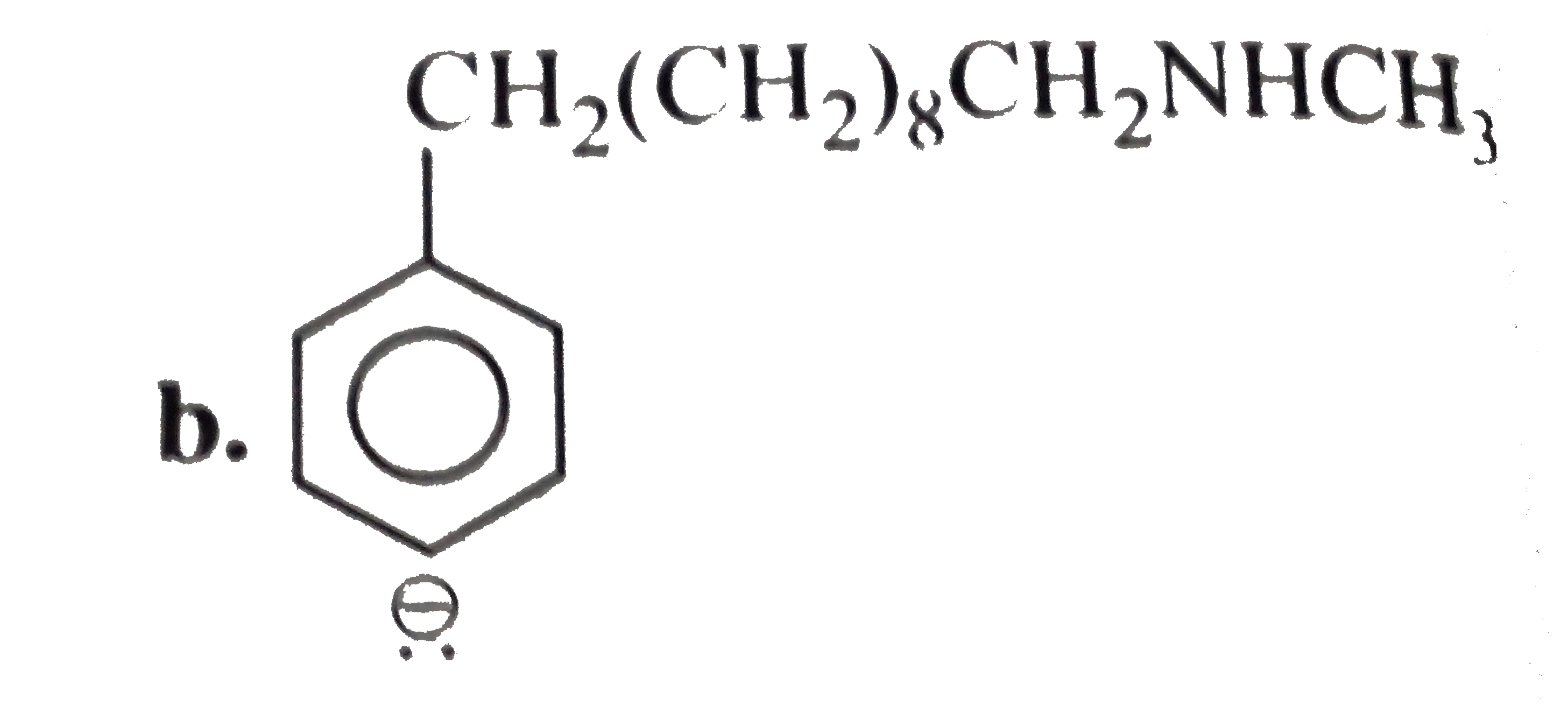
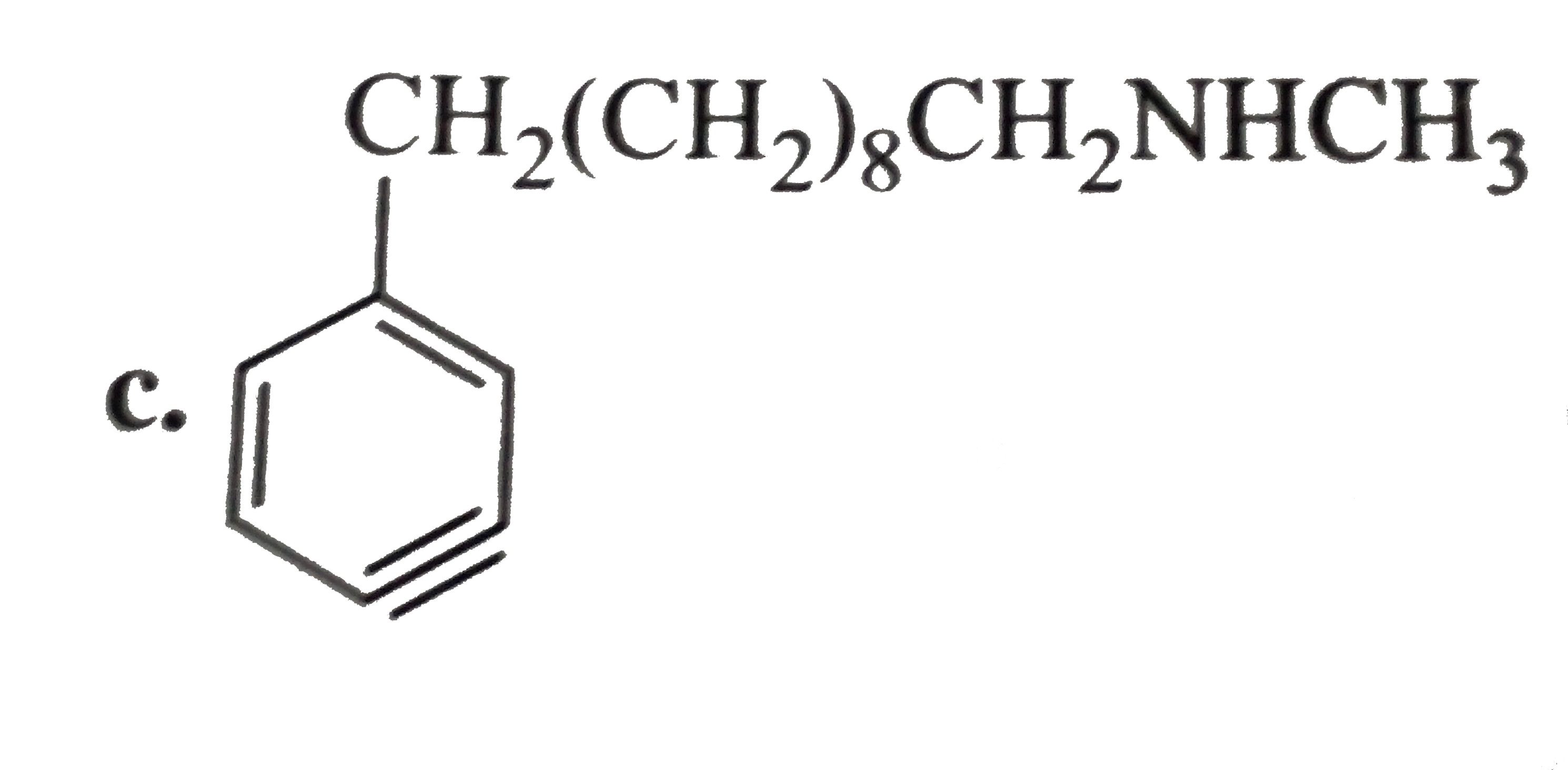
a. b. The formation of (D) form (C ) proceeds via the formation of which of the following intermediate species ? |
|
Answer»
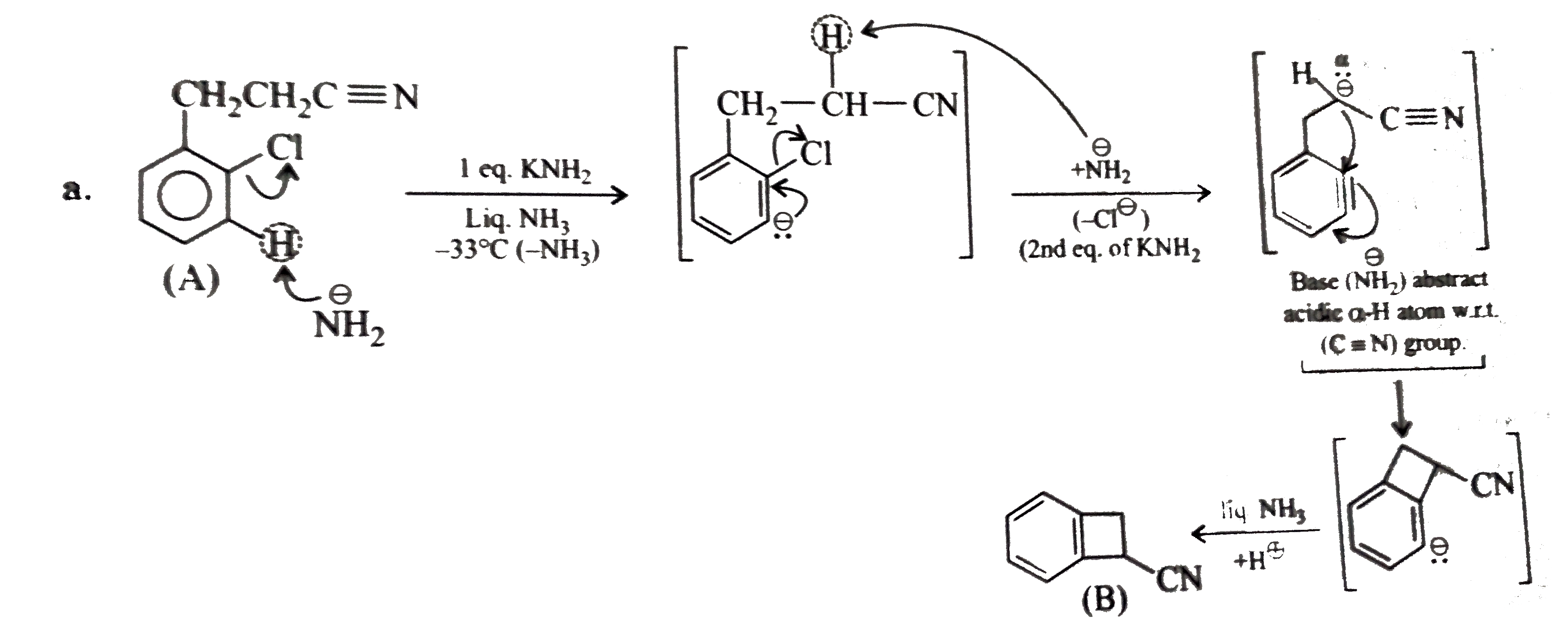 B. 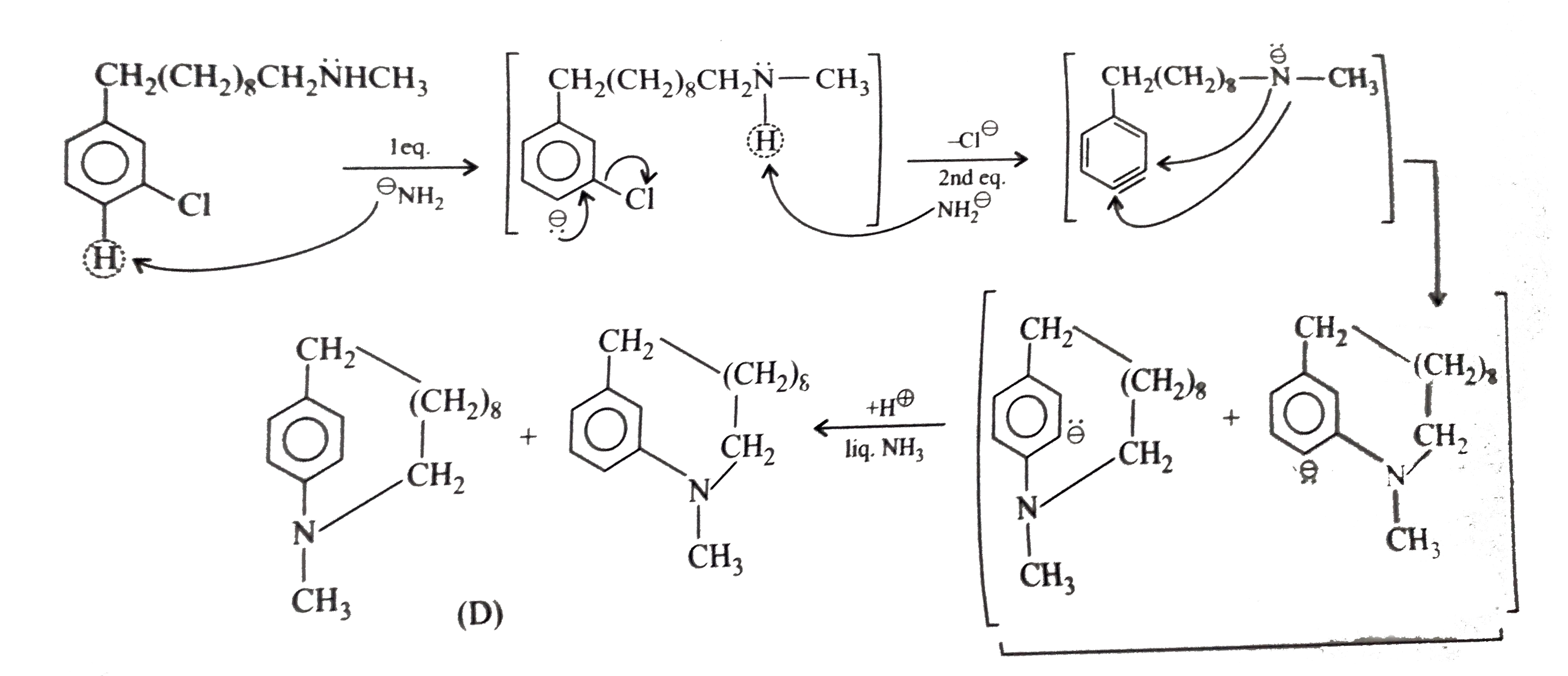
|
|
| 91341. |
A+B. In this reaction A and B are .......... |
|
Answer» `CaCO_3 + H_2` |
|
| 91342. |
A+B hArr C+D. If initially the concentration of A and B are both equal but at equilibrium , concentration of D will twice of that of A , then what will be the equilibrium constant of the reaction ? |
|
Answer» `4/9` |
|
| 91343. |
A+B hArr C+D if intially the concentration A and B are equal but at equilibrium concentration of D will be twice thatof A then what will be the equilibrium constant of the reaction. |
