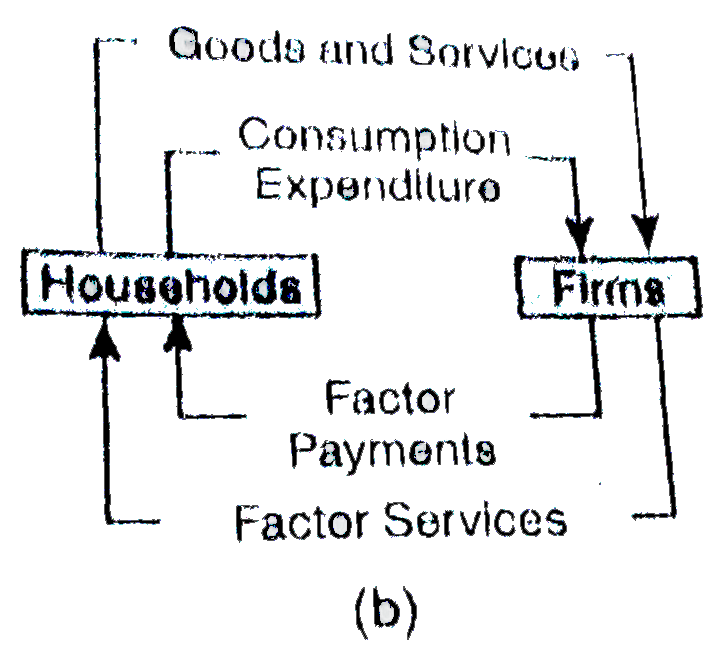Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 1551. |
Explain the effect of an increase in bank rate on credit creation by commerical banksORWhat isbank ratepolicy ? Howdoes itworkas a methodof creditcontrol ? ORHowdo changein bankrate affect moneycreationby CommericalBanks ? Explain .Explain how 'bank rate' ishelfulin controlling credit creation ? |
| Answer» Solution :The rate at which COMMERCIAL banks can borrow money from RBI, when they run short of reserves, is known as BANK rate. When the Central Bank increases the bank rate, it increases the cost of borrowing and hence, discourages the BORROWERS from TAKING a LOAN. Due to this, the process of credit creation and flow of money also reduces. | |
| 1552. |
Managed floating exchange rate is influenced by |
|
Answer» Government |
|
| 1553. |
Indirect taxes are not convenient to realise. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1554. |
Differentiate between Cardinal and Ordinal Utility . |
Answer» SOLUTION :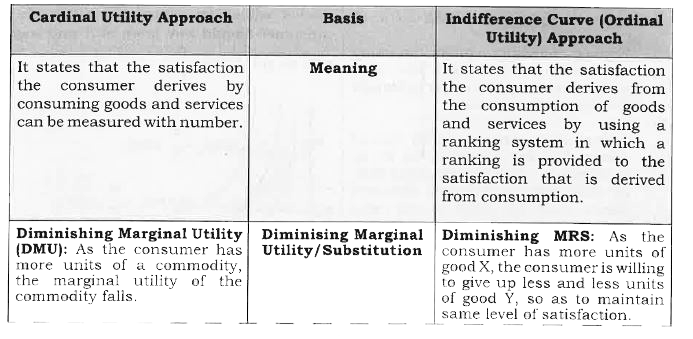 
|
|
| 1555. |
_______ theory is based on assumption that supply creates its own demand. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1557. |
All points on the dudget line give equal satisfaction to the consumer. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :False : All points on an IC GIVE equal satisfaction. | |
| 1558. |
Howcontrollingmoneyif helpful in reducingexcess demand ? |
| Answer» Solution :EXCESS demandoccurswhenaggregatedemandexceds ' aggregatesuplyat fullemployment' ONE ofthecusesof excess DEMAND is DEFICIT financingi.e.,printingofcurrencynotesif money supply iscurtailed thesewill be less stockof money (purchasingpower ) withthepeople.Asa RESULT, peoplewilldemadlessofgoodsand services , in thisway excess demandis reduced . | |
| 1559. |
How can Reserve Bank of India help in bringing down the foreign exchange rate which is very high ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The Reserve Bank of INDIA can DEVALUE India rupee for bringing down the high RATE of foreign exchange, PRI can sell foreign exchange from its RESERVES to bring down its value. | |
| 1560. |
Suppose MPC is 0.8. How much increase in investment is required to increase National income by 2000 crore. Calculate. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :400 CRORE | |
| 1561. |
Assume that in the market for a good Z there is a simultaneous increase in demand and the quantity supplied. The result will be: |
|
Answer» An INCREASE in EQUILIBRIUM price and quantity. |
|
| 1562. |
Marginal utility of the first unit is equal to Total Utility . |
| Answer» Solution :TRUE : MU = `"TU"_n- "TU"_n- "TU"_(n-1)=TU_1-"TU"_0 = TU_1` . | |
| 1563. |
Comment on the following statement: "In the short run, a firm's total costs will be zero if the firm chooses to produce nothing". |
|
Answer» Solution :The STATEMENT is likely to be FALSE. If a firm has any fixed costs at all, the firm.s total costs will not be equal to zero EVEN if it produces zero output. Value: Analytic |
|
| 1564. |
Give two examples of intermediate goods. |
| Answer» Solution :CLOTH PURCHASED by TAILOR, machine purchased by a DEALER of machines. | |
| 1565. |
Under perfect competition a firm is …………………. . |
|
Answer» PRICE MAKER and not price TAKER |
|
| 1566. |
The consumption function curve is : |
|
Answer» UPWARD sloping |
|
| 1567. |
Gross Domestic Capital Formation can be calculated as : |
|
Answer» Gross FIXED Capital Formation + Inventory Investment |
|
| 1568. |
Government raises its expenditure on producingpublic goods. Which economic value economic value does it reflect ? Explain. |
|
