Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 2251. |
Discuss the differences between a central bank and a commercial bank. |
| Answer» Solution :The following are the differences between central bank and commercial BANKTHE bank, which monitors, regulates and CONTROLS the financial system of the economy is known as Central Bank. The financial institution which RECEIVES the deposits from people and advances them money is known as Commercial Bank.Central Bank is the BANKER to banks, government, and financial institution, whereas Commercial Bank is the banker to the citizens.The Central Bank is the supreme monetary authority of the country. As against this, the commercial bank does not have such authority and powers.The Central Bank of India i.e. the Reserve Bank of India is governed by RBI Act, 1934. Conversely, the Commercial Bank are regulated by the Banking Regulation Act, 1949.The Central Bank is a publicly owned institution while the Commercial Bank can be publicly or privately owned institution.The Central Bank does not exist for making a profit, whereas commercial bank operates for making a profit for its owners.The Central Bank is the fundamental source of money supply in the economy. On the contrary, the commercial bank does not perform such function.The Central Bank does not deal with the general public, but Commercial Bank does.The Central Bank has got the authority to print and issue the notes. On the other hand, the commercial bank does not have such authority.The main purpose of Central Bank is public welfare and ECONOMIC development. In contrast Commercial Bank, which runs for-profit motive.There is only one Central Bank in every country, but the Commercial Banks are many which serve the whole country. | |
| 2252. |
Demand for a commodity refer to: |
|
Answer» 1.quantity of the commodity demanded at a certain PRICE during any PARTICULAR PERIOD of time. |
|
| 2253. |
Production in an economy is below its potential due to unemployment. Government starts employment generation schemes. Explain its effect using production possibilities curve. |
Answer» Solution :UNEMPLOYMENT in economy leads to underutilization of RESOURCES which compels an economy to remain on less efficient PPC. HENCE the AD should be raised to increase employment. So the government should start some schemes through which can be generated. As a result the point of actual operation will MOVE to or move nearer to the situation where there is a no unemplyment. We can see in the diagram, P is the point of operation will move on to the right side of Production Possibility curve when the new employment schemes will be introduced. The point of operation shifts from point P to point M or T or any other point on the production possibility curve AB. 
|
|
| 2254. |
The rate at which the central bank lends money to commerical banks |
|
Answer» CRR |
|
| 2255. |
The government budget of a hypothetical economy presents the following information, which of the following value represents Primary Deficit. (all fig. in Rs crore) {:(A,"Revenue",=,"25,000"),(B,"Capital Receipts",=,"30,000"),(C,"Capital Expenditure",=,"35,000"),(D,"Revenue Receipts",=,"30,000"),(E,"Interest Payments",=,"10,000"),(F,"Borrowings",=,"20,000"):} |
|
Answer» RS 12,000 |
|
| 2256. |
If Marginal Rate of Substitution is increasing throughout, the Indifference Curve will be : (choose the correct alternative) |
|
Answer» DOWNWARD SLOPING convex |
|
| 2257. |
What is the importance of distinction between intermediate and final goods ? |
| Answer» Solution :The difference between intermediate and FINAL GOODS is impotant to avoid double counting. If value on intermediate goods is taken then it will cause the problem of double counting. When intermediate goods are used as raw MATERIALS in the PRODUCTION of final goods the value of intermediate goods gets automatically included in the value of final goods.Therefore value of only final goods is taken into estimation of `NI`. | |