|
Answer» `4/9` |
|
| 91344. |
A+B formed can be distinguished by : |
|
Answer» iodofrom  Ethanol will GIVE iodoform test but 2-methyl propanal will FAIL in iodoform test `:.` Answer is (a) . |
|
| 91345. |
A, B, C are with molecular formula C_(8)H_(11)N three isomeric amines. A and B react with CHCl_(3)+KOH but not C. C reacts with NaNO_(2)+HCl to give yellow oily liquid. A and B on treatment with Br_(2) and acetic acid separately produced compounds D (C_(8)H_(9)NBr_(2)) and E(C_(8)H_(8)N Br_(3)). compound C may be |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 91346. |
A, B, C are with molecular formula C_(8)H_(11)N three isomeric amines. A and B react with CHCl_(3)+KOH but not C. C reacts with NaNO_(2)+HCl to give yellow oily liquid. A and B on treatment with Br_(2) and acetic acid separately produced compounds D (C_(8)H_(9)NBr_(2)) and E(C_(8)H_(8)N Br_(3)). compound A is |
|
Answer»

|
|
| 91347. |
A, B, C are with molecular formula C_(8)H_(11)N three isomeric amines. A and B react with CHCl_(3)+KOH but not C. C reacts with NaNO_(2)+HCl to give yellow oily liquid. A and B on treatment with Br_(2) and acetic acid separately produced compounds D (C_(8)H_(9)NBr_(2)) and E(C_(8)H_(8)N Br_(3)). The name of compound B is likely to be |
|
Answer» 3, 4 – DIMETHYL aniline |
|
| 91348. |
