Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 1651. |
Give the narrow definition of money |
| Answer» | |
| 1652. |
The major problemin energy sector is : |
|
Answer» LACK of finance |
|
| 1653. |
Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) is bringing in attractive jobs to the educated urban youths in India. Though highly remunerative, these jobs involve long and inconvenient working hours. What is the impact of BPO on the supply of labour? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :With the increase in DEMAND higher WAGES are being paid to BPO workers. In response the supply of labour has been INCREASING. Value: Analytic | |
| 1654. |
Reserve Bank of India has reduced CRRfrom 4.25% to 4%. Will this step help in controlling inflation in India ?Name any one value violated in the question. |
|
Answer» Solution :This step is not likely to check inflation because a cut in CRR is supposed to RELEASES more liquidity in the economy. This will increase lending capacity of commercial banks resulting in more consumption EXPENDITURE and investment expenditure. Hence, this step MAY PROVE inflationary instead of checking price rise. VALUE violated - Social responsibility. |
|
| 1655. |
When in the supply of a commodity called elastic ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The supply of a COMMODITY is called elastic when the percentage CHANGE in quantity supplied is more than percentage change in price, then `ES gt 1` and the result is KNOWN as more than unit elastic supply. | |
| 1656. |
Explain the effect of depreciation of domestic currency on exports. |
|
Answer» Solution :With the depreciation of the domestic currency, the demand for the exports (by the NATIVE country) rises. This is because depreciation of domestic currency results in the FALL in the price of the domestic currency in terms of foreign currency. This makes the exports cheaper and dearer and thereby their foreign demand increases. `{:("Original Exchange Rate : 1$ = Rs 45"),(" New Exchange Rate : 1$ = Rs 50"):}} {:("Depreciation of"),("Indian RUPEE"):}` In the above case, Indian Rupee has depreciated in terms of US from Rs 45 to Rs 50. Consequent to this fall in the Indian Rupee, the demand for Inidan exports will rise, as it is more cheaper for the Americans to BUY the same goods at lower price of Rs 50. Thus, as they can buy more goods USING the same 1$ (as before), so this would raise the demand for Indian exports. |
|
| 1657. |
Define money .How was it evolved ? |
| Answer» | |
| 1658. |
What is the law of diminishing marginal product? |
| Answer» Solution :The LAW of diminishing marginal product states that when we applied more and more units of variable FACTOR to a given quantity of FIXED factor, total product INCREASES at a diminishing rate and marginal product falls . | |
| 1659. |
State the various components of the Income Method that are used to calculate national income. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :the various components of the INCOME Method that are used to calculate NATIONAL income1.Wages, supplementsand salaries2. Net INTEREST3. Rental income of the person4.Income of unincorporated enterprise5.Corporate profit before tax6.indirect taxes7.Depreciation | |
| 1660. |
What is government budget? Explain its major components. OR Explain: (a) Allocation of Resources, and (b) Economic Stability as objectives of Government Budget |
|
Answer» Solution :Government Budget is defined as a statement of planned receipts and planned expenditure of the government during a fiscal year: Its major components are: I. Revenue Receipts : the receipts which neither create a LIABILITY nor lead to reduction in assets. II. Capital Receipts: the receipts which either create a Iiability or lead to reduction In assets. III. Revenue Expenditures: the expenditure which does not lead to any creation of assets or reduction in liabilities. IV.Capital expenditures: the expenditure which leads to creation of assets or reduction in Liabilities. OBJECTIVES of Government Budget: (a) Allocation of Resources In the economy There are many non-profitable economic activities which are not undertaken by the private sector LIKE, water supply, sanitation. etc., but are necessarily undertaken by government in public interest. 80, Government can undertake these activities in order to create social welfare. In addition, government can encourage the private sector through tax concessions, subsidies, etc., to undertake certain production in public interest. (b) Economic stability Economic Stability means absence of Large-scale fluctuation in prices. Such fluctuations create UNCERTAINTIES in the economy. Government can exercise control over these fluctuations through taxes and expenditure. For example, under inflationary situations, government may discourage spending by increasing taxes or reducing its own expenditure, whereas, under deflationary conditions, government may encourage spending by giving tax concessions, subsidies, etc. |
|
| 1661. |
A firm earns a revenue of 50rs when the market price of a good is 10rs. The market price increases by 15rs and the firm now earns a revenue of 150rs. What is the price elasticity of the firm's supply curve ? |
Answer» Solution :  Price Elasticity of SUPPLY (ES) `=(DeltaQ)/(DeltaP)XX(P)/(Q)=(5)/(5)xx(10)/(5)=2` ES=2 (Supply is HIGHLY ELASTIC as ES gt1) ES is always positive due to direct relationship between price and quantity supplied. |
|
| 1662. |
What is the relationship between total variable cost and marginal cost? Explain. |
|
Answer» <P> Solution :Marginal cost is the slope of the TOTAL variable cost curve. It.s relationship is as given:(i) When Marginal Cost FALLS, Total Variable Cost increases at a DIMINISHING rate. (ii) When Marginal Cost is MINIMUM `("at point P"_(1))`, Total Variable Cost is at its inflexion point `("at point P"_(1))`. (iii) When Marginal Cost rises, Total Variable Cost increases at an increasing rate. 
