Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 2301. |
What are secondary function of money ? |
| Answer» Solution :Secondary functions of MONEY are (i) standard of deffered payment and (II) store of VALUE. | |
| 2302. |
Explain constituent of environment. |
| Answer» Solution :Environmentrefersto totalplanetary inheritanceand totalityof all resources and includesall the biotic and ABIOTICFACTORS INFLUENCING eachother. Biotic elements consist of LIVING organismslike birds, ANIMALS,forests, plants, fisheries , etc.Abioticelements are AIR,water, land, sunlight, etc. | |
| 2303. |
Explain the effect of the following on demand for a good: (i) Rise in Income for Normal Goods. (ii) Rise in Income for Inferior Goods. |
Answer» Solution :(i) Rise in INCOME for Normal Goods: 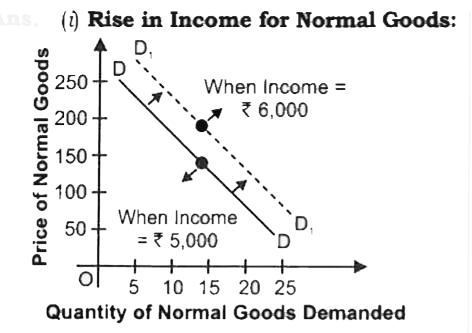 (a) For normal commodity, with a rise in income, the demand of the commodity also riseand vice-versa. (B) Shortly, direct relationship of a consumer(say from Rs 5000to Rs 6000), the demand of normal goods shifts rightward from DDto`D_(1)D_(1)` as shown in above figure. . (II) Rise in Income for Inferior Goods: (ii) Rise in Income for Inferior Goods: 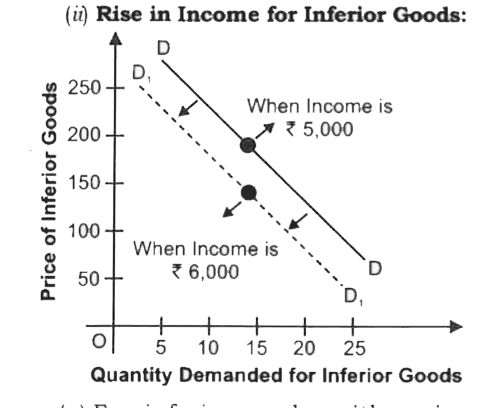 (a) For inferiorgoods, with a rise in income,the demand of the commodity falls and vice-versa. (b) Shortly, INVERSE relationship exists between income of a consumer and demand of inferior goods. (c ) due to rise in income of a consumer (say from Rs 5000 to Rs 6000), the demand of inferior goods shifts leftward from DD to `D_(1)D_(1)` as shown in adjacement figure: |
|
| 2304. |
Which branch of economic solves the problem of "what, how and for whom" to produce in the economy ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :MICROECONOMICS | |
| 2305. |
Distinguish between balance on trade account and balance on current account.ORDistinguish between Balance of trade and Balance on current account of the Balance of Payments account. OR Distinguish between trade account and current account of balance of payments account. |
| Answer» Solution :CURRENT Account is an account showing the trade of merchandise, whereas the Capital Account gives place to all capital transactions. While current account is used to KEEP a TRACK on the movement of money in and out the economy, during a PARTICULAR period. | |
| 2306. |
The incidence of tax refers to : |
|
Answer» LEVEL and rate of TAXATION |
|
| 2307. |
A perfectly competitive firm faces market price equal to Rs. 15. (i) Derive its total revenue schedule for the range of output from 0 to 10 units. (ii) Suppose the market priceincreases to17. Will the new TR curve be flatter or steeper? |
Answer» Solution : NEW TR CURVE will be a steeper STRAIGHT line as the one in perfect competition. |
|
| 2308. |
Define domestic income OR Define domestic product . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2309. |
What is meant by effective demand ? |
| Answer» Solution :The LEVEL of AGGREGATE demand required to ACHIEVE full employment equilibrium is called EFFECTIVE demand. | |
| 2310. |
What is marginal propensity to consume ? How is it related to marginalpropensity to save ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Marginal propensity to CONSUME (MPC) refers to the ratio of CHANGE in CONSUMPTION expenditure to change in total INCOME.MPC = `("Change in Consumption"(DeltaC))/("Change in Income"(DeltaY))` MPC is related to marginal propensity to save (MPS). Discuss "Relationship between MPC and MPS". |
|
| 2311. |
Why AR curve (demand curve) under monopolistic competition is more elastic than AR curve under monopoly? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) AR curve under both the MARKETS slope DOWNWARDS. (ii) However, AR curve under monopolistic COMPETITION is more elastic as compared to AR curve under monopoly because of PRESENCE of close substitutes. (iii) AR curve is less elastic in monopoly because of no close substitutes. |
