Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 1451. |
Other things remaining unchanged, when in a country, price of foreign currency rises, national income is |
|
Answer» LIKELY to RISE |
|
| 1452. |
In an economuy, the following transactions take place : ** A sells goods of Rs. 20 crores to B, Rs. 30 crores to C, Rs. 40 crores to households and goods worth Rs. 10 crores remain unsold. Value of inputs of firm A is assumed to be zero. ** B sells his output worth Rs. 40 crores to C, Rs. 60 crores to D and Rs. 50 crores to final consumption. ** C sellshis output worth Rs. 100 crores to D, Rs. 100 crores to households and exports worth Rs. 100 crores. ** D sells Rs. 300 crores to households and Rs. 100 crores to government. Calculate : (i) Value Added by each firm, (ii) Total Value Added , (iii) Total Consumption Expenditure. |
Answer» 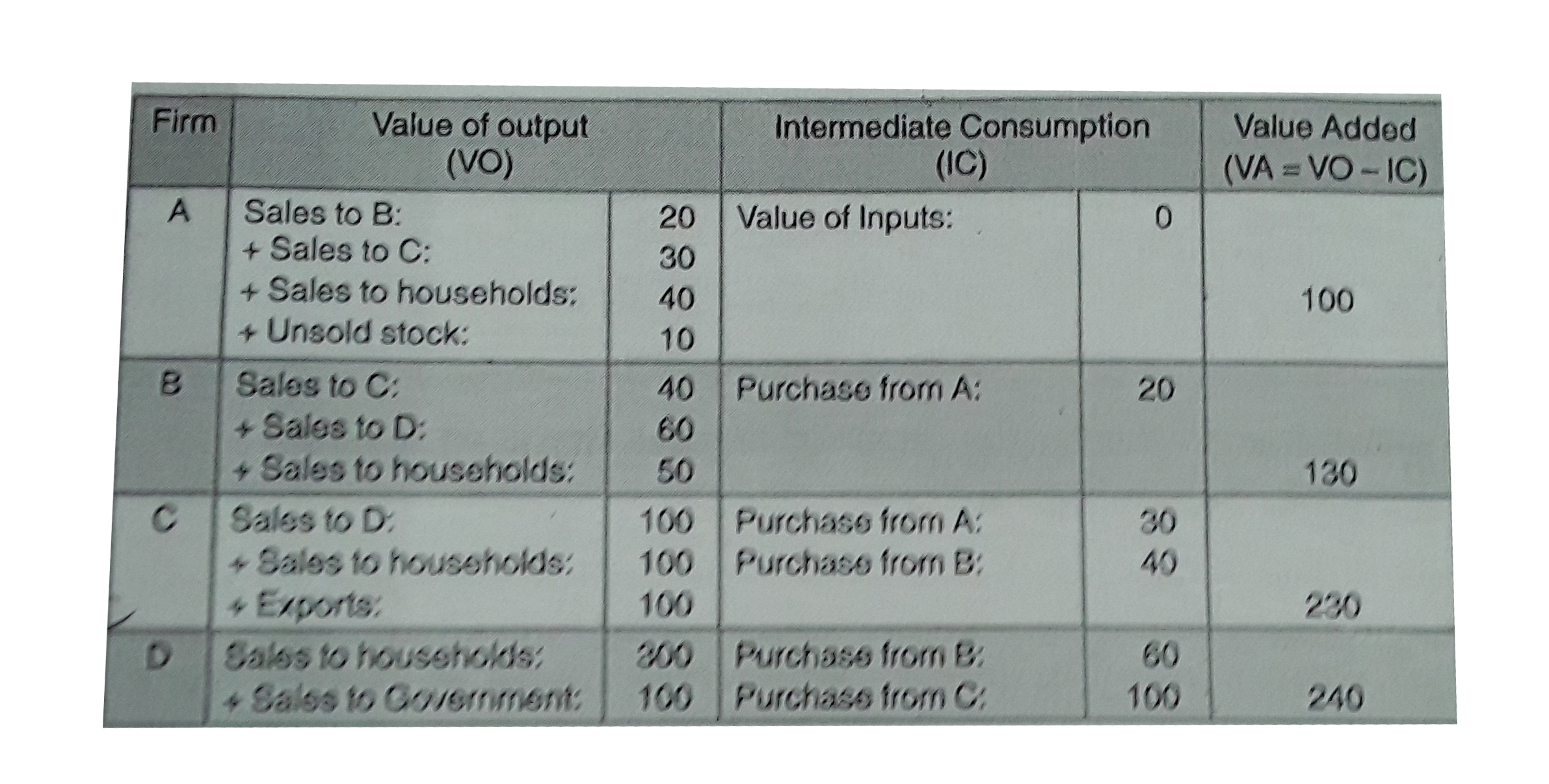 (i) Value Added by each FIRM Value added by firm `A= GVA_(MP)` of A = Rs. 100 crores Value added by firm `B=GVA_(MP)` of B = Rs. 130 crores Value added by firm `C=GVA_(MP)` of C = Rs. 230 crores Value added by firm `D= GVA_(MP)` of D = Rs. 240 crores (ii) Total Value Added `GDP_(MP)= sum GVA_(MP)=100+130+230+240= Rs. 700` crores (iii) Total CONSUMPTION Expenditure = Sales to HOUSEHOLDS by A + Sales to households by B + Sales to households by C + Sales to households by D + Sales to GOVERNMENT by D `=40+50+100+100+300` Rs. 590 crores |
|
| 1453. |
Calculate Investment from the following |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Investment=100 | |
| 1454. |
Calculate ''sales'' from the following data : {:(,"(Rs in lakhs)"),("Intermediate costs",700),("Consumption of fixed capital",80),("Change in stock",(-)50),("Subsidy",60),("Net value added at factor cost",1300),("Exports",50):} |
|
Answer» Solution :`NVA_(FC) = Rs 1,300` `GDP_(MP) = NVA_(FC)`- Subsidies + Consumption of FIXED capital `= 1,300 - 60 + 80 = Rs 1,320` Also we know that: `GDP_(MP)=` Sales + CHANGE in STOCK - INTERMEDIATE Cost Sales = `GDP_(MP)-` Change in stock + Intermediate Cost `= 1,320 - (-50) + 700` i.e. Sales = Rs 2,070 lakhs |
|
| 1455. |
