Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 39451. |
A metal metre scale gives correct measurement at 0^(@) C. It is generally used at a temperature of 40^(@) C. The correction to be made for every metre is ( alpha = 10^(-6) //1^(@) C) |
|
Answer» `4 XX 10^(-5) m` |
|
| 39452. |
A tank of height 5 m is full of water. There is a hole of cross-sectional area 1cm^(2) in its bottom. The volume of water that will come out from this hole per second is (g=10m//s^(2)) |
|
Answer» `10^(-3)m^(3)//s` |
|
| 39453. |
Speed of sound in air is 331 ms^(-1) at 0^(@)C. Prove that it increases at a rate of 0.6 ms^(-1).^(@)C^(-1) for small temperature increase. |
| Answer» | |
| 39454. |
A mass 'm' attached to a spring oscillates with a period 2 seconds when the mass is increased by 2kgthe period increases by 1 second. The initial mass 'm' is |
| Answer» ANSWER :B | |
| 39455. |
A light ray is incident normally on a glass slab of thickness t and refractive index mu as shown in the figure. Then find time taken by the light ray to travel through the slab. |
Answer» SOLUTION : From the figure distance TRAVELLED by the LIGHT ray through the SLAB is t. Velocity of light in glass `=(distance travell ed) / (TIME)` `c/mu=t/ (time) , time = (mu t)/c` |
|
| 39456. |
An unknown planet orbits the sun with distance twice the semi major axis distance of the Earth's orbit. It the Earths time period is T_(1) , what is the time period of this period is planet? |
|
Answer» Solution :By Kepler.s 3rd LAW`T^(2)prop a^(3)` TIME periodof unknownplanet = `T_(2)` Time PERIOD of EARTH =`T_(1)` Distance of unknown PLANET from the Sun= `a_(2)` `(T_(1)^(2))/(T_(2)^(2)) = (a_(1)^(2))/(a_(2)^(3))` `T_(2) = ((a_(2))/(a_(1)))^(3/2)T_(1)""a_(2)=2a` `T_(2) = ((2a_(1))/(a_(1)))^(3/2)T_(1) rArrT_(2) =2sqrt(2)T_(1)` |
|
| 39457. |
Assertion : The moment of inertia of a rigid body reduces to its minimum value, when the axis of rotation passes through its centre of gravity. Reason : The weight of a rigid body always acts through its centre of gravity. |
|
Answer» If both ASSERTION and reason are TRUE and reason is the CORRECT explanation of assertion. |
|
| 39458. |
What is the period of a simple pendulum whose length is 50 cm? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39459. |
A beaker full of hot water is kept in a room. It cools from 80^(@) C " to " 75^(@)Cin t_(1)minutes, 75^(@) C to 70^(@)Cin t_(2) minutes and 70^(@)C " to " 65^(@)C in t_(3) minutes in the same surroundings. Then |
|
Answer» `t_(1) = t_(2) = t_(3)` |
|
| 39460. |
In a given process on an ideal gas, dW = 0and dQ lt 0. Then for the gas |
|
Answer» The temperature DECREASES |
|
| 39461. |
Two bodies of masses m_(1) and m_(2) are initially at rest a infinite distance apart. They are then allowed to move towards each other under mutual gravitaitonal attraction. Their relative velocity of approach at a separation distance r between them is |
|
Answer» `[2G((m_(1)-m_(2)))/(r)]^(1//2)` |
|
| 39462. |
What is free fall of a body ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The MOTION of a body falling TOWARDSTHE Earth froma small altitude `(h lt lt R)`, PURELY under the force of gravity is CALLED free fall. | |
| 39463. |
A block of mass m is resting on an inclined plane. The inclination of the plane to the horizontal is gradually increased. It is found that when angle of inclination is theta , the block just begins to slide down the plane. What is the minimum force F applied parallel to the plane that would just make the block move up the plane? |
| Answer» Solution :`2mgsin theta` | |
| 39464. |
Which of the following is a dimensionless quantity? |
|
Answer» Specific heat THEREFORE strain is a dimensionless quantity. |
|
| 39465. |
Which one of the following pairs of physical quantities do not have the same dimensions? |
|