a. b. c. Acetone on reaction with NH_(2)OH gives one compound, whereas acetaldehyde gives two compounds that can be separated. Why? d. Acetone on reaction with HCN gives one compound, whereas acetaldehyde gives two compounds that are difficult to separate. Why? e. Butan-2-one gives sodium bisulphite addition product, whereas pentan-3-one does not. Why? (Test to differentiate Butan-2-one and pentan-3-one) f. h. There are two (-NH_(2)) groups in semicarbazide, of them which group reacts with (C=O) group and why? |
Answer» Solution :a. 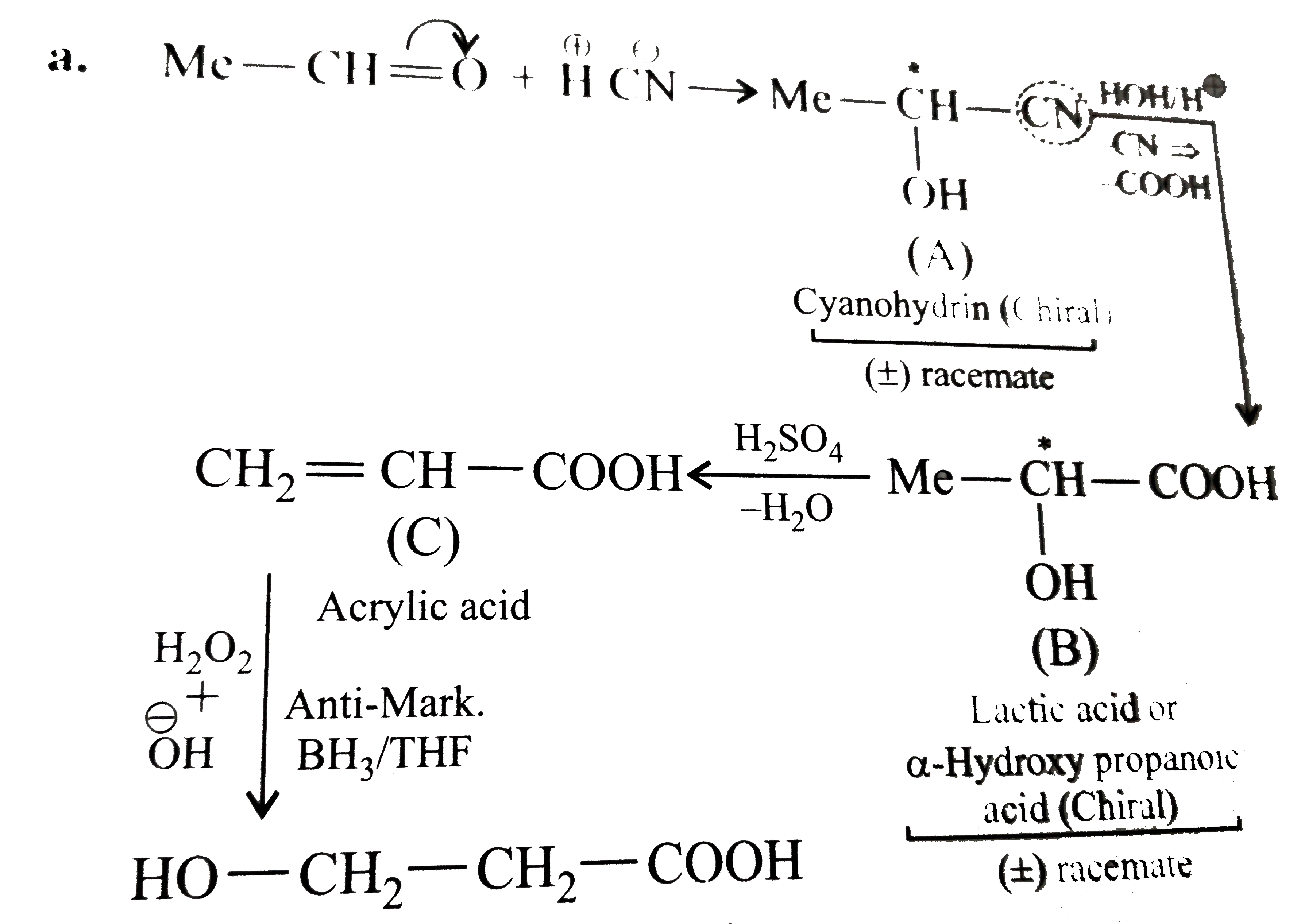 b. 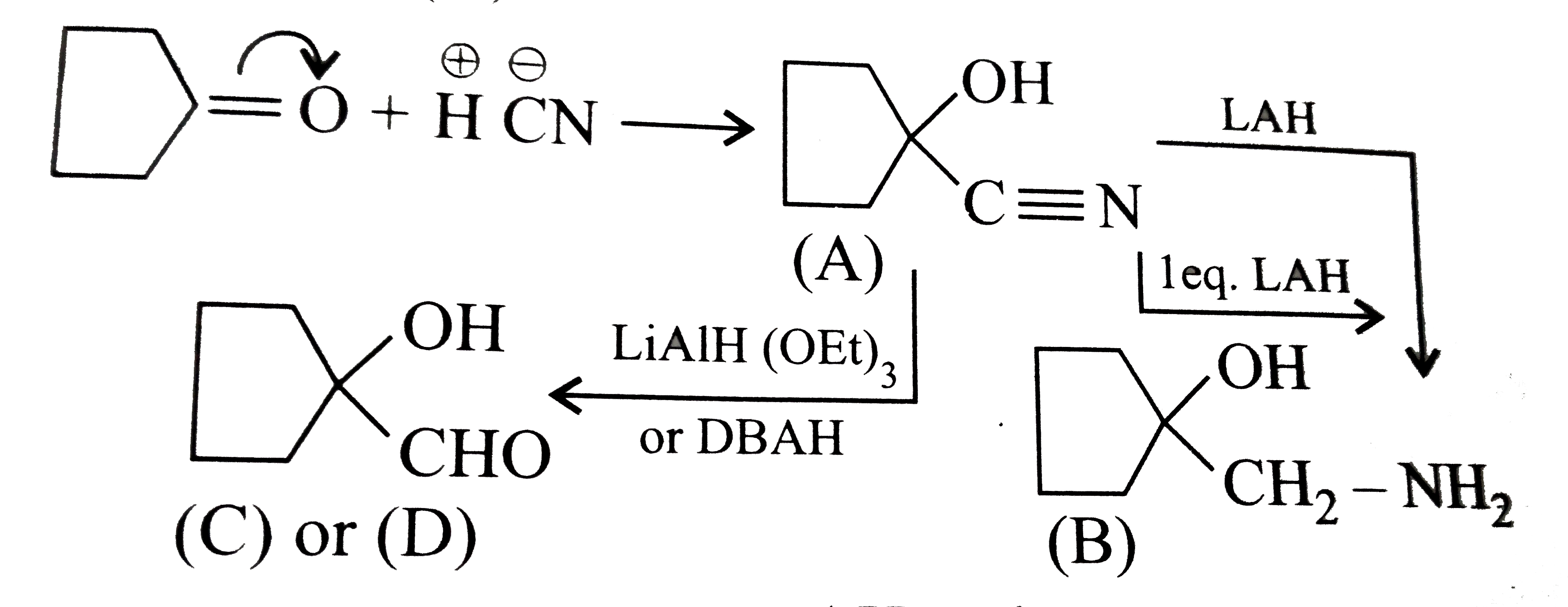 With one equivalent of LAH at low temperature, the reaction can be used to avoid over-reduction and proceed only upto aldehyde stage. Deactivated reducing agents