| 2258. |
Depreciation of fixed capital assets refers to : |
|
Answer» NORMAL WEAR and TEAR |
|
| 2259. |
Direct tax is called direct because it is collected directly from________ : |
|
Answer» The PRODUCER on GOODS produced |
|
| 2260. |
Calculate (a) Revenue Deficit , (b) Fiscal Deficit and (b) Primary Deficit from the following data : |
| Answer» SOLUTION :{(a)₹10 , 000 CRORES , (B)₹12 , 000 crores , (C)₹9,000 crores} | |
| 2261. |
Economics territory is one in which the following move freely : |
|
Answer» People |
|
| 2262. |
"The rising portion of the SMC curve is the firm supply curve of competitive firm". Explain. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) The supply curve of the firm tells us the quantity of the product that a firm is willing and able to produce and sell at each possible price. (ii) The firm will produce and supply an output at the point at which Price is equal to Marginal cost. The derivation of the supply curve is explained with the help of the given figure.  (iii) The SMC of the firm is given. Let us initially assume that the market price is `OP_(1)`. The firm will produce and supply an output of `OX_(1)`because at `e_(1)`, price = MC. (`OX_(1)` is the equilibrium output supplied, as MC - MR and MC cuts MR from below). (IV) Suppose the market price RISES to `OP_(2)`, then the firm will produce and sell `OX_(2)` level, because at `e_(2)` level price = MC = MR. (v) Similarly, as market price increases to `OP_(3)`, quantity supplied increases to `OX_(3)`. However, the firm will not supply any quantity if the price falls below OP. (vi) At OP price, the firm will produce and sell OX output. For any price below OP the firm will not produce and sell ANYTHING. The supply will be zero UNITS. Having the above information, the supply schedule can be determined as, `{:("Price of Product","Units Supplied"),(OP,OX),(OP_(1),OX_(1)),(OP_(2),OX_(2)),(OP_(3),OX_(3)):}` (vii) If the market price falls below theminimum of the SAVC, the supply curve jumps to the small segment (OP) on the vertical axis at which there is zero supply. Therefore, two discontinuous [(OP) + (e.s)] pieces define the short run supply curve for the perfectly competitive firm. |
|
| 2263. |
Define investment multiplier. How is it releated to marginal propensity to consume? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :An investment multiplier REFERS to the concept that any increase in PUBLIC or private investment SPENDING has a more than proportionate positive impact on aggregate income and the general economy.The larger an investment's multiplier, the more EFFICIENT it is at creating and distributing wealth throughout an economy. it is positively related to Marginal propensity to come (MPC) as k=1/1-MPC | |
| 2264. |
Because of destruction caused by war, a country's PPF will shift to the left. |
| Answer» Solution :True: Country.s PPF will SHIFT to the LEFT, this will be DUE to the fact that the country.s capacity to PRODUCE will get reduced. | |
| 2266. |
Currency created by the Central Bank (RBI) is called bank money |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2267. |
Total product always increases whether there is increasing returns or diminishing returns to a factor. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :True: As when there is INCREASING return, total PRODUCT increases at increasing rate and when there are DIMINISHING returns, total product increases at a diminishing rate. | |
| 2268. |
Infiationanddeflationarebothbutinflationisworse . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2269. |
Which of the following is not an indirect tax ? |
|
Answer» SALES tax |
|
| 2270. |
Define indirect tax . Give two examples of indirect taxes . |