|
| 2312. |
The measure of price elasticity of demand of a normal good carries minus sign while price elasticity of supply carries plus sign. Explain why ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Mathematically speaking, price ELASTICITY of demand is case of Normal good is negative, since the change in QUANTITY demanded is in opposite direction to the change in price as there is inverse relationship EXISTS between price of Normal Good and Quantity demanded for Normal Good. (ii) Price elasticity of supply in case of Normal good is positive, since the change in quantity supplied is in same direction to the change in price as there is positive relationship exists between price of Normal Good and Quantity supplied for Normal Good. (iii) So, in Nutshell, .Minus sign. ATTACHED with price elasticity of demand shows LAW of Demand and .Plus sign. attached with price elasticity of supply shows Law of Supply. |
|
| 2313. |
If indifference curve is straight line downward sloping , |
|
Answer» MRS is INCREASING |
|
| 2314. |
Name the items that are excluded from the Balance of Trade account, but included in the Balance of Payments account. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2315. |
Categorise the following into direct tax or indirect tax Financial help received from foreign countries . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2316. |
What is the relation between MPC and MPS. |
| Answer» Solution :The sum of MPC and MPS is equal to unity (i.e., MPC + MPS = 1).SYMBOLICALLY:Y =C + Sor∆Y = ∆C + ∆SBy DIVIDING both SIDES by AY, we get:∆Y/∆Y = ∆C/∆Y = ∆S/∆YORI = MPC + MPS | |
| 2317. |
Explain with diagram , the relationship between TU and MU. |
Answer» Solution :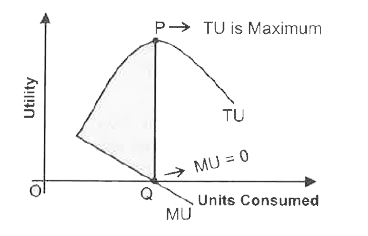 (i) When MU DECREASES, TU INCREASES at a diminishing rate. ( As shown in figure till consumption level OQ ). (II) When MU is zero , TU is constant and maximum at P. (iii) When MU is negative , TU starts diminishing. |
|
| 2318. |
What is meant by trade deficit? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2319. |
Sale of govermment securities by the central bank in the open market is an appropriate policy to check depression in the economy. |
| Answer» Solution :False. To CHECK depression, the central bank should PURCHASE GOVERNMENT securities from the OPEN MARKET. | |
| 2320. |
Giving reasons, state whether the following statements are true or false. (i) Average product will increase only when marginal product increases. (ii) With increase in level of output, average fixed cost goes on falling till it reaches zero. (iii) Under diminishing returns to a factor, total product continues to increase till marginal product reaches zero. |
Answer» Solution :(i) False, the average product does not only rise when the marginal product increases. But, there also exist a region where average product continues to rise corresponding to the falling marginal product. This can be explained with the help of the following diagram.  As we can see in the region AB, the average product continues to rise even when the marginal product is falling. The reason BEHIND this can be attributed to the fact that the marginal comonent alway CHANGE (rise/fall) at a faster rate in contrast to the average component. (ii) False, with increase in the level of output, the average fixed cost continues to fall but it never reaches zero because average fixed cost is a rectangular hyperbola. That is, it can never be zero. This can be explained with the help of the following diagram.  As we can see that the average fixed cost being a rectangular hyperboal tends to be zero, but HOWEVER, it can never be zero. (iii) True, under diminshing returns to a factor, total product continues to increase till marginal product reaches zero. This can be explained with the help of the following diagram.  As we can see from the above figure, the total product continues to increase till the marginal product reaches zero. This is because from the point I till the point B as more and more labour inputs are combined with the constant level of fixed factor, it leads to the fuller utilization of the fixed factor. Consequently, the marginal product of the ADDITIONAL labour units falls, whereas, TP continues to rise. The moment, where, the MP of the last labour unit becomes exactly equal to zero, then the TP reaches its maximum POINTS. |