|
|
| 1663. |
Define externality. |
| Answer» Solution :Externalities refer to benefits (positive externalities) or HARMS (negative externalities) which are caused one unit to ANOTHER with no payment RECEIVED for the BENEFIT and no payment made for the HARM. | |
| 1664. |
What is mulliplier? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Investment multiplier (K) is the RATIO of INCREASE in income `(DeltaY)` due to an increase in investment `(DeltaI)` i.e. `K=(DeltaY)/(DeltaI)` | |
| 1665. |
China is a big manufacturer of telephone instuments.It has recently become a member of WTO,which means that it does export a large number of telephone instuments to India. (i)How will it affect the price and quantity sold to telephone instuments in India? (ii)Suppose that the demand for telephone instuments is relatively elastic.How will it effect India's total expenditure on telephone instuments? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i)The supply of telephone INSTUMENTS in India will increase.An increase in supply of telephone instuments will RESULT in a rightward shift of the supply curve from SS to `S_(1)S_(1)` as SHOWN. (ii)The supply curve shifts rightward from SS to `S_(1)S_(1)`. With new supply curve `S_(1)S_(1)` there is excesssupply at initial price OP because at price OP supply is PB and demand is PA, so there is excess supply of AB at price OP.  Due to this excesss supply ,competition among the producer will fall the price.Due to this fall in price there is downward movement along the supply curve (Contractio in supply)From B to C and similarly there is downward movement along the demand curve (Explansion in demand) From A to C. So ,FINALLY equilibrium price falls from OP to `OP_(1)` and equilibrium quantity rises from OQ to `OQ_(1)`. Conclusion :Due to increase in number of firms, (a)Equilibrium price of telephones fall OP to `OP_(1)` (b)Equalibrium quantity of telephones rises from OQ to `OQ_(1)` . (iii)For a product with relatively elastic demand a fall in the price of a commodity results in a relatively elastic expenditure by the consymers.Thus,the total expenditure on telephone will increase. |
|
| 1666. |
The concept of " Outsourcing work " is a good source of supply of foreign currency and employment generation ? Do you agree this in context of india ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Yes, I agree with this. Rinse in outsourcing services (BPO's, KPO's etc) has led to huge inflow of FOREIGN exchange into the country. Moreover , outsourcing work has also created LARGE number of employment opportunities. | |
| 1667. |
When demand increases more than proportionately than the increase in supply, equilibrium price will fall. |
| Answer» Solution :FALSE: When demand increases PROPORTIONATELY more than INCREASE in supply, EQUILIBRIUM price will rise. | |
| 1668. |
Calculate (a) value added by firms A, B andC and (b) final expenditures by different sectors: {:(,,(Rs."lakh")),((i),"Purchases of raw materials and services by firm A:",),(,"""From Fims B",1000),(,"""From Firms C",2000),(,"Sales of materials by Firm A:",),(,"""To Firms B",500),(,"""To Firms B",700),(,"Sales by Firm A:",),(,"""To general government",),(,"""To Rest of the world",300),(,"""To Households",1300):} |
|
Answer» FINAL exp : byHH=1300, by Govt. =1200, By R/W =300 |
|
| 1669. |
Distinguish between APC and MPC. |
| Answer» Solution :APC can be greater than one (before the break-even point), but the VALUE of MPC cannot be more than one (as a person cannot change his consumption by an AMOUNT which is more than c HANGE in his income). | |
| 1670. |
In the following cases, wich currency is appreciating and which one is depreciating : (i) A change from 3$ =2=£ "to" 4 $ =2 £ (ii) A change from Rs.95 =2US $ "to" Rs. 150=3US$ (iii) A change from Rs. 140=2£ "to" Rs. 60 =1 £ (iv) A change from Rs.52=1 Singapore $"to" Rs. 50=1 Singapore $ |
|
Answer» SOLUTION : (i)`£ ` is appreciating and `$` is DEPRECIATING (II) `$` is appreciating and `RS.` is depreciating (iii) `Rs.` is appreciating and `£` is depreciating (iv) `Rs.` is appreciating and SINGAPORE `$` is depreciating |
|
| 1671. |
At the time of inflation, Government should opt for surplus budget. Do you agree with the given statement ? |
| Answer» Solution :Yes, I agree with the GIVEN statements. Surplus budget refers to a budget where estimated total receipts are morethan estimated total expenditure. In caseof surplus budget, government takes more money fromthe economy than it INJECTS into it. It results a fall in aggregate demandand PRICE level in the economy and help to COMBAT INFLATIONARY situation. | |
| 1672. |
What is meant by foreign exchange rate ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FOREIGN exchanges RATE REFERS to the rate at which on currency is exchagesd for the other | |
| 1673. |
Are the following statements true or false ? Give reasons. All purchased by a production unit from other production units are intermediate products. |
|