| Answer» Solution :When the liability to pay a tax is on one person and the burden of that tax falls onsome other person , it is CALLED INDIRECT tax , e.g., SALES tax and EXCISE duties . | |
| 2271. |
Differentiate between increase in demand and expansion in demand(increases in quantity demanded). |
Answer» SOLUTION :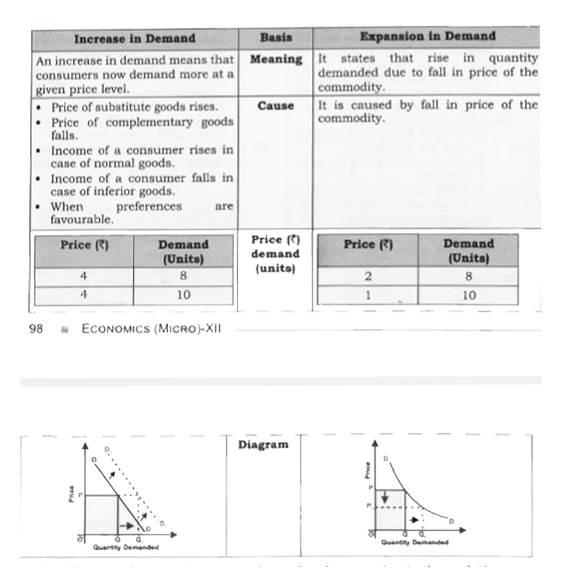
|
|
| 2272. |
Values of rupee is falling against dollar. How is it negative for the economy? |
| Answer» Solution :Falling value of rupee against DOLLAR implies depreciation of DOMESTIC currency in terms of dollar. It means external purchasing power is low now which will increase expenditure on IMPORTS from USA, travelling to USA, INVESTMENTS in USA etc. | |
| 2273. |
Are the following normal residents of Indian economy? (i) Indian workers employed in the power projects of Nepal on daily wages and crossing into Indian territory every week. (ii) Indians working in the U.S.A embassy in India. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) INDIAN WORKERS in Nepal are normal residents of INDIA because they live in India and their centre of ECONOMIC interest lies in India. (ii) Indians working in the USA embassy in India are normal residents of India because they live in India and their economic interest lies in India. |
|
| 2274. |
Imports create leakages in the circular flow of income. Do you agree ? How in your opinion the leakages can be corrected ? |
| Answer» Solution :I agree that imports CAUSE outflow of FOREIGN EXCHANGE implying withdrawals from the circular flow of income. Yet we cannot do away with certain necessary imports. In case of other GOODS, we should develop the preference for domestically produced goods, also we should develop IMPORT substitution. | |
| 2275. |
The categories of transactions that are included in current account of Balance of Payments are: |
|
Answer» Exports and imports of GOODS |
|
| 2276. |
If the age cost is falling, |
|
Answer» MARGINAL cost is rising |
|
| 2277. |
Differentiate between decrease in demand and contraction in demand (decrease in quantity demanded). |
Answer» SOLUTION :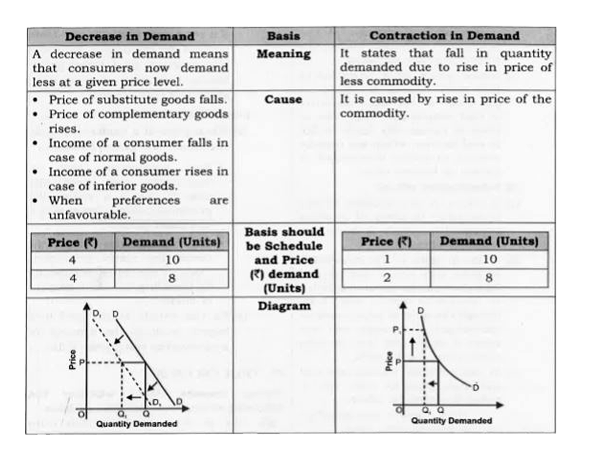
|
|
| 2278. |
Price elasticity of supply of a good is 0.8. Is the supply elastic or inelastic and why ? |
| Answer» Solution :When PES=0.8 PES is inelastic because percentage CHANGE in QUANTITY SUPPLIED is LESS than percentage change in price. | |
| 2279. |
Explain the meaning of deficit in balance of payments. |
| Answer» Solution :Deficit in BOP refers to a situation when receipts of the country arising out of autonomous transactions are less than the corresponding PAYMENTS to the rest of the world during the period of an accounting year. It highlights our net liabilities towards rest of the world.Significance of deficit in BoP:There is positive as well as negative significance of deficit in BoP. The positive significance is that, BoP deficit may be occurring on account of such capital imports which are essential to speed up the process of GROWTH and development in the economy. The negative significance is that it highlights our liabilities to the rest of the world. GREATER the liability, greater is the strain on our GDP by the way of payments to the rest of the world. | |
| 2280. |
Which one is included in National Income ? |
|
Answer» Winning from Lottery |
|
| 2281. |
Categorise the following into direct tax or indirect tax Property tax |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2282. |
How does an increase in price of an input affect the supply curve of a firm ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) This also influenece the supply SINCE price of inputs (rent, wages, interest, profit) constitutes the cost of production of a commodity. (II) An increase in the price of an INPUT may lead to RISE in cost of production which will thereby decrease the production of a commodity shifting the supply curve to the left as shown. 