|
| 2321. |
Give the meaning of Nominal GDP and Real GDP. Which of these is the indicator of economic welfare ? |
| Answer» Solution :NOMINAL GDP:When GDp of the given year is ESTIMATED on the basis of price of the same year , it is called nominal GDPReal GDP:When GDP of givenyear isestimatedon the basis ofprice of the BASE year, it is called REAL GDPReal GDP is the indicator of economic WELFARE | |
| 2322. |
Governmenthas started spending moreon providing free services like education and health to the poor. Explain the economic value it reflects . |
| Answer» Solution :Spending on free services to the poor raises their STANDARD of living and at the same TIME helps in reductionin income inequalities . It ALSO helps in raising productionpotential of the country by raising the efficiency level of the WORKING class among the poor. | |
| 2323. |
In an economy an increase in investment leads to an increase in national income three times more than increase in investment. Calculate MPC. |
|
Answer» Solution :SINCE increase in NATIONAL income (Y) is three times more than increase in investment, it means total increase in (Y) is four times, i.e. MULTIPLIER (K) is 4. `K=(1)/(1-MPC)` `4=(1)/(1-MPC)` `4-4MPC=1 or 4MPC=3` `HENCE, MPC=(3)/(4)=0.75` |
|
| 2324. |
Explain the Law of Variable Proportions with the help of total product and marginal product curves. |
|
Answer» Solution :The law of variable proportions explains the relationship between inputs and outputs in the short run. In the short run, some factors of production (input) are fixed and other factors input are variables. The quantity of output can be increased by increasing the use of variable input. As more and more units of variable input are employed, the proportion between the fixed and variable factors keeps on changing. The output passes through three phases. These three phases are identified with respect to the marginal product. Phase I: TP increases at an increasing rate. In The First phase of production the marginal product rises and reaches its highest point. This is the phase of Increasing Returns to a factor and during this phase, total product increases at an increasing rate. Phase II: TP increases at a diminishing rate. In this phase, Marginal Product is declining, but is positive. Inthis phase total product incrases but at a diminishing rate. This phase ENDS when Marginal Product is ZERO and Total Product is at its maximum level. A producer always operates in this stage. Phase III : TP is falling. In phase of production, Marginal Product is and negative. Here total product STARTS falling.  These phses are shown graphically in diagram. The reasons for the Operation of the Law are: 1. Optimus combination of factors: The phase of incrasing marginal product is due to optimum combination of factors that is required for any given technology, therefore fixed factors get better utilized. 2. However, when more and more units of variable factors are employed to a fixed factor, the fixed factor cannot absorb it and there is overcrowding of variable factors due to which the marginal product falls and becomes negative. This is the phase of diminishing marginal product. |
|
| 2325. |
What is the relationship between marginal propensity to save and marginal propensity to consume ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The SUM TOTAL of MPC and MPS is EQUAL to one, i.e.MPC + MPS = 1. | |
| 2326. |
What is meant by economic transactions? How can they be categorised? |