Answer» Work and energy Dimensions of surface tension `=[MT^(-2)]` |
|
| 39466. |
Rocket is the only means of travel in space - explain. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Usually, a VEHICLE applies some force on its surrounding objects, the reaction force exerted by those objects on the vehicle is actually responsible for its motion. On the other hand, let a system of two comparable masses be initially at rest , so that the total momentum is zero. let one of the masses be somehow detached, and allowed to move with a certain momentum in a definite DIRECTION. then the other mass would acquire an equal momentum in the opposite direction.Hence, the total momentum will STILL be zero. i.e., be conserved. in this way, the masses can acquire motion without any external force, and without the aid of the surrounding objects. A rocket in space utilises this principle. the spaceship and the fuel constitude the two different masses. As the fuel is ejected backwards, the spaceship successfully moves forward. It should be noted that , in space, (1) on external force can be applied on a vehicle, and (2) the vacuum in outer space can provide no surrounding object.A rocket is, therefore, the only MEANS of travel in outer space. |
|
| 39467. |
A uniform rope of length 12 m and mass6 kg hangs vertically from a rigid support . A block of mass2 kg is attached to the free end of the rope . A transverse pulse of wavelengths 0.06 m is produced at the lower end of the rope . What is the wavelength of the pulse when it reaches the top of the rope? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Tension at the LOWER end of the rope , `T_(1) = 2 G = 2 xx 9.8 = 19.6 N` Tension at the upper end of rope , Let `v_(1) and v_(2)` be the SPEEDS of pulse at the lower and upper end , respectively . So `v = SQRT (((T_(1))/(m))), v_(2) = sqrt(((T_(2))/(m)))` On dividing , we get `(v_(2))/( v_(1)) = sqrt(((T_(2))/( T_(1)))) = sqrt(((78.4)/(19.6))) = sqrt(4) = 2` As frequency is independent of medium , therefore if `lambda_(1) and lambda_(2)` are wavelengths at lower and upper ends respectively . Then `v_(1) = n lambda_(1) and v_(2) = n lambda_(2)` So, `(lambda_(2))/(lambda_(1)) = (v_(2))/( v_(1)) = 2` Therefore , the wavelength of pulse at upper end ` = 2 lambda`. `= 2 xx 0.06 = 0.12 m` |
|
| 39468. |
A 3m long ladder weighing 20 kg leans on a frictionless wall. Its feet rest on the floor 1 m from the wall as shown in Fig.7.27. Find the reaction forces of the wall and the floor. |
Answer» Solution : The ladder AB is 3 m long, its foot A is at distance `AC = 1 m` from the wall. From Pythagoras theorem, `BC = 2 SQRT(2) m`. The forces on the ladder are its weight W acting at its centre of gravity D, reaction forces `F_(1) and F_(2)` of the wall and the floor respectively. FORCE `F_(1)` is perpendicular to the wall, SINCE the wall is frictionless. Force `F_(2)`is resolved into two components, the normal reaction N and the force of friction F. Note that F PREVENTS the ladder from sliding away from the wall and is therefore directed toward the wall. For translational equilibrium, taking the forces in the vertical direction, `N – W = 0` (i) Taking the forces in the horizontal direction, `F – F_(1) = 0` (ii) For ROTATIONAL equilibrium, taking the moments of the forces about A, `2sqrt(2)F_(1)-(1//2)W=0` (iii) Now `W = 20 g = 20 × 9.8 N = 196.0 N` From (i) `N = 196.0 N` From (iii) `F_(1)=W//4sqrt(2)=196.0//4sqrt(2)=34.6N` From (ii) `F=F_(1)=34.6N` `F_(2)=sqrt(F^(2)+N^(2))=199.0N` The force `F_(2)` makes an angle `α` with the horizontal, `tanalpha=N//F=4sqrt(2),alpha=tan^(-1)(4//sqrt(2))~~80^(@)` |
|
| 39469. |
(A) : At critical temperature, surface tension of a liuid becomes zero. (R ) : At this temperature, intermolecular forces for liquids and gases become equal. Liquid can expand without any restriction. |