such as lithium triethoxyaluminium hydride or DBAH may also be used. Mechanism: 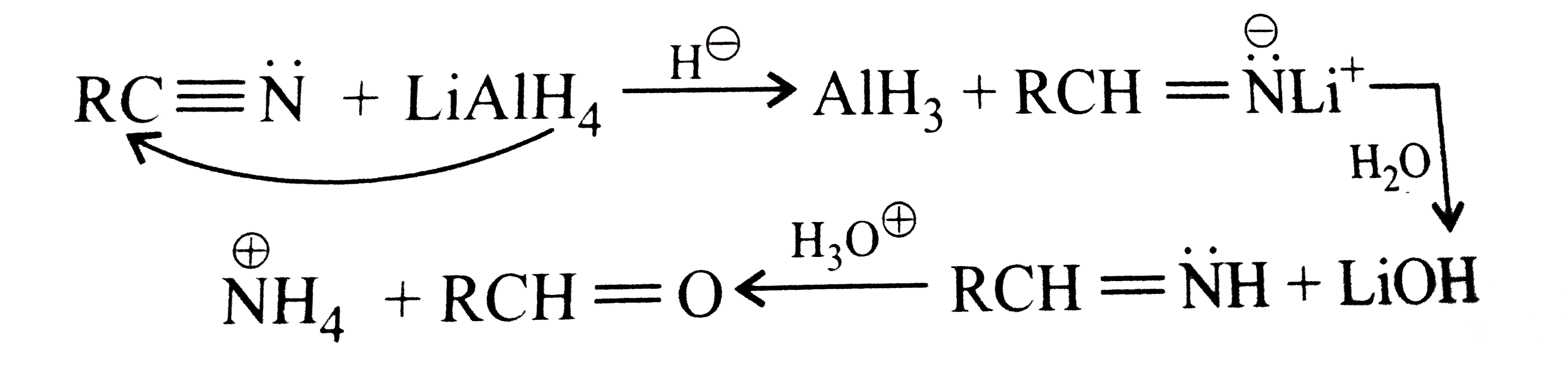 c. i. 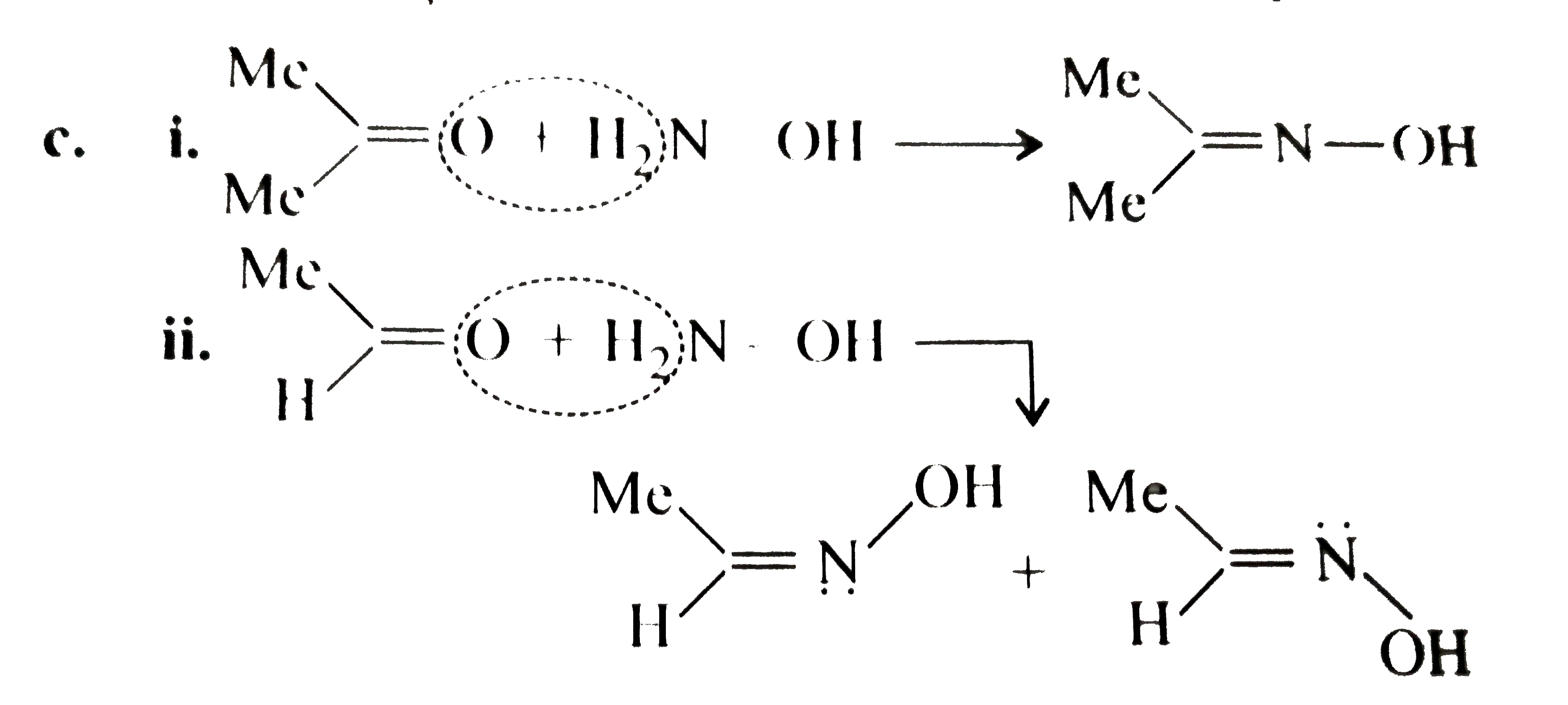 ii. 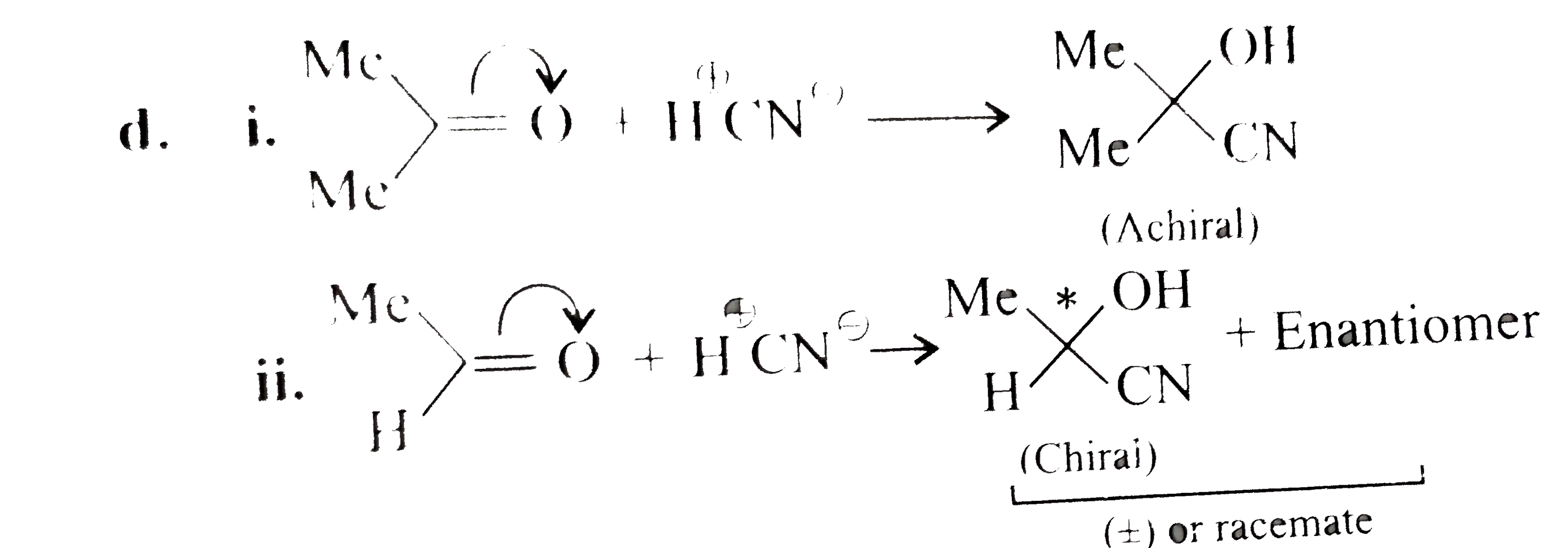 It gives geometrical isomers (disastereomers) which can be separated. Similar reactions are possible with other derivatives of ammonia, i.e., `NH_(2)NH_(2), PhNHNH_(2), 2,4-DNP`, semicarbazide `(H_(2)N NHCONH_(2))`, etc. SIMILARLY, `HCHO`, `PhCOPh` (benzophenone),`MeCH_(2)COCH_(2)Me` (pentan`-3-`one), etc.,will GIVE one compound, whereas `MeCHO`,`PhCOMe` (acetophenone),`PhCHO`, and `MeCH_(2)COMw` (butan`-2-`one) will give two geometrical isomers. d. i. 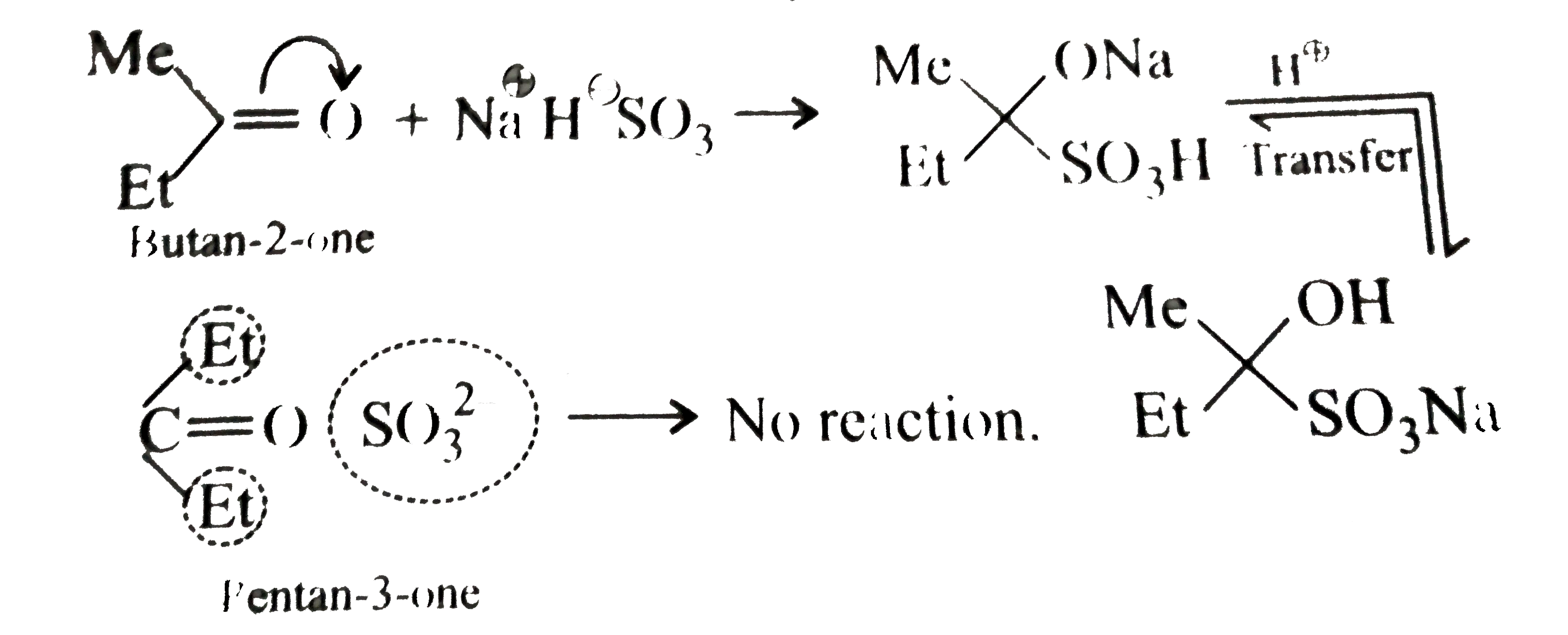 ii.  