Answer» Solution :Increased expenditureon producing PUBLIC goods such as school buildings, hospitals, defence services and maintaining LAW and order IMPLIES availability of increased public services to the people of the COUNTRY. For INSTANCE, more expenditure on maintaining law and order raises the sense of security among the people. Clearly, such expenditure by the government on producing public goods ensures welfare of the people. Value - Public welfare |
|
| 1569. |
Explain the significance of distinction between autonomous and accommodating transactions in BOP account. |
| Answer» Solution :Autonomous TRANSACTIONS are MADE with the motive of earning profit WHEREAS accommodating transactions are made to cover up DEFICIT or SURPLUS in BOP. The significance of distinction is that deficit/surplus in BOP equals the deficit/surplus in autonomous transactions only. | |
| 1570. |
From the following data about a government budget, find out (a) Revenue deficit, (b) Fiscal deficit and (c) Primary deficit: {:(,"(Rs arab)"),((i) "Capital receipts net of borrowings",95),((ii) "Revenue expenditure",100),((iii)" Interest payment",10),((iv) "Revenue receipts",80),((v) " Capital expenditure",110):} |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Revenue deficit = (II) - (iv) `= 100 - 80` `= 20` (Rs arab) Fiscal deficit `= (v + ii -iv -i)` `= 110 + 100 - 80 - 95` `= 35` (Rs arab) Primary deficit = Fiscal defict - (iii) `= 35 - 10` `= Rs 25` arab |
|
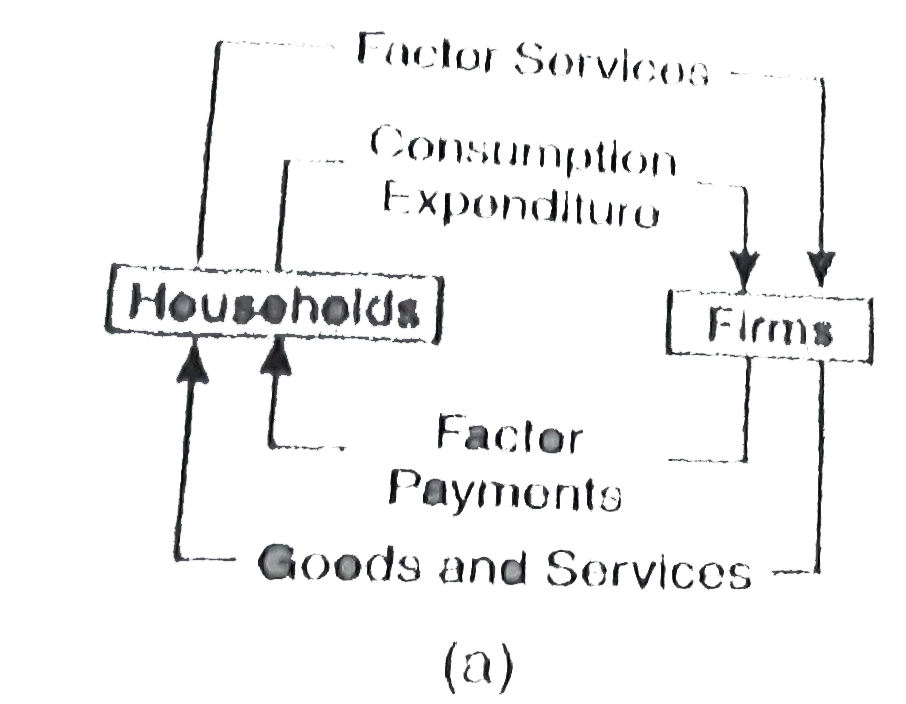
| 1571. |
Circular Flow of income is correctly represented in the diagram : |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 1572. |
find investment from the following : National Income = Rs. 500 Autonomous consumption = Rs. 100 Marginal propensity to consume =0.75 |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`Y=bar(C)+MPC. Y+I` `500=100+(0.75xx500)+I` `I=500-100-375= RS. 25` |
|
| 1573. |
An economy is in equilibrium. From the following data, calculate the marginal propensity to save: Given the behaviour of marginal product and total product as more and more units of only one input are employed while keeping other inputs as constant. (a) Income = 10,000 (b) Autonomous consumption = 500 (c) Consumption expenditure = 8,000 |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`Y=C+I` `Y=overset(-)C+MPC(Y)` `8000=500+MPC(10000)` `MPC=(8000-500)/(10000)=(7500)/(10000)=0.75` `MPS=1-MPC=1-0.75=0.25 or 1//4` |
|
| 1575. |
The function of money which facilitaes borrowing and lending transactions |
|
Answer» a store of VALUE |
|
| 1576. |
Explain feature (implication) of large number of sellers and buyers' in perfect competition. |
|
Answer» Solution :Large number of sellers - (i) The words .large number. simply states that the number of sellers is large enough to render a single seller.s SHARE in total market supply of the product insignificant. (ii) Insignificant share means that if only one individual firm reduces or raises its own supply, the prevailing market price remains unaffected. (iii) The prevailing market price is the one which was set through the intersection of market demand and market supply forces, for which all the sellers and all the buyers together are responsible. (iv) One single seller has no option but to sell what it produces at this market determined price. This position of an individual firm in the total market is referred to as price taker. This is a unique FEATURE of a PERFECTLY competitive market. . Large number of buyers - (i) The words .large number. simply states that the number of buyers is large enough, that an individual buyer.s share in total market demand is insignificant, the buyers cannot influence the market price on his own by changing his demand. (ii) This makes a single buyer also a price taker. To sum up, the feature "large number" indicates INEFFECTIVENESS of a single seller or a single buyer in influencing the prevailing market price on its own, rendering him simply a price taker. |