What is 'current account deficit' in the balance of payments? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1456. |
if higher levelof incomeleads to increasein expenditureand ADwhichinturnleadstohigher levelofoutput , whycan'tgovernmentprintmorecurrencynotesto achieve higherlevelof AD andGDP ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION : and INCREASEIN ADprintingnotesdoesot meanthatoutputin theeconomywillincrease automaticallyNodoubtto meetincreaseddemandtheproduces will beinducedtoproducemorebysubstantiallythusmerelyprintingmorenoteswouldonlycausegreaterpressureofdemand on theavailablegoodsandservicesresultingininflationintheeconomy . | |
| 1457. |
What is meant by autonomous transactions? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1458. |
Calculate aggregate demand (AD) aggregate supply (AS) for all levels and the equilivbrium leveul of income from the given schedule, if the investment is fixed at 20crores: |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :AD:40,45,50,,55,60,70,75,80,85,90, AS:0,10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90, EQUILIBRIUM LEVEL of income=80crores |
|
| 1459. |
AD curve is represented by_ curve inthe income determination analysis. |
|
Answer» CONSUMPTION+ Saving+investment |
|
| 1460. |
Explain "black marketing' as a direct consequence of price celling . |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Black marketing may be termed as a direct consequence of price CEILING. (II) Black market is a market under which the commodity is bought and SOLD at a price higher than the maximum fixed by the Government . (iii) It arises DUE to presence of consumers who may be willing to pay higher price for the commodity than to go WITHOUT it. |
|
| 1461. |
How does an increase in the number of firms in a market affect the market supply curve ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) When the number of firms in the industry increases, market supply also increases due to large number of producers producing that commodity. `(II)` So, due to INCREASE in market supply, the supply curve SHIFTS rightward as shown. 