|
|
| 2283. |
State the steps to be taken in computation of national income by the Production Method OR Explain the difference between GDP at constant prices and GDP at current prices |
| Answer» | |
| 2284. |
If the demand for a commodity increases, its supply curve remaining the same, the market price of the commodity will rise. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :True: Increase in demand implies a RIGHTWARD shift of the demand curve. New demand curve will INTERSECT the given supply curve at a HIGHER PRICE. The equilibrium price will rise. | |
| 2285. |
Which economic systemIndia adopted after independence ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :MIXED ECONOMIC SYSTEM | |
| 2286. |
What is meant by balance of trade (BOT) ? |
| Answer» Solution :BOT is the DIFFERENCE between MONEY VALUE of exports and IMPORTS of material goods (visible items) only. | |
| 2287. |
Explain any two methods of credit control used by central bank.ORDiscuss the meaningof anytwo methods of controlling credit which may be adopted by the centralbank |
| Answer» Solution :(i) Margin Requirement: A margin refers to the difference between market value of the security offered for loan and the amount loan offered by the Commercial Banks. During inflation, supply of credit is reduced by RAISING the requirement of margin. During deflation supply of credit is INCREASED by lowering the requirementof ‘margin’. This measure is often used to discourage the flow of credit into speculative business activities. (ii) Moral suasion: It refers to moral PRESSURE exercised by the Central Bank on the Commercial Bank to be restricted and selective in lending during inflation, and to be liberal in lending during deflation. GENERALLY, this measure is used as a selective credit control instrument to channelize the flow of credit to priority areas. | |
| 2288. |
Will the following factor income be included in domestic factor income of lndia ? Give reasons for your (i) Compensation of employees to the resident of Japan working in Indian embassy in Japan. (ii) Payment of fees to a Chartered Accountant by a firm. (iii) Rent received by an Indian resident from Russian embassy in India. (iv) Compensation given by insurance company to an injured worker. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) YES it will be included as it is part of Factor Income earned in domestic territory of the country. (ii) Payment OFFERED to a Chartered Accountant is an intermediate expenditure for the firm. Hence it is to be deducted from the value of output of the firm to obtain value added. Hence it is not included in domestic factor income of INDIA. (iii) No, as rent received be INDIAN RESIDENT from Russian embassy will be part of Factor Income received from abroad as Russian Embassy is not part of domestic territory of the country. (iv) No, as compensation is given by insurance company to employee and not by employer. |
|
| 2289. |
What does the Balance of Payments Account record? Distinguish between the ''balance on current account'' and the ''balance of trade'' in this account. |
| Answer» Solution :The balance of payments (BOP), ALSO known as balance of INTERNATIONAL payments, summarizes all TRANSACTIONS that a COUNTRY's individuals, companies and government bodies complete with individuals, companies and government bodies outside the country.Balance on current ACCOUNT and balance on capital account are interrelated. A deficit in the current account must be settled by a surplus on the capital account. A surplus in the current account must be matched by a deficit on the capital account. | |
| 2290. |
Classify the following as intermediate goods or final goods : Seeds purchased by a farmer. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :INTERMEDIATE GOODS | |
| 2291. |
Primary deficit in a government budget equals : |
|
Answer» Interest PAYMENTS |
|
| 2292. |
Can the value of MPC be greater than one ? |
| Answer» Solution :The VALUE of MPC cannot be greater than one. The MAXIMUM value of MPC can be one (i.e., when the entire additional income is CONSUMED and NOTHING is saved out of it). | |
| 2293. |
What is meant by transfer income ? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2294. |
Distinguish between developmental and non-developmental expenditure. |
|