|
| 1577. |
A consumer is in equilibrium where indifference curve equals budget line ? |
| Answer» Solution :False : CONSUMER will be EQUILIBRIUM where IC is TANGENT to the BUDGET line. | |
| 1578. |
Identify the following as revenue receipts or capital receipts . Give reasons : (i) Loan from the IMF . ""(ii) Grants received from World Bank . (iii)Profit tax "" (iv) Sale of shares held by government in Maruti Udyog Limited . (v) Borrowings from public ""(vi) Bus fare . (vii) Fees of government hospital . |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) It is a CAPITAL RECEIPT as it CREATES LIABILITY for the government . (ii) It is a revenue receipt as it neither creates any liability nor reduces any asset of the government . (iii) It is a revenue receipt as it neither creates any liability nor reduces any asset of the government . (iv) It is a capital receipt as it reduces assets of the government. (V) It is a capital receipt as it creates liability for the government . (vi) It is a revenue receipt as it neither creates any liability nor reduces any asset of the government . (vii) It is a revenue receipt as it neither creates any liability nor reduces any asset of the government . |
|
| 1579. |
Is credit card a form of money ? Give reasons for you answer. |
| Answer» Solution :Credit card is not a form of money. The reason is that moneyis what we pay for goods and serviceswheras credit card is a store of wealth lent by the bank. For EXAMPLE, when you use a credit card to buy a PAIR of shoes, you are notbuying shoes with your money. In fact you are TAKING a LOAN from the bank which has issued you the credit card. | |
| 1580. |
When the value of average propensity to save is negative, the value of marignal propensity to save will also be negative. |
| Answer» Solution :False. : The VALUE of MPS can never be NEGATIVE. It varies between 0 and 1. | |
| 1581. |
This functionof CentralBankinvolvesbuyingand sellingof government securities fromor to the publicand commercial banks. |
|
Answer» SELECTIVE Credit Control |
|
| 1582. |
Only one Product X is produced in the country. Its output during the years 2012 and 2013 was 100 units and 100 units respectively. The market price of the product during the year was Rs 50 and Rs 55 per units respectively. Calculate the percetage change in real GDP and nominal GDP in year 2013 using 2012 as the base year. |
Answer» SOLUTION :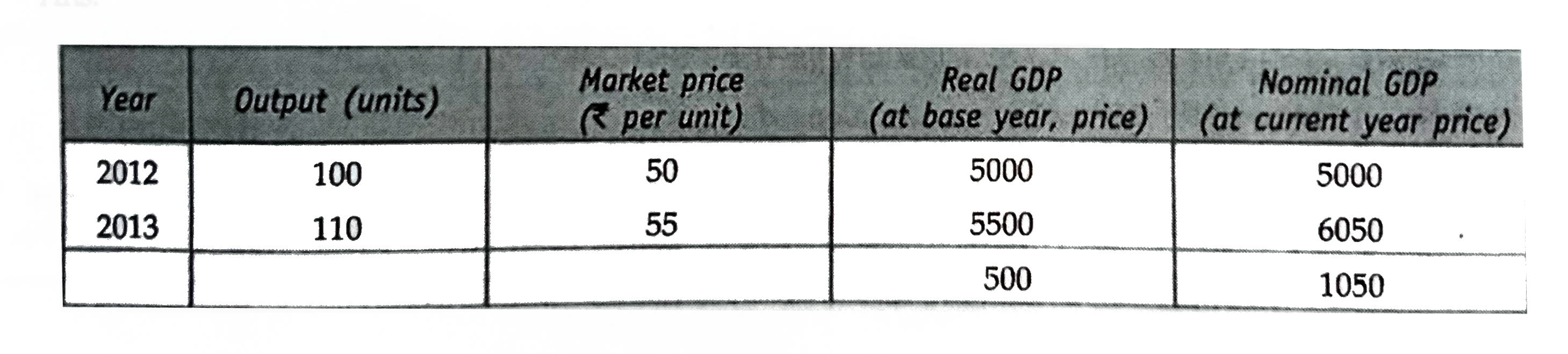 % chage in real `GDP= (Delta" in Real GDP")/("BASE year Real GDP")xx100=500/5000xx100=10%` % change in NOMINAL `GDP=(Delta "in nominal GDP")/("Base year nominal GDP")xx100=1050/5000xx100=21%` |
|
| 1583. |
Explain how non-monetary exchanges are a limitation in taking gross domestic product as an index of welfare. |
| Answer» Solution :The major limitation of GDP as an index of WELFARE of country is that GNP does not take into ACCOUNT those transactions that are not expressed in MONETARY terms.Non-monetary exchanges are not CONSIDERED for the estimation of domestic income. | |
| 1584. |
Which among the following are final and which are intermediate products? (i) A machine purchased for installation in a factory (ii) Fees paid to the lawyer by a producer (iii) Milk purchased by a hotel. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) A machine PURCHASED for installation in a factory is a final product because expenditure on machine is investment expenditure. (ii) FEES paid to the lawyer by a PRODUCER is an intermediate expenditure to the producer. It is because theproducer BUYS the services of a lawyer (another producer) for completely using as in production during the year. (iii) Milk purchased by a hotel is intermediate product to the hotel because it is purchased from another production UNIT for resale indirectly. |