Answer» Note : As per CBSE guidelines , no marks will be given if REASON to the answer is not explained. |
|
| 1674. |
Give the meaning of ex-ante saving. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Ex-ante saving refers to the amount which savers PLAN to save at different LEVELS of INCOME in an ECONOMY. | |
| 1675. |
What is credit money ? |
| Answer» Solution :Credit money REFERS to the money whose INTRINSIC ( COMMODITY ) value is LESS than its face value e.g., cheque , drafts, currency notes ,etc. | |
| 1676. |
Explain the relationship between Total Product, Average Product and Marginal Product. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) In the beginning Total Product, Average Product and MARGINAL Product all increase, but Marginal Product `gt` Average Product and Total Product `gt` Marginal Product. (ii) When Marginal Product = 0, Total Product is MAXIMUM and constant and Average Product is decreasing. (iii) Thereafter, both Average Product and Marginal Product CONTINUE to DECLINE, but Marginal Product `lt` Average Product and Total Product declines at an absolute term. (iv) Marginal Product can be zero and negative but Average Product and Total Product can never be zero. |
|
| 1677. |
With the rise in price, quantity demanded for the goods falls and it is known as decrease in demand. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1678. |
Excess of foreign exchange receipts over foreign exchange payments on account of accommodating transactions equals deficit in BOP. |
| Answer» Solution :False as deficit in BOP is excess of FOREIGN exchange payments over foreign exchange receipts on ACCOUNT of autonomous TRANSACTIONS. | |
| 1679. |
When marginal revenue falls to zero, average revenue becomes maximum |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FALSE : It is so because in case of the marginal REVENUE is zero the AVERAGE revenue should be diminishing. | |
| 1680. |
What efforts should be made in an economy for the continuous use of exhaustible natural resources in production? |
|
Answer» Solution :There are various efforts, namely, (i) To INCREASE use of renewable resources (ii) To EXPLORE the substitutes of resources (III) To reduce the wastage of resources. (iv) To spread awareness about the effectively and OPTIMUM use of natural resources. Value: Environmental conservation |
|
| 1681. |
Calculate Net Indirect Tax. |
|
Answer» It means Net Indirect Tax = GNP at MP - Depreciation -Net Factor income from abroad - NDP at FC = 7, 000- 600 - (-) 400 - 6, 200 = ₹ 600 CRORES |
|
| 1682. |
According to recent media reports : 'USA has accusedChina of currency devaluationto promoteits exports' . In the light of the given media report comment, how exports can be promoted through the currencydevaluation? Also analyse its effect on national income of China. |
|
Answer» Solution :The concern of USA is VALID because DEVALUATION by China adverselyeffects exports of USA. Devaluation by Chinagives a competitive edge forChinese goods in the INTERNATIONAL market becauseChinese goods become cheaper. This increasesChinese exports but at the same time adverselyaffectsU.S exports as U.S. goods become relatively costlier in the internationalmarket. National income of China will rise. It is because devaluation by Chinamakes chinese exportscheaper in theinternational market, leading TOINCREASE in exports.At the same time it MAKES imports by China costlierleading todecrease in imports. Effect on both exports and imports of China together lead to increase in 'net exports' , acomponent income when estimated through the expenditure method. |
|
| 1683. |
Given below are four statements. Indicate for each whether it reflects ar. increase or decrease in demand, quantity demanded, supply, quantity supplied. (i) Air Deccan reduces its average plane fare by 30% in order to attract more passengers. (ii) The government grants export subsidy to producers of oranges in Nagpur to increase the sale of oranges abroad. (iii) Wheat farmers decide to withhold wheat as the market price is low. (iv) OPEC decides to increase the international oil price. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) INCREASE in QUANTITY DEMANDED (II) Increase in supply. (III) Decrease in supply. (iv) Decrease in quantity demanded. |
|
| 1684. |
Are the following statements true or false ? Give reasons. Primary deficit is the difference between revenue deficit and interest payments . |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FALSE . Primary deficit is the difference between FISCAL and INTEREST payments. | |
| 1685. |
definemarginalpropensityto consume(MPC). |
| Answer» SOLUTION :MPCrefers to theproportionto additionalincome`( DELTA Y)`whichis spentinadditionalconsumption`(DeltaC)`symbolically: MPC `=Delta C//Delta Y.` | |
| 1686. |
In which form of market there is product differentiation? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION. | |
| 1687. |
Explain three factors that lead to an economic problem. |
|