| Answer» Solution :Economic transactions refer to those transactions which involve transfer of the title or ownership of goods, services, money and assets. They are broadly categorised as:1) Visible items: These include all types of PHYSICAL goods which are exported and imported. These are called visible items as they are made of some matter or material and can be seen, touched and measured. The movement of such items is open and can be verified by the CUSTOM officials.2) Invisible Items: Invisible items of trade refer to all types of services like shipping, banking, insurance,etc, which are given and received. These are called invisible items as they cannot be seen, FELT, touched or measured.3) UNILATERAL Transfers: Unilateral transfers include gifts, personal remittances and other one-way transactions. Since, these transactions do not involve any claim for repayment, they are also known as unrequited transfers.4) Capital Transfers: These RELATE to capital receipts and capital payments. | |
| 2327. |
Why is tax not a capital receipt |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Because it neither CREATES government's LIABILITY nor reduces its ASSETS. | |
| 2328. |
What is meant by diminishing returns to a factor? |
| Answer» Solution :DIMINISHING returns to a FACTOR refer to a phase when TOTAL product INCREASES at a decreasing rate and marginal product falls, but remains positive with the INCREASE in variable factor. | |
| 2329. |
Why are selling costs not incurred in perfect competition? |
| Answer» Solution : SELLING costs are not incurred in perfect COMPETITION as there exists perfect KNOWLEDGE among the BUYERS and sellers. | |
| 2330. |
What is the meaning of invisible items? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2331. |
Which of the following employments desirable : |
|
Answer» FORMAL |
|
| 2332. |
Distinguish between full employment equilibrium and underemployment equilibrium. |
Answer» SOLUTION :
|
|
| 2333. |
How are following treated in the estimation of national income ? Payment for cloth by a garment manufacturing firm. |
| Answer» Solution :It is an intermediate expenditure for the firm because it INVOLVES PURCHASE of goods by ONE PRODUCTION unit (firm) from another production unit. So, it is deducted from the value of output of the firm to arrive at the value added. So, it is not INCLUDED in national income. | |
| 2334. |
How many chocolates will a consumer have, , if they are available free of cost? |
|
Answer» Solution :In case of FREE chocolates, consumer will carry on the consumption TILL his total utility is maximum . It means , till the additional chocolates gives positive satisfaction, consumer will keep on having chocolates. Let us understand this with the help of the figure SHOWS in Question 1 Consumer will STOP the consultation at the point of satiety (point .Q.), i.e , where marginal utility is equal to zero |
|
| 2335. |
Distinguish between average propensity to save and marginal propensity to save. The value of which of these two can be negative and when ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :APS refers to RATIO of absolute SAVINGS to absolute income. It is CALCULATED by applying following formula-APS= S/YMPS refers to ratio of change in savings to change in income. It is calculated by applying following formula-MPS= dS/dYThe value of APS can be negative when income is less than consumption or when savings are negative | |
| 2336. |
Giving reasons, state whether the following statements are true or false: (i) Saving are a stock. (ii) Butter is only a final product. |
|
Answer» (ii) False. BUTTER can be a final product or an intermediate product. It is final product when purchased for CONSUMPTION, and an intermediate product when purchased for reselling. |
|
| 2337. |
Potential labour force of India consists of : |
|
Answer» PEOPLE in a PARTICULAR AGE group. |
|
| 2338. |
The value of ____ can never be negative, while ____ can have a value equal to one. |