|
| 1585. |
Giving reason identify whether the following are final expenditures or intermediate expenditure : (i) Expenditure on maintenance of an office building. (ii) Expenditure on improvement of a machine in a factory. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Expenditure on maintenance of office building is an INPUT in the production of final good. So, this will be treated as intermediate expenditure. Expenditure on improvement of machinery in a factory is an ADDITION to the existing CAPITAL. | |
| 1586. |
Explain "difficulty in storing wealth" problem faced in the barter system of exchange. |
| Answer» Solution :The BARTER SYSTEM of exchange faced the problem of difficulty in storing wealth because in barter system the GOODS were exchanged for goods and the goods are perishable in nature so they can't be stored as wealth for LONG. | |
| 1587. |
Explain the conditions of consumer's equilibrium under indifference curve approach. |
|
Answer» Solution :There are two conditions for consumer equilibrium under indifferences curves approach are: (i) MRS = Ratio of Prices (ii) MRS Continuosly Falls. Explanation: (i) Let the two GOODS X and Y. The FIRST condition for consumer's equilibrum is that `S = Px//Py`. Now suppose MRS is greater than `Px//Py`. It mean that the consumer is WILLING to pay more for X than the price prevailing in the market. He will start buying more of X. As a result MRS continues to fall. It becomes equal to the ratio of prices and the equilibrium is established. (ii) Unless MRS continuously falls, the equilibrium cannot be established. All other points lying on the budget line (such as point B and point C) are inferior to `(x_(1)^(**) x_(2)^(**))` as they lie on a lower IC (i.e., `IC_(1)`). Thus, the consumer will rearrange his consumptionand will attempt to reach the equilibrium point, where the marginal rate of substitution is equal to the price ratio. Let's suppose that instead of point E, the consumer is at point B. At this point, MRS is greater than the price ratio. `["i.e., " MRS gt (P_(1))/(P_(2))]` In this case, the consumer would tend to move towards point E by GIVING -up some amount of goods 2 in order to consumer more units of good 1. The consumer will continue to give-up the consumption of good 2, until, he reaches the point E, where, MRS becomes equal to the price ratio. On the other hand, for all other points, such as point C, MRS is lesser than the price ratio. `|"i.e., " MRS lt (P_(1))/(P_(2))|` In this case, the consumer would tend to move towards point E by giving up some amount of good 1 to consumer more units of good 2. Thus, we can conclude that if the consumer is consuming any bundle other than the optimum one, then he would rearrange his consumption bundle in such a manner that the equality between the MRS and the price ratio is established and he ATTAINS the state of equilibrium. |
|
| 1588. |
A producer starts a business by investing his own savings and hiring the labour. Identify implicit and explicit costs from this information. Explain. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) For producing a commodity, a firm REQUIRES factor inputs (like services of land, labour, capital etc.) and non-factor inputs (like raw material, electricity, fuel etc.). (ii) Actual money spent by a firm on BUYING and hiring of factor and non- factor inputs is called explicit cost. As per question, a producer is hiring the labour, than the WAGES and salary paid to labour is a explicit cost. (iii) IMPLICIT cost is the imputed or ESTIMATED value of inputs supplied by the owner of the firm himself. As, per question, if a producers start a business by investing his own savings, than the imputed interest on self-supplied capital he earned is a implicit cost. |