Answer» Solution :Economic problem ARISES becauseof scarcity of resources in relation to demand for them. (i) Wants are unlimited: (a) This is a basic fact of human life. Human wants are unlimited. (b) They are not only unlimited but also grow and multiplyvery fast. (ii) Resources are limited: (a) The resources to produce goods and services to satisfy human wants are available in limited quantities. Land, labour, capital and entrepreneurship are the basic scarce resources. (b) These resources are available in limited quantities in EVERY ECONOMY, big or small, developed or underdeveloped, rich or POOR. Some economies may have more or one or two resources but not all the resources. (c ) For example, Indian economy has RELATIVELY more labour but less capital and land. The U.S. economy has relatively more land but less labour. No economy in the world is comfortable in all the resources. (iii) Resources have alternative uses: (a) Generally a resource has many alternative uses. (b) A worker can be employed in a factory, in a school, in a government office, self employed and so on. (c ) Like this, nearly all resources have alternative uses. But the problem is that which resource should be put to which use. |
|
| 1688. |
Calculate the value of imports when balance of trade is Rs (-) 400 crores and the value of exports is Rs 300 crores. |
|
Answer» So, Imports = Exports - Balance of trade = 300 - (-) 400 = RS 700 crores |
|
| 1689. |
Change in stock is negative when : |
|
Answer» CLOSING stock ` GT` OPENING stock |
|
| 1690. |
If borrowings and other liabilitiesare added to the budgetary deficit , we get : |
|
Answer» FISCAL DEFICIT |
|
| 1691. |
From the following data about an economy, calculate (a) equilibrium level of national income and (b) total consumption expenditure at equilibrium level of national income. (i) C =200 +0.5Y (ii) Investment expenditure is 1500 |
| Answer» SOLUTION :24001900 | |
| 1692. |
Multiplier is_ related to MPC |
|
Answer» DIRECTLY |
|
| 1693. |
How are following treated in the estimation of national income ? Commission received by a dealer from the buyer and seller of a house. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :YES, it will be included in the national INCOME as it is the income of the DEALER for his prodctive SERVICES. | |
| 1694. |
Which of the following is included in compensation of employees ? |
|
Answer» Dearness Allowance |
|
| 1695. |
What are primary function of money ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Primary FUNCTION of MONEY are (i) medium of EXCHANGE and (ii) MEASURE of value . | |
| 1696. |
In balance of payments, repayment of loans by Indian government to Japanese Government will be reflected as credit item. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :False. It will be REFLECTED as debit item as it leads to OUTFLOW of FOREIGN exchange. | |
| 1697. |
What is money supply ? Or Whatis meant by Repo Rate ? |
|
Answer» Solution :It REFERS to themoneyin circulationin THEECONOMY at agiven pointof TIME. OR Reverse REPO Rateis the rate at whichcentral BANK of a country (RBI in India ) borrowsfundsfromcommercial bankswithinthe country. |
|
| 1698. |
Give reasons for the following statements: (i) A production Possibility Frontier is always a downward sloping concave curve. (ii) An efficient economy would always produce a combination of goods that lies on the given Production Possibility Fontier. (iii) Growth of an economy is represented in the form of a rightward shift of a ProductionPossibility Frontier. |
Answer» Solution :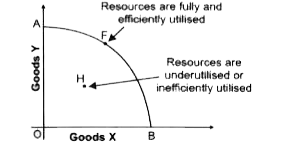 (i) A PPF slopes DOWNWARD to indicate if an economy chooses to produce more of one commodity, then it would have to reduce the production of another commodity. The concave shape of PPF is due to Increase in Marginal Opportunity Cost (ii) Any point on a GIVEN PPF presents aproduction possibilitywhere in all the available resources in an economy get fully utilised. Any combinationlocated below the given PPF shows an underutilization of available resources. LIKEWISE, any point to the right of the PPF is beyond the available resources. (iii) By economic GROWTH, we mean that an economy has developed GREATER capacity to producelarger quantity of goods by acquiring more resources. Graphically, this would be representedby an rightward shift of PPF. |
|
| 1699. |
Diminishing marginal returns for the first four units of a variable input is exhibited by the total product sequence: |
|
Answer» 50, 50, 50, 50 |
|
| 1700. |
Disucss, the changes that will take place in the economic when planned saving is less than planned investment. |
| Answer» Solution :This would result in undesired build-up of unsold stock. Consequently, AD falls short of AS. Due to excess supply resulting from the stock piling of unsold goods, i.e., UNINTENDED inventories, the producers will cut down employment and will produce less. National income will fall and as a result PLANNED SAVING will start Jailing until it becomes equal to planned INVESTMENT. It is at this POINT that equilibrium level of income is determined. | |