|
|
| 1462. |
Expenditure made on establishment of Metro Rail line in Delhi is a capital expenditure. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1463. |
Current account of Balance of Payments account records only exports and imports of goods and services. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FALSE. In ADDITION to exports and IMPORTS of goods and services, current account also RECORDS unilateral receipts and payments. | |
| 1464. |
State one fiscal measure that can be reduce the gap between rich and poor . |
|
Answer» Solution :1. Taxes should be increased on rich and the amount can be used to BENEFIT the POOR. 2 . Govt. can increase its EXPENDITURE to PROVIDE free SERVICES of education, health etc. (any one of these) |
|
| 1465. |
Suppose that the demand curve for the XYZ Co. slopes downward and to the right. We can conclude that |
|
Answer» The firm operates in a perfectly COMPETITIVE market. |
|
| 1466. |
Capital and investment are : |
|
Answer» Both FLOWS |
|
| 1467. |
Distinguish between ex-ante variable and ex-post variables. What is the significance of this distinction in macroeconomics ? |
| Answer» Solution :Ex-ante variables are those whose VALUE is PLANNED or expected during a period. Ex-post variables are those whose value is what is REALIZED at the end of the period. The significance of distinction is that theory of income DETERMINATION is based on ex-ante variables. | |
| 1468. |
Government provides subsidies to producers and transfer payments to the households. It increases government expenditure. How can this excessive expenditure be reduced ? |
| Answer» Solution :As a WELFARE PROVIDING agency, the GOVERNMENT is SUPPOSED to help the society (here producers and the households), however there should be some administrative checks enforced to evaluate the requirement of the society. Some influential producers and households MAY not require this help from the government, hence only productive expenditure should be incurred by the government. | |
| 1469. |
How should the following be treated in estimating national income of a country ? Give reasons. Expenditure on providing police services by the government. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :YES, as it a part of GOVERNMENT final consumption expenditure. | |
| 1470. |
Comment upon the degree of elasticty of demand for Good X, in the following given situation, if the price of the commodity rises from ₹5 per unit to ₹ 7 per unit and the quantity demand falls from 20 units to 16 units using proportionate method. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i)`{:("Price (Rs.)","Quantity (in UNITS)","Total Expenditure in Rs."("Price"xx"Quantity")),("5","20","100"),("7","16","112"):}` So, above table shows positive relationship between price and total expenditure, which shows Inelastic Demand `(ED lt 1)`. (ii)`{:("Initial Price (P) = 5","Initial Quantity (Q) = 20"),("New Price "(P_(1))=7,"New Quantity "(Q_(1))=16),("Change in price "(Delta P)=2,"Change in Quantity "(Delta Q)=(-)4):}` Price Elasticity of demand `(ED)=(Delta Q)/(Delta P)xx(P)/(Q)` `=(-4)/(2)xx(5)/(20)` `=(-)0.5` [Negative sign of ED indicates the INVERSE relationship between price and Quantity DEMANDED] ED = 0.5 [ED `lt 1` (Inelastic Demand)]. |
|
| 1471. |
Autonomous items are also known as 'below the line' items. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :False. Autonomous items are also KNOWN as 'above the LINE' items. (Accommodating items are also known as 'below the line' items.) | |
| 1472. |