|
| 1589. |
When will balance of trade show a deficit? |
| Answer» Solution :Balance of TRADE will SHOW deficit when IMPORTS of goods are more than their EXPORTS. | |
| 1590. |
What is likely to be the impact of "Make in India" appeal to the foreign investors by the Prime Minister of India, on the production possibilities frontier of Indian ? Explain. OR What is likely to be the impact of efforts towards reducing unemployment on the production potential of the economy? Explain. |
|
Answer» <P> Solution :"Make in India" appeal to the foreign investors by the Prime MINISTER of India will lead to the large scale inflow of foreign capital which will result in the increase in the availability of resources in the economy, thereby shifting the Production Possibility Curve (PPC) parallely to the right from AB to CD as shown in the OR Due to the efforts towards reducing unemployment. The point which was EARLIER below the Production possibility curve (INDICATING under utilisation of resources) will shift close to or on the PPC (indicating better utilisation of resources). This movement is being depicted in the below graph with the help of the ARROW from point P. 
|
|
| 1591. |
The equilibrium level of income is determined where planned aggregate demand is equal to |
|
Answer» PLANNED consumption |
|
| 1592. |
Explain why budget line is downward sloping ? |
| Answer» Solution :BUDGET line is downward sloping because if a CONSUMER wants to BUY more of one COMMODITY , he has to buy LESS of other goods, given money income. | |
| 1593. |
If income of the buyer decreases, demand for inferior goods decreases. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1594. |
What is the difference between matginal propensity to consume and marginal propensity to save ? What is the relation between the two ? |
| Answer» Solution :MPC refers to ratio of change in consumption to change in income.whereas MPS refers to ratio of change in SAVINGS to change in income.Relationship between MPC and MPS-MPC+MPS=1 | |
| 1595. |
In perfect competition every firm of the industry is price maker. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :False: In perfect competition, every firm is a PRICE TAKER. | |
| 1596. |
Which of the following is not a component of domestic income ? |
|
Answer» NET factor income from abroad |
|
| 1597. |
Will the following be included in the national income of a country? Give reason for your answer. (i) Scholl fees paid by students. (ii) Purchase of new shares of a domestic firm. (iii) Gifts received from abroad. (iv) Furniture purchased by households. |
|
Answer» (ii) Not included because it does not LEAD to cration of any good or service. (III) Not included because it is a trasnfer payment. (IV) Included because it is a final consumption expenditure. |
|
| 1598. |
If the Nominal GDP is Rs.600 and Price Index (base=100) is 120, calculate the Real GDP. |
|
Answer» Solution :Real GDP = `("NOMINAL GDP")/("PRICE Index of current year")xx100` `=(600)/(120)xx100=Rs.500` |
|
| 1599. |
The government_ its spending to correct the situation of excess demand. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1600. |
If MC is more than MR at a particular level of output, how will a producer react to maximise the profit? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The Producer will reduce the production to maximise the PROFIT. Value: ANALYTIC |
|