It gives enantiomers (optical isomers) due to the chiral centre. They arae difficult to separate since the chemical and physical properties of enantiomers are same. HOWEVER, they can be separated by biochemical method using enzymes and making their diastereomers. Similarly, `HCHO, MeCOMe, PhCOPh` (benzopehenone), `MeCH_(2)COCH_(2)Me` (pentan`-3-`one) will give only one compound, whereas `MeCHO, PhCOMe` (acetophenone), and `MeCOCH_(2)Me` (butan`-2-`one) will give two optical isomers. e. 3-Pentanone undergoes `NA` reaction with `HCN`, `NH_(3)`, `ROH`, etc., but with `NaHSO_(3)`, it does not react. This is due to the following: i. Large-sized nucleophile `(SO_(3)^(2-))`. ii. Due to steric hindrance by two bulky ethyl group. 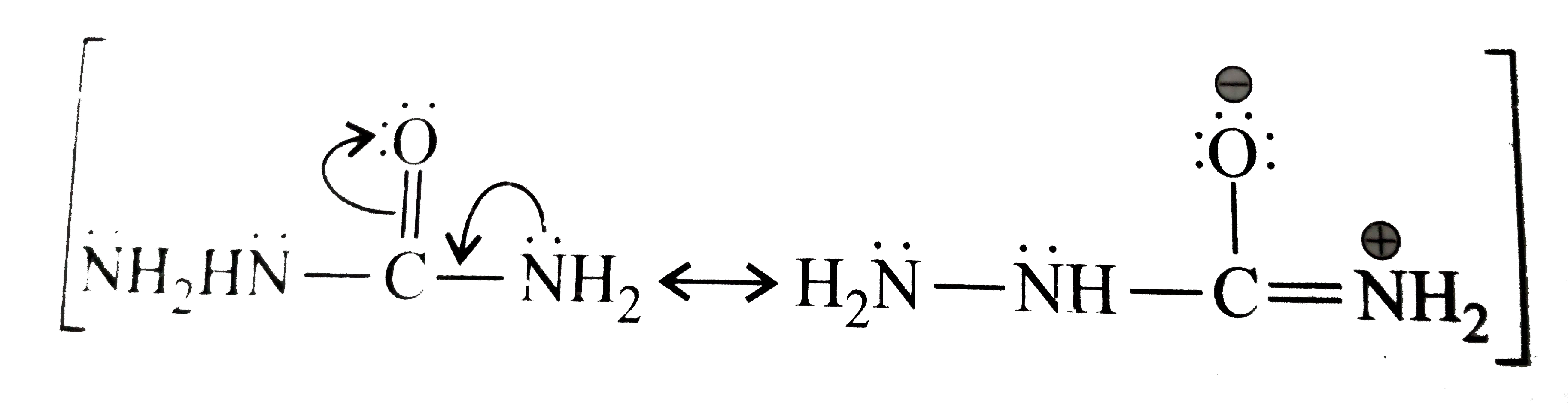 f. No reaction, since ketone does not react with monohydric alcohol. h. Semicarbazide `(overset(a)NH_(2)NHCOoverset(b)NH_(2))` reacts with `(C=O)` with `(overset(a)NH_(2))` group, since `(overset(b)NH_(2))` group closer to `(C=O)` group is deactivated by resonance stabilisation. Hence, `(overset(b)NH_(2))` group no longer acts as nucleophile. So, `(overset(a)NH_(2))` group is more nucleophilic than the `(overset(b)NH_(2))` group. |
|
| 91349. |
A, B and Cin the following reaction ? |
|
Answer» `A:C_(2)H_(5)CH_(2)-NHC_(6)H_(5)` |
|
| 91350. |
(A), (B) and (C) are three non-cyclic functional isomers of a carbonyl compound with molecular formula C_4H_(8)O. Isomers (A) and (C) give positive Tollens' test whereas isomer (B) does not give Tollens' test but gives positive Iodoform test. Isomers (A) and (B) on reduction with Zn(Hg)/conc. HCl give the same product (D). (a) Write the structures of (A), (B), (C) and (D). (b) Out of (A), (B) and (C) isomers, which one is least reactive towards addition of HCN ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) STRUCTURES of A, B, C and D are given below : `UNDERSET("Butanal-1")(A=CH_(3)CH_(2)CH_(2)CHO)` `underset("Butan-2-one")(B=CH_(3)COCH_(2)CH_(3))` `underset("2-Methylpropanal")(C=CH_(3)-underset(CH_(3))underset(|)(CH)-CHO)` `underset("Butane")(D=CH_(3)CH_(2)CH_(2)CH_(3))` (b) B i.e., `CH_3COCH_2CH_3` is the LEAST reactive towards addition of HCN. |
|