Market for a good is in equilibrium. There is increase in supply for this goods. Explain the chain of effects of this change. Use diagram. Or How will equilibrium price and quantity be affected when there is increase in supply? Or Explain the chain effect of increase in supply of a good on its price, supply and demand. Use diagram. Or How does an increase in supply of a commodity affect its equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity? Explain with the help of a diagram. Or Market for a good is in equilibrium. Supply of the good 'increases'. Explain the chain of effects of this change . |
|
Answer» Solution :As given in the examination problem that market for a good is in equilibrium. So, we assume that INITIAL price is OP as shown in given figure. In the given figure price is on vertical axis and QUANTITY demanded and supplied is on horizontal axis. But due to INCREASE in supply the supply curve shifts rightward from SS to `S_(1)S_(1)`. With new supply curve `S_(1)S_(1)` there is excess supply at initial price OP because at price OP, supply is PB and demand is PA, so there is excess supply of AB at price OP. Due to this excess supply competition among the producer will make the price fall. Due to this fall in price there is downward movement along the supply curve (Contraction in supply) from B to C and similarly, there is downward movement along the demand curve (Expansion in demand) from A to C. So, finally, equilibrium price falls from OP to `OP_(1)` and equilibrium quantity rises from OQ to `OQ_(1)`. conclusion Due to increase in supply, (i) Equilibrium price falls from OP to `OP_(1)`. (i) Equilibrium quantity rises from OQ to `OQ_(1)` ` (##FM_M_ECO_XII_P1_C12_E02_041_S01.png" WIDTH="80%"> |
|
| 1473. |
Explain the meaning of opportunity cost with the help of production possibility schedule. |
|
Answer» Solution :The cost of enjoying more of ONE good in terms of sacrificing the benefit of another good is called opportunity cost of the additional unit of the good. Let us consider the example of the economy producing two GOODS-consumer goods and capital goods assuming the level of resources and echnology remain same. The following schedule depicts the different possible comb nations of the consumer goods and the capital goods that the economy can produce with its resource endowment and the available technology. This schedule is called production possibility schedule. Production Possibility schedule refers to the table SHOWING different production possibilities of two goods with the given resources & technology.  From the schedule, we can see that point A shows, if all the resources are utilized in the production of the consumer goods, then 50 units of consumer goods can be PRODUCED with zero units of capital goods. On the other hand, point E shows that if all the resources are utilized in the production of the capital goods, then 4 units of capital goods can be produced with zero units of consumer goods. Also, consider the movement from point B to point C. It implies that the economy is diverting resources from the production of consumer goods to the production of capital goods. In order to the produce one additional unit of capital goods, the economy needs to sacrifice four units of consumer goods. Thus, the opportunity cost of producing one additional unit of capital goods is four units of consumer goods. |
|
| 1474. |
Discuss in brief the various precautions of value added method. |
| Answer» Solution :Precautions of value ADDED methods are.* Value on purchase and purchase of second hand good is not to be counted.* Commission on sale and purchase of second hand GOODS is must be counted.* Value of Intermediate goods is not to be included.* Imputed value on SELF consumptions while self production is included.*Services of self consumptions like DROP children to school is not estimated | |
| 1475. |
If there are two commodities , consumer is in equilibrium if ("MU"_x)/("Income")=("MU"_y)/("Income") |
| Answer» Solution :False : A CONSUMER is in EQUILIBRIUM only when `("MU"_x)/P=("MU"_y)/P` . Because here consumer behaviour MATCHES with the MARKET behaviour. | |