|
Answer» Both (A) and (R ) are true and (R ) is the correct EXPLANATION of (A) |
|
| 39470. |
The body projected with velocity 30ms^(-1) reaches its maximum height in 1.5s. Find its range (g=10ms^(-2)) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39471. |
Why can.t two persons each of say 100 kg standing 1m a part experience any gravitational attractionbetween them? |
| Answer» Solution : ACCORDING to Newton.s law of gravitation the force of ATTRACTION between the two persons turns out to be `10^(-7) N`which is very very small. Hence the persons in question do not experience the MINUTE force that exists between them. | |
| 39472. |
Two masses M_(1) and M_(2) connected by means of a string which is made to pass over light, smooth pulley are in equilibrium on a fixed smooth wedge as shown in figure. If theta = 60^(@) and alpha = 30^(@), the ratio of M_(1) to M_(2) is |
|
Answer» `1:2` |
|
| 39473. |
A particle in SHM is described by the displacement function, X(t) = B sin (omega t + alpha), omega (2pi)/T. If the initial (t = 0) position of the particle is lem and its initial velocity is pi cm//s, what are its amplitude uninitial phase angle ? The angular frequency of the particle is pi//s, nsqrt(2), mpi//4 then n & m are |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39474. |
At 20^(@)C to attain the terminal velocity how fast will an aluminium sphere of radii I mm fall through water. Assume flow to be laminar flow and specific gravity (AI) -2.72 |
|
Answer» 5m/s |
|
| 39475. |
Temperature of a body theta is slightly more than the temperature of the surroundings theta_(0). Its rate of cooling ( R ) versus temperature of body theta is plotted, its shape would be |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 39476. |
The system as shown in fig is released from rest. Calculate the tension in the strings and force exerted by the strings on the pulley. Assuming pulleys and strings are massless |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`T_(1)-1g=1a"____(1)"` `T_(2)-T_(1)=3a"____(2)"` `2g-T_(2)=2A"____(3)"` Solving the above equations, we get, `a=(g)/(6)m//s^(2)` 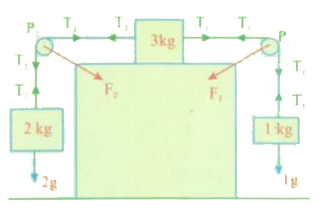 `T_(1)=(7g)/(6)N, T+(2)=(5g)/(3)N` FORCE on pulley `P_(1)` is `F_(1)=sqrt(T_(1)^(2)+T_(1)^(2))` `=sqrt2T_(1)=(7g)/(3sqrt2)N` Force on pulley `P_(2)` is `F_(2)=sqrt(T_(2)^(2)+T_(2)^(2))` `=sqrt2T_(2)=(5sqrt2g)/(3)N` |
|
| 39477. |
Figure below shows two paths that may be taken by a gas to go from state A to a state C. In process AB, 400 Jof heat is added to the system and in proces BC, 100 J of heat isadded to the system. The heat absorbed by the system in the process AC will be |
|
Answer» Solution :As initial and final points are same so `Delta U_(ABC) = Delta U_(AC)` AB is isochoric PROCESS. `Delta W_(AB) = 0` `Delta Q_(AB) = Delta U_(AB) = 400 J` B is isobaric process. `Delta Q_(BC) = Delta U_(BC) + Delta W_(BC)` `100 = Delta U_(BC) + 6 xx 10^(4)` `(4 xx 10^(-3) - 2 xx 10^(-3))` `100 = Delta U_(BC) + 12 xx 10` `Delta U_(BC) = 100 - 120 = -20 J` As, `Delta U_(ABC) = Delta U_(AC)` `Delta U_(AB) + Delta U_(BC) = Delta Q_(AC) - Delta W_(AC)` `400 - 20 = Delta Q_(AC) - (2 xx 10^(4) xx 2 xx 10^(-3) + (1)/(2) xx 2 xx 10^(-3) xx 4 xx 10^(4))` `380 = Delta Q_(AC) - (40 + 40), Delta Q_(AC) = 380 + 80 = 460 J` 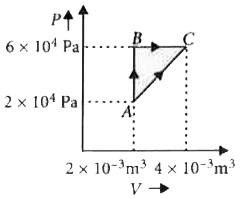
|
|
| 39478. |
Pressure at a point inside a liquid does not depend on |
|
Answer» the nature of the liquid |
|
| 39479. |
The shadow of a pole standing on a level around is found to be 45 m longer when the Sun's altitude is 30^(@) than when it was 60^(@). Determine the height of the pole. [Given sqrt(3) = 1.73] |
|
Answer» Solution :Solution `(x-45)/(H) = COT 30^(@) RARR h = (x+45)/(cot 30^(@))` `x/h = cot 60^(@)` SUBSTITUTING the value of x in the above equation `h = (h cot 60^(@) + 45)/(cot 30^(@))` `h cot 30^(@) = h cot 60^(@) + 45` `h = (45)/(cot 30^(@) - cot 60^(@)) = (45)/(sqrt(3) - (1)/(sqrt(3))) = 38.97` m |