Answer» Solution :1. `ul("Developmental expenditure")` directly CONTRIBUTES to development of the economy WHEREAS, `ul("non-developmental expenditure")` does not directly contributes to development, but it lubricates the wheels of economic development. 2. `ul("Developmental expenditure")` is PRODUCTIVE in nature as it adds to the FLOW of goods and services, whereas, `ul("non - developmental expenditure")` is not concerned with productivity of the working class. |
|
| 2295. |
Microeconomics is also called |
|
Answer» THEORY of INCOME and EMPLOYMENT |
|
| 2296. |
In a government budget , revenue deficit is ₹35 crores . If revenue receipts are ₹ 70 crores and capital expenditure ₹ 120 crores , then how much is the revenue expenditure . |
|
Answer» Solution :Revenue Deficit = Revenue EXPENDITURE - Revenue Receipts ₹35 CRORES = REVENUEEXPENDITURE - ₹70 crores Revenue Expenditure = ₹35 crores + ₹ 70 crores = ₹105 crores. |
|
| 2297. |
If you were to be appointed as Finance Minister of india, which of direct taxes or indirect taxes would you prefer and why ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Both direct and indirect taxes WOULD be FULLY UTILISED as they are not competitive but complementary to each other. Being source of government income, both are needed to achieve the main objectives of economy such as (i) to raise resources for the government, (ii) to raise RATE of investment through curtailment of consumption and (iii) to raise the incremental saving ratio. Value - Analytical. |
|
| 2298. |
State any three factors which lead to decrease in demand. |
Answer» Solution :The condition are :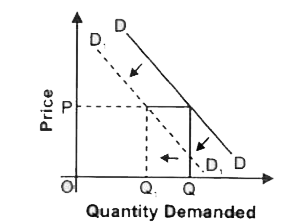 (i) Price of substitute GOODS falls. (ii) Price of COMPLEMENTARY goods rises. (iii) Income of a consumer falls in CASE of normal goods. (iv) Income of a consumerr rises in case of inferior goods. (V) When a PREFERENCE becomes unfavourable. |
|
| 2299. |
Explain the producer's equilibrium with MR/MC approach (when price falls with the rise in output). |
Answer» Solution :When there is no fixed price and price falls with the rise in output, MR curve slope downwards. PRODUCER aims to produce that level of output at which MC is equal to MR and MC curve cuts the MR curve from below. Let us understand this with the HELP of following table:  According to Table, both the conditions of equilibrium are satisfied at 4 units of output. MC is equal to MR and MC is rising. MC is more than MR when output is produced after 4 units of output. So, Producer.s Equilibrium will be achieved at 4 units of output. Let us understand the determination of equilibrium with the help of a diagram:  Producer.s Equilibrium is determined at OQ level of output corresponding to point E as at this point, MC = MR and MC curve cuts MR curve from below. In Figure, output is shown on the horizontal axis and revenue and COSTS on the vertical axis. Producer.s equilibrium will be determined at OQ level of output corresponding to point E because at this, the following two conditions are met: (i) MC=MR, and (ii) MC curve cuts the MR curve from below. When `MRgtMC`, then producer will continue to produce as long as MR BECOMES equal to MC. It is so because firm will find it profitable to raise the output level. When `MRltMC`, then producer will cut down the production as long as MR becomes equal to MC. It is so because firm will find it unprofitable to produce an extra unit. So, it starts reducing the level of output till MR = MC. So, the producer is at equilibrium at OQ units of output. |
|
| 2300. |
Explain the store of value function of money. |
| Answer» Solution :Money also serves as a store of value. It is a ‘repository of purchasing power over time’. A store of value i.e., money is used to save purchasing power from the time income is RECEIVED until the time it is spent. Money is one such MEDIUM in which one wishes to hold wealth. Money is thus a means of saving.Because of perfect liquidity, money acts a store of value. By liquidity, we mean convertibility of assets into cash. Money, like bonds, GOVERNMENT securities etc. is an asset because it is a claim. Money being the most liquid asset among all assets (stocks, lands, jewellery, etc.) people PREFER to keep their assets in the form of money. Liquid assets facilitate transactions of all kinds of goods and SERVICES. | |