| 1476. |
Higher indifference curve represents higher level of satisfaction to the consumer'. Explain the statement, also state the underlying assumption related to this property of indifference curve. |
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) Higher IC lying above and to the right of another IC represents a higher LEVEL of satisfaction. All combinations of goods X and Y lying on the higher INDIFFERENCE CURVE `IC_2` have more satisfaction than lower indifference curve `"IC"_1` as shown in figure given here. 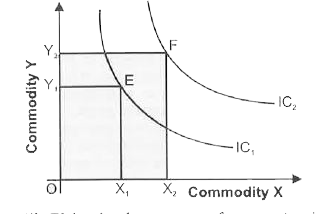 (ii) This is because of monotonic preferences , as monotonic preferences state that we must have atleast more of one good and no less that of other goods (means other goods can be equal or greater , but not less). The figure above shows that bundle `F("Ox"_2+"OY"_2)` is monotonicpreferred to bundle `F("Ox"_1+"OY"_1)`So , if bundle F is monotonic preferred to bundle E than F bundle gives more satisfaction than that of Bundle E. (iii) It can be seen from the above DIAGRAM that all combinations of `IC_2` contain a large quantity of both X and Y, than all combinations of `"IC"_1 ` . For, e.g. , point E lying on `"IC"_1` represents `"OX"_1` units of X and `"OY"_1` units of Y. Point F lying on `"IC"_2` represents more units of Y, i.e `"OY"_1` as well as more units of X, i.e. `"OX"_2` . The consumer gets greater satisfaction from a lager pieces of goods than from a smaller amount . Hence , point F shall be on a higher IC and Shall be more preferable to point E, lying on lower IC. |
|
| 1477. |
Under what condition increase in demand would not make any effect on equilibrium quantity? |
|
Answer» Solution :CASE I: When supply decreases at the same rate as the demand increase In the given diagram PRICE is measured on vertical axis and quantity demanded and supplied is measured on horizontal axis. Initially, the equilibrium price is OP and equilibrium quantity is OQ. But when, "demand increases and supply decreases but at the same rate", then, (i) Equilibrium price RISES from OP to` OP_(1)` and (ii) Equilibrium quantity remains constant at OQ. Case II: When supply becomes perfectly inelastic In the given diagram price ismeasured on vertical axis and quantity demanded and supplied is measured on horizontal axis. Initially, the equilibrium price is OP and equilibrium quantity is OQ. But when "supply becomes perfectly inelastic and demand increase" then, (i) Equilibrium price rises from OP to `OP_(1)` and (ii) Equilibrium quantity remains constant at OQ. ` (##FM_M_ECO_XII_P1_C12_E02_019_S01.png" width="80%"> ` (##FM_M_ECO_XII_P1_C12_E02_019_S02.png" width="80%"> |
|
| 1478. |
What are the functions of a central bank? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The FUNCTIONS of a central bank are : (i) Currency authority (ii) BANKER's bank and superivsion (iii)Banker's bank and supervision ltbvrgt (iv) Controller of money supply and credit (v) Custodian of FOREIGN exchange reserves. |
|
| 1479. |
If MPS 0.2 how much new investment is required to make the national income rise by600 cror ? Explain. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :120 CRORE | |
| 1480. |
Where is 'borrowings from abroad' recorded in the Balance of Payments Accounts? Give reasons. |
| Answer» Solution :Borrowings by a country from the FOREIGN countries or from the international money market are recorded in the Capital Account of the BOP. As these borrowings results in inflow of foreign EXCHANGE into the country. HENCE, they are recorded as positive ITEMS in the Capital Account of BOP. | |
| 1481. |
Define aggregate suppIy. |
| Answer» Solution :Aggregate Supply REFERS to the ESTIMATED money VALUE of all the FINAL goods and services planned to be produced in an economy | |