|
Answer» APS, APC |
|
| 2339. |
Name any three variables of macroeconomics. |
| Answer» Solution :(i) Aggregate DEMAND, (II) Aggregate SUPPLY, and (iii) NATIONAL INCOME. | |
| 2340. |
Give the meaning of 'Opportunity Cost'. |
| Answer» Solution :Opportunity COST is the cost of the NEXT BEST alternative. | |
| 2341. |
Classify the following as intermediate goods or final goods : Cloth used by a tailor. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :INTERMEDIATE GOODS | |
| 2342. |
Total consumption in the economy can never be more than national income. |
| Answer» Solution :FALSE. : Consumption is more than NATIONAL INCOME before the break-even POINT. | |
| 2343. |
Classify government expenditure |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The public expenditure (or government expenditure ) is MAINLY classified in the following THREE ways : (i) Revenue and capital expenditure (ii) Plan and non-plan expenditure (iii) Development and non-developmentexpenditure . |
|
| 2344. |
Contraction of supply is the result of |
|
Answer» Decrease in the NUMBER of producers |
|
| 2345. |
If entire additional income is saved then MPC is |
|
Answer» zero |
|
| 2346. |
Explain the effect of appreciation of domestic currency on imports |
| Answer» Solution :If the external value of DOMESTIC currency is INCREASED in the foreign exchange MARKET then it is known as APPRECIATION of the domestic currency. The imports will increase as they become cheaper because of the appreciation of domestic currency. | |
| 2347. |
Differentiate , between Short Period and Long Period. |
Answer» SOLUTION :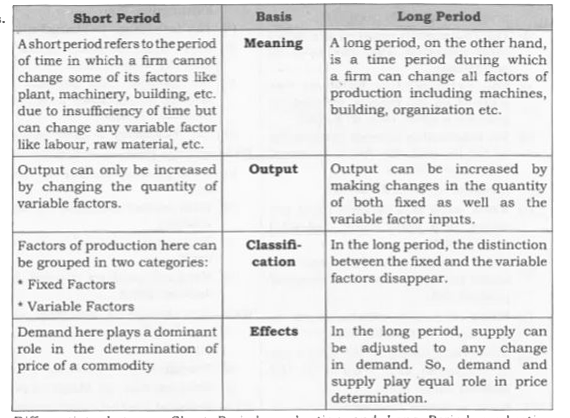
|
|
| 2348. |
Define final products |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Goods and SERVICES which are purchased for CONSUMPTION or for INVESTMENT are final products | |
| 2349. |
Which economicsystem China adopted in 1949? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Socialistsystem | |
| 2350. |
If at a given price of the commodity there is excess supply, how will the equilibrium price be reached? Explain with the help of a diagram. OR How will equilibrium price be reached when there is excess supply? Explain with a diagram. OR Explain the series of changes that will take place if market price is higher than equilibrium price. OR At a given price ofa commodity there is excess supply. Is it an equilibrium price? If not, how will the equilibrium price be reached? (use diagram) OR Suppose price of a good is higher than equilibrium price. Explain changes that will establish equilibrium supply. |
|
Answer» Solution :If at a given price there is excess supply as shown in the given FIGURE. In the given figure, the excess supply of AB at price `P_(1)` will create a competition among the producers, which will reduce the price from `P_(1)` to P. It can be explained in the following cases: (i)Downward movement along the supply curve (CONTRACTION in supply):Due to excess supply of AB, the competition among the producers will reduce the price. As we KNOW, positive relationship EXISTS between price and quantity supplied. So fall in price `P_(1)` to P leads to fall in supply from B to E. (ii) Downward movement along the demand curve (Expansion in demandj: Due to excess supply of AB, the competition among the producers will reduce the price. As we know inverse relationship exits between price and quantity demanded. So, fall in price from `P_(1)` to P, leads to rise in demand from A to E. It can be explained with the help of the following schedule. In the above schedule at price 5, there is excess supply. This excess supply, leads to fall in price till we reach the equilibrium at price 3. Note: Contraction in supply and expansion in demand have to bee done simultaneously to reach the equilibrium. ` (##FM_M_ECO_XII_P1_C12_E02_038_S01.png" width="80%"> ` (##FM_M_ECO_XII_P1_C12_E02_038_S02.png" width="80%"> |
|