|
| 39480. |
A calorimeter full of hot water is hung in vaccum. It will |
|
Answer» Cool by CONDUCTION |
|
| 39481. |
A rod of length 1 m having cross-sectional area 0.75m^(2) conducts heat at 6000Js^(-1). Then the temperature difference acorss the rod is, if K=200Wm^(-1)K^(-1) |
|
Answer» `20^(0)C` |
|
| 39482. |
A square plate of side length 2m has a groove made in the shape of two quarter circles joining at the centre of the plate. The plate is free to rotate about vertical axis passing through its centre. The moment of inertia of the plate about this axis is 4 kg - m^(2). A small block of mass 1 kg enters the groove at end A travelling with a velocity of 2//s parallel to the side of the square plate. The block move along the frictionless groove of the horizontal plate and comes out at the other end B with speed V. Find V assuming that width of the groove is negligible. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39483. |
The period of a simple pendulum suspended from the ceiling of a car is T when the car is at rest. If the car moves with a constant acceleration the perod of the pendulum |
|
Answer» UNALTERED |
|
| 39484. |
Consider a uniform U-tube with a diaphragm at the bottom and filled with a liquid to different heights in each limb as shown in Fig. Now imagine that the diaphragm is punctured so that the liquid flows from left to right. (a) Show that the application of Bernoulli's particle to points (1) and Diaphragm (2) leads to a constradiction. (b) Explain why Bernoulli's principle is not applicabe here |
|
Answer» Solution : LET the height of the liquid in the LIMBS (1) and (2) be` y_1 and y_2` and the velocity of the liquid be `v_1 and v_2` respectively. Applying Bernoulli.s equation to the points (1) and (2) ` "" P + (1)/(2) rho v_1^(2)= P+ (1)/(2)rho v_2^(2)+ rho gy_2` Where P is the atmospheric pressure But ` ""v_1 =v_2=0 ` ` therefore ""rho gy_1= rho gy_2` `"" y_1= y_2` This is a contradictionbecause `y_1 ` is not equal to `y_2` (b)Bernouli.s PRINCIPLE cannot be applied here because the flow is not steady. |
|
| 39485. |
If |vecAxxvecB|=sqrt(3)vecA*vecB, then |vecA+vecB|=? |
|
Answer» `(A^2+B^2+AB)^(1/2)` |
|
| 39486. |
Figureshows a plot of the transverse displacements of the particles of a string at t = 0 through which a travelling wave is passing in the positive x-direction. The wave speed is 20 cms^-1. Find (a) the amplitude, (b) the wavelength, (c) the wave number and (d) the frequency of the wave.. |
|
Answer» a. amplitude `A=1mm` b. `Wavelength LAMDA=4cm` c. Wave NUMBER `N=(2PI)/lamda` `=((2xx3.14))/4` `=1.57cm^-1` `(wave number =k)` d. Frequencey `f=1/T=20/4=5Hz` `(where time period T=lamada/v)` |
|
| 39487. |
A car is travelling in steady rain with constant acceleration in a stright line. When it begins to move the driver sees tha the rain drops make track an an angle of 37^(@) with the vertical. After 20 sec the rain drops make track at an angle 53^(@) with vertical in same direction . Rain is falling at 3 m/s. Find acceleration of car in cm//s^(2) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39488. |
A small particle of mass on is projected with an initial velocity v at an angle 8 with x axis in X-Y plane as shown in Figure. Find the angular momentum of the particle. |
|
Answer» Solution :Let the particle of mass m cross a horizontal distance x in time t. ANGULAR momentum `vecL= int vec TAU dt` But `vectau= vecr xx vec F` `vecr=xhati+yhatj and vecF=-mg hatj`  `:. Tau=(x hati+y hatj)xx(hati xx hatj)=-mgx hatk` `vecL=-mg int (x dt) hatk=- mgv cos theta( intdt) hatk)` Let INITIAL time =0 and final time `t=t_(1)` `:. vecL= mgv cos theta( underset(0) OVERSET(t_(f)) int t dt) hatk=-(1)/(2) mgv cos theta t_(f)^(2) hatk` Negative SIGN indicates, `vecL` point inwards |