| 1482. |
Union Budget is the budget of : |
|
Answer» CENTRAL GOVERNMENT |
|
| 1483. |
What is a commercial bank? |
| Answer» Solution :A commercial bank is a FINANCIAL institution which performs the FUNCTIONS of accepting DEPOSITS and giving LOANS for investments with the AIM of earning profit. | |
| 1484. |
Imports of goods and services raises the ______ of foreign exchange. |
|
Answer» SUPPLY |
|
| 1485. |
Will a profit-maximizing firm in a competitive market ever produce a positive level of output in the range where the marginal cost is falling? Give an explanation. |
Answer» SOLUTION :No, as sufficient condition of producer equilibrium is Marginal Cost must be rising when Marginal Cost = Marginal REVENUE. It can be explained with the help of following diagram:  Point F is not a producer equilibrium because at this point, marginal cost = marginal revenue when marginal cost is falling. It is so because after point F, and output Q 1. `MR[AQ_(1)]gtMC[BQ_(1)]`, then producer will CONTINUE to PRODUCE as long as MR BECOMES equal to MC as firm will find it profitable to raise the output level. |
|
| 1486. |
What are the implication of a large revenue deficit ? Give two measures to reduce this deficit . |
|
Answer» Solution :REVENUE deficit is the excess of government's revenue EXPENDITURE over its revenue RECEIPTS . It MEANS LARGE borrowings to cover the deficit . Two measures to reduce revenue deficit are : (i) Government should reduce its expenditure . (ii) Government should increase its revenue . `""` (Refer to Section 10.6.1) |
|
| 1487. |
A rise is supply of a currency would lead to its appreciation, assuming no change in other factor. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FALSE. It will LEAD to DEPRECIATION of the CURRENCY. | |
| 1488. |
Classify the following into gross fixed capital formation and change in stocks. (i) Expenditure on construction of Metro by DMRC. (ii) Rise in number of cattles in a poultry farm. (iii) New machines purchased by a sugar manufacturing company. (iv) Construction of a new house by a consumer. (v) Decrease in the level of stock of wheat in a year. |
| Answer» Solution :ITEMS (i), (iii) and (iv) are part of GROSS fixed CAPITAL formation as they ADD to the capital stock of the economy. Items (ii) and (V) are part of change in stock. | |
| 1489. |
Stock variable is defined as a variable which is : |
|
Answer» Measured over a period of tome |
|
| 1490. |
''MC can be calculated both from total cost and total variable cost and is not affected by total fixed cost''. Discuss. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The given statement is correct. MC is not at all AFFECTED by total fixed COST (TFC). MC is addition to TC or TVC when one more unit of output is produced.As TFC REMAINS same with the increase in output, MC is independent of fixed cost and is affected just by change in variable costs. | |
| 1491. |
Supply of money refers to quantity of money : |
|
Answer» During the YEAR only |
|
| 1492. |
Explain the short run supply curve of the firm. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) The supply curve of the firm tells us the QUANTITY of the product that a firm is willing and able to produce and sell at each possible price. (ii) The firm will produce and supply an output at the point at which Price is equal to Marginal cost. The derivation of the supply curve is explained with the help of the given figure.  (iii) The SMC of the firm is given. Let us initially assume that the market price is `OP_(1)`. The firm will produce and supply an output of `OX_(1)`because at `e_(1)`, price = MC. (`OX_(1)` is the equilibrium output supplied, as MC - MR and MC cuts MR from below). (iv) Suppose the market price rises to `OP_(2)`, then the firm will produce and sell `OX_(2)` level, because at `e_(2)` level price = MC = MR. (V) Similarly, as market price increases to `OP_(3)`, quantity supplied increases to `OX_(3)`. However, the firm will not supply any quantity if the price falls below OP. (vi) At OP price, the firm will produce and sell OX output. For any price below OP the firm will not produce and sell anything. The supply will be zero units. Having the above INFORMATION, the supply schedule can be determined as, `{:("Price of Product","Units Supplied"),(OP,OX),(OP_(1),OX_(1)),(OP_(2),OX_(2)),(OP_(3),OX_(3)):}` (vii) If the market price falls below theminimum of the SAVC, the supply curve jumps to the small segment (OP) on the vertical AXIS at which there is zero supply. Therefore, two discontinuous [(OP) + (e.s)] pieces define the SHORT run supply curve for the perfectly competitive firm. |
|
| 1493. |
Give the meaning of : (a) Autonomous consumption, (b) Full employment. |
| Answer» Solution :Autonomous consumption refers to expenditure taking place when disposable incomes LEVEL are at zero. These causes CONSUMERS to BORROW MONEY or withdraw from saving accounts.Full employment refers to situationwhen persons are willing to work are getting work at prevailing wage rate. | |
| 1494. |
Other things remaining unchanged, when in a country price of foreign currency rises, national income is |
|
Answer» LIKELY to RISE |
|
| 1495. |
As Per the government budget , the interest payments are estimated at ₹10 , 000 crores , which is 40% of primary deficit . Calculate fiscal deficit ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Let , Primary Deficit = x Interest Payment = `40%` of x =`0.40` x ₹ 10 , 000 CRORES = `0.40` x x = ₹ 10 , 000 crores `div 0. 40` =₹ 25 , 000 crores Primary Deficit= FISCAL Deficit - Interest Payment ₹ 25 , 000 crores = Fiscal Deficit-₹ 10 , 000 crores Fiscal Deficit =₹ 25, 000 crores +₹ 10 , 000 crores =₹ 35 , 000 crores. |
|
| 1496. |
Using a diagram explain what will happen to the PPC of Bihar if the river Kosi causes widespread floods? |
|
Answer» Solution :If the river Kosi causes widespread floods in BIHAR, it will LEAD to destruction of resources in Bihar. This will SHIFT the PPC LEFTWARD. INITIALLY PPC is PP. With floods, the PPC will shift to `P_(1)P_(1)`. Value: Analytic 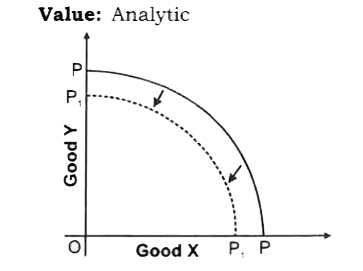
|
|
| 1497. |
A newsteel plant comes up in Jharkhand.Many people who were previously unemployed in the area are now employed. How will this affect demand curve for TV? |
| Answer» Solution :The demand CURVE for TV will shift towards right. It happens because of increase in the income of the people DUE to EMPLOYMENT in NEW STEEL plant. | |
| 1498. |
Differentaite between a) Devaluation and Depreciation b) Revaluation and Appreciation. |
Answer» Solution :a) DIFFERENCE between DEVALUATION and Depreciation of currency.  B) Difference between REVALUATION and Appreciation of currency. 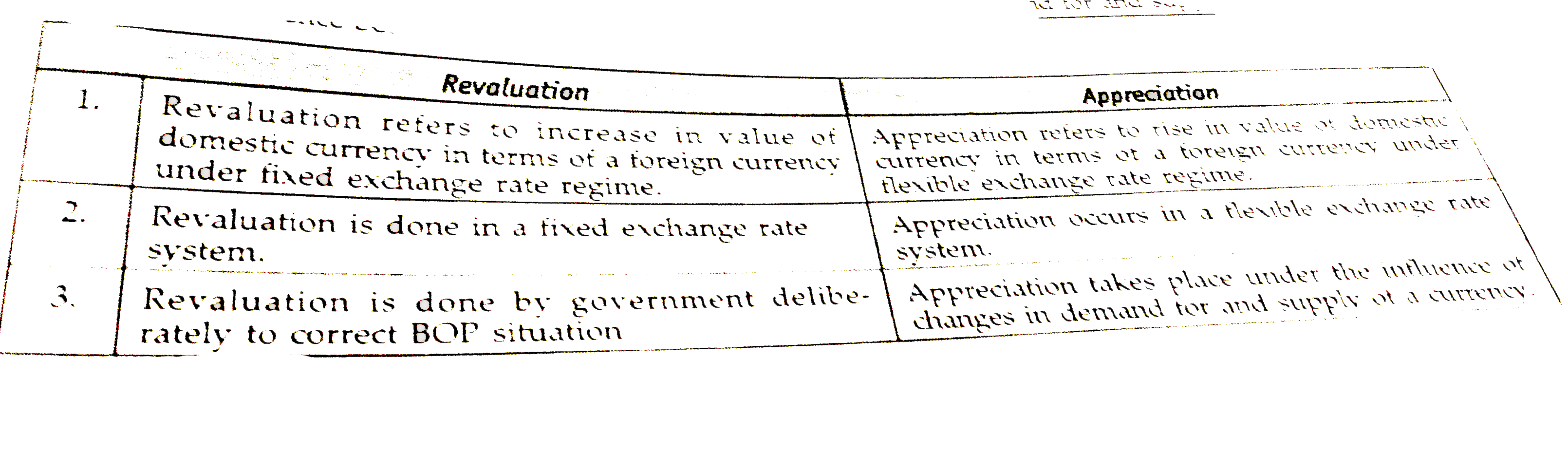
|
|
| 1499. |
What is the price elasticity of supply of M.F. Husain paintings ? |
|
Answer» Solution :The PRICE elasticity of supply of M.F. Husain paintaings is zero, because no MATTER how high price rises, no more PAINTINGS can ever be PRODUCED. VALUE : Critical thinking |
|
| 1500. |
Write down the three identities of calculating the GDP of a country by the three methods. Also briefly explain why each of these should give us the same value of GDP. |
|
Answer» Solution :National INCOME `equiv` National expenditure. NI by three methods is same. The only difference is that product method, NI is calculated at production level, with income METHODE NI is measured at DISTRIBUTION level and with expenditure methode, NI is measured at disposal level. It is because value of production causes generation of income which further causes expenditure. |
|