|
| 39489. |
A proton is kept at rest. A positively charged particle is released from rest at a distance .d. in its field. Consider two experiments, one in which the charged particle is a proton and in another a position. In the same time .t. the work done on the two moving charged particles is |
|
Answer» Same as the same force law is INVOLVED in the two experiments |
|
| 39490. |
A wire of length L and radius r is clamped rigidly at one end. When the other end of the wire is pulled by a force f its length increases by l. Another wire of the same material of length 2L and radius 2r is pulled by a force 2f. Then find the increase in length of this wire. |
|
Answer» `l/2` `therefore l = ( fL )/( pi r ^(*2) Y)` Now for increase in LENGTH for second wire, `l . = ((2 f ) (2L ))/( pi (2r) ^(2) l )= (4F L )/( 4pi r ^(2) l )` `l .=l` |
|
| 39491. |
A manometer contains a liquid of density rho. The difference in the levels when the manometer rotates at a constant angular velocity omega about one of its vertical limbs. (Let 1 be the length of horizontal tube) |
|
Answer» `( omega^(2) l^(2) )/( 2g)` |
|
| 39492. |
Unit of impulse of force and energy gradient are equal. |
|
Answer» `(U/y=-F)N` |
|
| 39493. |
The angular velocityof the earth about its polar axis so that the weight of the body at the equator will be zero is |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 39494. |
A cylindrical container has mass M and height H. the centre of mass of the empty container is at height (H)/(2) from the base. A liquid, when completley filled in the container, has mass (M)/(2) this liquid is poured in the empty contaienr. (a) How does the centre of mass of the system (container+liquid) move as the height (x) of liquid column changes from zero to H? Explain your answer qualitatively. Draw a graph showing the variation of height of centre of mass of the system (x_(cm)) with x. (b) Find the height of liquid column x for which the centre of mass is at its lowest position. |
|
Answer» (b) `x=(SQRT(6)-2)H` |
|
| 39495. |
Two cars moving with speeds 40 km/hr and 80 km/hr respectively with uniform acceleration. How many times the stopping distance of car with 80 km/hr is greater than another car ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Four times ACCORDING to EQUATION, `d = (v _(0) ^(2))/(2a)` |
|
| 39496. |
All particles of a body are situated at a distance R from the origin. The distance of centre of mass of the body from the orign is |
| Answer» ANSWER :B | |
| 39497. |
A planet revolves around sun in an elliptical orbit of ecentricity 'e'. If 'T' is the time period of the planet then show that the time spent by the planet between the end of the minor axis and close to sun it T((1)/(4)-(e)/(2pi)) |
|
Answer» Solution :`(dA)/(d t)` = constant, `(t_(AB))/(T) = ("(Area) SAB")/("(Area) ellipse") = ((PI ab)/(4)-(1)/(2)b(ea))/(pi ab)` 
|
|
| 39498. |
At the same temperature a drop of water of diameter 1 mm is broken into 10^6 equal water droplets of spherical shape. How much mechanical work should be done in forming the new surface area ? Surface tension of water =0.074 N. m^-1. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`230xx10^-7 J` | |
| 39499. |
A force of 10 N acts on a body of mass 1.0 kg at rest. Find the work done in 4 seconds. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :F = 10 N,m = 1.0 kg , u = 0, t = 4s, acceleration `a = (F)/(m) xx (10)/(1) = 10MS^(-1)`. Its displacement `S=ut+(1)/(2)at^(2)=0+(1)/(2)(10)4^(2)=80m` The work done W = FS = MAS = `1.0 xx 10 xx 80 = 800j` |
|
| 39500. |
A man coveres 60 cm distance in one minute on the surface of earth. The distance he will cover on the surface of moon in one minute is(g_(m) = (g_(e))/(6)) |
| Answer» Answer :A | |



